Spring读源码系列番外篇08---BeanWrapper没有那么简单--中
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring读源码系列番外篇08---BeanWrapper没有那么简单--中相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Spring读源码系列番外篇08---BeanWrapper没有那么简单--中
引子
这篇文章需要依赖于对属性访问器PropertyAccessor的理解,也就是上篇文章的内容:Spring读源码系列番外篇08—BeanWrapper没有那么简单–上
如果说上篇文章所说的PropertyAccessor你没有接触过和听过,那么本文即将要说的重点:BeanWrapper你应该多少有所耳闻吧~
BeanWrapper可以简单的把它理解为:一个方便开发人员使用字符串来对Java Bean的属性执行get、set操作的工具。关于它的数据转换使用了如下两种机制:
- PropertyEditor:隶属于Java Bean规范。PropertyEditor只提供了String <->Object的转换。
- ConversionService:Spring自3.0之后提供的替代PropertyEditor的机制(BeanWrapper在Spring的第一个版本就存在了~)
按照Spring官方文档的说法,当容器内没有注册ConversionService的时候,会退回使用PropertyEditor机制。言外之意:首选方案是ConversionService
其实了解的伙伴应该知道,这不是BeanWrapper的内容,而是父接口PropertyAccessor的内容,更具体应该是TypeConverterDelegate的内容
类型转换相关的文章:
Spring读源码系列番外篇—01–PropertyValue相关类
Spring读源码系列番外篇—02—PropertyResolver的结构体系剖析—上
Spring读源码系列番外篇—03—PropertyResolver的结构体系剖析—下
Spring读源码系列番外篇—06----类型转换—下—ConversionService相关家族
BeanWrapper
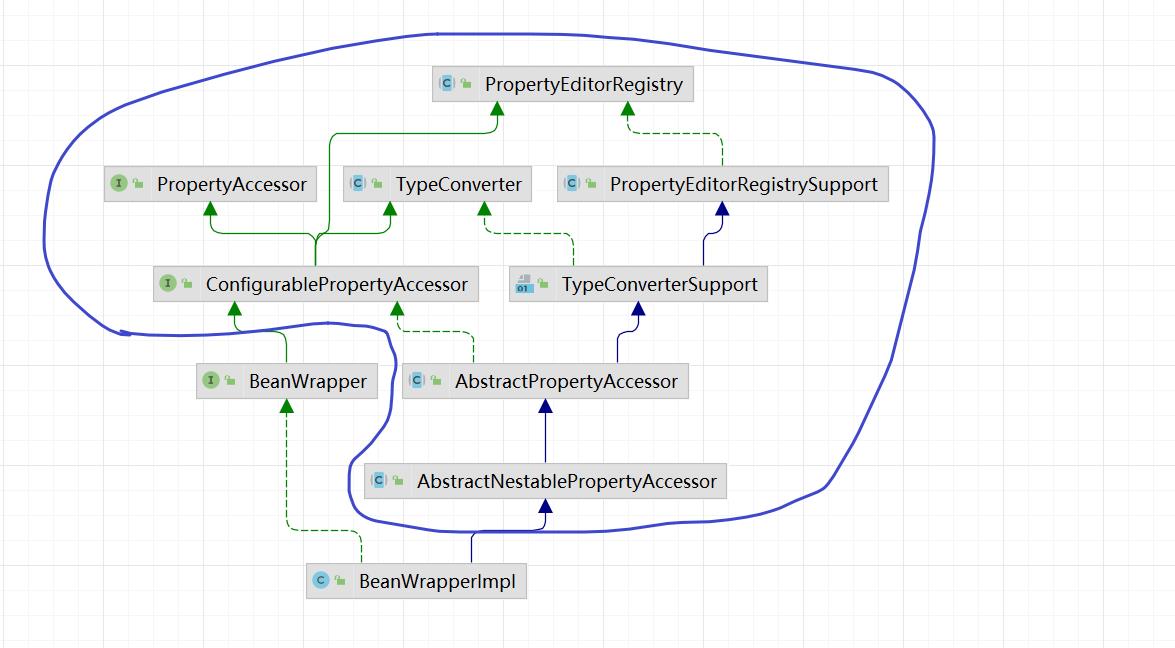
圈出来的一部分已经全部都讲解过了,不清楚的可以去看上集,对于BeanWrapper来说,bean属性操作,类型转换,转换器管理相关功能都已经实现了,那么BeanWrapper接口又增加了哪些额外的功能呢?
