数据结构 图
Posted qnbk
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构 图相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
图
基本概念
图是由顶点集合及顶点间的关系组成的一种数据结构:G = (V, E),
其中:
顶点集合V = x|x属于某个数据对象集是有穷非空集合;
E = (x,y)|x,y属于V或者E = <x, y>|x,y属于V && Path(x, y)是顶点间关系的有穷集合,也叫做边的集合。
(x, y)表示x到y的一条双向通路,即(x, y)是无方向的;Path(x, y)表示从x到y的一条单向通路,即Path(x, y)是有方向的。
**顶点和边:图中结点称为顶点,**第i个顶点记作vi。两个顶点vi和vj相关联称作顶点vi和顶点vj之间有一条边, 图中的第k条边记作ek,ek = (vi,vj)或<vi,vj>。
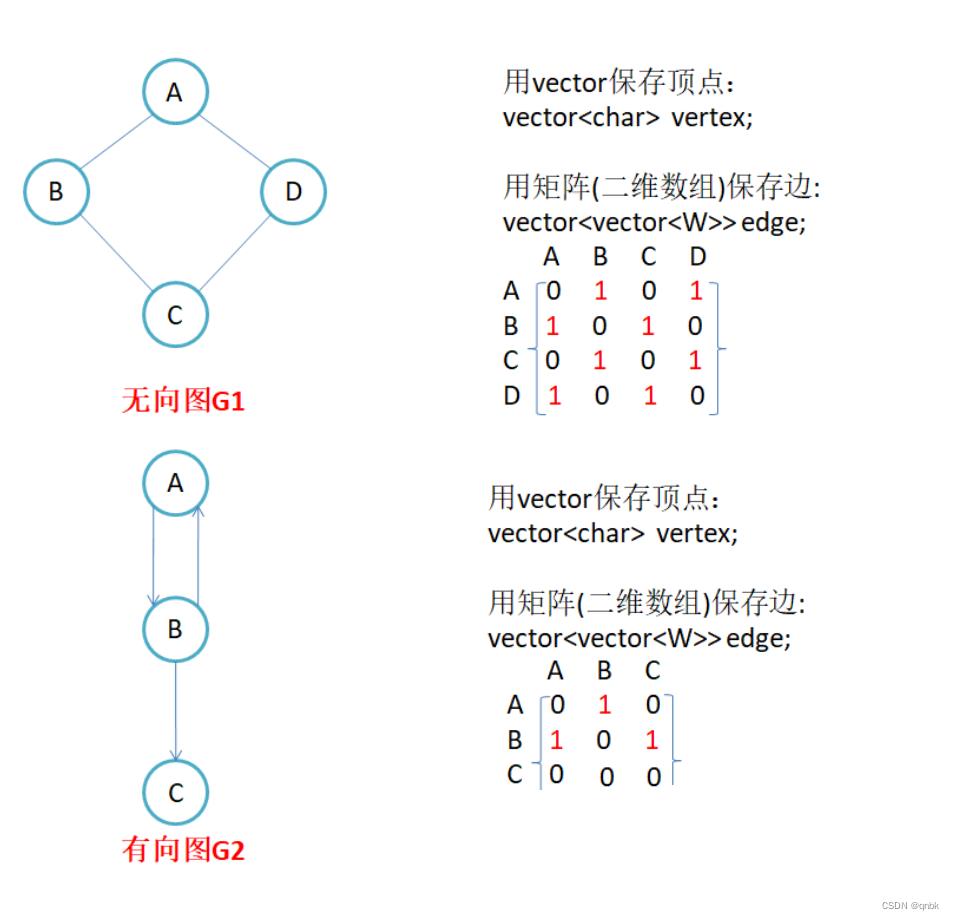
有向图和无向图:在有向图中,顶点对<x, y>是有序的,顶点对<x,y>称为顶点x到顶点y的一条边(弧),<x, y>和<y, x>是两条不同的边,在无向图中,顶点对(x, y)是无序的,顶点对(x,y)称为顶点x和顶点y相关联的一条边,这条边没有特定方向,(x, y)和(y,x)是同一条边,注意:无向边(x,y)等于有向边<x, y>和<y, x>。
G1和G2为无向图。
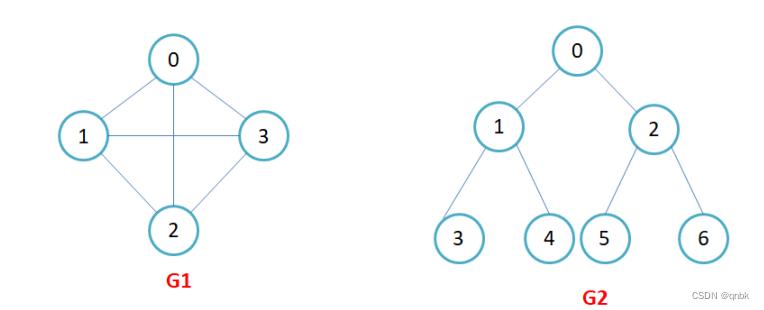
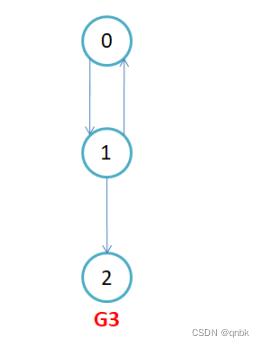
G3为有向图。
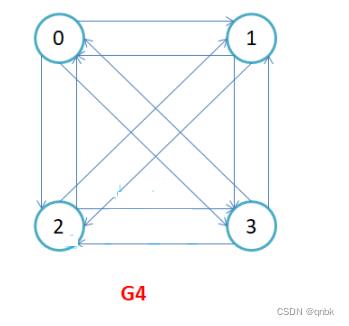
完全图:在有n个顶点的无向图中,若有n * (n-1)/2条边,即任意两个顶点之间有且仅有一条边,则称此图为无向完全图,如图G1;在n个顶点的有向图中,若有n * (n-1)条边,即任意两个顶点之间有且仅有方向相反的边,则称此图为有向完全图,如图G4
邻接顶点:在无向图中G中,若(u, v)是E(G)中的一条边,则称u和v互为邻接顶点,并称边(u,v)依附于顶点u和v;在有向图G中,若<u, v>是E(G)中的一条边,则称顶点u邻接到v,顶点v邻接自顶点u,并称边<u, v>与顶点u和顶点v相关联
顶点的度:顶点v的度是指与它相关联的边的条数,记作deg(v)。在有向图中,顶点的度等于该顶点的入度与出度之和,其中顶点v的入度是以v为终点的有向边的条数,记作indev(v);顶点v的出度是以v为起始点的有向边的条数,记作outdev(v)。因此:dev(v) = indev(v) + outdev(v)。注意:对于无向图,顶点的度等于该顶点的入度和出度,即dev(v) = indev(v) = outdev(v)。
