k8s 组件介绍-API Server API Server简介
Posted lwb444
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了k8s 组件介绍-API Server API Server简介相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
API Server简介
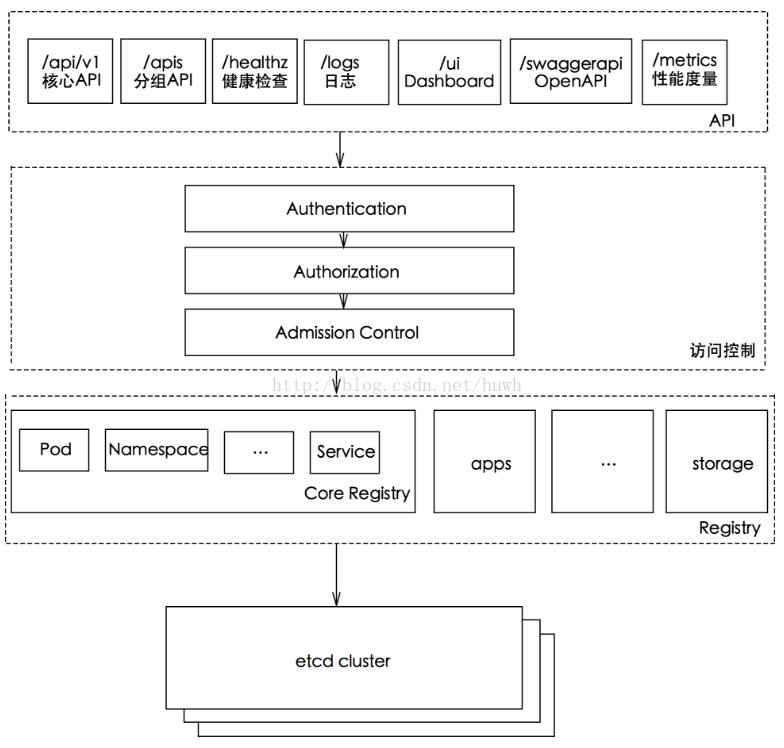
k8s API Server提供了k8s各类资源对象(pod,RC,Service等)的增删改查及watch等HTTP Rest接口,是整个系统的数据总线和数据中心。
kubernetes API Server的功能:
- 提供了集群管理的REST API接口(包括认证授权、数据校验以及集群状态变更);
- 提供其他模块之间的数据交互和通信的枢纽(其他模块通过API Server查询或修改数据,只有API Server才直接操作etcd);
- 是资源配额控制的入口;
- 拥有完备的集群安全机制.
kube-apiserver工作原理图
如何访问kubernetes API
k8s通过kube-apiserver这个进程提供服务,该进程运行在单个k8s-master节点上。默认有两个端口。
k8s通过kube-apiserver这个进程提供服务,该进程运行在单个k8s-master节点上。默认有两个端口。
1. 本地端口
- 该端口用于接收HTTP请求;
- 该端口默认值为8080,可以通过API Server的启动参数“--insecure-port”的值来修改默认值;
- 默认的IP地址为“localhost”,可以通过启动参数“--insecure-bind-address”的值来修改该IP地址;
- 非认证或授权的HTTP请求通过该端口访问API Server。
2.安全端口
- 该端口默认值为6443,可通过启动参数“--secure-port”的值来修改默认值;
- 默认IP地址为非本地(Non-Localhost)网络端口,通过启动参数“--bind-address”设置该值;
- 该端口用于接收HTTPS请求;
- 用于基于Tocken文件或客户端证书及HTTP Base的认证;
- 用于基于策略的授权;
- 默认不启动HTTPS安全访问控制。
kubernetes API访问方式
Kubernetes REST API可参考https://kubernetes.io/docs/api-reference/v1.6/
1. curl
|
|
2. Kubectl Proxy
Kubectl Proxy代理程序既能作为API Server的反向代理,也能作为普通客户端访问API Server的代理。通过master节点的8080端口来启动该代理程序。
kubectl proxy --port=8080 &
具体见kubectl proxy --help
3. kubectl客户端
命令行工具kubectl客户端,通过命令行参数转换为对API Server的REST API调用,并将调用结果输出。
命令格式:kubectl [command] [options]
具体可参考Kubernetes常用命令
4. 编程方式调用
使用场景:
1、运行在Pod里的用户进程调用kubernetes API,通常用来实现分布式集群搭建的目标。
2、开发基于kubernetes的管理平台,比如调用kubernetes API来完成Pod、Service、RC等资源对象的图形化创建和管理界面。可以使用kubernetes提供的Client Library。
具体可参考https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go。
通过API Server访问Node、Pod和Service
k8s API Server最主要的REST接口是资源对象的增删改查,另外还有一类特殊的REST接口—k8s Proxy API接口,这类接口的作用是代理REST请求,即kubernetes API Server把收到的REST请求转发到某个Node上的kubelet守护进程的REST端口上,由该kubelet进程负责响应。
1. Node相关接口
关于Node相关的接口的REST路径为:/api/v1/proxy/nodes/{name},其中{name}为节点的名称或IP地址。
|
|
这里获取的Pod信息来自Node而非etcd数据库,两者时间点可能存在偏差。如果在kubelet进程启动时加--enable-debugging-handles=true参数,那么kubernetes Proxy API还会增加以下接口:
|
|
2. Pod相关接口
|
|
3. Service相关接口
|
|
Pod的proxy接口的作用:在kubernetes集群之外访问某个pod容器的服务(HTTP服务),可以用Proxy API实现,这种场景多用于管理目的,比如逐一排查Service的Pod副本,检查哪些Pod的服务存在异常问题。
集群功能模块之间的通信
kubernetes API Server作为集群的核心,负责集群各功能模块之间的通信,集群内各个功能模块通过API Server将信息存入etcd,当需要获取和操作这些数据时,通过API Server提供的REST接口(GETLISTWATCH方法)来实现,从而实现各模块之间的信息交互。
1. kubelet与API Server交互