官方解释:Spring低级JavaBeans基础设施的中央接口。通常来说并不直接使用BeanWrapper,而是借助BeanFactory或者DataBinder来一起使用~
提供分析和操作标准 JavaBeans 的操作:获取和设置属性值(单独或批量)、获取属性描述符以及查询属性的可读性和可写性的能力。
此接口支持嵌套属性,可以将子属性的属性设置为无限深度。
BeanWrapper 的“extractOldValueForEditor”设置默认为“false”,以避免由 getter 方法调用引起的副作用。将此设置为“true”以将当前属性值公开给自定义编辑器。
//@since 13 April 2001 很清晰的看到,它也是个`PropertyAccessor`属性访问器
public interface BeanWrapper extends ConfigurablePropertyAccessor
// @since 4.1
void setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(int autoGrowCollectionLimit);
int getAutoGrowCollectionLimit();
Object getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> getWrappedClass();
// 获取属性们的PropertyDescriptor 获取属性们
PropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors();
// 获取具体某一个属性~
PropertyDescriptor getPropertyDescriptor(String propertyName) throws InvalidPropertyException;
BeanWrapper相当于一个代理器,Spring委托BeanWrapper完成Bean属性的填充工作。关于此接口的实现类,简单的说它只有唯一实现类:BeanWrapperImpl
BeanWrapperImpl
 它作为BeanWrapper接口的默认实现,它足以满足所有的典型应用场景,它会缓存Bean的内省结果而提高效率。
它作为BeanWrapper接口的默认实现,它足以满足所有的典型应用场景,它会缓存Bean的内省结果而提高效率。
在Spring2.5之前,此实现类是非public的,但在2.5之后给public了并且还提供了工厂:PropertyAccessorFactory帮助第三方框架能快速获取到一个实例~
注意:自动注册来自 org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors 包的默认属性编辑器,除了 JDK 的标准 PropertyEditors 之外,它还适用。应用程序可以调用 registerCustomEditor(Class, java.beans.PropertyEditor) 方法来为特定实例注册一个编辑器(即它们不在应用程序之间共享)
public class BeanWrapperImpl extends AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor implements BeanWrapper
/**
缓存此对象的自省结果,以防止每次遇到 JavaBeans 自省的成本。
*/
@Nullable
//CachedIntrospectionResults:为 Java 类缓存 JavaBeans PropertyDescriptor 信息的内部类。不适合应用程序代码直接使用。
private CachedIntrospectionResults cachedIntrospectionResults;
/**
* The security context used for invoking the property methods.
*/
@Nullable
private AccessControlContext acc;
public BeanWrapperImpl()
this(true);
/**
registerDefaultEditors:是否注册默认的Editors
*/
public BeanWrapperImpl(boolean registerDefaultEditors)
super(registerDefaultEditors);
//object是被包裹的对象
public BeanWrapperImpl(Object object)
super(object);
public BeanWrapperImpl(Class<?> clazz)
super(clazz);
public BeanWrapperImpl(Object object, String nestedPath, Object rootObject)
super(object, nestedPath, rootObject);
private BeanWrapperImpl(Object object, String nestedPath, BeanWrapperImpl parent)
super(object, nestedPath, parent);
setSecurityContext(parent.acc);
/**
* Set a bean instance to hold, without any unwrapping of @link java.util.Optional.
*/
public void setBeanInstance(Object object)
this.wrappedObject = object;
this.rootObject = object;
//真正做类型转换的委托类
this.typeConverterDelegate = new TypeConverterDelegate(this, this.wrappedObject);
setIntrospectionClass(object.getClass());
@Override
public void setWrappedInstance(Object object, @Nullable String nestedPath, @Nullable Object rootObject)
super.setWrappedInstance(object, nestedPath, rootObject);
setIntrospectionClass(getWrappedClass());
/**
Set the class to introspect.
