LinkedHashMap实现解析
Posted 水田如雅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LinkedHashMap实现解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1,基本核心结构
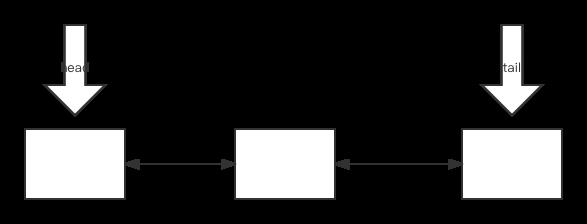
LinkedHashMap继承HashMap,除了有那些HashMap内部的结构外,还定义了 一个双向链表,
/**
* HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries.
*/
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V>
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next)
super(hash, key, value, next);
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
头结点代表最老的结点,尾结点代表最年轻的结点,也就是如果允许按照访问顺序排,总把最近访问的结点,放到尾部;
2,put操作
对于LinkedHashMap,在创建结点时候:
// link at the end of list
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p)
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
都会把结点加入链表尾部;
另外,对于LinkedHashMap,put时候还会执行:afterNodeAccess和afterNodeInsertion
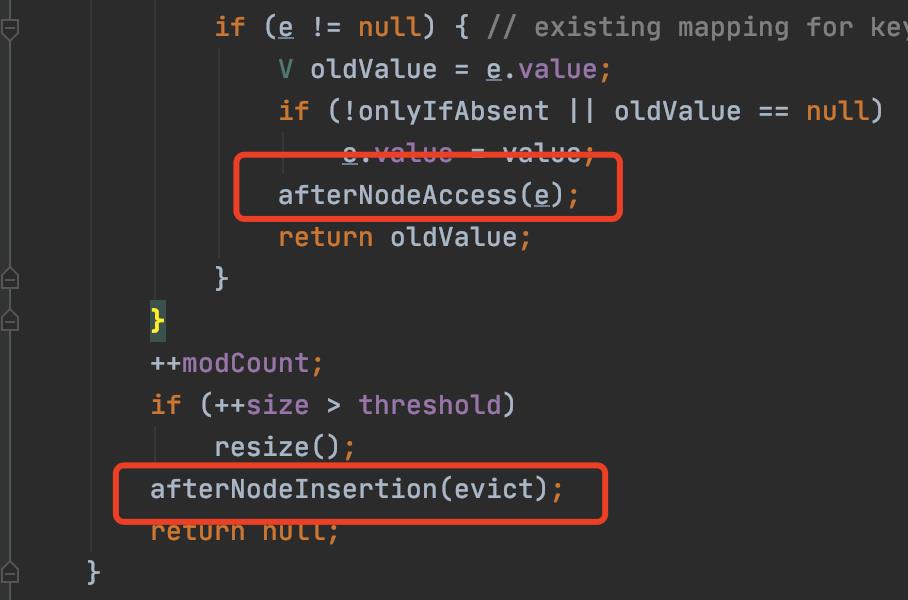
这俩方法是专门留给LinkedHashMap的,先afterNodeAccess:
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e)
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
tail = p;
++modCount;
先看accessOrder:
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
*
* @serial
*/
final boolean accessOrder;
就是个链表的挪动,对于key已经存在的,修改了旧的值之后,要把它挪动到链表的尾部;
对于map插入完成之后,还要进行afterNodeInsertion:
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first))
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
这个主要是插入一个值之后,是否要移除链表中最老的结点;
3,get操作
public V get(Object key)
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
getNode:
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key)
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null)
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null)
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
while ((e = e.next) != null);
return null;
首先是检查头结点,如果是返回头结点;
之后检查头结点的下一个结点,如果是红黑树,取树结点;
最后如果是链表,就拿每一个链表的key赫尔hash比对;
访问完之后,如果有设置accessOrder,需要将访问的结点放到链表尾部;
以上是关于LinkedHashMap实现解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章