linux C 线程池
Posted 牧羊少年Zhao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了linux C 线程池相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Linux 多线程编程之 线程池 的原理和一个简单的C实现,提高对多线程编
程的认知,同步处理等操作,以及如何在实际项目中高效的利用多线程开
发。
1. 线程池介绍
为什么需要线程池???
目前的大多数网络服务器,包括Web服务器、Email服务器以及数据库服务
器等都具有一个共同点,就是单位时间内必须处理数目巨大的连接请求,
但处理时间却相对较短。
传统多线程方案中我们采用的服务器模型则是一旦接受到请求之后,即创
建一个新的线程,由该线程执行任务。任务执行完毕后,线程退出,这就
是是“即时创建,即时销毁”的策略。尽管与创建进程相比,创建线程的时
间已经大大的缩短,但是如果提交给线程的任务是执行时间较短,而且执
行次数极其频繁,那么服务器将处于不停的创建线程,销毁线程的状态,
这笔开销将是不可忽略的。
线程池为线程生命周期开销问题和资源不足问题提供了解决方案。通过对
多个任务重用线程,线程创建的开销被分摊到了多个任务上。其好处是,
因为在请求到达时线程已经存在,所以无意中也消除了线程创建所带来的
延迟。这样,就可以立即为请求服务,使应用程序响应更快。而且,通过
适当地调整线程池中的线程数目,也就是当请求的数目超过某个阈值时,
就强制其它任何新到的请求一直等待,直到获得一个线程来处理为止,从
而可以防止资源不足。
2. 线程池结构
2.1 线程池任务结点结构
线程池任务结点用来保存用户投递过来的的任务,并放入线程池中的线程来执行,任务结构如下:
// 线程池任务结点
struct worker_t { void * (* process)(void * arg); /*回调函数*/ int paratype; /*函数类型(预留)*/ void * arg; /*回调函数参数*/ struct worker_t * next; /*链接下一个任务节点*/ };
2.2 线程池控制器
线程池控制器用来对线程池进行控制管理,描述当前线程池的最基本信息,包括任务的投递,线
程池状态的更新与查询,线程池的销毁等,其结构如下:
/*线程控制器*/ struct CThread_pool_t { pthread_mutex_t queue_lock; /*互斥锁*/ pthread_cond_t queue_ready; /*条件变量*/ worker_t * queue_head; /*任务节点链表 保存所有投递的任务*/ int shutdown; /*线程池销毁标志 1-销毁*/ pthread_t * threadid; /*线程ID*/ int max_thread_num; /*线程池可容纳最大线程数*/ int current_pthread_num; /*当前线程池存放的线程*/ int current_pthread_task_num; /*当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/ int current_wait_queue_num; /*当前等待队列的的任务数目*/ int free_pthread_num; /*线程池允许最大的空闲线程数/*/ /** * function: ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit * description: 向线程池投递任务 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * process 回调函数 * arg 回调函数参数 * return Valr: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int (* AddWorkUnlimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /** * function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit * description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * process 回调函数 * arg 回调函数参数 * return Val: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int (* AddWorkLimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum * description: 获取线程池可容纳的最大线程数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 */ int (* GetThreadMaxNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum * description: 获取线程池存放的线程数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 线程池存放的线程数 */ int (* GetCurrentThreadNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum * description: 获取当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和 */ int (* GetCurrentTaskThreadNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum * description: 获取线程池等待队列任务数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 等待队列任务数 */ int (* GetCurrentWaitTaskNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolDestroy * description: 销毁线程池 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int (* Destroy)(void * pthis); };
2.3 线程池运行结构

解释:
1) 图中的线程池中的"空闲"和"执行"分别表示空闲线程和执行线程,空闲线程指在正在等待任务的线程,
同样执行线程指正在执行任务的线程, 两者是相互转换的。当用户投递任务过来则用空闲线程来执行
该任务,且空闲线程状态转换为执行线程;当任务执行完后,执行线程状态转变为空闲线程。
2) 创建线程池时,正常情况会创建一定数量的线程, 所有线程初始化为空闲线程,线程阻塞等待用户
投递任务。
3) 用户投递的任务首先放入等待队列queue_head 链表中, 如果线程池中有空闲线程则放入空闲线程中
执行,否则根据条件选择继续等待空闲线程或者新建一个线程来执行,新建的线程将放入线程池中。
4) 执行的任务会从等待队列中脱离,并在任务执行完后释放任务结点worker_t
3. 线程池控制 / 部分函数解释
3.1 线程池创建
创建 max_num 个线程 ThreadPoolRoutine,即空闲线程
/** * function: ThreadPoolConstruct * description: 构建线程池 * input param: max_num 线程池可容纳的最大线程数 * free_num 线程池允许存在的最大空闲线程,超过则将线程释放回操作系统 * return Val: 线程池指针 */ CThread_pool_t * ThreadPoolConstruct(int max_num, int free_num) { int i = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)malloc(sizeof(CThread_pool_t)); if(NULL == pool) return NULL; memset(pool, 0, sizeof(CThread_pool_t)); /*初始化互斥锁*/ pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->queue_lock), NULL); /*初始化条件变量*/ pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_ready), NULL); pool->queue_head = NULL; pool->max_thread_num = max_num; // 线程池可容纳的最大线程数 pool->current_wait_queue_num = 0; pool->current_pthread_task_num = 0; pool->shutdown = 0; pool->current_pthread_num = 0; pool->free_pthread_num = free_num; // 线程池允许存在最大空闲线程 pool->threadid = NULL; pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)malloc(max_num*sizeof(pthread_t)); /*该函数指针赋值*/ pool->AddWorkUnlimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit; pool->AddWorkLimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit; pool->Destroy = ThreadPoolDestroy; pool->GetThreadMaxNum = ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum; pool->GetCurrentThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum; pool->GetCurrentTaskThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum; pool->GetCurrentWaitTaskNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum; for(i=0; i<max_num; i++) { pool->current_pthread_num++; // 当前池中的线程数 /*创建线程*/ pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[i]), NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool); usleep(1000); } return pool; }
3.2 投递任务
/** * function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit * description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * process 回调函数 * arg 回调函数参数 * return Val: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg) { // int FreeThreadNum = 0; // int CurrentPthreadNum = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; /*为添加的任务队列节点分配内存*/ worker_t * newworker = (worker_t *)malloc(sizeof(worker_t)); if(NULL == newworker) return -1; newworker->process = process; // 回调函数,在线程ThreadPoolRoutine()中执行 newworker->arg = arg; // 回调函数参数 newworker->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*插入新任务队列节点*/ worker_t * member = pool->queue_head; // 指向任务队列链表整体 if(member != NULL) { while(member->next != NULL) // 队列中有节点 member = member->next; // member指针往后移动 member->next = newworker; // 插入到队列链表尾部 } else pool->queue_head = newworker; // 插入到队列链表头 assert(pool->queue_head != NULL); pool->current_wait_queue_num++; // 等待队列加1 /*空闲的线程= 当前线程池存放的线程 - 当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/ int FreeThreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num; /*如果没有空闲线程且池中当前线程数不超过可容纳最大线程*/ if((0 == FreeThreadNum) && (pool->current_pthread_num < pool->max_thread_num)) { //-> 条件为真进行新线程创建 int CurrentPthreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num; /*新增线程*/ pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)realloc(pool->threadid, (CurrentPthreadNum+1) * sizeof(pthread_t)); pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[CurrentPthreadNum]), NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool); /*当前线程池中线程总数加1*/ pool->current_pthread_num++; /*分配任务线程数加1*/ pool->current_pthread_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/ pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready)); return 0; } pool->current_pthread_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/ pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready)); // usleep(10); //看情况 return 0; }
投递任务时先创建一个任务结点保存回调函数和函数参数,并将任务结点放入等待队列中,在代码中
注释"//->条件为真创建新线程",realloc() 会在保存原始内存中的数据不变的基础上新增1个sizeof(pthread_t)
大小内存。之后更新current_pthread_num,和current_pthread_task_num;并发送信号
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_read)),给一个处于条件阻塞等待状态的线程,即线程ThreadPoolRoutin()
中的pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_read), &(pool->queue_lock))阻塞等待接收信号,重点讲互
斥锁和添加变量:
pthread_mutex_t queue_lock; /**< 互斥锁*/
pthread_cond_t queue_ready; /**< 条件变量*/
这两个变量时线程池实现中很重要的点,这里简要介绍代码中会用到的相关函数功能;
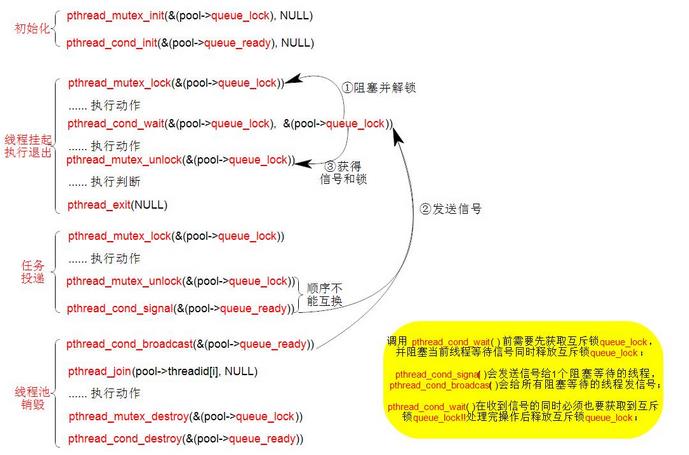
3.3 执行线程
/** * function: ThreadPoolRoutine * description: 线程池中执行的线程 * input param: arg 线程池指针 */ void * ThreadPoolRoutine(void * arg) { CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)arg; while(1) { /*上锁,pthread_cond_wait()调用会解锁*/ pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*队列没有等待任务*/ while((pool->current_wait_queue_num == 0) && (!pool->shutdown)) { /*条件锁阻塞等待条件信号*/ pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_ready), &(pool->queue_lock)); } if(pool->shutdown) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); pthread_exit(NULL); // 释放线程 } assert(pool->current_wait_queue_num != 0); assert(pool->queue_head != NULL); pool->current_wait_queue_num--; // 等待任务减1,准备执行任务 worker_t * worker = pool->queue_head; // 去等待队列任务节点头 pool->queue_head = worker->next; // 链表后移 pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); (* (worker->process))(worker->arg); // 执行回调函数 pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); pool->current_pthread_task_num--; // 函数执行结束 free(worker); // 释放任务结点 worker = NULL; if((pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num) > pool->free_pthread_num) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); break; // 当线程池中空闲线程超过 free_pthread_num 则将线程释放回操作系统 } pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); } pool->current_pthread_num--; // 当前线程数减1 pthread_exit(NULL); // 释放线程 return (void *)NULL; }
