Linux驱动之平台设备驱动模型简析(驱动分离分层概念的建立)
Posted andy_fly
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux驱动之平台设备驱动模型简析(驱动分离分层概念的建立)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Linux设备模型的目的:为内核建立一个统一的设备模型,从而有一个对系统结构的一般性抽象描述。换句话说,Linux设备模型提取了设备操作的共同属性,进行抽象,并将这部分共同的属性在内核中实现,而为需要新添加设备或驱动提供一般性的统一接口,这使得驱动程序的开发变得更简单了,而程序员只需要去学习接口就行了。
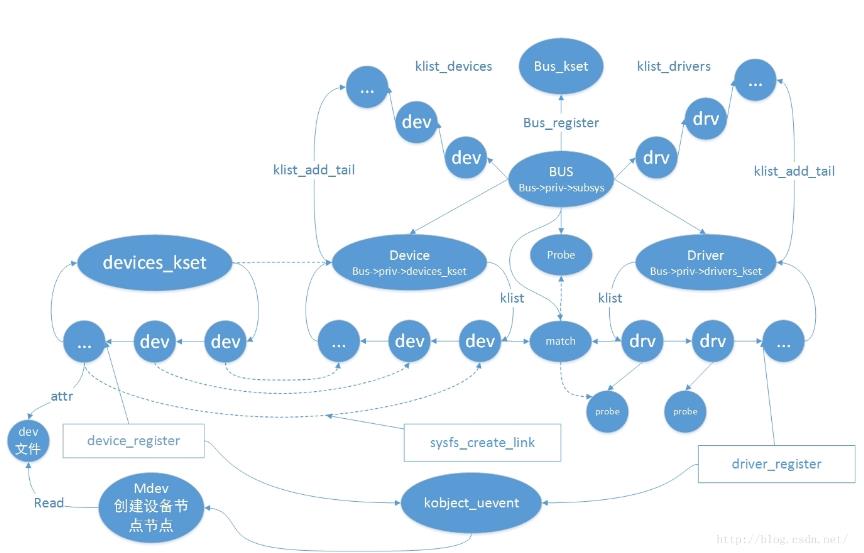
对于整个设备总线驱动模型的样子,如下图。简单来说,bus 负责维护注册进来的devcie 与 driver,每注册进来一个device 或者 driver 都会调用 Bus->match 函数 将device 与 driver 进行配对,并将它们加入链表,如果配对成功,调用Bus->probe或者driver->probe函数。注意:一个device 只能配对一个driver;而一个driver可以对应多个device。其它诸如devices_kset、kobject_uevent这里不关心,这个涉及的内容比较深入,暂时不去分析。
platform平台设备驱动是基于设备总线驱动模型的,如下图,这篇主要是记录平台设备的驱动与设备的注册匹配过程
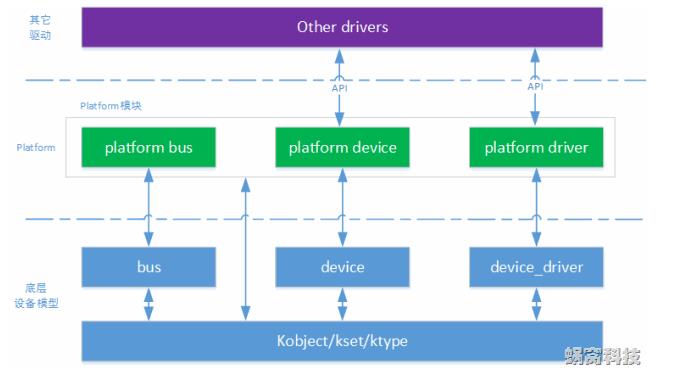
以上参考自
platform_bus提供platform_device_register、platform_driver_register等函数供platform_device层与platform_driver调用。
platform_driver属于驱动层,会在里面提供file_operations结构体供应用层调用、创建设备节点文件对应相应的驱动
platform_device属于设备层,会在里面提供resource资源文件供驱动层调用
下面是一个例子,分别编写了Led_dev.c设备文件和Led_drv.c驱动文件。列出程序源码,再根据源码分析Led_dev与Led_drv注册与匹配过程
Led_dev.c的程序源码:
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/version.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/interrupt.h> #include <linux/list.h> #include <linux/timer.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/serial_core.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> /* 分配/设置/注册一个platform_device */ static struct resource led_resource[] = { [0] = { .start = 0x56000050, .end = 0x56000050 + 8 - 1, .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM, }, [1] = { .start = 5, .end = 5, .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, } }; static void led_release(struct device * dev) { } static struct platform_device led_dev = { .name = "myled", .id = -1, .num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(led_resource), .resource = led_resource, .dev = { .release = led_release, }, }; static int led_dev_init(void) { platform_device_register(&led_dev); return 0; } static void led_dev_exit(void) { platform_device_unregister(&led_dev); } module_init(led_dev_init); module_exit(led_dev_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Led_drv.c的程序源码:
/* 分配/设置/注册一个platform_driver */ #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/version.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/interrupt.h> #include <linux/irq.h> #include <linux/sched.h> #include <linux/pm.h> #include <linux/sysctl.h> #include <linux/proc_fs.h> #include <linux/delay.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/input.h> #include <linux/irq.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h> #include <asm/io.h> static int major; static struct class *cls; static volatile unsigned long *gpio_con; static volatile unsigned long *gpio_dat; static int pin; static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { //printk("first_drv_open\\n"); /* 配置为输出 */ *gpio_con &= ~(0x3<<(pin*2)); *gpio_con |= (0x1<<(pin*2)); return 0; } static ssize_t led_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos) { int