多态?那不有手就行
Posted Lockey-s
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多态?那不有手就行相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
多态
向上转型
在上一篇 包和继承 当中我们写继承的关系的时候,写了这样的代码:
Bird bird = new Bird("圆圆");
当然,我们也可以写成这样:
Bird bird = new Bird("圆圆");
Animal bird2 = bird;
或者下面这样:
Animal bird2 = new Bird("圆圆");
此时 bird2 就是一个父类(Animal)的引用,指向一个子类(Bird)的实例,这就是向上转型。就像可以把:你给笔记本电脑充电了吗?说成:你给电脑充电了吗? 因为笔记本电脑也是电脑。
为什么叫向上转型:因为在程序设计当中,有很多场景。为了表示这种关系,就可以把他们的关系图画出来,父类通常在子类的上方。所以就叫做向上转型,表示往父类的方向转。
向上转型–方法传参
class Animal
public String name;
public Animal(String name)
this.name = name;
public void eat(String food)
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
class Cat extends Animal
public Cat(String name)
super(name);
class Bird extends Animal
public Bird(String name)
super(name);
public void fly()
System.out.println(this.name + "正在飞 ︿( ̄︶ ̄)︿");
public class Test4
public static void feed(Animal animal)
animal.eat("谷子");
public static void main(String[] args)
Bird bird = new Bird("圆圆");
feed(bird);
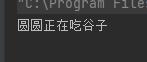
这里的圆圆就是发生了向上转型,通过方法传参,拼接了吃谷子。
向上转型–方法返回
public class Test
public static void main(String[] args)
Animal animal = findMyAnimal();
public static Animal findMyAnimal()
Bird bird = new Bird("圆圆");
return bird;
在这里方法 findMyAnimal 返回的就是一个 Animal 类型的引用, 但是实际上对应到 Bird 的实例。
**当然也可以通过直接进行赋值完成向上转型。**就是最上面的那种赋值方法。
动态绑定
动态绑定出现在子类和父类有相同方法名的时候。代码如下:
class Animal
public String name;
public Animal(String name)
this.name = name;
public void eat(String food)
System.out.println("这里是动物");
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
class Bird extends Animal
public Bird(String name)
super(name);
public void eat(String food)
System.out.println("这里是小鸟");
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
public class Test4
public static void main(String[] args)
Animal animal1 = new Animal("圆圆");
animal1.eat("谷子");
Animal animal2 = new Bird("扁扁");
animal2.eat("谷子");
结果如下:
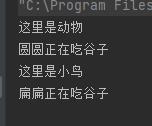
通过输出我们可以发现:
animal1 和 animal2 虽然都是 Animal 类型的引用, 但是animal1 指向 Animal 类型的实例。
animal2 指向 Bird 类型的实例. 针对 animal1 和 animal2 分别调用 eat 方法, 发现 animal1.eat() 实际调用了父类的方法, 而 animal2.eat() 实际调用了子类的方法。
所以,我们可以知道:在 Java 当中调用某个类的方法, 究竟执行了哪段代码 (是父类方法的代码还是子类方法的代码) , 要看究竟这个引用指向的是父类对象还是子类对象. 这个过程是程序运行时决定的(而不是编译期), 因此称为 动态绑定。