每个Node节点上的kubelet定期就会调用API Server的REST接口报告自身状态,API Server接收这些信息后,将节点状态信息更新到etcd中。kubelet也通过API Server的Watch接口监听Pod信息,从而对Node机器上的POD进行管理。
|
监听信息 |
kubelet动作 |
备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 新的POD副本被调度绑定到本节点 | 执行POD对应的容器的创建和启动逻辑 | |
| POD对象被删除 | 删除本节点上相应的POD容器 | |
| 修改POD信息 | 修改本节点的POD容器 |
2. kube-controller-manager与API Server交互
kube-controller-manager中的Node Controller模块通过API Server提供的Watch接口,实时监控Node的信息,并做相应处理。
3. kube-scheduler与API Server交互
Scheduler通过API Server的Watch接口监听到新建Pod副本的信息后,它会检索所有符合该Pod要求的Node列表,开始执行Pod调度逻辑。调度成功后将Pod绑定到目标节点上。

API Server参数介绍
API Server 主要是和 etcd 打交道,并且对外提供 HTTP 服务,以及进行安全控制,因此它的命令行提供的参数也主要和这几个方面有关。下面是一些比较重要的参数以及说明(不同版本参数可能会有不同):
| 参数 | 含义 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| –advertise-address | 通过该 ip 地址向集群其他节点公布 api server 的信息,必须能够被其他节点访问 | nil |
| –allow-privileged | 是否允许 privileged 容器运行 | false |
| –admission-control | 准入控制 | AlwaysAdmit |
| –authorization-mode | 授权模式 ,安全接口上的授权 | AlwaysAllow |
| –bind-address | HTTPS 安全接口的监听地址 | 0.0.0.0 |
| –secure-port | HTTPS 安全接口的监听端口 | 6443 |
| –cert-dir | TLS 证书的存放目录 | /var/run/kubernetes |
| –etcd-prefix | 信息存放在 etcd 中地址的前缀 | “/registry” |
| –etcd-servers | 逗号分割的 etcd server 地址 | [] |
| –insecure-bind-address | HTTP 访问的地址 | 127.0.0.1 |
| –insecure-port | HTTP 访问的端口 | 8080 |
| –log-dir | 日志存放的目录 | |
| –service-cluster-ip-range | service 要使用的网段,使用 CIDR 格式,参考 kubernetes 中 service 的定义 |
API Server安装和运行
API Server 是通过提供的 kube-apiserver 二进制文件直接运行的,下面的例子指定了 service 分配的 ip 范围,etcd 的地址,和对外提供服务的 ip 地址:
-
/usr/bin/kube-apiserver
-
-
--service-cluster-ip-range=10.20.0.1/24
-
-
--etcd-servers=http://127.0.0.1:2379
-
-
--advertise-address=192.168.8.100
-
-
--bind-address=192.168.8.100
-
-
--insecure-bind-address=192.168.8.100
-
-
--v=4
直接访问 8080 端口,API Server 会返回它提供了哪些接口:
-
[root@localhost vagrant]# curl http://192.168.8.100:8080
-
-
{
-
"paths": [
-
"/api",
-
"/api/v1",
-
"/apis",
-
"/apis/apps",
-
"/apis/apps/v1alpha1",
-
"/apis/autoscaling",
-
"/apis/autoscaling/v1",
-
"/apis/batch",
-
"/apis/batch/v1",
-
"/apis/batch/v2alpha1",
-
"/apis/extensions",
-
"/apis/extensions/v1beta1",
-
"/apis/policy",
-
"/apis/policy/v1alpha1",
-
"/apis/rbac.authorization.k8s.io",
-
"/apis/rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1alpha1",
-
"/healthz",
-
"/healthz/ping",
-
"/logs/",
-
"/metrics",
-
"/swaggerapi/",
-
"/ui/",
-
"/version"
-
]
-
}
而目前最重要的路径是 /api/v1,里面包含了 kubernetes 所有资源的操作,比如下面的 nodes:
-
