《TensorFlow实战Google深度学习框架(第二版)》学习笔记及书评
Posted 李英俊小朋友
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《TensorFlow实战Google深度学习框架(第二版)》学习笔记及书评相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
《TensorFlow实战Google深度学习框架(第二版)》学习笔记
文章目录
写在前面
-
封面

-
读后感
-
先说结论:不推荐
-
这本书我老老实实从头到尾看了一遍,所有的代码都是手敲了一遍。这本书对于想TensorFlow入门的小伙伴来说,可以看到 第8章 了解一下循环神经网络的原理,第8章最后的例子举的真的是很烂,用循环神经网络去预测sin函数曲线,我是真的佩服这种例子都能想得出来。循环神经网络,不应该找一个经典的,与时间有关的具有时间累积效应的例子之类的吗,比如说钢材随时间的损坏程度之类的(我瞎编的)。后面的第9章写的真的是,可能是我理解能力不够,一个完整的例子就完完整整把代码铺上可以吗?前面说过的代码也铺上可以吗,不会重复的。书里总是出现各种各样的函数,说前面介绍过了,这里与前面类似所以不写了。一个完整的处理框架这么重要的函数说不写就不写了吗?真的是对于我这种读者造成了非常大的困扰。洋洋洒洒那么多代码敲下来,最后因为被省略的代码,导致这个程序无法运行。也不能与书中给出的结果相比对,真的是气炸了。。。书里还有很多数据处理的部分,在前面处理了一部分数据,给出了处理数据的框架,到后面完整版代码的时候,处理数据部分就省略了。所以读者并不知道数据长啥样,然后就给出结果了,为了证明这个程序是能跑的,结果一粘贴,太不负责任了吧。(特别是第9章自然语言处理部分,明明不知道数据是啥样,还是硬着头皮把所有的代码敲了一遍,哎。。。)
-
下面是Page250关于Seq2Seq模型的代码实现数据部分的代码
# 假设输入数据已经用了9.2.1小节中的方法转换成了单词编号的格式。 SRC_TRAIN_DATA = "/path/to/data/train.en" 源语言输入文件。 TRG_TRAIN_DATA = "/path/to/data/train.zh" 目标语言输入文件。 -
我只想说假如你妹啊,这里把数据长啥样和数据处理部分加进来不行吗,我也没有train.en也没有train.zh。这个翻译模型我连样本都没有玩个锤子啊。。。

-
以上仅代表个人观点,本人表达能力理解能力都有限,如果感觉我言辞激烈,那肯定是你理解的问题。。。
-
1. TensorFlow图像处理函数学习总结
-
图像编码处理+图像大小调整+图像翻转+图像色彩调整+处理标注框
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # coding=utf-8 """ @author: Li Tian @contact: 694317828@qq.com @software: pycharm @file: figure_deal_test1.py @time: 2019/1/21 10:06 @desc: 用TensorFlow对jpeg格式图像进行编码/解码 """ # matplotlib.pyplot是一个python的画图工具。在这一节中使用这个工具来可视化经过TensorFlow处理的图像。 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf # 读取图像的原始数据。 image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile('F:/Python3Space/figuredata_deal/krystal.jpg', 'rb').read() with tf.Session() as sess: # 对图像进行jpeg的格式解码从而得到图相对应的三维矩阵。