路径: 在图G = (V, E)中,若从顶点vi出发有一组边使其可到达顶点vj,则称顶点vi到顶点vj的顶点序列为从顶点vi到顶点vj的路径。
路径长度: 对于不带权的图,一条路径的路径长度是指该路径上的边的条数;对于带权的图,一条路 径的路径长度是指该路径上各个边权值的总和。
简单路径与回路:若路径上各顶点v1,v2,v3,…,vm均不重复,则称这样的路径为简单路径。若路 径上第一个顶点v1和最后一个顶点vm重合,则称这样的路径为回路或环。
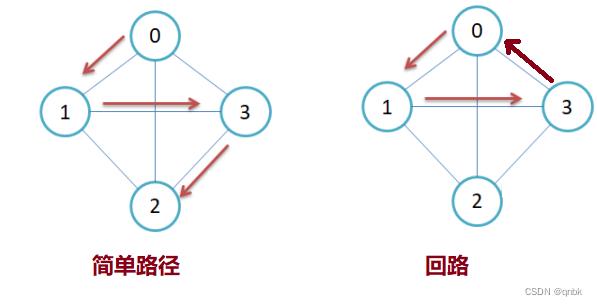
子图:设图G = V, E和图G1 = V1,E1,若V1属于V且E1属于E,则称G1是G的子图。
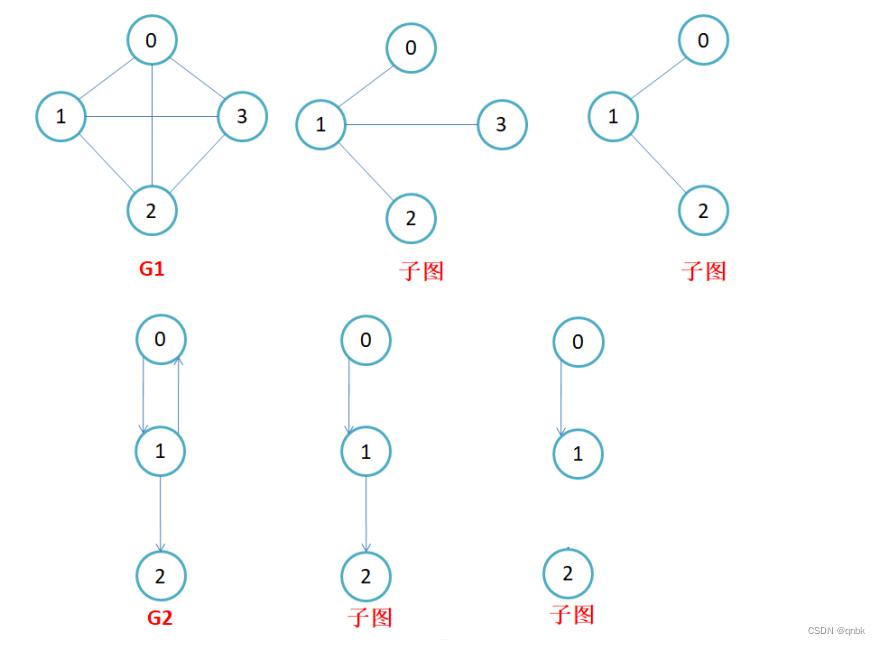
连通图:在无向图中,若从顶点v1到顶点v2有路径,则称顶点v1与顶点v2是连通的。如果图中任意一 对顶点都是连通的,则称此图为连通图。
强连通图:在有向图中,若在每一对顶点vi和vj之间都存在一条从vi到vj的路径,也存在一条从vj到 vi的路径,则称此图是强连通图。
生成树:一个连通图的最小连通子图称作该图的生成树。有n个顶点的连通图的生成树有n个顶点和n- 1条边。
图的存储结构
因为图中既有节点,又有边(节点与节点之间的关系),因此,在图的存储中,只需要保存:节点和边关系即可。节点保存比较简单,只需要一段连续空间即可
邻接矩阵
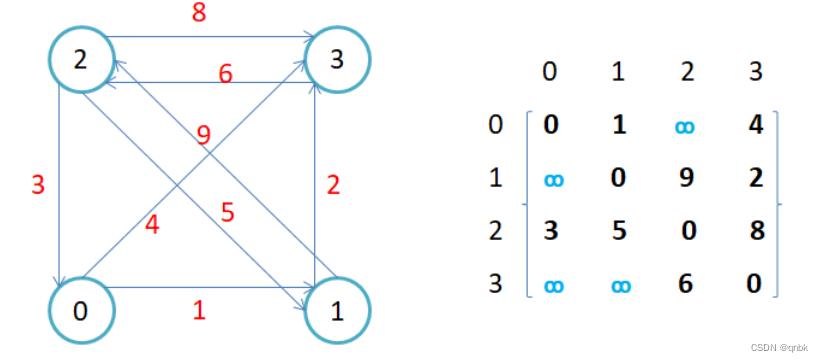
因为节点与节点之间的关系就是连通与否,即为0或者1,因此邻接矩阵(二维数组)即是:先用一个数组将定点保存,然后采用矩阵来表示节点与节点之间的关系。
注意:
- 无向图的邻接矩阵是对称的,第i行(列)元素之和,就是顶点i的度。有向图的邻接矩阵则不一定是对称 的,第i行(列)元素之后就是顶点i的出(入)度。
- 如果边带有权值,并且两个节点之间是连通的,上图中的边的关系就用权值代替,如果两个顶点不通,则使用无穷大代替。
- 用邻接矩阵存储图的有点是能够快速知道两个顶点是否连通,缺陷是如果顶点比较多,边比较少时,矩阵中存储了大量的0成为系数矩阵,比较浪费空间,并且要求两个节点之间的路径不
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
namespace Matrix//邻接矩阵
template<class V, class W,bool Direction = false>//默认是无向
class Graph