? ~ http http://192.168.8.100:8080/api/v1/nodes
-
-
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
-
-
Content-Length: 112
-
-
Content-Type: application/json
-
-
Date: Thu, 08 Sep 2016 08:14:45 GMT
-
-
{
-
-
"apiVersion": "v1",
-
-
"items": [],
-
-
"kind": "NodeList",
-
-
"metadata": {
-
-
"resourceVersion": "12",
-
-
"selfLink": "/api/v1/nodes"
-
}
-
}
API 以 json 的形式返回,会通过 apiVersion 来说明 API 版本号,kind 说明请求的是什么资源。不过这里面的内容是空的,因为目前还没有任何 kubelet 节点接入到我们的 API Server。对应的,pod 也是空的:
-
? ~ http http://192.168.8.100:8080/api/v1/pods
-
-
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
-
-
Content-Length: 110
-
-
Content-Type: application/json
-
-
Date: Thu, 08 Sep 2016 08:18:53 GMT
-
-
{
-
-
"apiVersion": "v1",
-
-
"items": [],
-
-
"kind": "PodList",
-
-
"metadata": {
-
-
"resourceVersion": "12",
-
-
"selfLink": "/api/v1/pods"
-
-
}
-
-
}
添加节点
添加节点也非常简单,启动 kubelet 的时候使用 --api-servers 指定要接入的 API Server 就行。kubelet 启动之后,会把自己注册到指定的 API Server,然后监听 API 对应 pod 的变化,根据 API 中 pod 的实际信息来管理节点上 pod 的生命周期。
现在访问 /api/v1/nodes 就能看到已经添加进来的节点:
-
? ~ http http://192.168.8.100:8080/api/v1/nodes
-
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
-
Content-Type: application/json
-
Date: Thu, 08 Sep 2016 08:27:44 GMT
-
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
-
{
-
"apiVersion": "v1",
-
"items": [
-
{
-
"metadata": {
-
"annotations": {
-
"volumes.kubernetes.io/controller-managed-attach-detach": "true"
-
},
-
"creationTimestamp": "2016-09-08T08:23:01Z",
-
"labels": {
-
"beta.kubernetes.io/arch": "amd64",
-
"beta.kubernetes.io/os": "linux",
-
"kubernetes.io/hostname": "192.168.8.100"
-
},
-
"name": "192.168.8.100",
-
"resourceVersion": "65",
-
"selfLink": "/api/v1/nodes/192.168.8.100",
-
"uid": "74e16eba-759d-11e6-b463-080027c09e5b"
-
},
-
"spec": {
-
"externalID": "192.168.8.100"
-
},
-
"status": {
-
"addresses": [
-
{
-
"address": "192.168.8.100",
-
"type": "LegacyHostIP"
-
},
-
{
-
"address": "192.168.8.100",
-
"type": "InternalIP"
-
}
-
],
-
"allocatable": {
-
"alpha.kubernetes.io/nvidia-gpu": "0",
-
"cpu": "1",
-
"memory": "502164Ki",
-
"pods": "110"
-
},
-
"capacity": {
-
"alpha.kubernetes.io/nvidia-gpu": "0",
-
"cpu": "1",
-
"memory": "502164Ki",
-
"pods": "110"
-
},
-
"conditions": [
-
{
-
"lastHeartbeatTime": "2016-09-08T08:27:36Z",
-
"lastTransitionTime": "2016-09-08T08:23:01Z",
-
"message": "kubelet has sufficient disk space available",
-
"reason": "KubeletHasSufficientDisk",