这个就是用来执行任务的线程,在初始化创建线程时所有线程都全部阻塞在pthread_cond_wait()处
此时的线程就为空闲线程,也就是线程被挂起,当收到信号并取得互斥锁时, 表明任务投递过来
则获取等待队列里的任务结点并执行回调函数; 函数执行结束后回去判断当前等待队列是否还有任
务,有则接下去执行,否则重新阻塞回到空闲线程状态。
4. 完整代码实现
4.1 CThreadPool.h 文件
/** * 线程池头文件 * **/ #ifndef _CTHREADPOOL_H_ #define _CTHREADPOOL_H_ #include <pthread.h> /*线程池可容纳最大线程数*/ #define DEFAULT_MAX_THREAD_NUM 100 /*线程池允许最大的空闲线程,超过则将线程释放回操作系统*/ #define DEFAULT_FREE_THREAD_NUM 10 typedef struct worker_t worker_t; typedef struct CThread_pool_t CThread_pool_t; /*线程池任务节点*/ struct worker_t { void * (* process)(void * arg); /*回调函数*/ int paratype; /*函数类型(预留)*/ void * arg; /*回调函数参数*/ struct worker_t * next; /*链接下一个任务节点*/ }; /*线程控制器*/ struct CThread_pool_t { pthread_mutex_t queue_lock; /*互斥锁*/ pthread_cond_t queue_ready; /*条件变量*/ worker_t * queue_head; /*任务节点链表 保存所有投递的任务*/ int shutdown; /*线程池销毁标志 1-销毁*/ pthread_t * threadid; /*线程ID*/ int max_thread_num; /*线程池可容纳最大线程数*/ int current_pthread_num; /*当前线程池存放的线程*/ int current_pthread_task_num; /*当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/ int current_wait_queue_num; /*当前等待队列的的任务数目*/ int free_pthread_num; /*线程池允许最大的空闲线程数/*/ /** * function: ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit * description: 向线程池投递任务 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * process 回调函数 * arg 回调函数参数 * return Valr: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int (* AddWorkUnlimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /** * function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit * description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * process 回调函数 * arg 回调函数参数 * return Val: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int (* AddWorkLimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum * description: 获取线程池可容纳的最大线程数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 */ int (* GetThreadMaxNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum * description: 获取线程池存放的线程数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 线程池存放的线程数 */ int (* GetCurrentThreadNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum * description: 获取当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和 */ int (* GetCurrentTaskThreadNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum * description: 获取线程池等待队列任务数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 等待队列任务数 */ int (* GetCurrentWaitTaskNum)(void * pthis); /** * function: ThreadPoolDestroy * description: 销毁线程池 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int (* Destroy)(void * pthis); }; /** * function: ThreadPoolConstruct * description: 构建线程池 * input param: max_num 线程池可容纳的最大线程数 * free_num 线程池允许存在的最大空闲线程,超过则将线程释放回操作系统 * return Val: 线程池指针 */ CThread_pool_t * ThreadPoolConstruct(int max_num, int free_num); /** * function: ThreadPoolConstructDefault * description: 创建线程池,以默认的方式初始化,未创建线程 * * return Val: 线程池指针 */ CThread_pool_t * ThreadPoolConstructDefault(void); #endif // _CTHREADPOOL_H_
4.2 CThreadPool.c 文件
/** * 线程池实现 * **/ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <assert.h> #include "CThreadPool.h" void * ThreadPoolRoutine(void * arg); /** * function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit * description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * process 回调函数 * arg 回调函数参数 * return Val: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg) { // int FreeThreadNum = 0; // int CurrentPthreadNum = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; /*为添加的任务队列节点分配内存*/ worker_t * newworker = (worker_t *)malloc(sizeof(worker_t)); if(NULL == newworker) return -1; newworker->process = process; // 回调函数,在线程ThreadPoolRoutine()中执行 newworker->arg = arg; // 回调函数参数 newworker->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*插入新任务队列节点*/ worker_t * member = pool->queue_head; // 