TensorFlow还提供了tf.image.decode_png函数对png格式的图像进行解码。 # 解码之后的结果为一个张量,在使用它的取值之前需要明确调用运行的过程。 img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data) imag_data = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data, dtype=tf.float32) # 调整图像调整大小 # 0:双线性插值法 resized_0 = tf.image.resize_images(imag_data, [300, 300], method=0) # 1:最近邻居法 resized_1 = tf.image.resize_images(imag_data, [300, 300], method=1) # 2:双三次插值法 resized_2 = tf.image.resize_images(imag_data, [300, 300], method=2) # 3:面积插值法 resized_3 = tf.image.resize_images(imag_data, [300, 300], method=3) # 对图像进行裁剪和填充 croped = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(imag_data, 1000, 1000) padded = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(imag_data, 3000, 3000) # 用过比例调整图像大小 central_cropped = tf.image.central_crop(imag_data, 0.5) # 将图像上下翻转 flipped_0 = tf.image.flip_up_down(imag_data) # 将图像左右翻转 flipped_1 = tf.image.flip_left_right(imag_data) # 将图像沿对角线翻转 transposed = tf.image.transpose_image(imag_data) # 随机图像翻转 flipped_2 = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(imag_data) flipped_3 = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(imag_data) # 图像亮度调整 adjusted = tf.image.adjust_brightness(imag_data, -0.5) # 色彩调整的API可能导致像素的实数值超出0.0-1.0的范围,因此在输出最终图像前需要将其值截断在0.0-1.0范围区内,否则 # 不仅图像无法正常可视化,以此为输入的神经网络的训练质量也可能收到影响。 adjusted_0 = tf.clip_by_value(adjusted, 0.0, 1.0) # 将图像的亮度+0.5 adjusted = tf.image.adjust_brightness(imag_data, 0.5) adjusted_1 = tf.clip_by_value(adjusted, 0.0, 1.0) # 在[-max_delta, max_delta)的范围随机调整图像的亮度。 