-
"status": "False",
-
"type": "OutOfDisk"
-
},
-
{
-
"lastHeartbeatTime": "2016-09-08T08:27:36Z",
-
"lastTransitionTime": "2016-09-08T08:23:01Z",
-
"message": "kubelet has sufficient memory available",
-
"reason": "KubeletHasSufficientMemory",
-
"status": "False",
-
"type": "MemoryPressure"
-
},
-
{
-
"lastHeartbeatTime": "2016-09-08T08:27:36Z",
-
"lastTransitionTime": "2016-09-08T08:24:56Z",
-
"message": "kubelet is posting ready status",
-
"reason": "KubeletReady",
-
"status": "True",
-
"type": "Ready"
-
}
-
],
-
"daemonEndpoints": {
-
"kubeletEndpoint": {
-
"Port": 10250
-
}
-
},
-
"images": [
-
{
-
"names": [
-
"172.16.1.41:5000/nginx:latest"
-
],
-
"sizeBytes": 425626718
-
},
-
{
-
"names": [
-
"172.16.1.41:5000/hyperkube:v0.18.2"
-
],
-
"sizeBytes": 207121551
-
},
-
{
-
"names": [
-
"172.16.1.41:5000/etcd:v3.0.4"
-
],
-
"sizeBytes": 43302056
-
},
-
{
-
"names": [
-
"172.16.1.41:5000/busybox:latest"
-
],
-
"sizeBytes": 1092588
-
},
-
{
-
"names": [
-
"172.16.1.41:5000/google_containers/pause:0.8.0"
-
],
-
"sizeBytes": 241656
-
}
-
],
-
"nodeInfo": {
-
"architecture": "amd64",
-
"bootID": "48955926-11dd-4ad3-8bb0-2585b1c9215d",
-
"containerRuntimeVersion": "docker://1.10.3",
-
"kernelVersion": "3.10.0-123.13.1.el7.x86_64",
-
"kubeProxyVersion": "v1.3.1-beta.0.6+fbf3f3e5292fb0",
-
"kubeletVersion": "v1.3.1-beta.0.6+fbf3f3e5292fb0",
-
"machineID": "b9597c4ae5f24494833d35e806e00b29",
-
"operatingSystem": "linux",
-
"osImage": "CentOS Linux 7 (Core)",
-
"systemUUID": "823EB67A-057E-4EFF-AE7F-A758140CD2F7"
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
],
-
"kind": "NodeList",
-
"metadata": {
-
"resourceVersion": "65",
-
"selfLink": "/api/v1/nodes"
-
}
-
}
我们可以看到,kubelet 收集了很多关于自身节点的信息,这些信息也会不断更新。这些信息里面不仅包含节点的系统信息(系统架构,操作系统版本,内核版本等)、还有镜像信息(节点上有哪些已经下载的 docker 镜像)、资源信息(Memory 和 Disk 的总量和可用量)、以及状态信息(是否正常,可以分配 pod等)。
和 API Server 通信
编写的 yaml 文件转换成 json 格式,保存到文件里。主要注意的是,我们指定了 nodeName 的名字,这个名字必须和之前通过 /api/v1/nodes 得到的结果中 metadata.labels.kubernetes.io/hostname 保持一致:
-
[root@localhost vagrant]# cat nginx_pod.yml
-
apiVersion: v1
-
kind: Pod
-
metadata:
-
name: nginx-server
-
spec:
-
NodeName: 192.168.8.100
-
containers:
-
- name: nginx-server
-
image: 172.16.1.41:5000/nginx
-
ports:
-
- containerPort: 80
-
volumeMounts:
-
- mountPath: /var/log/nginx
-
name: nginx-logs
-
- name: log-output
-
image: 172.16.1.41:5000/busybox
-
command:
-
- bin/sh
-