Needs to be called when the target object changes.
*/
protected void setIntrospectionClass(Class<?> clazz)
if (this.cachedIntrospectionResults != null && this.cachedIntrospectionResults.getBeanClass() != clazz)
this.cachedIntrospectionResults = null;
/**
* Obtain a lazily initialized CachedIntrospectionResults instance
* for the wrapped object.
* spring很喜欢懒加载这个功能
*/
private CachedIntrospectionResults getCachedIntrospectionResults()
if (this.cachedIntrospectionResults == null)
this.cachedIntrospectionResults = CachedIntrospectionResults.forClass(getWrappedClass());
return this.cachedIntrospectionResults;
/**
* Set the security context used during the invocation of the wrapped instance methods.
* Can be null.
*/
public void setSecurityContext(@Nullable AccessControlContext acc)
this.acc = acc;
/**
* Return the security context used during the invocation of the wrapped instance methods.
* Can be null.
*/
@Nullable
public AccessControlContext getSecurityContext()
return this.acc;
/**
* Convert the given value for the specified property to the latter's type.
此方法仅用于 BeanFactory 中的优化。使用 convertIfNecessary 方法进行编程转换。
*/
@Nullable
public Object convertForProperty(@Nullable Object value, String propertyName) throws TypeMismatchException
//CachedIntrospectionResults:为 Java 类缓存 JavaBeans PropertyDescriptor 信息的内部类。不适合应用程序代码直接使用。
CachedIntrospectionResults cachedIntrospectionResults = getCachedIntrospectionResults();
//先从缓存中获取当前属性对应的属性描述符
PropertyDescriptor pd = cachedIntrospectionResults.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
if (pd == null)
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), getNestedPath() + propertyName,
"No property '" + propertyName + "' found");
//再从缓存中获取类型描述符
TypeDescriptor td = cachedIntrospectionResults.getTypeDescriptor(pd);
if (td == null)
td = cachedIntrospectionResults.addTypeDescriptor(pd, new TypeDescriptor(property(pd)));
//进行属性转换操作
return convertForProperty(propertyName, null, value, td);
private Property property(PropertyDescriptor pd)
GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor gpd = (GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) pd;
return new Property(gpd.getBeanClass(), gpd.getReadMethod(), gpd.getWriteMethod(), gpd.getName());
@Override
@Nullable
protected BeanPropertyHandler getLocalPropertyHandler(String propertyName)
//先获取到对应的属性描述符
PropertyDescriptor pd = getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
return (pd != null ? new BeanPropertyHandler(pd) : null);
@Override
protected BeanWrapperImpl newNestedPropertyAccessor(Object object, String nestedPath)
return new BeanWrapperImpl(object, nestedPath, this);
@Override
protected NotWritablePropertyException createNotWritablePropertyException(String propertyName)
PropertyMatches matches = PropertyMatches.forProperty(propertyName, getRootClass());
throw new NotWritablePropertyException(getRootClass(), getNestedPath() + propertyName,
matches.buildErrorMessage(), matches.getPossibleMatches());
@Override
public PropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors()
return getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptors();
@Override
public PropertyDescriptor getPropertyDescriptor(String propertyName) throws InvalidPropertyException
BeanWrapperImpl nestedBw = (BeanWrapperImpl) getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath(propertyName);
String finalPath = getFinalPath(nestedBw, propertyName);
PropertyDescriptor pd = nestedBw.getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptor(finalPath);
if (pd == null)
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), getNestedPath() + propertyName,
"No property '" + propertyName + "' found");
return pd;
//bean属性管理器
private class BeanPropertyHandler extends PropertyHandler
private final PropertyDescriptor pd;
public BeanPropertyHandler(PropertyDescriptor pd)
