Shell编程进阶篇(完结)
Posted 涂小刀
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Shell编程进阶篇(完结)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.1 for循环语句
在计算机科学中,for循环(英语:for loop)是一种编程语言的迭代陈述,能够让程式码反复的执行。
它跟其他的循环,如while循环,最大的不同,是它拥有一个循环计数器,或是循环变数。这使得for循环能够知道在迭代过程中的执行顺序。
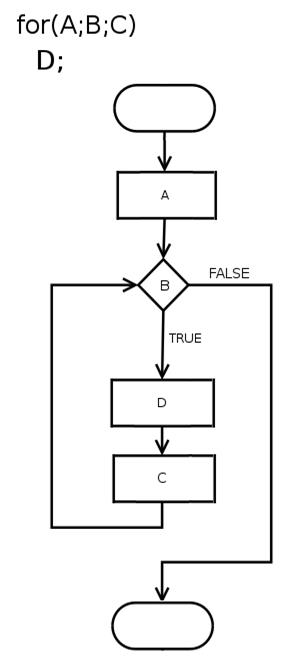
1.1.1 shell中的for循环
shell中的for 循环与在c中不同,它包含三种形式:第一种结构是列表for 循环;第二种结构就是不带列表的for循环;第三种就类似于C语言。
① 列表for循环(常用)
#!/bin/bash
for i in 取值列表
do
循环主体/命令
done
② 不带列表for循环(示例)
#!/bin/absh
echo "惨绿少年的博客是:"
for i
do
echo "$i"
done
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn for]# sh for2.sh http://blog.znix.top 惨绿少年的博客是: http://blog.znix.top
③ 类似C语言的风格(这种用法常在C语语言中使用)
for((exp1;exp2;exp3))
do
指令...
done
编写类似C语言风格脚本
for((i=0;i<=3;i++))
do
echo $i
done
脚本执行过程
1.1.2 不同语言的For循环
Shell中的两种样式
# 样式一:
for i in 1 2 3
do
echo $i
done
# 样式二:
for i in 1 2 3;do echo $i;done
JAVA
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
//循环语句;
}
PHP
for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) {
# statements;
}
VB
For i = 1 To 5 ===PASCAL=== for not i=1 do begin i=0; writeln(\'Go on!\'); end. \'循环语句 Next i
swift
var x = 0
for i in 1...100{
x += i
}
print(x)
//5050
for _ in 1...100{
x += 1
}
print(x)
// 100
var box = [1,2,3,4,5]
for i in box{
print(i)
}
/*
1
2
3
4
5
*/
---
1.2 for循环相关练习题
1.2.1 【练习题1】批量生成随机字符文件名案例
使用for循环在/clsn目录下批量创建10个html文件,其中每个文件需要包含10个随机小写字母加固定字符串clsn,名称示例如下:
[root@znix C19]# ls /clsn apquvdpqbk_clsn.html mpyogpsmwj_clsn.html txynzwofgg_clsn.html bmqiwhfpgv_clsn.html udrzobsprf_clsn.html vjxmlflawa_clsn.html jhjdcjnjxc_clsn.html qeztkkmewn_clsn.html jpvirsnjld_clsn.html ruscyxwxai_clsn.html
脚本内容
[root@clsn for]# cat make_file.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: make_file.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-08 11:01:19
# Description:
#############################################################
[ -d /clsn ] || mkdir -p /clsn
rpm -qa |grep pwgen &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 1 ]
then
yum install pwgen -y &>/dev/null
fi
cd /clsn &&\\
for i in {1..10}
do
#File_Name=`uuidgen |tr "0-9-" "a-z"|cut -c 1-10`
File_Name2=`pwgen -1A0 10`
touch ${File_Name2}_clsn.html
done
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn for]# ls -l /clsn -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 aegheiriek_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 aifohxique_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 caexahween_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 ciefaivaib_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 eixongooph_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 foozaivedo_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 ireeteethu_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 ohmeebivae_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 oiceehahth_clsn.html -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 12月 8 19:41 sheewaehoo_clsn.html
1.2.2 【练习题2】批量改名特殊案例
【练习题1】中结果文件名中的clsn字符串全部改成znix(最好用for循环实现),并且将扩展名html全部改成大写。
jpvirsnjld_clsn.html ===> jpvirsnjld_znix.HTML
脚本内容:
[root@clsn for2]# cat rename_file.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: rename_file.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-08 11:31:56
# Description:
#############################################################
cd /clsn &&\\
File_name=`ls |sed -r \'s#(.*)_clsn.html#\\1#g\'`
for i in $File_name
do
if [ -f ${i}_clsn.html ]
then
mv ${i}_clsn.html ${i}_znix.HTML
else
echo "文件修改完成."