args: [-c, ‘tail -f /logdir/access.log‘]
-
volumeMounts:
-
- mountPath: /logdir
-
name: nginx-logs
-
volumes:
-
- name: nginx-logs
-
emptyDir: {}
使用 curl 执行 POST 请求,设置头部内容为 application/json,传过去文件中的 json 值,可以看到应答(其中 status 为 pending,表示以及接收到请求,正在准备处理):
-
# curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://192.168.8.100:8080/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods --data @nginx_pod.json
-
{
-
"kind": "Pod",
-
"apiVersion": "v1",
-
"metadata": {
-
"name": "nginx-server",
-
"namespace": "default",
-
"selfLink": "/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/nginx-server",
-
"uid": "888e95d0-75a9-11e6-b463-080027c09e5b",
-
"resourceVersion": "573",
-
"creationTimestamp": "2016-09-08T09:49:28Z"
-
},
-
"spec": {
-
"volumes": [
-
{
-
"name": "nginx-logs",
-
"emptyDir": {}
-
}
-
],
-
"containers": [
-
{
-
"name": "nginx-server",
-
"image": "172.16.1.41:5000/nginx",
-
"ports": [
-
{
-
"containerPort": 80,
-
"protocol": "TCP"
-
}
-
],
-
"resources": {},
-
"volumeMounts": [
-
{
-
"name": "nginx-logs",
-
"mountPath": "/var/log/nginx"
-
}
-
],
-
"terminationMessagePath": "/dev/termination-log",
-
"imagePullPolicy": "Always"
-
}
-
],
-
"restartPolicy": "Always",
-
"terminationGracePeriodSeconds": 30,
-
"dnsPolicy": "ClusterFirst",
-
"nodeName": "192.168.8.100",
-
"securityContext": {}
-
},
-
"status": {
-
"phase": "Pending"
-
}
-
}
返回中包含了我们提交 pod 的信息,并且添加了 status、metadata 等额外信息。
等一段时间去查询 pod,就可以看到 pod 的状态已经更新了:
-
? http http://192.168.8.100:8080/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods
-
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
-
Content-Type: application/json
-
Date: Thu, 08 Sep 2016 09:51:29 GMT
-
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
-
{
-
"apiVersion": "v1",
-
"items": [
-
{
-
"metadata": {
-
"creationTimestamp": "2016-09-08T09:49:28Z",
-
"name": "nginx-server",
-
"namespace": "default",
-
"resourceVersion": "592",
-
"selfLink": "/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/nginx-server",
-
"uid": "888e95d0-75a9-11e6-b463-080027c09e5b"
-
},
-
"spec": {
-
"containers": [
-
{
-
"image": "172.16.1.41:5000/nginx",
-
"imagePullPolicy": "Always",
-
"name": "nginx-server",
-
"ports": [
-
{
-
"containerPort": 80,
-
"protocol": "TCP"
-
}
-
],
-
"resources": {},
-
"terminationMessagePath": "/dev/termination-log",
-
"volumeMounts": [
-
{
-
"mountPath": "/var/log/nginx",
-
"name": "nginx-logs"
-
}
-
]
-
},
-
{
-
"args": [
-
"-c",
