时序特征相关系数的稳定性分析,真的很重要
Posted Python学习与数据挖掘
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了时序特征相关系数的稳定性分析,真的很重要相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在时序中,特征也许是具有时效性的,比如在某些市场环境下,股票的收益更看重公司的市盈率,另外的行情时,有看重换手率。本质上,可以反映为:在时间上,特征与目标变量之间相关性的不稳定。
为此,我们能做一些相关性分析,帮我们找到这些时间上不稳定的特征,剔除它们,并让模型更加鲁棒。喜欢本文记得收藏、点赞、关注。
【注】文末提供技术交流群
这里,直接上例子:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入数据
train_df = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
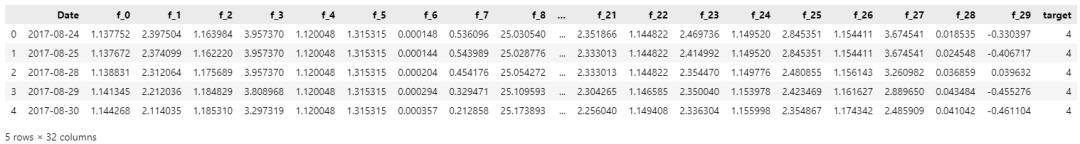
train.head()
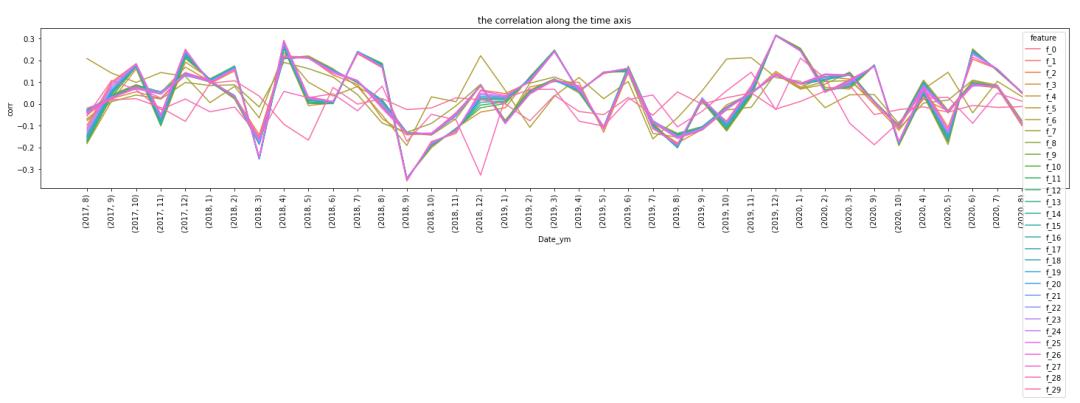
先对训练集数据,每月统计特征与target的相关性:
# 获取(年,月)特征
train_df['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(train_df['Date'])
train_df['Date_year'] = train_df['Date'].dt.year
train_df['Date_month'] = train_df['Date'].dt.month
def concat_year_month(year, month):
return (year, month)
train_df['Date_ym'] = train_df.apply(lambda x:concat_year_month(x['Date_year'], x['Date_month']), axis=1)
# 针对每月,统计特征与target的相关性
date_yms = train_df['Date_ym'].unique()
corr_df = []
for date_ym in date_yms:
curr_df = train_df[train_df['Date_ym']==date_ym]
curr_corr_df = curr_df.corr()
curr_corr_df = curr_corr_df['target'].reset_index()
curr_corr_df.rename(columns='index':'feature', 'target':'corr', inplace=True)
curr_corr_df['Date_ym'] = str(date_ym)
corr_df.append(curr_corr_df)
corr_df = pd.concat(corr_df, axis=0).reset_index(drop=True)
再观察每月各个特征相关性,随着时间变化的情况:
USE_COLS = [f for f in corr_df['feature'].unique() \\
if f not in ['Date', 'Date_year', 'Date_month', 'target']] # 训练时用的列名
corr_df = corr_df[corr_df['feature'].isin(USE_COLS)]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(25,4))
fig = sns.lineplot(data=corr_df, x='Date_ym', y='corr', hue='feature')
fig.set_xticklabels(date_yms, rotation=90)
plt.title('the correlation along the time axis')
plt.show()
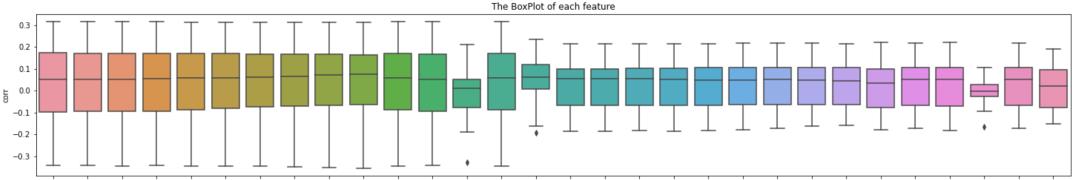
也可以看下,各个特征的月度相关性的标准差:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(25,4))
fig = sns.boxplot(data=corr_df.sort_values('feature'), x='feature', y='corr')
plt.xticks(rotation=90)
plt.title('The BoxPlot of each feature')
plt.show()
我们打印看看,top相关性标准差大的特征有哪些:
top_corrStd_fnum = 10 # 选择top相关性标准差大的特征的数量
top_corrStd_feats = corr_df.groupby('feature').std().reset_index().sort_values('corr', ascending=False)['feature'].iloc[:top_corrStd_fnum].to_list()
print(top_corrStd_feats)