public:
Graph(const V* vertexs, size_t n)
_vertexs.reserve(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
_vertexs.push_back(vertexs[i]);
_VIndexMap[_vertexs[i]] = i;
_matrix.resize(n);
for (auto& e : _matrix)
e.resize(n);
size_t GetVertexIndex(const V& v)//得到顶点的下标
auto ret = _VIndexMap.find(v);
if (ret != _VIndexMap.end())
return ret->second;
else
throw invalid_argument("不存在顶点");
return -1;
void AddEdge(const V& src,const V& dst,const W& w)//添加边
size_t srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
size_t dstindex = GetVertexIndex(dst);
_matrix[srcindex][dstindex] = w;
if (Direction == false)
_matrix[dstindex][srcindex] = w;
void BFS(const V& src)
size_t srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
vector<bool> visited;//顶点有没有被访问过
visited.resize(_vertexs.size(),false);
queue<int> q;
q.push(srcindex);
visited[srcindex] = true;
size_t d = 1;
size_t dSize = 1;
while (!q.empty())
size_t front = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%s的%d度:\\n", src.c_str(), d);
while (dSize--)
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++)
if (visited[i] == false && _matrix[srcindex][i] != W())
printf("[%d:%s] ", i, _vertexs[i].c_str());
visited[i] = true;
q.push(i);
dSize = q.size();
++d;
std::cout << std::endl;
void _DFS(size_t srcIndex,vector<bool> visited)
printf("[%d:%s]->", srcIndex, _vertexs[srcIndex].c_str());
visited[srcIndex] = true;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++)
if (visited[i] == false && _matrix[srcIndex][i] != W())
_DFS(i, visited);
void DFS(const V& src)
size_t srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
vector<bool> visited;//顶点有没有被访问过
visited.resize(_vertexs.size(), false);
_DFS(srcindex, visited);
private:
vector<V> _vertexs;//顶点集合
vector<vector<W>> _matrix;//存储边的集合的矩阵
map<string, int> _VIndexMap;//顶点和下标之间的映射关系
;
邻接表
邻接表:使用数组表示顶点的集合,使用链表表示边的关系。类似哈希桶,把一个相连的边用链式结构挂在后面
无向图邻接表存储:
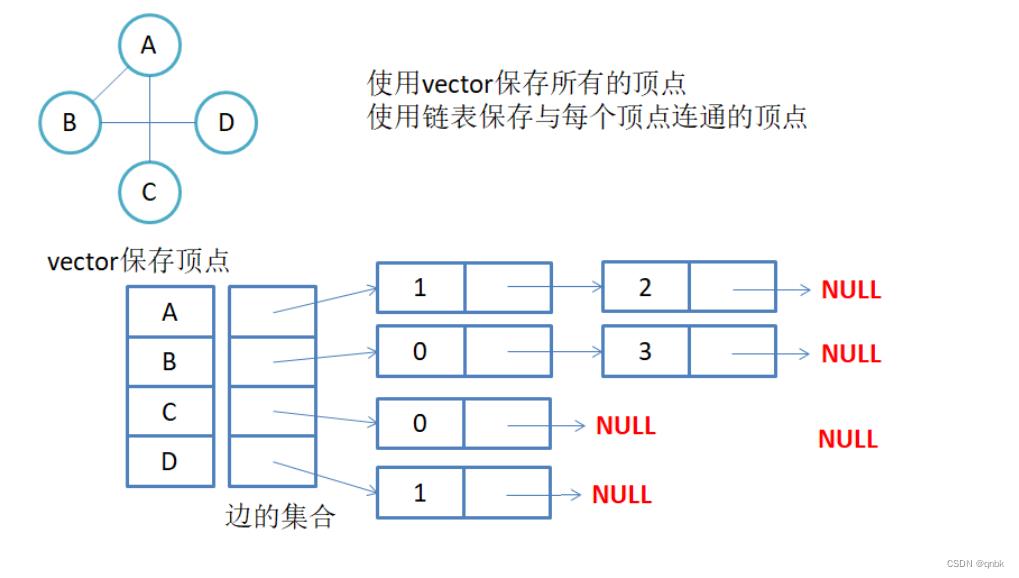
无向图中同一条边在邻接表中出现了两次。如果想知道顶点vi的度,只需要知道顶点vi边链表集合中结点的数目即可。
有向图邻接表存储:
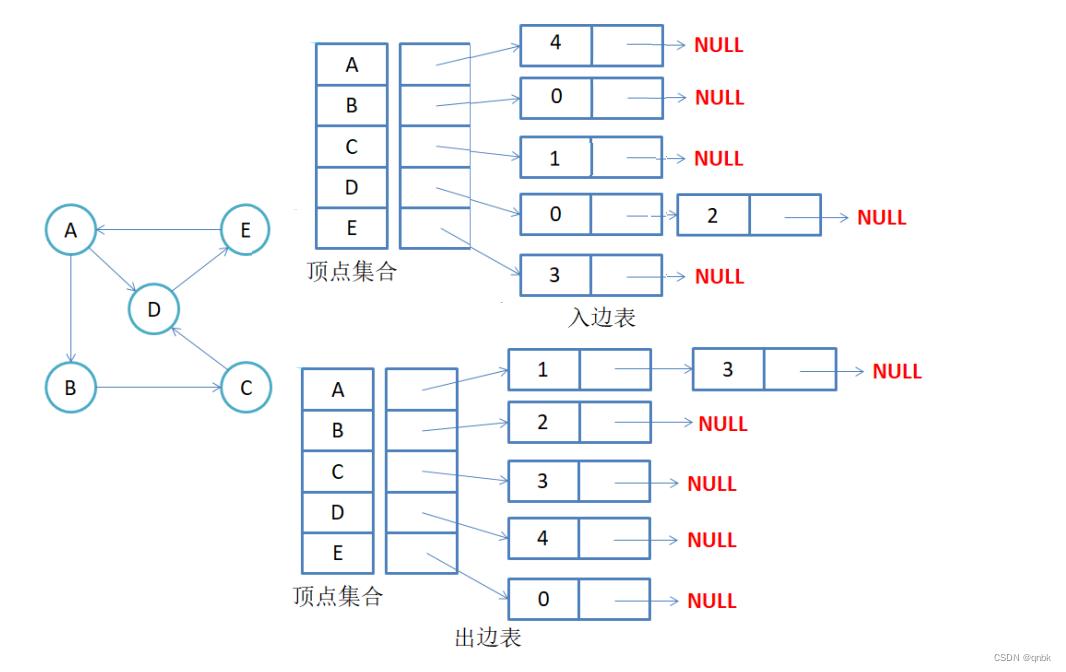
注意:有向图中每条边在邻接表中只出现一次,与顶点vi对应的邻接表所含结点的个数,就是该顶点的出度,也称出度表,要得到vi顶点的入度,必须检测其他所有顶点对应的边链表,看有多少边顶点的dst取值是i。
namespace LinkTable//邻接表
template<class W>
struct LinkEdge//邻接边
int _srcIndex;
int _dstIndex;
W _w;
LinkEdge<W>* _next;
LinkEdge(const W& w)
:_srcIndex(-1)
, _dstIndex(-1)
, _w(w)
, _next(nullptr)
;
template<class V, class W, bool Direction = false>//默认是无向