adjusted_2 = tf.image.random_brightness(imag_data, max_delta=0.5) # 改变图像的对比度 adjusted_3 = tf.image.adjust_contrast(imag_data, 0.5) adjusted_4 = tf.image.adjust_contrast(imag_data, 5) adjusted_5 = tf.image.random_contrast(imag_data, 0.1, 10) # 调整图像色相 adjusted_6 = tf.image.adjust_hue(imag_data, 0.1) adjusted_7 = tf.image.adjust_hue(imag_data, 0.6) adjusted_8 = tf.image.random_hue(imag_data, 0.3) # 调整图像饱和度 adjusted_9 = tf.image.adjust_saturation(imag_data, -5) adjusted_10 = tf.image.adjust_saturation(imag_data, 5) adjusted_11 = tf.image.random_saturation(imag_data, 0, 5) # 图像标准化:将图像上的亮度均值变为0,方差变为1,。 adjusted_12 = tf.image.per_image_standardization(imag_data) # 处理标注框 # 将图像缩小一些,这样可视化能让标准框更加清楚。 # img_data_deal = tf.image.resize_images(imag_data, [180, 267], method=1) # 图像的输入是一个batch的数据,也就是多张图像组成四维矩阵,所以需要将解码之后的图像矩阵加一维 batched_1 = tf.expand_dims(tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data, tf.float32), 0) boxes = tf.constant([[[0.05, 0.05, 0.9, 0.7], [0.35, 0.47, 0.5, 0.56]]]) result = tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(batched_1, boxes) # 随机截取图像上有信息含量的部分 # 可以通过提供标注框的方式来告诉随机截取图像的算法哪些部分是“有信息量”的 begin, size, bbox_for_draw = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(tf.shape(img_data), bounding_boxes=boxes, min_object_covered=0.4) # 通过标注框可视化随机截取得到的图像 batched_2 = tf.expand_dims(tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data, tf.float32), 0) image_with_box = tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(batched_2, bbox_for_draw) # 截取随机出来的图像。 distorted_image = tf.slice(img_data, begin, size) plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 步骤一(替换sans-serif字体) plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 步骤二(解决坐标轴负数的负号显示问题) # ''' fig1 = plt.figure(1, (16, 16), dpi=250) ax = plt.subplot(331) ax.set_title('原图') plt.imshow(imag_data.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(332) ax.set_title('双线性插值法') plt.imshow(resized_0.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(333) ax.set_title('最近邻居法') plt.imshow(resized_1.