单片机实现简易版shell的方法和原理
Posted kimalittlestar
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了单片机实现简易版shell的方法和原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Rt-thread 中有一个完整的finsh(shell )系统,使用串口做命令行输入输出.但是想要用这个炫酷的工具就必须要上rtthread系统,或者花大力气将其移植出来.于是我就自己写了一个类似于这样的插件.只需要把一对.c/.h文件加入到你的工程,就可以实现这个简易版的shell.
git: https://github.com/KimAlittleStar/ExternFunc
ExternFunc.c

1 #include "stdio.h"
2 #include "string.h"
3 #include "ExternFunc.h"
4 #include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
5
6 #define MATCH_CASE_ENABLE 0 //函数调用名称大小写是否敏感 1表示敏感 0 表示不敏感
7
8 void show(int i);
9 void showcircle(char ch,int r);
10
11 static int ExternFunc_Find(char* funcname);
12 static void ExternFunc_list(void);
13 static void ExternFunc_SocReset(void);
14 static unsigned char matchString(const char* str1,const char* str2);
15
16 const CALLFUNCTIONTABLE functable[] =
17 {
18 EXPOTRFUNC(LIST,ExternFunc_list, ,函数列表),
19 EXPOTRFUNC(RST,ExternFunc_SocReset,,芯片软件复位),
20 EXPOTRFUNC(circle,showcircle,%c %d,串口显示一个圆),
21 EXPOTRFUNC(九九乘法表,show,%d,%d乘法表)
22 };
23 //EXPOTRFUNC( 函数别名命令行调用的名字 |真正的函数名 | 函数传参的格式字符串 |这个函数的简介)
24 void simplefunction(char* str,unsigned int sum,float dee,char ch)
25 {
26
27 printf("接收到的字符串是:%s,
28 接收到的字符是: %c
29 接受到的数字是 %d
30 接收到的小数是 %f __
",str,ch,sum,dee);
31 }
32
33 void showcircle(char ch,int r)
34 {
35 for(int i = 1; i<=(2*r); i++)
36 {
37 for(int j = 1; j<(2*r); j++)
38 {
39 if(((i-r)*(i-r)+(j-r)*(j-r))<=(r*r))
40 printf("%c ",ch);
41 else
42 printf("%c ",‘ ‘);
43 }
44 printf("
");
45 }
46 }
47
48 void show(int i)
49 {
50 for(int qq = 1;qq<= i;qq++)
51 {
52 for(int j = 1;j<=qq;j++)
53 {
54 printf("%dx%d=%2d ",j,qq,j*qq);
55 }
56 printf("
");
57 }
58 }
59 //以上是示例的测试函数
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85 //以下是真正的实现函数
86
87 //找到对应函数的 函数指针 返回数组号
88 // 输入: "circle * 16" return 2
89 static int ExternFunc_Find(char* funcname)
90 {
91 int size = sizeof(functable)/sizeof(functable[0]);
92 for(int i = 0; i<size; i++)
93 {
94 if(matchString(funcname,functable[i].FuncName) == 0)
95 return i;
96 }
97 return -1;
98 }
99
100
101 //因为需要兼容字符串,所以需要二维数组 最多可以传参字符串长度为 (100-1)*4
102 static void* args[7][100] = {0};
103
104 //外部调用函数,传入字符串自动找到对应函数 并执行.(不会打印返回值)
105 void ExternFunc_excute(char* str)
106 {
107 char* ptemp;
108 char ch;
109 ptemp = strstr(str," ");
110 if(ptemp == NULL)
111 {
112 ptemp = str+strlen(str);
113 ch = *ptemp;
114 }
115 else
116 {
117 ch = ‘�‘;
118 *ptemp = ‘�‘;
119 ptemp++;
120 }
121
122
123
124
125 int loc = ExternFunc_Find(str); //寻找函数
126 if(loc == -1)
127 {
128 printf("%s are not find
the function list :
",str);
129 ExternFunc_list();
130 return ;
131 }
132
133 if(ch != ‘�‘)
134 *ptemp = ch;
