FreeModbus RTU 移植指南
Posted 研究是为了理解
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了FreeModbus RTU 移植指南相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
FreeModbus 简介
FreeModbus 是一个免费的软件协议栈,实现了 Modbus 从机功能:
- 纯 C 语言
- 支持 Modbus RTU/ASCII
- 支持 Modbus TCP
本文介绍 Modbus RTU 移植。
移植环境:
- 裸机
- Keil MDK 编译器
- Cortex-M3 内核芯片(LPC1778/88)
移植概述
1.体系架构相关
| 项目 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| INLINE | 宏,编译器相关,内联指令或关键字 |
| PR_BEGIN_EXTERN_C PR_END_EXTERN_C | 宏,按照 C 代码编译 |
| ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( ) EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( ) | 宏,进入临界区和退出临界区 |
| BOOL UCHAR CHAR USHORT SHORT ULONG LONG | 数据类型 |
| TRUE FALSE | 宏,BOOL 类型变量的值 |
2.定时器
需要移植的定时器函数
| 定时器函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BOOL xMBPortTimersInit( USHORT usTim1Timerout50us ) | 初始化,由协议栈回调, usTim1Timerout50us 的单位是 50us |
| void vMBPortTimersEnable( ) | 使能定时器,协议栈回调 定时器计数器清零,然后开始计数 |
| void vMBPortTimersDisable( ) | 禁止定时器,由协议栈回调 定时器计数器清零,停止计数 |
| void prvvTIMERExpiredISR( void ) | 通知协议栈定时器中断发生,需手动安装到定时器中断服务函数中 |
3.串口
需要移植的函数
| 定时器函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BOOL xMBPortSerialInit( UCHAR ucPORT, ULONG ulBaudRate, UCHAR ucDataBits, eMBParity eParity ) | 初始化串口硬件,由协议栈回调 |
| void vMBPortSerialEnable( BOOL xRxEnable, BOOL xTxEnable ) | 使能/禁止串口发送和接收,由协议栈回调 |
| BOOL xMBPortSerialPutByte( CHAR ucByte ) | 通过串口发送一字节数据 |
| BOOL xMBPortSerialGetByte( CHAR * pucByte ) | 从串口接收一字节数据 |
| void prvvUARTRxISR( void ) | 通知协议栈串口接收中断发生,协议栈会进行数据接收处理。需手动安装到串口接收中断服务函数中 |
| void prvvUARTTxReadyISR( void ) | 通知协议栈串口发送中断发生,协议栈会进行数据发送。需手动安装到串口发送中断服务函数中 |
4.事件
事件相关回调函数需要移植:
| 事件回调函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BOOL xMBPortEventInit( void ) | 初始化 |
| BOOL xMBPortEventPost( eMBEventType eEvent ) | 事件投递 可以在这个函数中解析事件,并执行自己的事件函数。 |
| BOOL xMBPortEventGet( eMBEventType * eEvent ) | 获取事件 |
mb_config.h 文件属于协议栈的一部分,直接修改不合理
assert,直接调用 C 标准库函数, 但这个依赖硬件
移植细节
并不是所有函数都需要重头编写,协议栈 \\freemodbus\\demo\\BARE\\port\\ 文件夹下给出了移植框架:
port
|---- port.h :体系架构相关
|---- porttimer.c :定时器相关
|---- portserial.c :串口相关
|---- portevent.c :事件相关
1.体系架构
port.h 文件:
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "cmsis_compiler.h"
#define INLINE __INLINE
#define PR_BEGIN_EXTERN_C extern "C"
#define PR_END_EXTERN_C
#ifndef assert
#define assert(ignore) ((void)0)
#endif
#define ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( ) EnterCriticalSection()
#define EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( ) ExitCriticalSection()
typedef uint8_t BOOL;
typedef unsigned char UCHAR;
typedef char CHAR;
typedef uint16_t USHORT;
typedef int16_t SHORT;
typedef uint32_t ULONG;
typedef int32_t LONG;
#ifndef TRUE
#define TRUE 1
#endif
#ifndef FALSE
#define FALSE 0
#endif
void EnterCriticalSection(void);
void ExitCriticalSection(void);
进入和退出临界区函数,实际上是开关中断,这部分点击这里可以获取详细的信息。我们新建一个 port.c 文件,在这个文件中实现一个可以嵌套使用的进入和退出临界区代码:
#include "cmsis_compiler.h"
static uint32_t nesting_count = 0;
static uint32_t old_state;
void EnterCriticalSection(void)
uint32_t cur_state;
cur_state = __get_PRIMASK();
__disable_irq();
if(nesting_count == 0)
old_state = cur_state;
nesting_count ++;
void ExitCriticalSection(void)
nesting_count --;
if(0 == nesting_count)
__set_PRIMASK(old_state);
2.定时器
Modbus RTU 使用超时机制判断数据帧结束:串口超过 3.5 个字符传输时间没有收到数据,则认为一帧结束。
这需要一个硬件定时器。
协议栈会根据传入的波特率自动计算 3.5 个字符传输时间是多少,单位是 50us,简化后的代码如下所示:
/* If baudrate > 19200 then we should use the fixed timer values t35 = 1750us.