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(334) ax.set_title('双三次插值法') plt.imshow(resized_2.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(335) ax.set_title('面积插值法') plt.imshow(resized_3.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(336) ax.set_title('对图像进行裁剪') plt.imshow(croped.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(337) ax.set_title('对图像进行填充') plt.imshow(padded.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(338) ax.set_title('比例调整图像大小') plt.imshow(central_cropped.eval()) fig2 = plt.figure(2, (16, 16), dpi=250) ax = plt.subplot(331) ax.set_title('图像上下反翻转') plt.imshow(flipped_0.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(332) ax.set_title('图像左右翻转') plt.imshow(flipped_1.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(333) ax.set_title('沿对角线翻转') plt.imshow(transposed.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(334) ax.set_title('随机上下翻转') plt.imshow(flipped_2.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(335) ax.set_title('随机左右翻转') plt.imshow(flipped_3.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(336) ax.set_title('亮度调整-0.5') plt.imshow(adjusted_0.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(337) ax.set_title('亮度调整+0.5') plt.imshow(adjusted_1.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(338) ax.set_title('亮度随机调整') plt.imshow(adjusted_2.eval()) fig3 = plt.figure(3, (16, 16), dpi=250) ax = plt.subplot(331) ax.set_title('对比度调整+0.5') plt.imshow(adjusted_3.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(332) ax.set_title('对比度调整+5') plt.imshow(adjusted_4.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(333) ax.set_title('对比度随机调整') plt.imshow(adjusted_5.