class Graph
typedef LinkEdge<W> Edge;
public:
Graph(const V* vertexs, size_t n)
_vertexs.reserve(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
_vertexs.push_back(vertexs[i]);
_VIndexMap[_vertexs[i]] = i;
_linktable.resize(n, nullptr);
size_t GetVertexIndex(const V& v)//得到顶点的下标
auto ret = _VIndexMap.find(v);
if (ret != _VIndexMap.end())
return ret->second;
else
throw invalid_argument("不存在顶点");
return -1;
void AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& w)//添加边
size_t srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
size_t dstindex = GetVertexIndex(dst);
Edge* sd_edge = new Edge(w);
sd_edge->_srcIndex = srcindex;
sd_edge->_dstIndex = dstindex;
//头插
sd_edge->_next = _linktable[srcindex];
_linktable[srcindex] = sd_edge;
if (Direction == false)
//无向图
Edge* ds_edge = new Edge(w);
ds_edge->_srcIndex = dstindex;
ds_edge->_dstIndex = srcindex;
ds_edge->_next = _linktable[dstindex];
_linktable[dstindex] = ds_edge;
private:
vector<V> _vertexs;//顶点集合
map<string, int> _VIndexMap; //顶点和下标之间的映射关系
vector<Edge*> _linktable;//边的集合的邻接表
;
图的遍历
给定一个图G和其中任意一个顶点v0,从v0出发,沿着图中各边访问图中的所有顶点,且每个顶点仅被遍历一次。"遍历"即对结点进行某种操作的意思。
图的广度优先遍历
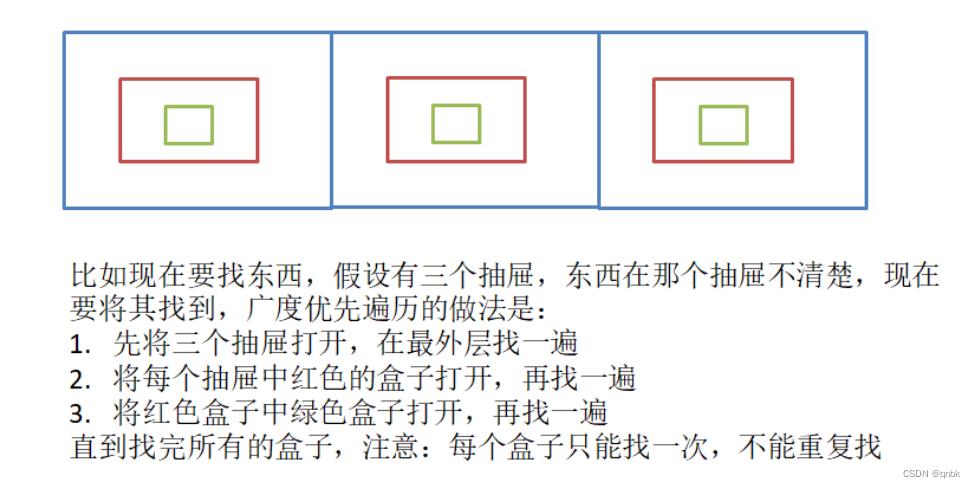