exit
fi
done
查看结果
[root@clsn for2]# ls /clsn/ aeyaesughi_znix.HTML caireasipi_znix.HTML uahahnieli_znix.HTML aifaepheeb_znix.HTML eathixoong_znix.HTML zalipageen_znix.HTML akuipheeye_znix.HTML ietoothaik_znix.HTML apheikieno_znix.HTML lachohtaif_znix.HTML
1.2.2.1 批量改名其他方式
rename 方式(最方便,专业改名)
rename txt jpg *
非 for 循环方式批量改名(使用sed命令进行拼接,然后交给bash执行)
ls *jpg|sed -r \'s#(.*).jpg#mv & \\1.mp4#\'|bash
1.2.3 【练习题3】批量创建特殊要求用户案例
批量创建10个系统帐号clsn01-clsn10并设置密码(密码为随机数,要求字符和数字等混合)。
脚本内容:
[root@clsn for2]# cat add_user.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: add_user.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-08 11:52:21
# Description:
#############################################################
Passwd_File=/tmp/`uuidgen`.txt
>$Passwd_File
chmod 400 $Passwd_File
for i in clsn{01..10}
do
userdel -r "$i" &>/dev/null
id $i &>/dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
useradd $i
PassWd=`uuidgen`
echo $PassWd |passwd --stdin $i &>/dev/null
echo "用户名:$i 密码:$PassWd" >>$Passwd_File
echo -e "\\033[32m $i 用户创建成功!\\033[0m"
else
echo "$i 用户已存在"
fi
if [ "$i" == "clsn10" ]
then
echo "用户密码请查看文件 $Passwd_File"
fi
done
查看成的密码文件
[root@clsn for2]# cat /tmp/3e5c18d9-f878-4d06-931e-5bbcc810c3dc.txt 用户名:clsn01 密码:3d4644d0-9cf4-49db-8928-1a8346972c32 用户名:clsn02 密码:70798c3a-c8e3-42a0-9942-d4011ce4b4b3 用户名:clsn03 密码:db2a0f1d-2e49-44f5-a5b2-69b352b30120 用户名:clsn04 密码:62d2e0c6-b755-4b00-ad2d-c98f9ca9f258 用户名:clsn05 密码:eaa3471b-d04f-4d7c-8b7e-3d75172a483b 用户名:clsn06 密码:fb260a11-cd47-4b97-ab49-0cae7a755262 用户名:clsn07 密码:16ee7a1f-8aac-4537-b1aa-7fc75beb8754 用户名:clsn08 密码:0dde8823-b97d-4c88-9258-3a68a3b53eba 用户名:clsn09 密码:daf14ec4-ba9f-4593-9773-1557fdf605dc 用户名:clsn10 密码:6f1b452c-00b2-44a1-9f43-5f658d3a9124
脚本执行过程:
1.2.3.1 批量创建用户并设置随机密码(不使用shell循环)
方法一
echo user{1..20}|xargs -n1|sed -r \'s#(.*)#useradd \\1 \\&\\& echo \\1 >>/tmp/passwd.txt \\&\\& echo $RANDOM |md5sum |cut -c 1-5>>/tmp/passwd.txt \\&\\& echo `tail -1 /tmp/passwd.txt`|passwd --stdin \\1#g\'|bash
方法二
echo user{1..20}|xargs -n1|sed -r \'s#(.*)#useradd \\1 \\&\\& pass=`echo $RANDOM |md5sum |cut -c 1-5` \\&\\& echo $pass |passwd --stdin \\1 \\&\\& echo \\1 $pass>>/tmp/user_passwd.txt#g\'|bash
方法三
echo user{1..20}|xargs -n1|sed -r \'s#(.*)#useradd \\1 \\&\\& pass=`echo $RANDOM |md5sum |cut -c 1-5` \\&\\& echo \\1:$pass>>/tmp/user_passwd.txt \\&\\& chpasswd</tmp/user_passwd.txt#g\'|bash
1.2.4 【练习题4】扫描网络内存活主机案例
写一个Shell脚本,判断10.0.0.0/24网络里,当前在线的IP有哪些?