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(334) ax.set_title('色相调整+0.1') plt.imshow(adjusted_6.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(335) ax.set_title('色相调整+0.6') plt.imshow(adjusted_7.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(336) ax.set_title('色相随机调整') plt.imshow(adjusted_8.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(337) ax.set_title('饱和度调整-5') plt.imshow(adjusted_9.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(338) ax.set_title('饱和度调整+5') plt.imshow(adjusted_10.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(339) ax.set_title('饱和度随机调整') plt.imshow(adjusted_11.eval()) # ''' fig4 = plt.figure(4, (16, 16), dpi=250) ax = plt.subplot(221) ax.set_title('图像标准化') plt.imshow(adjusted_12.eval()) ax = plt.subplot(222) ax.set_title('处理标注框') plt.imshow(result[0].eval()) ax = plt.subplot(223) ax.set_title('随机生成的包含一定信息量的边框') plt.imshow(image_with_box[0].eval()) ax = plt.subplot(224) ax.set_title('随机截取图像上信息含量的部分') plt.imshow(distorted_image.eval()) # 使用pyplot工具可视化得到的图像。 # plt.show() # ''' fig1.savefig('F:/Python3Space/figuredata_deal/figure1.jpg', bbox_inches='tight') fig2.savefig('F:/Python3Space/figuredata_deal/figure2.jpg', bbox_inches='tight') fig3.savefig('F:/Python3Space/figuredata_deal/figure3.jpg', bbox_inches='tight') # ''' fig4.savefig('F:/Python3Space/figuredata_deal/figure4.jpg', bbox_inches='tight') # 将表示一张图像的三维矩阵重新按照jpeg格式编码并存入文件中,打开这张图像,可以得到和原始图像一样的图像。 # encoded_image = tf.image.encode_jpeg(imag_data) # with tf.gfile.GFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Python3Space/figuredata_deal/output.jpg', 'wb') as f: # f.write(encoded_image.eval()) -
运行结果:
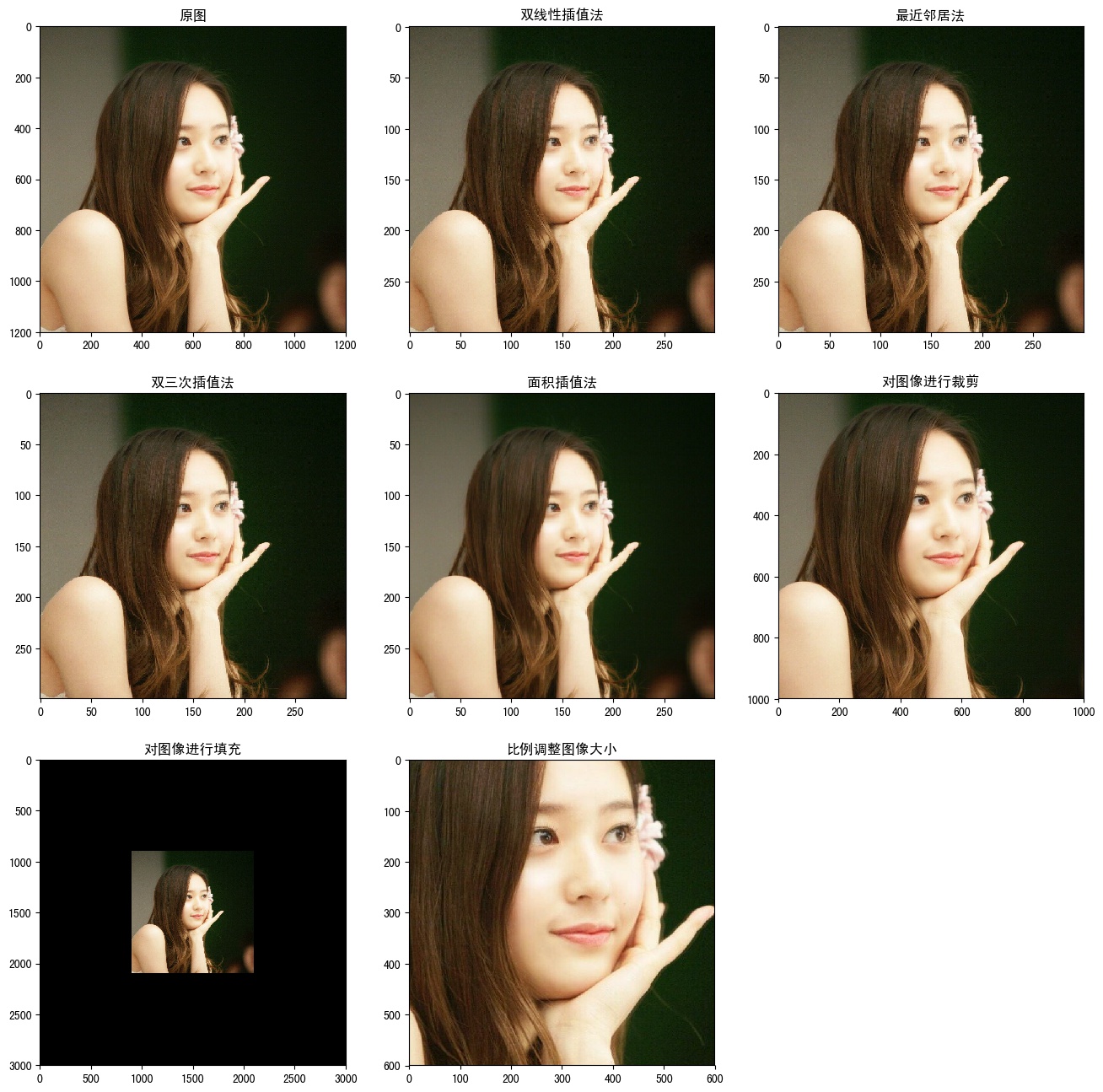
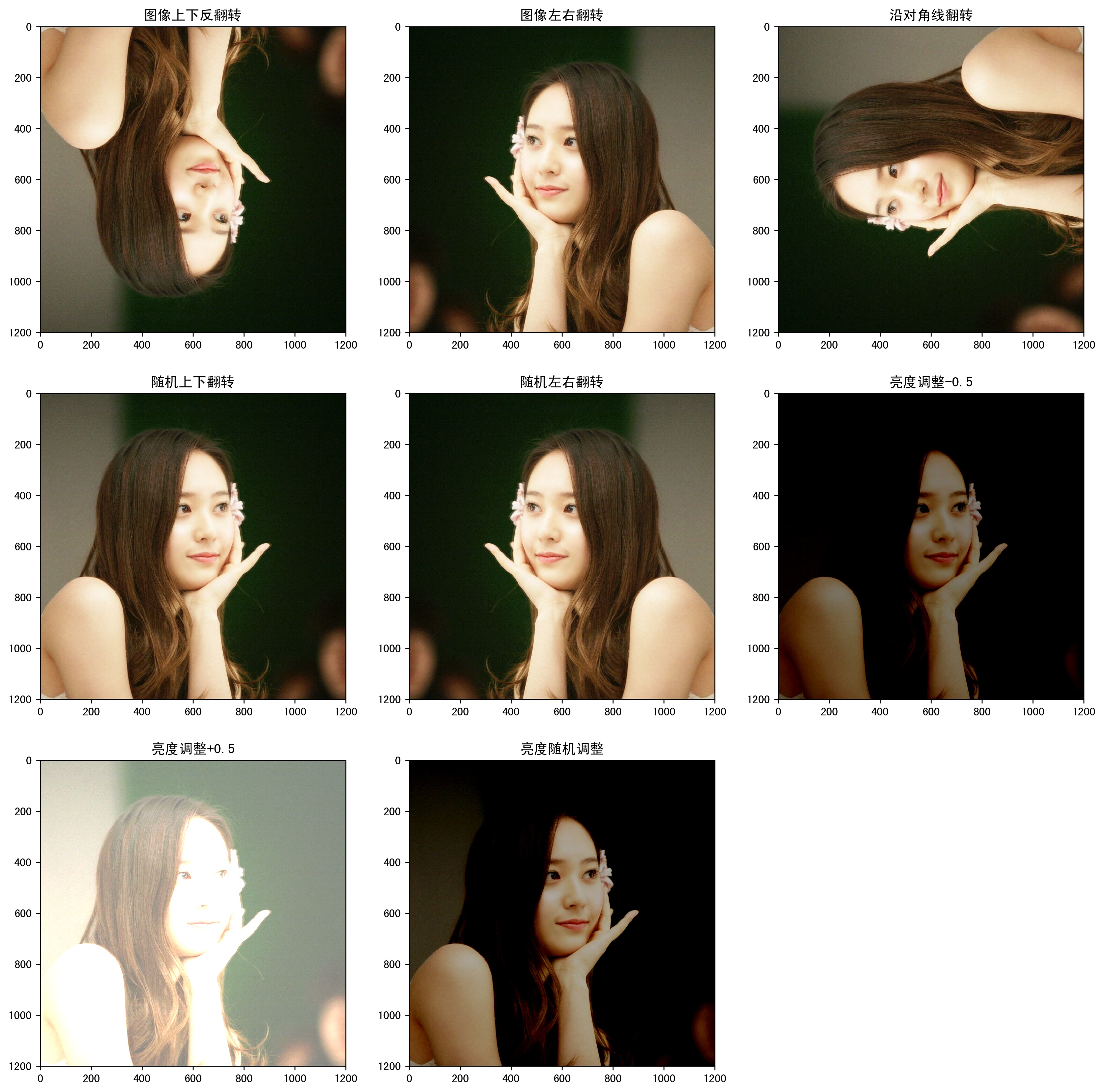
