LeetCode树(共94题)
Posted zhangwanying
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode树(共94题)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【94】Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
【95】Unique Binary Search Trees II (2018年11月14日,算法群)
给了一个 n,返回结点是 1 ~ n 的所有形态的BST。
题解:枚举每个根节点 r, 然后递归的生成左右子树的所有集合,然后做笛卡尔积。

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int n) { 13 if (n == 0) {return vector<TreeNode*>();} 14 return generateTrees(1, n); 15 } 16 17 vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int begin, int end) { 18 vector<TreeNode*> ret; 19 if (begin > end) { 20 ret.push_back(nullptr); 21 return ret; 22 } 23 if (begin == end) { 24 TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(begin); 25 ret.push_back(root); 26 return ret; 27 } 28 for (int r = begin; r <= end; ++r) { 29 vector<TreeNode*> leftSon = generateTrees(begin, r - 1); 30 vector<TreeNode*> rightSon = generateTrees(r + 1, end); 31 for (auto leftEle : leftSon) { 32 for (auto rightEle : rightSon) { 33 TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(r); 34 root->left = leftEle; 35 root->right = rightEle; 36 ret.push_back(root); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 return ret; 41 } 42 };
这题还能用 dp 解答,估计能快点。dp怎么解答看discuss。
【96】Unique Binary Search Trees (2018年11月14日,算法群相关题复习)
给了一个 n, 返回结点是 1 ~ n 的 BST 有多少种形态。
题解:dp, dp[k] 代表 k 个结点的 BST 有多少种形态。dp[0] = 1, dp[1] =1, dp[2] = 2。dp[k] = sigma(dp[left] * dp[k - left - 1]) (0 <= left < k)

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int numTrees(int n) { 4 // f[0] = 1, f[1] = 1, f[2] = 2, 5 // f[k] = sigma(f[i] * f[k-i-1]) (i belongs [0, k-1]) 6 vector<int> dp(n+1, 0); 7 dp[0] = dp[1] = 1; dp[2] = 2; 8 for (int k = 3; k <= n; ++k) { 9 for (int left = 0; left <= k-1; ++left) { 10 int right = k - left - 1; 11 dp[k] += dp[left] * dp[right]; 12 } 13 } 14 return dp[n]; 15 } 16 };
【98】Validate Binary Search Tree
写个函数检查一棵树是不是BST
题解:直接判断左儿子比根小,右儿子比跟大是会WA的... 举个会WA的例子。

 View Code
View Code
【99】Recover Binary Search Tree
【100】Same Tree
【101】Symmetric Tree
【102】Binary Tree Level Order Traversal (2019年1月26日,谷歌tag复习)
二叉树的层级遍历
题解:bfs,这题不上代码。
【103】Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal (2019年1月26日,谷歌tag复习)
二叉树的层级遍历,zigzag版本
题解:用两个栈,不是用队列了。

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) { 13 if (!root) { 14 return vector<vector<int>>(); 15 } 16 stack<TreeNode*> stk, stk2; 17 stk.push(root); 18 vector<vector<int>> ret; 19 int line = 0; 20 while (!stk.empty()) { //stk: [7, 15] 21 const int size = stk.size(); // size = 2 22 vector<int> rows; 23 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { 24 TreeNode* cur = stk.top(); stk.pop(); //cur = 15, 7 25 rows.push_back(cur->val); //rows = {15} 26 if (line & 1) { // 27 if (cur->right) { 28 stk2.push(cur->right); //stk2 : 7 29 } 30 if (cur->left) { 31 stk2.push(cur->left); //stk2 : 7, 15 32 } 33 } else { 34 if (cur->left) { 35 stk2.push(cur->left); 36 } 37 if (cur->right) { 38 stk2.push(cur->right); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 ret.push_back(rows); //[[3], [20, 9], ] 43 line ^= 1; //line = 0; 44 swap(stk, stk2); // stk = [7, 15] 45 } 46 return ret; 47 } 48 };
【104】Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
【105】Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
【106】Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
给中序遍历 和 后序遍历, 重建二叉树。
题解:没啥难度,一次ac
 View Code
View Code
【107】Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
【108】Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
给一个增序的vector, 建立一棵高度平衡的BST.
这个题一开始懵了,不会做。。。信不信考到你就挂了orz
思路是二分的思想,从root开始建树,然后左儿子,右儿子。
 View Code
View Code
【110】Balanced Binary Tree (2019年1月26日,谷歌tag复习)
判断一棵树是不是高度平衡的二叉树。
题解:分别判断左儿子和右儿子是不是高度平衡的二叉树。然后判断左儿子的高度和右儿子的高度是否相差小于等于1.