方法重写
就像刚刚写的 eat 方法,子类实现了父类的同名方法,并且参数的类型和个数完全相同,就称之为:覆写/重写/覆盖
重写的注意
- 重写和重载完全不一样.。
- 普通方法可以重写, static 修饰的静态方法不能重写。
- 重写中子类的方法的访问权限不能低于父类的方法访问权限。
- 重写的方法返回值类型不一定和父类的方法相同(但是建议最好写成相同, 特殊情况除外)。
重写方法的权限
如果我们把子类当中的权限改成比父类小的话,就会报错。代码如下:
class Animal
public String name;
public Animal(String name)
this.name = name;
public void eat(String food)
System.out.println("这里是动物");
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
class Bird extends Animal
public Bird(String name)
super(name);
private void eat(String food)
System.out.println("这里是小鸟");
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
public class Test4
public static void main(String[] args)
Animal animal1 = new Animal("圆圆");
animal1.eat("谷子");
Animal animal2 = new Bird("扁扁");
animal2.eat("谷子");
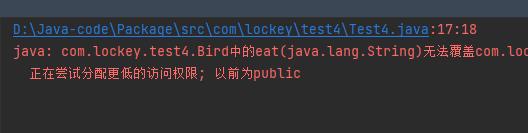
就会导致无法完成重写,所以我们在写的时候一定要注意权限的范围。
重写和重载的区别
如下图所示:
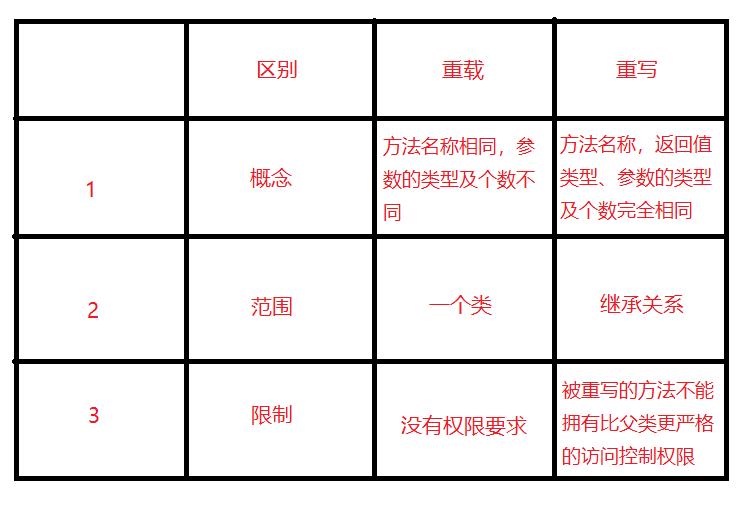
理解多态
学了向上转型,动态绑定,方法重写之后,我们就可以使用多态的形式来设计程序了,写一些弗雷可以兼容子类的代码。例如,打印多种形状:
class Shape
public void draw()
System.out.println("Shape::draw()");
class Rect extends Shape
public void draw()
System.out.println("♦");
class Flower extends Shape
//alt + insert 快捷键输出重写的方法
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("❀");
class Triangle extends Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("🔺");
class Cycle extends Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("●");
public class Test
// 打印单个图形
public static void drawShape(Shape shape)
shape.draw();
public static void main(String[] args)
Shape shape1 = new Flower();
Shape shape2 = new Cycle();
Shape shape3 = new Rect();
drawMap(shape1);
drawMap(shape2);
drawMap(shape3);
运行的结果如下:
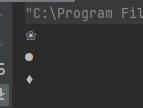
这里类的代码是由类的实现者写的,main 函数是由类的调用者写的。当类的调用者在写 drawMap 方法的时候,就会通过父类去看一个调用那个子类的方法。
使用多态的好处
类调用者对类的使用成本进一步降低
- 封装是为了让类的调用者不知道类的是实现细节。
- 多态的话,会让类的调用者连类的类型都不知道,只需要知道有这个方法就行了。
所以,可以把多态看作是更进一步的封装。
能够降低代码量,避免使用大量的 if else
如果我们需要一次性打印很多形状,基于多态的话,就可以直接写成这样的代码:
public static void main(String[] args)
Rect rect = new Rect();
Flower flower = new Flower();
Triangle triangle = new Triangle();
Shape[] shapes = triangle,rect,triangle,rect,flower,new Cycle();
for (Shape s: shapes)
s.draw();
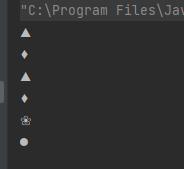
运行结果就是这样,通过多态去调用,就不用使用 if else 了。