指向任务队列链表整体 if(member != NULL) { while(member->next != NULL) // 队列中有节点 member = member->next; // member指针往后移动 member->next = newworker; // 插入到队列链表尾部 } else pool->queue_head = newworker; // 插入到队列链表头 assert(pool->queue_head != NULL); pool->current_wait_queue_num++; // 等待队列加1 /*空闲的线程= 当前线程池存放的线程 - 当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/ int FreeThreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num; /*如果没有空闲线程且池中当前线程数不超过可容纳最大线程*/ if((0 == FreeThreadNum) && (pool->current_pthread_num < pool->max_thread_num)) { int CurrentPthreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num; /*新增线程*/ pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)realloc(pool->threadid, (CurrentPthreadNum+1) * sizeof(pthread_t)); pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[CurrentPthreadNum]), NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool); /*当前线程池中线程总数加1*/ pool->current_pthread_num++; /*分配任务线程数加1*/ pool->current_pthread_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/ pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready)); return 0; } pool->current_pthread_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/ pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready)); // usleep(10); //看情况 return 0; } /** * function: ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit * description: 向线程池投递任务 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * process 回调函数 * arg 回调函数参数 * return Valr: 0 成功 * -1 失败 */ int ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg) { // int FreeThreadNum = 0; // int CurrentPthreadNum = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; /*给新任务队列节点分配内存*/ worker_t * newworker = (worker_t *)malloc(sizeof(worker_t)); if(NULL == newworker) return -1; newworker->process = process; // 回调函数 newworker->arg = arg; // 回调函数参数 newworker->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*新节点插入任务队列链表操作*/ worker_t * member = pool->queue_head; if(member != NULL) { while(member->next != NULL) member = member->next; member->next = newworker; // 插入队列链表尾部 } else pool->queue_head = newworker; // 插入到头(也就是第一个节点,之前链表没有节点) assert(pool->queue_head != NULL); pool->current_wait_queue_num++; // 当前等待队列的的任务数目+1 int FreeThreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num; /*只判断是否没有空闲线程*/ if(0 == FreeThreadNum) { int CurrentPthreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num; pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)realloc(pool->threadid, (CurrentPthreadNum+1)*sizeof(pthread_t)); pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[CurrentPthreadNum]),NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool); pool->current_pthread_num++; if(pool->current_pthread_num > pool->max_thread_num) pool->max_thread_num = pool->current_pthread_num; pool->current_pthread_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready)); return 0; } pool->current_pthread_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready)); // usleep(10); return 0; } /** * function: ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum * description: 获取线程池可容纳的最大线程数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return val: 线程池可容纳的最大线程数 */ int ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum(void * pthis) { int num = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); num = pool->max_thread_num; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); return num; } /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum * description: 获取线程池存放的线程数 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 线程池存放的线程数 */ int ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum(void * pthis) { int num = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); num = pool->current_pthread_num; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); return num; } /** * function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum * description: 获取当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和 * input param: pthis 线程池指针 * return Val: 当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和 */ int ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum(void * pthis) { int num = 0<以上是关于linux C 线程池的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章