* Otherwise t35 must be 3.5 times the character time.
*/
if( ulBaudRate > 19200 )
usTimerT35_50us = 35; /* 1800us. */
else
/* The timer reload value for a character is given by:
*
* ChTimeValue = Ticks_per_1s / ( Baudrate / 11 )
* = 11 * Ticks_per_1s / Baudrate
* = 220000 / Baudrate
* The reload for t3.5 is 1.5 times this value and similary
* for t3.5.
*/
usTimerT35_50us = ( 7UL * 220000UL ) / ( 2UL * ulBaudRate );
xMBPortTimersInit( ( USHORT ) usTimerT35_50us );
所以就可以根据传入的 3.5 个字符传输时间 usTimerT35_50us 来初始化硬件定时器。我的系统刚好有个 50us 中断一次的定时器,所以我直接使用这个定时器来移植,移植代码在 porttime.c 文件中:
#include <stdbool.h>
/* ----------------------- Platform includes --------------------------------*/
#include "port.h"
/* ----------------------- Modbus includes ----------------------------------*/
#include "mb.h"
#include "mbport.h"
static bool IsTimerEnable = false;
static USHORT Timerout50usCount = 0;
static USHORT Timerout50usCountCur = 0;
/* ----------------------- static functions ---------------------------------*/
static void prvvTIMERExpiredISR( void );
/* ----------------------- Start implementation -----------------------------*/
BOOL
xMBPortTimersInit( USHORT usTim1Timerout50us )
Timerout50usCount = usTim1Timerout50us;
IsTimerEnable = false;
return TRUE;
inline void
vMBPortTimersEnable( )
/* Enable the timer with the timeout passed to xMBPortTimersInit( ) */
IsTimerEnable = true;
Timerout50usCountCur = 0;
inline void
vMBPortTimersDisable( )
/* Disable any pending timers. */
IsTimerEnable = false;
Timerout50usCountCur = 0;
/*需手动安装到定时器中断服务函数*/
void
vMBPortTimersISR( )
if(IsTimerEnable)
Timerout50usCountCur ++;
if(Timerout50usCountCur >= Timerout50usCount)
prvvTIMERExpiredISR();
/* Create an ISR which is called whenever the timer has expired. This function
* must then call pxMBPortCBTimerExpired( ) to notify the protocol stack that
* the timer has expired.
*/
static void prvvTIMERExpiredISR( void )
( void )pxMBPortCBTimerExpired( );
有一点我很好奇, 3.5 个字符传输时间 usTimerT35_50us 为什么要格式化成 50us 的倍数?
我注意到代码 xMBPortTimersInit( ( USHORT ) usTimerT35_50us ) 在传递参数时进行了一次数据强制转换,也就是协议栈使用的 USHORT 数据类型,一般这个数据类型最大值是 65536,如果不转换成 50us 的倍数,低波特率(比如 1200bps )必然会出现数据溢出现象。
那协议栈为什么又非要使用 USHORT 数据类型呢?
不清楚,大概是当时主流 MCU 还不是 32 位的,USHORT 数据类型可以更快更节省 RAM 。
何时使能定时器?
- 启动协议栈(
eMBRTUStart) - 接收到 1 字节数据(
xMBRTUReceiveFSM):复位计数器,重新开始计时
何时关闭定时器?
- 停止协议栈(
eMBRTUStop) - 超时发生(3.5 个字符传输时间):收到新的数据帧,停止计时
定时器与接收关系密切,参与接收状态机的状态迁移:
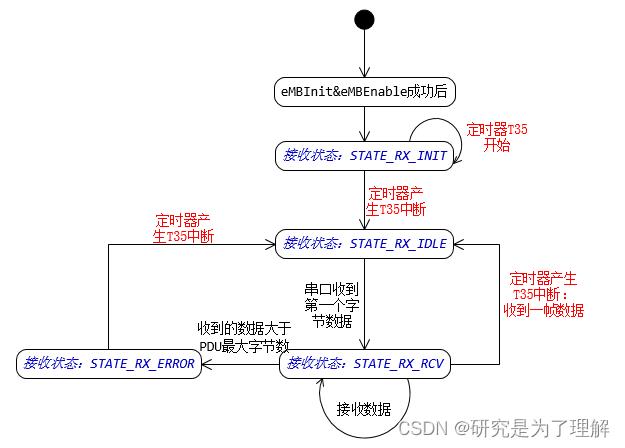
3.串口
串口用于收发数据。移植代码在 portserial.c 中:
#include "port.h"
/* ----------------------- Modbus includes ----------------------------------*/
#include "mb.h"
#include "mbport.h"
/* ----------------------- static functions ---------------------------------*/
static void prvvUARTTxReadyISR( void );
static void prvvUARTRxISR( void );
void down3_set_to_recv(void);
void down3_set_to_send(void);
void down3_put_byte( CHAR data);
void down3_get_byte(CHAR *pucByte);
void init_down3_uart2(UCHAR ucPORT, ULONG ulBaudRate, UCHAR ucDataBits, eMBParity eParity);
/* ----------------------- Start implementation -----------------------------*/
void
vMBPortSerialEnable( BOOL xRxEnable, BOOL xTxEnable )
/* If xRXEnable enable serial receive interrupts. If xTxENable enable
* transmitter empty interrupts.