可扩展能力更强
要新增一种新的形状的话,直接在类里面重写父类的方法就可以了,就像这样:
class green extends Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("❀");
向下转型
向下转型与向上转型恰好相反,是把父类对象转化为子类对象。相对来说不常见,但是也会用到。测试代码如下:
class Animal
protected String name;
public Animal(String name)
this.name = name;
public void eat(String food)
System.out.println("我是一只小动物");
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
class Bird extends Animal
public Bird(String name)
super(name);
public void eat(String food)
System.out.println("我是一只小鸟");
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
public void fly()
System.out.println(this.name + "正在飞");
public class test5
public static void main(String[] args)
Animal animal = new Bird("圆圆");
animal.eat("谷子");
运行结果如下:
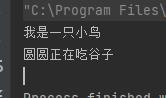
但是如果把行为改成 fly ,就会报错:
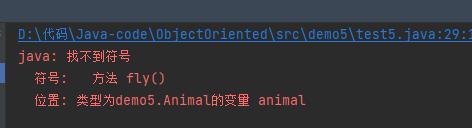
这里是因为 animal 的类型实际上是 Animal 类,编译器只知道有一个 eat 方法,没有 fly 方法,虽然 animal 实际引用的是一个 Bird 方法,但是编译器是以 Animal 的类型来寻找方法的。所以要使用 fly 方法的话,就要完成向下转型,这样写代码就可以了:
public static void main(String[] args)
Animal animal = new Bird("圆圆");
Bird bird = (Bird)animal;
bird.fly();
运行结果如下:
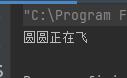
这样看似可以了,但是还会有问题,如果 animal 引用的对象是 cat 猫的话,就会报错,因为 Cat 是不能转化为 Bird 的:
public static void main(String[] args)
Animal animal = new Cat("小猫");
Bird bird = (Bird)animal;
bird.fly();
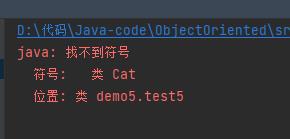
所以,为了向下转型更安全,我们可以先判断一下然后再转换,就像这样:
public static void main(String[] args)
Animal animal = new Cat("小猫");
if (animal instanceof Bird)
Bird bird = (Bird)animal;
bird.fly();
这样就可以解决向下转型的问题了。
super 关键字
前面的代码调用的是子类的方法,如果要调用父类的方法就要用到 super 关键字。
super 表示获取到父类实例的引用
这里常用的有两种方法:
- 使用了 super 来调用父类的构造器:
public Bird(String name)
super(name);
- 使用 super 关键字来调用父类的普通方法:
class Bird extends Animal
public Bird(String name)
super(name);
@Override
public void eat(String food)
//在这里让子类调用父类的接口
super.eat(food);
System.out.println("我是一只小鸟");
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃" + food);
public class test5
public static void main(String[] args)
Bird bird = new Bird("xxn");
bird.eat("ee");
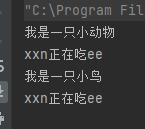
这里就完成了对父类方法的调用。
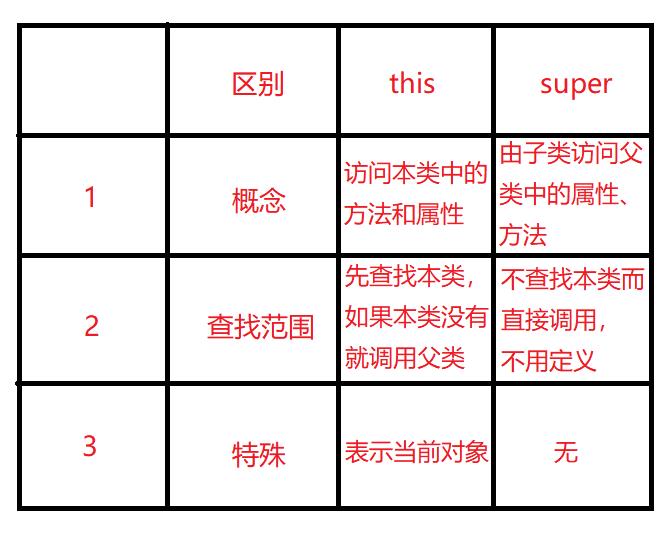
super 和 this 的区别
super 和 this 的区别如下图所示:
三级目录
以上是关于多态?那不有手就行的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章