脚本内容:
[root@clsn for]# cat scan_ip2.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: scan_ip.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-07 21:58:47
# Description:
#############################################################
Ip_File=/tmp/scan_ip.txt
>$Ip_File
for i in 10.0.0.{1..254}
do
ping -c 1 -W 1 $i &>/dev/null && \\
if [ $? -eq 0 ] ;then
echo "存活主机: $i" &>>$Ip_File
fi &
done
echo "使用 cat $Ip_File 查看扫描结果"
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn for]# time sh scan_ip2.sh 使用 cat /tmp/scan_ip.txt 查看扫描结果 real 0m0.290s user 0m0.001s sys 0m0.039s [root@clsn for]# cat /tmp/scan_ip.txt 存活主机: 10.0.0.180 存活主机: 10.0.0.254
1.2.5 【练习题5】筛选符合长度的单词案例
利用bash for循环打印下面这句话中字母数不大于6的单词(某企业面试真题)。
I am clsn Welcome to my blog http://blog.znix.top
脚本内容:
[root@clsn for]# vim changdu.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: changdu.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-07 22:36:48
# Description:
#############################################################
Word=\'I am clsn Welcome to my blog http://blog.znix.top\'
for i in $Word
do
#[ ${#i} -le 6 ] && echo $i #子串方法
a=`echo $i |wc -L`
if [ $a -le 6 ]
then
echo $i
fi
done
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn for]# sh changdu.sh I am clsn to my blog
方法二:
read -p "请输入要判断的语句:" a
set -- $a
for i in "$@"
do
if [ ${#i} -le 6 ];then
echo "$i"
fi
done
由 https://home.cnblogs.com/u/1233234 @贰佰 提供
使用expr 计算字符串长度
[root@clsn scripts]# expr length \'111\' 3
1.2.6 【练习题6】破解RANDOM随机数案例
已知下面的字符串是通过RANDOM随机数变量md5sum后,再截取一部分连续字符串的结果,请破解这些字符串对应的使用md5sum处理前的RANDOM对应的数字?
21029299 00205d1c a3da1677 1f6d12dd 890684b
脚本内容
[root@clsn for]# vim pojie.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: pojie.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-07 22:41:01
# Description:
#############################################################
md5File=/tmp/Randow_Md5.txt
Md5_Word="21029299 00205d1c a3da1677 1f6d12dd 890684b"
if [ ! -f $md5File ]
then
>$md5File
for i in {0..32767}
do
echo `echo $i |md5sum` $i >> $md5File
done
else
for num in $Md5_Word
do
grep $num $md5File
done
fi
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn for]# sh pojie.sh 2102929901ee1aa769d0f479d7d78b05 - 25667 00205d1cbbeb97738ad5bbdde2a6793d - 1346 a3da1677501d9e4700ed867c5f33538a - 25345 1f6d12dd61b5c7523f038a7b966413d9 - 7041 890684ba3685395c782547daf296935f - 10082
1.2.7 【练习题7】博客园博文爬虫案例
获取博客园(惨绿少年)博客列表倒序排序考试题
需求如下:
请把https://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/地址中的所有博文,按照时间倒序列表如下:
2017年12月8日 Shell编程基础篇-下
http://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/p/8006210.html
2017年12月7日 memcached 缓存数据库应用实践
http://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/p/7999510.html
高级要求:
生成html页面,并设置超链接。
结果如改网页展示:http://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/p/8007232.html
脚本内容:
[root@clsn htmp]# cat clsn_blog.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: clsn_blog.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-08 21:19:12
# Description:
#############################################################
Uri=\'http://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/default.html?page=\'
clsn_Html=/tmp/html/clsn.html
mkdir -p /tmp/html/
>$clsn_Html
for i in {1..6}
do
curl -s $Uri$i |grep -A 5 \'ImageLink\' |sed \'s#<.*div.*># #g\'|sed \'s#--#<br>#g\' >> $clsn_Html
echo \'<br>\' >>$clsn_Html
done
脚本成网页文件

1.2.7.1 51CTO博客爬虫案例
脚本内容
[root@clsn html]# cat oldboy_blog.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: oldboy_blog.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-08 22:30:57
# Description:
#############################################################
Uri=\'http://blog.51cto.com/oldboy/p\'
Blog_Index_File=/tmp/html/oldboy_blog.html
mkdir -p /tmp/html
> /tmp/html/oldboy_blog.html
for i in {1..29}
do
curl -s $Uri$i |grep -A 5 \'发布于\' |\\
sed \'/^.*zan fr.*/,+2d\'|\\
sed \'s#^--$#<br>#g\'|\\
sed \'s#<a.*fl">发布于:#<a>#g\'|\\
sed \'s#<sp.*an>##g\' >>\\
$Blog_Index_File
echo \'<br>\' >>$Blog_Index_File
done
附文本编码转码
[root@clsn for]# iconv --help
用法: iconv [选项...] [文件...]