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { 13 if (!root) {return true;} 14 int leftHeight = getHeight(root->left), rightHeight = getHeight(root->right); 15 if (abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) { 16 return false; 17 } 18 return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right); 19 } 20 int getHeight(TreeNode* root) { 21 if (!root) { return 0;} 22 if (!root->left && !root->right) {return 1;} 23 return max(getHeight(root->left), getHeight(root->right)) + 1; 24 } 25 };
【111】Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
【112】Path Sum
【113】Path Sum II
【114】Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
把一颗二叉树拍平成一个链表。如图。判空,莫忘。要取一个节点的子节点之前,要判断这个节点是否为空。
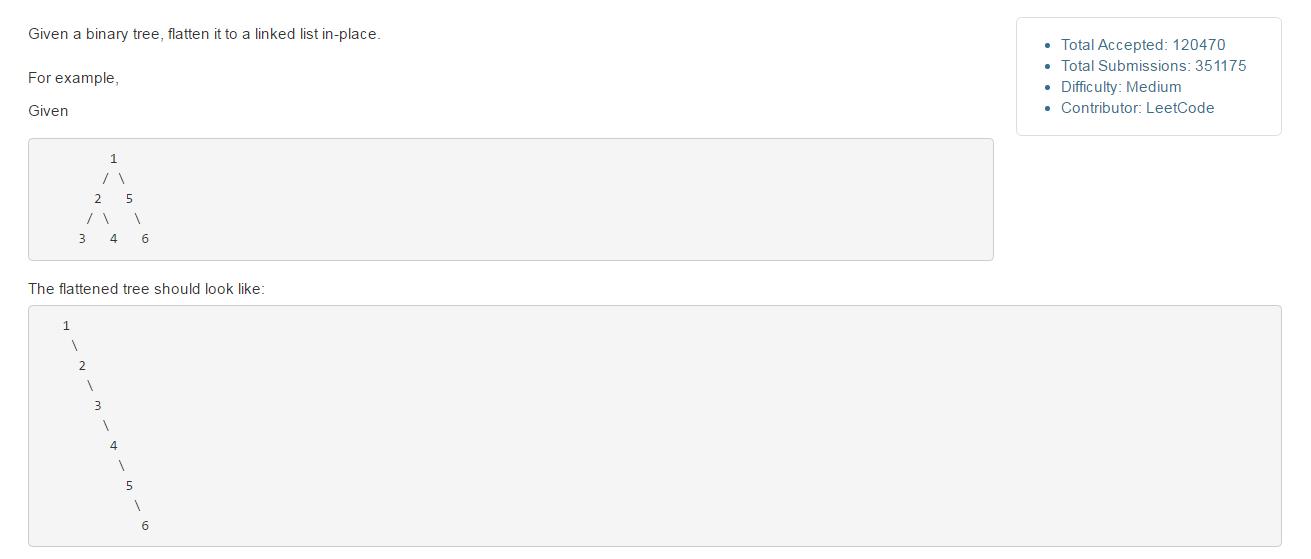
 View Code
View Code
【116】Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node (2019年1月26日,谷歌tag复习)
给了一个很特殊的满二叉树的结构,让我们把每层的节点都和它的兄弟/邻居节点连接起来。
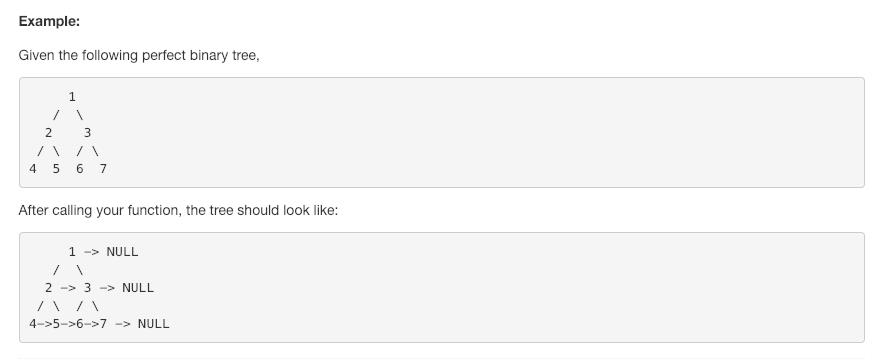
题解:我是用了 bfs 来解决这个问题的。