val; //printk("first_drv_write\\n"); copy_from_user(&val, buf, count); // copy_to_user(); if (val == 1) { // 点灯 *gpio_dat &= ~(1<<pin); } else { // 灭灯 *gpio_dat |= (1<<pin); } return 0; } static struct file_operations led_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自动创建的__this_module变量 */ .open = led_open, .write = led_write, }; static int led_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { struct resource *res; /* 根据platform_device的资源进行ioremap */ res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); gpio_con = ioremap(res->start, res->end - res->start + 1); gpio_dat = gpio_con + 1; res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ, 0); pin = res->start; /* 注册字符设备驱动程序 */ printk("led_probe, found led\\n"); major = register_chrdev(0, "myled", &led_fops); cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myled"); class_device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "led"); /* /dev/led */ return 0; } static int led_remove(struct platform_device *pdev) { /* 卸载字符设备驱动程序 */ /* iounmap */ printk("led_remove, remove led\\n"); class_device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 0)); class_destroy(cls); unregister_chrdev(major, "myled"); iounmap(gpio_con); return 0; } struct platform_driver led_drv = { .probe = led_probe, .remove = led_remove, .driver = { .name = "myled", } }; static int led_drv_init(void) { platform_driver_register(&led_drv); return 0; } static void led_drv_exit(void) { platform_driver_unregister(&led_drv); } module_init(led_drv_init); module_exit(led_drv_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
将上面两个程序编译后得到Led_dev.ko和Led_drv.ko两个模块,假设先加载Led_dev.ko文件:insmod Led_drv.ko。
列出执行加载操作后的程序流程:加载后会先调用led_drv_init函数,这个函数只是调用platform_driver_register函数。
platform_driver_register(&led_drv); led_drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;//platform_bus_type里面含有platform_match匹配函数 led_drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe; led_drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove; driver_register(&led_drv->driver); bus_add_driver(&led_drv->driver); driver_attach(&led_drv->driver); bus_for_each_dev(led_drv->driver->bus, NULL, &led_drv->driver, __driver_attach); while ((dev = next_device(&i)) && !error) { __driver_attach(dev, led_drv->driver); driver_probe_device(drv, dev); drv->bus->match(&led_dev->dev, drv);//最终调用到这个函数匹配,找到这个函数其实是platform_match函数 really_probe(&led_dev->dev, drv);//匹配成功调用 dev->driver = drv;//匹配驱动 drv->probe(dev);//调用led_drv->driver.probe函数 }
首先platform_driver_register函数会初始化driver.bus、driver.probe、driver.remove等变量
int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv) { drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type; if (drv->probe) drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe; if (drv->remove) drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove; if (drv->shutdown) drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown; if (drv->suspend) drv->driver.suspend = platform_drv_suspend; if (drv->resume) drv->driver.resume = platform_drv_resume; return driver_register(&drv->driver); }