135 int success = sscanf(ptemp,functable[loc].fmt,&args[0][1],&args[1][1],&args[2][1],&args[3][1],&args[4][1],&args[5][1]);
136
137 //为兼容 可以输入字符串而做出的妥协
138 int i = 0;
139 ptemp = (char*)functable[loc].fmt;
140 for(i = 0;i<7;i++)
141 {
142 if((ptemp=strstr(ptemp,"%")) !=NULL)
143 {
144
145 if(*(++ptemp) == ‘s‘)
146 args[i][0] = &args[i][1];
147 else
148 args[i][0] = args[i][1];
149 }else break;
150 }
151 if(i!= success)
152 {
153 printf("Err: 函数%s 参数应该为%d个,但只有%d
",functable[loc].FuncName,i,success);
154 return ;
155 }
156 //调用真正的函数
157 functable[loc].func(args[0][0],args[1][0],args[2][0],args[3][0],args[4][0],args[5][0],args[6][0]);
158 }
159
160
161 void ExternFunc_list(void)
162 {
163 static char isfirstPrint = 0;
164
165 int size = sizeof(functable)/sizeof(functable[0]);
166 printf("QuickComplet:");
167 for(int i = 0;i<size;i++)
168 {
169 printf(""%s"",functable[i].FuncName);
170 if(i != (size-1))
171 printf(",");
172 }
173 printf("
*---------------------------------------------------------
");
174 for(int i = 0; i<size; i++)
175 {
176 printf(" | %s(%s);%30s
",functable[i].FuncName,functable[i].fmt,functable[i].Introduction);
177 if(i != size-1)
178 printf(" |--------------------------------------------------------
");
179 }
180 printf("*---------------------------------------------------------
");
181 }
182
183
184
185
186 static void ExternFunc_SocReset(void)
187 {
188
189 __set_FAULTMASK(1);//关闭所有中断
190 NVIC_SystemReset();//复位
191 }
192
193
194 static unsigned char matchString(const char* str1,const char* str2)
195 {
196 char* ptemp1 = (char*) str1;
197 char* ptemp2 = (char*) str2;
198 while(*ptemp1 != ‘�‘ || *ptemp2 != ‘�‘)
199 {
200 #if MATCH_CASE_ENABLE==0
201 if(((*ptemp1-*ptemp2) == (‘A‘-‘a‘) || (*ptemp1-*ptemp2) == (‘a‘-‘A‘))&&
202 (*ptemp1>= ‘A‘ && *ptemp1<= ‘z‘ && *ptemp2>= ‘A‘ && *ptemp2<= ‘z‘))
203 {
204 ptemp1++;
205 ptemp2++;
206 }else if(*ptemp1 != *ptemp2) return 1;
207 #else
208 if(*ptemp1 != *ptemp2) return 1;
209 #endif
210
211 else
212 {
213 ptemp1++;
214 ptemp2++;
215 }
216 }
217 if(*ptemp1 == ‘�‘&& *ptemp2 == ‘�‘)
218 return 0;
219 else
220 return 0xFF;
221 }
ExternFunc.h

1 #ifndef EXTERNFUNC_H_INCLUDED
2 #define EXTERNFUNC_H_INCLUDED
3
4 #include "stdio.h"
5 #include "string.h"
6
7 typedef struct
8 {
9 const char * FuncName;
10 void *( (*func)(void* args,...));
11 const char * fmt;
12 const char * Introduction;
13 } CALLFUNCTIONTABLE;
14
15 #define EXPOTRFUNC(NAME,FUNC,FTM,INTRO) {#NAME,(void *(*)(void* args,...))FUNC,#FTM,#INTRO}
16
17 extern const CALLFUNCTIONTABLE functable[];
18
19 void ExternFunc_excute(char* str);
20
21
22 #endif // EXTERNFUNC_H_INCLUDED
里面内置了两个函数 一个LIST函数和 RST
LIST 指令是打印出当前所有的可以调用的函数信息
RST 是复位单片机(Cortex M0.3.4.7 系列可用) 主要原理:禁止所有中断 ,人为触发复位中断.