1 /** 2 * Definition for binary tree with next pointer. 3 * struct TreeLinkNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeLinkNode *left, *right, *next; 6 * TreeLinkNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} 7 * }; 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public: 11 void connect(TreeLinkNode *root) { 12 if (!root) { return; } 13 queue<TreeLinkNode* > que; 14 que.push(root); 15 while (!que.empty()) { 16 const int size = que.size(); 17 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { 18 TreeLinkNode* cur = que.front(); que.pop(); 19 if (i == size - 1) { 20 cur->next = nullptr; 21 } else { 22 cur->next = que.front(); 23 } 24 if (cur->left) { 25 que.push(cur->left); 26 } 27 if (cur->right) { 28 que.push(cur->right); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 return; 33 } 34 };
【117】Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II (2019年1月26日,谷歌tag复习)
本题和116的区别在于,给的树可能不是满二叉树。
题解:还是116的方法可以解。代码同116,一行都不用改。
【124】Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
【129】Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
【144】Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
【145】Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
【156】Binary Tree Upside Down
【173】Binary Search Tree Iterator
【199】Binary Tree Right Side View
【222】Count Complete Tree Nodes
【226】Invert Binary Tree
【230】Kth Smallest Element in a BST
【235】Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree (2019年1月29日,复习)
返回一棵 bst 的给定两个结点的最小公共祖先。
题解:如果这两个结点的值一个小于等于root,一个大于等于root,那么返回root。否则如果都比root小的话,就递归到左边结点,如果都比root大的话,就递归到右边结点。

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { 13 if (!root || !p || !q) {return nullptr;} 14 if (p->val <= root->val && q->val >= root->val || q->val <= root->val && p->val >= root->val) { 15 return root; 16 } 17 if (p->val < root->val && q->val < root->val) { 18 return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); 19 } 20 return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); 21 } 22 };
【236】Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree (2019年1月29日,复习)
给定一棵任意二叉树和两个结点p,q,返回p,q的最小公共祖先。
题解:比较简单想的一种解法就是从root开始分别做两个dfs,找 p 和 q 的路径,找到之后,返回公共的最后一个结点。

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { 13 if (!root) {return root;} 14 vector<TreeNode*> pathP, pathQ; 15 dfs(root, p, pathP); 16 dfs(root, q, pathQ); 17 reverse(pathP.begin(), pathP.end()); 18 reverse(pathQ.begin(), pathQ.end()); 19 TreeNode* res = root; 20 for (int i = 0; i < (int)min(pathP.size(), pathQ.size()); ++i) { 21 if (pathP[i] == pathQ[i]) { 22 res = pathP[i]; 23 } else { 24 break; 25 } 26 } 27 return res; 28 } 29 bool dfs(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, vector<TreeNode*>& path) { 30 if (!root) { return false; } 31 if (root == p || dfs(root->left, p, path) || dfs(root->right, p, path)) { 32 path.push_back(root); 33 return true; 34 } 35 return false; 36 } 37 };
还有一种递归的方法可以做。前提是 p, q这两个结点要保证在二叉树里面。
1. 如果当前node为空,或者等于p,q中的任意一个的话,那么就返回node。
2.分别递归调用node的左右子树,查看返回结果,如果leftRes == null ,就说明两个结点都在右子树里面,返回rightRes,如果rightRes == null, 说明两个结点都在左子树里面,返回leftRes。否则的话,一左一右说明应该返回当前层的node。

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { 13 if (!root) {return root;} 14 if (root == p || root == q) { 15 return root; 16 } 17 TreeNode* leftRes = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); 18 TreeNode* rightRes = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); 19 if (!leftRes) { 20 return rightRes; 21 } 22 if (!rightRes) { 23 return leftRes; 24 } 25 return root; 26 } 27 };
【250】Count Univalue Subtrees
返回一棵二叉树所有结点值都相同的子树的个数。
题解:叶子结点肯定是 univalue 的子树,如果不是叶子结点,就先判断它的左右儿子是不是 univalue subtree,如果是,在判断根节点和左右儿子结点这三个值是否相等,如果子树都不是 univalue 的了,那么包含根结点的更加不是了。
不要随便在leetcode里面用静态变量,不然一个新的case如果没有重新初始化静态变量就直接在原来case的基础上累加/变化了。

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 //如果是叶子结点,就直接+1, 如果不是叶子结点,就判断左右子树是不是uni-value tree,如果是,再判断root和左右儿子的值是否相等,不然如果子树不是 uni-val tree, 那么更大的树也肯定不是 uni-val tree。 11 class Solution { 12 public: 13 int countUnivalSubtrees(TreeNode* root) { 14 isSameVal(root); 15 return cnt; 16 } 17 bool isSameVal(TreeNode* root) { 18 if (!root) {return true;} 19 if (!root->left && !root->right) { 20 cnt++; 21 return true; 22 } 23 bool leftSame = isSameVal(root->left), rightSame = isSameVal(root->right); 24 if (!leftSame || !rightSame) { 25 return false; 26 } 27 if (!root->left && root->right && root->right->val == root->val) { 28 cnt++; 29 return true; 30 } else if (!root->right && root->left && root->left->val == root->val) { 31 cnt++; 32 return trueLeetCode前缀树 trie(共14题)LeetCode线段树 segment-tree(共9题)+ 树状数组 binary-indexed-tree(共5题)