其中platform_bus_type里含有platform_match函数,这个函数最终会被调用用来匹配Led_dev与Led_drv。
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = { .name = "platform", .dev_attrs = platform_dev_attrs, .match = platform_match, .uevent = platform_uevent, .suspend = platform_suspend, .suspend_late = platform_suspend_late, .resume_early = platform_resume_early, .resume = platform_resume, };
static int platform_match(struct device * dev, struct device_driver * drv) { struct platform_device *pdev = container_of(dev, struct platform_device, dev); return (strncmp(pdev->name, drv->name, BUS_ID_SIZE) == 0);//根据名称匹配dev与drv }
接着看到driver_register函数,通过层层调用,最终会从dev链表搜索,通过platform_match函数找到与Led_drv匹配的Led_dev。找到后调用really_probe函数,really_probe函数先是执行dev->driver = drv;这样就将dev与drv联系起来了,接着调用led_probe函数,初始化驱动。因为这时候还没有注册Led_dev.ko所以不会匹配成功。
接着加载Led_dev.ko文件:insmod Led_dev.ko。列出执行加载操作后的程序流程:加载后会先调用led_dev_init函数,这个函数只是调用platform_device_register函数。
platform_device_register(&led_dev); platform_device_add(&led_dev) device_add(&led_dev->dev); bus_attach_device(&led_dev->dev); device_attach(&led_dev->dev); if (dev->driver) {//如果设备的驱动程序已经存在 { device_bind_driver( &led_dev->dev);//试着链接驱动 } bus_for_each_drv(led_dev->dev->bus, NULL, &led_dev->dev, __device_attach); while ((drv = next_driver(&i)) && !error) { __device_attach(drv, &led_dev->dev); driver_probe_device(drv, &led_dev->dev); drv->bus->match(&led_dev->dev, drv);//最终调用到这个函数匹配,找到这个函数其实是platform_match函数 really_probe(&led_dev->dev, drv);//匹配成功调用 rv->bus->match(&led_dev->dev, drv);//最终调用到这个函数匹配,找到这个函数其实是platform_match函数 really_probe(&led_dev->dev, drv);//匹配成功调用 }
通过层层调用,最终定位到device_attach函数与Led_drv不同的是,Led_dev首先会确认自己是否已经有驱动存在,如果不存在才会从drv链表搜索,通过platform_match函数找到与Led_dev匹配的Led_drv。找到后调用really_probe函数,really_probe函数先是执行dev->driver = drv;这样就将dev与drv联系起来了,接着调用led_probe函数,初始化驱动。
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { struct resource *res; /* 根据platform_device的资源进行ioremap */ res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); gpio_con = ioremap(res->start, res->end - res->start + 1); gpio_dat = gpio_con + 1; res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ, 0); pin = res->start; /* 注册字符设备驱动程序 */ printk("led_probe, found led\\n"); major = register_chrdev(0, "myled", &led_fops); cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myled"); class_device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "led"); /* /dev/led */ return 0; }
在led_probe中,首先会从Led_dev的led_probe中获得相应的led_resource信息来配置IO端口,接着注册字符设备,然后创建设备描述符文件。这就是平台设备驱动模型整个注册匹配的过程。
与注册过程相反rmmod Led_drv最终会调用led_remove函数
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *pdev) { /* 卸载字符设备驱动程序 */ /* iounmap */ printk("led_remove, remove led\\n"); class_device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 0)); class_destroy(cls); unregister_chrdev(major, "myled"); iounmap(gpio_con); return 0; }
而执行rmmod Led_dev最终会通过层层调用到led_release函数,所以led_release函数必不可少,即使它是空的函数,什么也没做
static void led_release(struct device * dev) { }
以上全部就是对驱动的分离分层的实现。通过平台设备驱动模型实现。
以上是关于Linux驱动之平台设备驱动模型简析(驱动分离分层概念的建立)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章