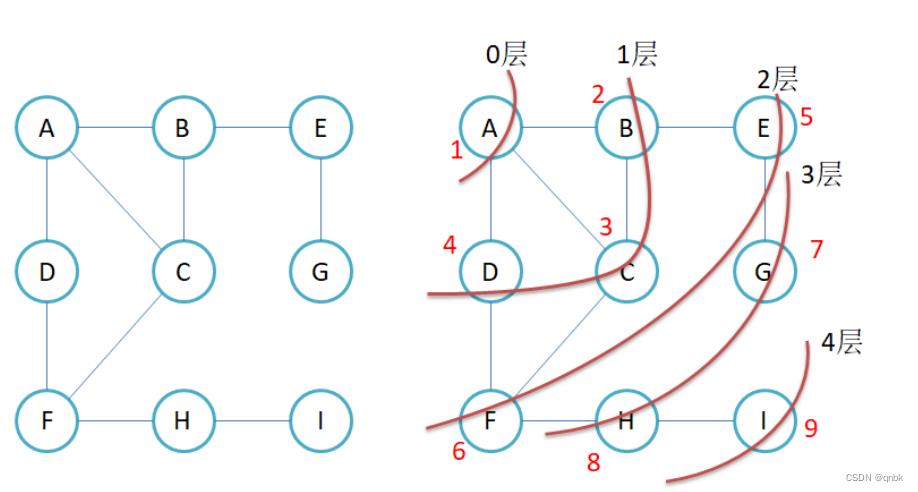
include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
namespace Matrix//邻接矩阵
template<class V, class W,bool Direction = false>//默认是无向
class Graph
public:
Graph(const V* vertexs, size_t n)
_vertexs.reserve(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
_vertexs.push_back(vertexs[i]);
_VIndexMap[_vertexs[i]] = i;
_matrix.resize(n);
for (auto& e : _matrix)
e.resize(n);
size_t GetVertexIndex(const V& v)//得到顶点的下标
auto ret = _VIndexMap.find(v);
if (ret != _VIndexMap.end())
return ret->second;
else
throw invalid_argument("不存在顶点");
return -1;
void AddEdge(const V& src,const V& dst,const W& w)//添加边
size_t srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
size_t dstindex = GetVertexIndex(dst);
_matrix[srcindex][dstindex] = w;
if (Direction == false)
_matrix[dstindex][srcindex] = w;
void BFS(const V& src)
size_t srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
vector<bool> visited;//顶点有没有被访问过
visited.resize(_vertexs.size(),false);
queue<int> q;
q.push(srcindex);
visited[srcindex] = true;
size_t d = 1;
size_t dSize = 1;
while (!q.empty())
size_t front = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%s的%d度:\\n", src.c_str(), d);