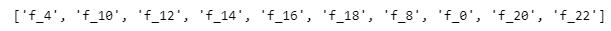
总结以上内容,打包函数如下:
def get_unstable_feats(df, top_fnum=10, corr_thresh=0.15):
"""对训练集数据,每月统计特征与target的相关性,
基于每个特征相关性的标准差,选择出TOP不稳定的特征,用于后续的特征选择工作
输入:
df (pd.DataFrame): 训练集
top_fnum (int): top不稳定特征数量
corr_thresh (float): 相关性的标准差阈值
注意:若选择corr_thresh,而不是top_fnum,只要将top_fnum设为None就好。
输出:
unstable_feats (list): 不稳定的特征
"""
# 获取(年,月)特征
df['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Date'])
df['Date_year'] = df['Date'].dt.year
df['Date_month'] = df['Date'].dt.month
def concat_year_month(year, month):
return (year, month)
df['Date_ym'] = df.apply(lambda x:concat_year_month(x['Date_year'], x['Date_month']), axis=1)
# 针对每月,统计特征与target的相关性
date_yms = df['Date_ym'].unique()
corr_df = []
for date_ym in date_yms:
curr_df = df[df['Date_ym']==date_ym]
curr_corr_df = curr_df.corr()
curr_corr_df = curr_corr_df['target'].reset_index()
curr_corr_df.rename(columns='index':'feature', 'target':'corr', inplace=True)
curr_corr_df['Date_ym'] = str(date_ym)
corr_df.append(curr_corr_df)
corr_df = pd.concat(corr_df, axis=0).reset_index(drop=True)
# 剔除非训练特征
USE_COLS = [f for f in corr_df['feature'].unique() if f not in ['Date', 'Date_year', 'Date_month', 'target']]
corr_df = corr_df[corr_df['feature'].isin(USE_COLS)]
# 基于每个特征相关性的标准差,选择出TOP不稳定的特征
if top_fnum != None:
top_corrStd_fnum = top_fnum # 选择top相关性标准差大的特征的数量
top_corrStd_feats = corr_df.groupby('feature').std().reset_index().sort_values('corr', ascending=False)['feature'].iloc[:top_corrStd_fnum].to_list()
elif corr_thresh != None:
corr_df = corr_df.groupby('feature').std().reset_index().sort_values('corr', ascending=False)
top_corrStd_feats = corr_df[corr_df['corr'] >= corr_thresh]['feature'].to_list()
print('Features with Unstable Correlation:', top_corrStd_feats)
return top_corrStd_feats
top_corrStd_feats = get_unstable_feats(train_df, top_fnum=10, corr_thresh=None)
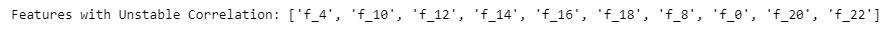
实际使用上述方法,确实对含冗余特征且存在明显相关性不稳定的数据集,有提分的帮助。
扩展:除了相关性分析,Kaggle常见的一个技巧:对抗验证也能做这块不稳定特征的筛选工作(参考:https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/ubiquant-market-prediction/discussion/312398)。
推荐文章
技术交流
欢迎转载、收藏、有所收获点赞支持一下!

目前开通了技术交流群,群友已超过2000人,添加时最好的备注方式为:来源+兴趣方向,方便找到志同道合的朋友
- 方式①、发送如下图片至微信,长按识别,后台回复:加群;
- 方式②、添加微信号:dkl88191,备注:来自CSDN
- 方式③、微信搜索公众号:Python学习与数据挖掘,后台回复:加群

以上是关于时序特征相关系数的稳定性分析,真的很重要的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章