//当前属性class类型,当前属性是否可读:即是否存在对应的get方法,是否可写:是否存在对应的set方法
super(pd.getPropertyType(), pd.getReadMethod() != null, pd.getWriteMethod() != null);
this.pd = pd;
//获取的是当前属性get方法返回值,即当前属性类型相关信息的封装
@Override
public ResolvableType getResolvableType()
return ResolvableType.forMethodReturnType(this.pd.getReadMethod());
//拿到当前属性的类型描述符
@Override
public TypeDescriptor toTypeDescriptor()
return new TypeDescriptor(property(this.pd));
@Override
@Nullable
public TypeDescriptor nested(int level)
return TypeDescriptor.nested(property(this.pd), level);
//获取当前属性的值
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getValue() throws Exception
//还是先定位get方法
Method readMethod = this.pd.getReadMethod();
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(readMethod);
return null;
);
try
return AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>)
() -> readMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), (Object[]) null), acc);
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae)
throw pae.getException();
else
//即使get方法是私有的也可以调用
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(readMethod);
//本质就是调用get方法获取当前属性的值,如果没有get方法,那么属性值就无法获取到
return readMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), (Object[]) null);
//设置属性值
@Override
public void setValue(@Nullable Object value) throws Exception
//定位set方法
Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
);
try
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>)
() -> writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex)
throw ex.getException();
else
//调用set方法设置新的值
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
从继承体系上,首先我们应该能看出来BeanWrapperImpl的三重身份:
- Bean包裹器
- 属性访问器(PropertyAccessor)
- 属性编辑器注册表(PropertyEditorRegistry)
从源码中继续分析还能再得出如下两个结论:
- 它给属性赋值调用的是Method方法,如readMethod.invoke和writeMethod.invoke
- 它对Bean的操作,大都委托给CachedIntrospectionResults去完成~
- 因此若想了解它,必然主要是要先了解java.beans.PropertyDescriptor和
- org.springframework.beans.CachedIntrospectionResults,首当其冲的自然还有Java内省。
Java内省Introspector
首先可以先了解下JavaBean的概念:一种特殊的类,主要用于传递数据信息。这种类中的方法主要用于访问私有的字段,且方法名符合某种命名规则。如果在两个模块之间传递信息,可以将信息封装进JavaBean中,这种对象称为“值对象”(Value Object),或“VO”。
因此JavaBean都有如下几个特征:
- 属性都是私有的;
- 有无参的public构造方法;
- 对私有属性根据需要提供公有的getXxx方法以及setXxx方法;
- getters必须有返回值没有方法参数;setter值没有返回值,有方法参数;
符合这些特征的类,被称为JavaBean;JDK中提供了一套API用来访问某个属性的getter/setter方法,这些API存放在java.beans中,这就是内省(Introspector)。
内省和反射的区别
- 反射:Java反射机制是在运行中,对任意一个类,能够获取得到这个类的所有属性和方法;它针对的是任意类
- 内省(Introspector):是Java语言对JavaBean类属性、事件的处理方法
反射可以操作各种类的属性,而内省只是通过反射来操作JavaBean的属性
内省设置属性值肯定会调用seter方法,反射可以不用(反射可直接操作属性Field)
反射就像照镜子,然后能看到.class的所有,是客观的事实。
内省更像主观的判断:比如看到getName()内省就会认为这个类中有name字段,但事实上并不一定会有name;
通过内省可以获取bean的getter/setter
既然反射比内省比内省强大这么多,那内省用在什么时候场景呢?下面给出一个示例来说明它的用武之地:
// 就这样简单几步,就完成了表单到User对象的封装~
public void insertUser(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception
User user = new User();
// 遍历:根据字段名去拿值即可(此处省略判空、类型转换等细节,不在本文讨论范围)
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = Introspector.getBeanInfo(User.class).getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds)
pd.getWriteMethod().invoke(user, request.getParameter(pd.getName()));
通过内省可以很轻松的将form表单的内容填充进对象里面,比反射轻松省力多了。其实像MyBatis这种框架,底层都用到了Java的内省机制。
内省的API主要有Introspector、BeanInfo、PropertyDescriptor等,下面就以他三为例来操作一个JavaBean:
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Child
private String name;
private Integer age;
使用Introspector + BeanInfo:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IntrospectionException
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Child.class);
BeanDescriptor beanDescriptor = beanInfo.getBeanDescriptor();
MethodDescriptor[] methodDescriptors = beanInfo.getMethodDescriptors();
PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.以上是关于Spring读源码系列番外篇08---BeanWrapper没有那么简单--中的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章