while (dSize--)
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++)
if (visited[i] == false && _matrix[srcindex][i] != W())
printf("[%d:%s] ", i, _vertexs[i].c_str());
visited[i] = true;
q.push(i);
dSize = q.size();
++d;
std::cout << std::endl;
private:
vector<V> _vertexs;//顶点集合
vector<vector<W>> _matrix;//存储边的集合的矩阵
map<string, int> _VIndexMap;//顶点和下标之间的映射关系
;
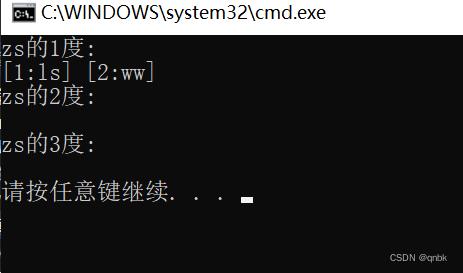
void Test()
string a[] = "zs", "ls", "ww", "zl" ,"mk";
Graph<string, int> g1(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(string));
g1.AddEdge("zs","ls",100);
g1.AddEdge("zs", "ww",200);
g1.AddEdge("ww", "zl",300);
g1.AddEdge("ww", "mk", 300);
g1.BFS("zs");
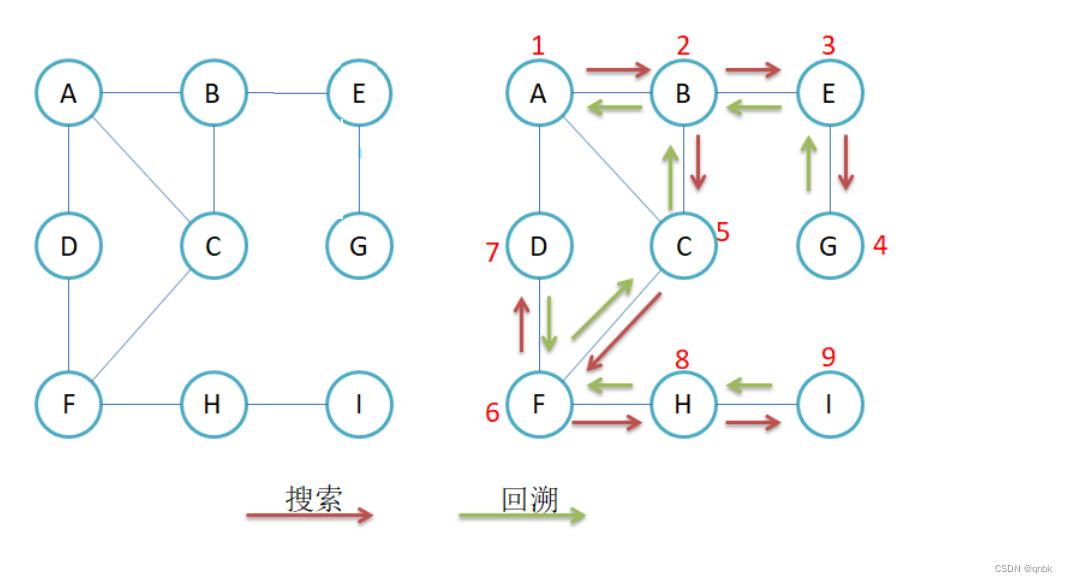
图的深度优先

#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
namespace Matrix//邻接矩阵
template<class V, class W,bool Direction = false>//默认是无向
class Graph
public:
Graph(const V* vertexs, size_t n)
_vertexs.reserve(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
_vertexs.push_back(vertexs[i]);
_VIndexMap[_vertexs[i]] = i;
_matrix.resize(n);
for (auto& e : _matrix)
e.以上是关于数据结构 图的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章