转换给定文件的编码。
输入/输出格式规范:
-f, --from-code=名称 原始文本编码
-t, --to-code=名称 输出编码
信息:
-l, --list 列举所有已知的字符集
输出控制:
-c 从输出中忽略无效的字符
-o, --output=FILE 输出文件
-s, --silent 关闭警告
--verbose 打印进度信息
-?, --help 给出该系统求助列表
--usage 给出简要的用法信息
-V, --version 打印程序版本号
长选项的强制或可选参数对对应的短选项也是强制或可选的
常用:
iconv -f gb2312 -t utf-8 -c clsn.html
1.3 while循环语句
在编程语言中,while循环(英语:while loop)是一种控制流程的陈述。利用一个返回结果为布林值(Boolean)的表达式作为循环条件,当这个表达式的返回值为“真”(true)时,则反复执行循环体内的程式码;若表达式的返回值为“假”(false),则不再执行循环体内的代码,继续执行循环体下面的代码。
因为while循环在区块内代码被执行之前,先检查陈述是否成立,因此这种控制流程通常被称为是一种前测试循环(pre-test loop)。相对而言do while循环,是在循环区块执行结束之后,再去检查陈述是否成立,被称为是后测试循环。
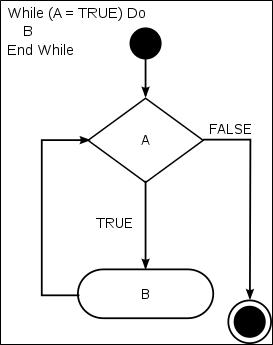
1.3.1 shell中while语法
while 条件
do
命令
done
1.3.2 while 使用场景
多用于创建守护进程
【示例1】:while实现web服务器搭建
脚本代码
[root@clsn scripts]# vim web_view.sh #!/bin/bash ############################################################# # File Name: web_view.sh # Version: V1.0 # Author: clsn # Organization: http://blog.znix.top # Created Time : 2017-12-11 10:07:24 # Description: ############################################################# while true do echo "ok" | nc -l 81 done
客户端进行访问测试
[root@clsn html]# curl 10.0.0.180:81 ok
服务端显示结果:
[root@clsn scripts]# sh web_view.sh GET / HTTP/1.1 User-Agent: curl/7.29.0 Host: 10.0.0.180:81 Accept: */*
【示例2】:while创建定时任务
脚本内容:
#!/bin/bash
while true
do
uptime
sleep 0.6
done
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn while]# sh while1.sh 15:01:52 up 2 days, 6:02, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 15:01:53 up 2 days, 6:02, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 15:01:53 up 2 days, 6:02, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 15:01:54 up 2 days, 6:02, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 15:01:55 up 2 days, 6:02, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 15:01:55 up 2 days, 6:02, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
说明:
sleep 与 usleep
sleep 单位 秒 sleep 1 休息1秒
usleep 单位 微秒 usleep 1000000 休息1s
1微秒等于百万分之一秒(10的负6次方秒)
时间测试
[root@clsn while]# time sleep 0.1 real 0m0.102s user 0m0.001s sys 0m0.000s
1.3.3 while 作用
补充定时任务功能,执行小于1秒的定时任务
循环执行某些操作,例如水果菜单
示例1:使用while循环实现水果菜单的重复使用
脚本内容
脚本执行过程

示例2:计算1-100的和
方法一 (bc命令实现)
echo `seq -s + 1 100`|bc
方法二(while循环方法)
[root@clsn while]# cat jishan.sh #!/bin/bash ############################################################# # File Name: jishan.sh # Version: V1.0 # Author: clsn # Organization: http://blog.znix.top # Created Time : 2017-12-09 15:18:44 # Description: ############################################################# i=1 while [ "$i" -le 100 ] do ((b=b+i)) ((i++)) done echo $b
示例3:实现类似手机通讯计费功能
脚本内容:
[root@clsn scripts]# cat while/shouji.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: shouji.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-09 15:56:09
# Description:
#############################################################
sum=1000
i=15
while [ $sum -ge 15 ]
do
cat<<EOF
=================
1.发短信
2.查余额
3.账户充值
4.退出
=================
EOF
read -p "你要做什么呢?" Some
case "$Some" in
1)
sum=$((sum-i))
read -p "请输入发送短信的内容:"
read -p "请输入收信人:"
sleep 0.3
echo "发送成功."
