Linux磁盘管理
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux磁盘管理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
-
I/O ports(I/O设备地址):这些其实都是文件(Linux的思想就是一切皆文件),因此可以用open(),write(),read(),close()来进行操作
块设备:block,存取单位是‘块’,如:磁盘
字符设备:char,存取单位是‘字符’,如:键盘设备文件:关联至一个设备驱动程序,进而能够跟与之对应的硬件设备进行通信 设备号码: 主设备号(major number),标识设备类型 次设备号(minor number),标识同一个类型下的不同设备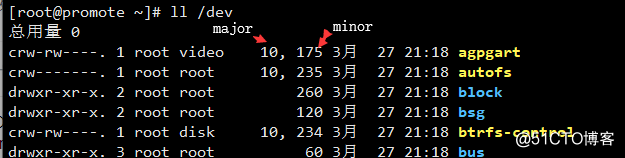
-
/dev/DEV_FILE:磁盘设备文件命名
CentOS5之前:
IDE:/dev/hd
SCSI,SATA,SAS,USB: /dev/sd
CentOS6,7 统一命名为:/dev/sd不同设备:a-z 如:/dev/sda, /dev/sdb 同一设备上不同分区:1,2,3... 如:/dev/sda1, /dev/sda2 -
磁盘分区表格式
MBR(Master Boot Record)与GPT(GUID partition Table)
MBR:在0磁道0扇区:有512bytes
boot loader:446bytes
分区表:64bytes
结束标志:2bytes
用MBR的话,最多有4个分区:3个主分区+1逻辑分区(逻辑分区可以有N个) - 分区工具
有fdisk,parted,sfdisk
1)fdisk:对于一块硬盘来讲,最多只能管理15个分区
语法:fdisk -l [-u] [device...]
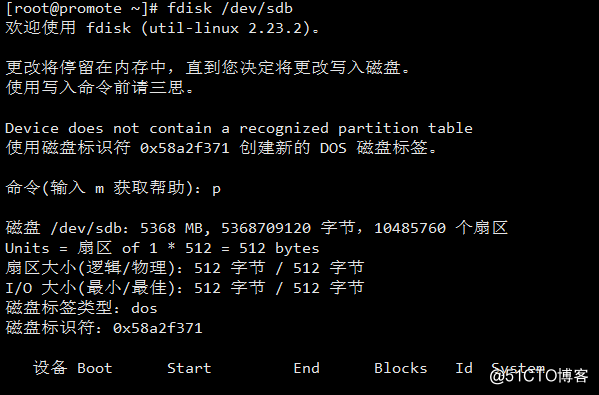
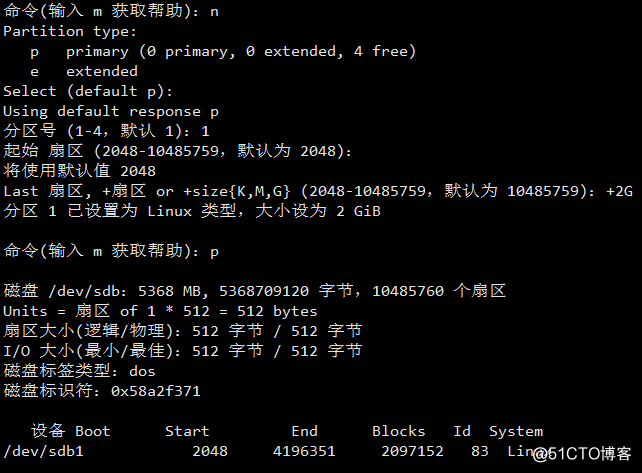
内建子命令:
命令操作
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition‘s system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)以上是关于Linux磁盘管理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章