-
"tail -f /logdir/access.log"
-
],
-
"command": [
-
"bin/sh"
-
],
-
"image": "172.16.1.41:5000/busybox",
-
"imagePullPolicy": "Always",
-
"name": "log-output",
-
"resources": {},
-
"terminationMessagePath": "/dev/termination-log",
-
"volumeMounts": [
-
{
-
"mountPath": "/logdir",
-
"name": "nginx-logs"
-
}
-
]
-
}
-
],
-
"dnsPolicy": "ClusterFirst",
-
"nodeName": "192.168.8.100",
-
"restartPolicy": "Always",
-
"securityContext": {},
-
"terminationGracePeriodSeconds": 30,
-
"volumes": [
-
{
-
"emptyDir": {},
-
"name": "nginx-logs"
-
}
-
]
-
},
-
"status": {
-
"conditions": [
-
{
-
"lastProbeTime": null,
-
"lastTransitionTime": "2016-09-08T09:49:28Z",
-
"status": "True",
-
"type": "Initialized"
-
},
-
{
-
"lastProbeTime": null,
-
"lastTransitionTime": "2016-09-08T09:49:44Z",
-
"status": "True",
-
"type": "Ready"
-
},
-
{
-
"lastProbeTime": null,
-
"lastTransitionTime": "2016-09-08T09:49:44Z",
-
"status": "True",
-
"type": "PodScheduled"
-
}
-
],
-
"containerStatuses": [
-
{
-
"containerID": "docker://8b79eeea60f27b6d3f0a19cbd1b3ee3f83709bcf56574a6e1124c69a6376972d",
-
"image": "172.16.1.41:5000/busybox",
-
"imageID": "docker://sha256:8c566faa3abdaebc33d40c1b5e566374c975d17754c69370f78c00c162c1e075",
-
"lastState": {},
-
"name": "log-output",
-
"ready": true,
-
"restartCount": 0,
-
"state": {
-
"running": {
-
"startedAt": "2016-09-08T09:49:43Z"
-
}
-
}
-
},
-
{
-
"containerID": "docker://96e64cdba7b05d4e30710a20e958ff5b8f1f359c8d16d32622b36f0df0cb353c",
-
"image": "172.16.1.41:5000/nginx",
-
"imageID": "docker://sha256:51d764c1fd358ce81fd0e728436bd0175ff1f3fd85fc5d1a2f9ba3e7dc6bbaf6",
-
"lastState": {},
-
"name": "nginx-server",
-
"ready": true,
-
"restartCount": 0,
-
"state": {
-
"running": {
-
"startedAt": "2016-09-08T09:49:36Z"
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
],
-
"hostIP": "192.168.8.100",
-
"phase": "Running",
-
"podIP": "172.17.0.2",
-
"startTime": "2016-09-08T09:49:28Z"
-
}
-
}
-
],
-
"kind": "PodList",
-
-
"metadata": {
-
"resourceVersion": "602",
-
"selfLink": "/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods"
-
}
-
}
可以看到 pod 已经在运行,并且给分配了 ip:172.17.0.2,通过 curl 也可以访问它的服务:
-
[root@localhost vagrant]# curl -s http://172.17.0.2 | head -n 5
-
-
<html>
-
<head>
-
<title>Welcome to nginx on Debian!</title>
-
<style>
kubectl -s http://ip:8080 get pods
以上是关于k8s 组件介绍-API Server API Server简介的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章