其他函数可以删除.
原理:
函数传参的值以第一个参数的地址基准,依次向后偏移,可变参数的值获取方式也是这么做的.那么我们只需要把相应的值摆列排放到指定位置即可.
实现的关键在于一个函数指针:
void *( (*func)(void* args,...));
强制转换成上述指针函数后可以传入不定参数,以适应不同函数,不同个传参值 ,不同的传参类型.
我们知道函数指针是指向函数的,里面存放的是函数的跳转地址.那么使用函数指针就是把某个函数的跳转地址存进来,等到 PC寄存器读取到之后,自动跳转到指定函数.上面这个函数指针指向一个什么函数呢?指向返回值为空类型指针 , 传参为 (void * args ,...) 格式的函数.而 printf 的函数原型 int printf(const char* str , ... ) ; 这个" ... " 代表可变参数.所以我们才可以同时 printf 多个值,同时 还带有 "... "的函数有哪些呢: sprintf ,scanf ,sscanf. 可能 sscanf 和 sprintf 大家见得不多.这里给大家示例一下怎么使用.大家就知道是什么功能了
1 char buff [100];
2 char *string = "hello world";
3 int a = 10;
4 sprintf(buff,"a = %d string = %s",a,string);
5
6 printf("%s",buff); //buff: "a = 10 string = hello world"
7
8 char ssbuff[100] = "%d %s";
9 int b;
10 char sstring[50];
11 sscanf(ssbuff,"10 HelloWorld",&b,sstring);
12 printf(" b = %d sstring = %s",b ,sstring); //b = 10 sstring = "HelloWorld"
实现原理参考文末跳转链接
根据这个原理.当我们把函数 void show(int a ,int b); 强制转换为 void* show(void* a,...) 只要我们在 调用show() 的时候 只传送两个参数即可.如果你传入了其他参数,那么会有影响嘛,会有,会影响到函数里面的其他的局部变量的值.但是我们做好局部变量值的初始化的话,就没关系啦,
怎么做到 对应的函数 传对应的值 ? 在functable 中需要输入 %c %d 就是对于输入格式的限定.同时在sscanf 中会返回转换一个int 表示成功转换数; 例如%d %c 正常的话会返回2 那么我只要检测 他返回的和我检测到的%号 的个数不匹配.那么我就报错,个数不匹配.
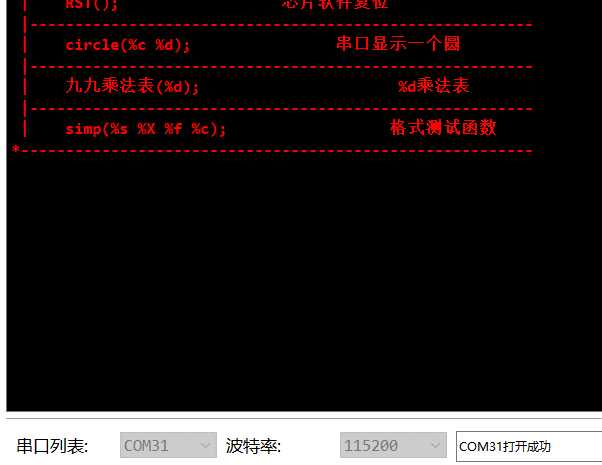
通过 使用 sscanf 将字符串转化为对应格式.灌入指定的函数中,就可以执行响应函数啦.
不过这么做有风险吗? 有 ,因为是强制类型转换,对于类型检查不严格(就没有类型检查) .可能会出现奇奇怪怪的现象. 同时 因为 float 是使用2进制的科学计数法在内存中存储. long long 类型和 double 是64 位宽,而我们的void* 是32位宽.所以 double 类型 long long 类型 float 类型 带有这三类的传参函数 和自定义的struct类型 参数值都会不正常.
printf 原理:http://www.cnblogs.com/ThatsMyTiger/p/6924462.html
以上是关于单片机实现简易版shell的方法和原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
