matlab 用改进的单纯形法(Modified Simplex Method)求解二次规划问题
Posted 白水baishui
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了matlab 用改进的单纯形法(Modified Simplex Method)求解二次规划问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
1. Wolf方法
这是一个不常用的方法,由wolf实现了matlab代码:Quadratic programming by Wolf’s method
在使用时,应当保证该function与自己计算二次规划问题的文件在同一目录下,并且matlab的“Current Folder”加载在该目录。
在注释中有一个使用样例,需要注意的是样例中的优化问题求解的是最大优化。
2. 应用示例
假设要求解最小优化问题:
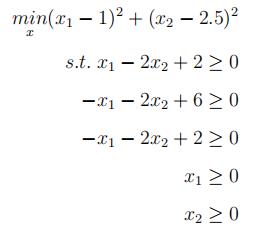
分析参数:
对
f
(
x
1
,
x
2
)
=
(
x
1
−
1
)
2
+
(
x
2
−
2.5
)
2
f(x_1,x_2)=(x_1-1)^2+(x_2-2.5)^2
f(x1,x2)=(x1−1)2+(x2−2.5)2展开可得:
f
(
x
1
,
x
2
)
=
x
1
2
+
x
2
2
−
2
x
1
−
5
x
2
+
7.25
f(x_1,x_2)=x_1^2+x_2^2-2x_1-5x_2+7.25
f(x1,x2)=x12+x22−2x1−5x2+7.25则其由最小优化问题改为最大优化问题为:
−
f
(
x
1
,
x
2
)
=
−
x
1
2
−
x
2
2
+
2
x
1
+
5
x
2
−
7.25
-f(x_1,x_2)=-x_1^2-x_2^2+2x_1+5x_2-7.25
−f(x1,x2)=−x12−x22+2x1+5x2−7.25
最大优化问题的二次型矩阵 D D D为: D = [ − 1 0 0 − 1 ] D=\\beginbmatrix -1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & -1 \\\\ \\endbmatrix D=[−100−1]
线性项系数 l l l 为: l = [ 2 5 ] l=\\beginbmatrix 2 \\\\ 5 \\\\ \\endbmatrix l=[25]
又由约束条件(约束条件无需更改)
A
x
⩽
b
Ax\\leqslant b
Ax⩽b:
−
x
1
+
2
x
2
⩽
2
x
1
+
x
2
⩽
6
x
1
+
x
2
⩽
2
\\beginaligned -x_1+2x_2 & \\leqslant 2 \\\\ x_1+x_2 & \\leqslant 6 \\\\ x_1+x_2 & \\leqslant 2 \\\\ \\endaligned
−x1+2x2x1+x2x1+x2⩽2⩽6⩽2
可得右约束列
b
b
b为:
b
=
[
2
6
2
]
b=\\beginbmatrix 2 \\\\ 6 \\\\ 2 \\\\ \\endbmatrix
b=⎣⎡262⎦⎤左约束矩阵
A
A
A为:
A
=
[
−
1
2
1
2
1
2
]
A=\\beginbmatrix -1 & 2 \\\\ 1 & 2 \\\\ 1 & 2 \\\\ \\endbmatrix
A=⎣⎡−111222⎦⎤
对
A
A
A和
b
b
b的三个约束条件
i
n
q
inq
inq 均为小于等于:
i
n
q
=
[
−
1
,
−
1
,
−
1
]
inq=[-1,-1,-1]
inq=[−1,−1,−1]
那么可以编写如下matlab代码:
D = [-1 0; 0 -1] % -x1^2 - x2^2 + 2x1 + 5x2 - 7.25 -> [-1 0; 0 -1]
l=[2; 5] % + 2x1 + 5x2 ->[2 5]
b=[2; 6; 2] % s.t. b
Mat=[-1, 2; 1,2; 1, 2] % s.t. A
inq=[-1, -1, -1] % <=
wolf(D,l,b,Mat,inq);
运行可得最优化结果:
ans=[0.2000;0.9000]
即: x 1 = 0.2000 ; x 2 = 0.9000 x_1=0.2000;x_2=0.9000 x1=0.2000;x2=0.9000
3. 可输出每次迭代的Wolf方法
为了方便观察每次的迭代值,我对Wolf方法进行了改编,在while循环里加入了代码(仅此一处):
if iter==1
opt = 1;
break;
end
在优化过程中,令iter分别等于1、2、3、…,即可得到第1、2、3、…次的迭代值。
改编后的Wolf方法如下,新加入的代码在wolf方法中已经被注释,要使用请取消%...%注释,不取消注释则与原Wolf方法无异:
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% The function wolf solves an QPP using Wolf or restricted entry simplex
% method.
%
% Input:- 1)D : The Hessian of the objective function. It is a required
% parameter.
% 2)l : The (column) vector of coefficient of linear terms in the
% objective function. It is a required parameter.
% 2)b : The (column) vector containing right hand side constant of
% the constraints. It is a required parameter.
% 3)Mat : The coefficient matrix of the left hand side of the
% constraints. it is a required parameter.
% 4)inq : A (row) vector indicating the type of constraints as 1
% for >=, 0 for = and -1 for <= constraints. If inq is not
% supplied then it is by default taken that all constraints
% are of <= type. It is an optional parameter.
% 5)minimize : This parameter indicates whether the objective
% function is to be minimized. minimized = 1 indicates
% a mimization problem and minimization = 0 stands for a
% maximization problem. By default it is taken as 0. It is an
% optional parameter.
%
% Example : max z=2x1+3x2-3x1^2+2x1x2-2x2^2
% s.t. x1+x2 >= 1
% 3x1+4x2 <= 3
% x1, x2 >= 0.
% Solution : D=[-3 1;1 -2];l=[2;3];b=[1;3];Mat=[1 1;3 4];inq=[1 -1].
% After supplying these inputs call wolf(D,l,b,Mat,inq).
%
% For theory of Wolf method and QPP one may see "Numerical
% Optimization with Applications, Chandra S., Jayadeva, Mehra A., Alpha
% Science Internatinal Ltd, 2009."
%
% This code has been written by Bapi Chatterjee as course assignment in the
% course Numerical Optimization at Indian Institute of Technology Delhi,
% New Delhi, India. The author shall be thankful for suggesting any
% error/improvment at bhaskerchatterjee@gmail.com.
%