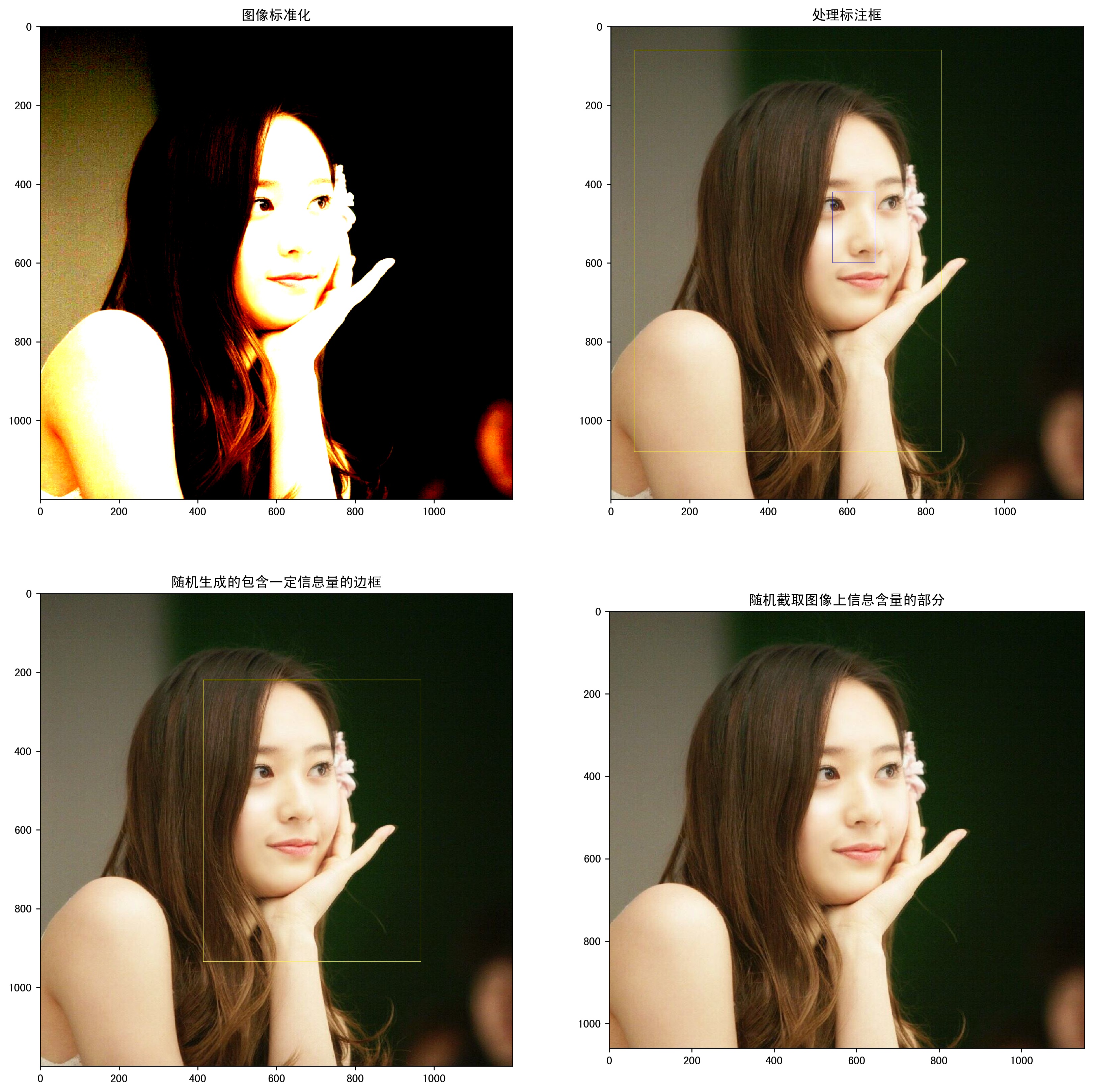





2. TensorFlow图像预处理完整样例
-
以下TensorFlow程序完成了从图像片段截取,到图像大小调整再到图像翻转及色彩调整的整个图像预处理过程
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # coding=utf-8 """ @author: Li Tian @contact: 694317828@qq.com @software: pycharm @file: figure_deal_test2.py @time: 2019/1/28 11:39 @desc: 图像预处理完整样例 """ import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 给定一张图像,随机调整图像的色彩。因为调整亮度,对比度,饱和度和色相的顺序会影响最后得到的结果。 # 所以可以定义多种不同的顺序。具体使用哪一种顺序可以在训练数据预处理时随机地选择一种。 # 这样可以进一步降低无关因素对模型的影响。 def distort_color(image, color_ordering=0): if color_ordering == 0: image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.) image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) elif color_ordering == 1: image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2) elif color_ordering == 2: # 还可以定义其他的排列,但是在这里就不再一一列出了。 # ... pass return tf.clip_by_value(image, 0.0, 1.0) # 给定一张解码后的图像、目标图像的尺寸以及图像上的标注框,此函数可以对给出的图像进行预处理。 # 这个函数的输入图像是图像识别问题中原始的训练图像,而输出则是深井网络模型的输入层。注意这里 # 只是处理模型的训练数据,对于预测的数据,一般不需要使用随机变换的步骤。。 def preprocess_for_train(image, height, width, bbox): # 如果没有提供标注框,则认为整个图像就是需要关注的部分。 if bbox is None: bbox = tf.constant([0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 1, 4]) # 转换图像张量的类型。 if image.dtype != tf.float32: image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32) # 随机截取图像,减小需要关注的物体大小对图像识别算法的影响。 bbox_begin, bbox_size, _ = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(tf.shape(image), bounding_boxes=bbox) distorted_image = tf.slice(image, bbox_begin, bbox_size) # 将随机截取的图像调整为神经网络层输入层的大小。大小调整的算法是随机选择的。 distorted_image = tf.image.resize_images(distorted_image, [height, width], method=np.random.randint(4)以上是关于《TensorFlow实战Google深度学习框架(第二版)》学习笔记及书评的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章