*/
if(xRxEnable)
down3_set_to_recv();
if(xTxEnable)
down3_set_to_send();
prvvUARTTxReadyISR();
BOOL
xMBPortSerialInit( UCHAR ucPORT, ULONG ulBaudRate, UCHAR ucDataBits, eMBParity eParity )
init_down3_uart2(ucPORT, ulBaudRate, ucDataBits, eParity);
return TRUE;
BOOL
xMBPortSerialPutByte( CHAR ucByte )
/* Put a byte in the UARTs transmit buffer. This function is called
* by the protocol stack if pxMBFrameCBTransmitterEmpty( ) has been
* called. */
down3_put_byte(ucByte);
return TRUE;
BOOL
xMBPortSerialGetByte( CHAR * pucByte )
/* Return the byte in the UARTs receive buffer. This function is called
* by the protocol stack after pxMBFrameCBByteReceived( ) has been called.
*/
down3_get_byte(pucByte);
return TRUE;
/*需手动安装到串口接收中断服务函数*/
void
vMBPortSerialRecvISR(void)
prvvUARTRxISR();
/*需手动安装到串口发送中断服务函数*/
void
vMBProtSerialSendISR(void)
prvvUARTTxReadyISR();
/* Create an interrupt handler for the transmit buffer empty interrupt
* (or an equivalent) for your target processor. This function should then
* call pxMBFrameCBTransmitterEmpty( ) which tells the protocol stack that
* a new character can be sent. The protocol stack will then call
* xMBPortSerialPutByte( ) to send the character.
*/
static void prvvUARTTxReadyISR( void )
pxMBFrameCBTransmitterEmpty( );
/* Create an interrupt handler for the receive interrupt for your target
* processor. This function should then call pxMBFrameCBByteReceived( ). The
* protocol stack will then call xMBPortSerialGetByte( ) to retrieve the
* character.
*/
static void prvvUARTRxISR( void )
pxMBFrameCBByteReceived( );
4.事件
协议栈使用前后台架构,中断产生 事件 ,主循环处理 事件 。
| 事件 | 生产者 | 消费者 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EV_READY | 定时器中断 (porttimer.c) prvvTIMERExpiredISR | 主循环 (mb.c) eMBPoll | 协议栈初始化完毕 |
| EV_FRAME_RECEIVED | 定时器中断 (porttimer.c) prvvTIMERExpiredISR | 主循环 (mb.c) eMBPoll | 接收到一帧数据 如果数据帧校验正确,则产生 EV_EXECUTE 事件 |
| EV_EXECUTE | 主循环 (mb.c) eMBPoll | 主循环 (mb.c) eMBPoll | 解析命令,生成应答数据,添加 CRC ,启动数据发送,数据将由串口发送中断发送 |
| EV_FRAME_SENT | 串口发送中断 (portserial.c) prvvUARTTxReadyISR | 主循环 (mb.c) eMBPoll | 应答数据全部发送完成 |
事件一般用队列实现,以便消费者来不及处理事件时,暂时保存事件。对于简单应用,如果满足消费者消费事件的速度 大于等于 生产者生产事件的速度,则可以使用协议栈 \\freemodbus\\demo\\BARE\\port\\portevent.c 文件中的源码,直接使用,不用修改:
#include "mb.h"
#include "mbport.h"
/* ----------------------- Variables ----------------------------------------*/
static eMBEventType eQueuedEvent;
static BOOL xEventInQueue;
/* ----------------------- Start implementation -----------------------------*/
BOOL
xMBPortEventInit( void )
xEventInQueue = FALSE;
return TRUE;
BOOL
xMBPortEventPost( eMBEventType eEvent )
xEventInQueue = TRUE;
eQueuedEvent = eEvent;
return TRUE;
BOOL
xMBPortEventGet( eMBEventType * eEvent )
BOOL xEventHappened = FALSE;
if( xEventInQueue )
*eEvent = eQueuedEvent;
xEventInQueue = FALSE;
xEventHappened = TRUE;
return xEventHappened;
在发送事件处就可以完成的功能,为什么要绕一圈非得用事件来完成呢?
方便解耦。
对于裸机环境,使用事件将处理过程从中断转移到主循环,从而使中断服务函数简单。
对于有操作系统的应用,事件可以方便的实现操作系统移植层,实现协议栈进程与中断之间的通讯。协议栈进程会因为等待事件而进入阻塞状态。
以上是关于FreeModbus RTU 移植指南的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章