echo "您当前余额为$sum"
;;
2)
echo "您当前余额为$sum"
;;
3)
read -p "请输入你要充值的金额:" ChongZhi
sum=$((sum+ChongZhi))
echo "充值成功,当前余额为$sum"
;;
4)
exit
;;
*)
echo "输入有误!"
exit 2
esac
done
echo "余额不足,请及时充值!"
1.4 获取取文件中的行,单词和字符
1.4.1 迭代获取文件中的每一行
方法一
while read line;
do
echo $line;
done < file.txt
方法二
cat file.txt|while read line do echo $line done
方法三
exec < file.txt
while read line;
do
echo line;
done
1.4.2 迭代获取每一个单词
for word in $line;
do
echo $word;
done
1.4.3 迭代获取每一个字符
word=participate
for ((i=0;i<${#word};i++))
do
echo ${word:1:1};
done
1.4.4 同时获取取文件中的行,单词和字符脚本
脚本内容
#!/bin/bash
n=1
while read i
do
echo "第${n}行 $i"
m=1
for x in $i
do
echo "第${m}个单词 $x"
echo $x|grep -o .
((m++))
done
((n++))
done < $1
脚本执行结果:

[root@clsn scripts]# sh lunxun.sh /etc/hosts 第1行 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 第1个单词 127.0.0.1 1 2 7 . 0 . 0 . 1 第2个单词 localhost l o c a l h o s t 第3个单词 localhost.localdomain l o c a l h o s t . l o c a l d o m a i n 第4个单词 localhost4 l o c a l h o s t 4 第5个单词 localhost4.localdomain4 l o c a l h o s t 4 . l o c a l d o m a i n 4 第2行 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 第1个单词 ::1 : : 1 第2个单词 localhost l o c a l h o s t 第3个单词 localhost.localdomain l o c a l h o s t . l o c a l d o m a i n 第4个单词 localhost6 l o c a l h o s t 6 第5个单词 localhost6.localdomain6 l o c a l h o s t 6 . l o c a l d o m a i n 6 第3行 10.0.0.1 mirrors.aliyuncs.com mirrors.aliyun.com 第1个单词 10.0.0.1 1 0 . 0 . 0 . 1 第2个单词 mirrors.aliyuncs.com m i r r o r s . a l i y u n c s . c o m 第3个单词 mirrors.aliyun.com m i r r o r s . a l i y u n . c o m 第4行 10.0.0.180 clsn 第1个单词 10.0.0.180 1 0 . 0 . 0 . 1 8 0 第2个单词 clsn c l s n
1.4.5 eval 命令用法
[root@clsn ~]# clsn=6
[root@clsn ~]# echo {1..$clsn}
{1..6}
[root@clsn ~]# eval echo {1..$clsn}
1 2 3 4 5 6
eval 命令的说明
[root@clsn ~]# help eval
eval: eval [参数 ...]
将参数作为 shell 命令执行。
将 ARGs 合成一个字符串,用结果作为 shell 的输入,
并且执行得到的命令。
退出状态:
以命令的状态退出,或者在命令为空的情况下返回成功。
1.5 break continue exit return
条件与循环控制及程序返回值命令表
| 命令 | 说明 |
| break n | 如果省略n,则表示跳出整个循环,n表示跳出循环的层数 |
| continue n | 如果省略n,则表示跳过本次循环,忽略本次循环的剩余代码,进人循环的下一次循环。 n表示退到第n层继续循环 |
| exit n | 退出当前Shell程序,n为上一次程序执行的状态返回值。n也可以省略,在下一个Shell里可通过"$?"接收exit n的n值 |
| return n | 用于在函数里作为函数的返回值,以判断函数执行是否正确。在下一个Shell里可通过"$?"接收exit n的n值 |
简单来说即:
break 跳出循环 continue 跳出本次循环 exit 退出脚本 return 与 exit 相同,在函数中使用
1.5.1 break命令说明
[root@clsn scripts]# help break
break: break [n]
退出 for、while、或 until 循环
退出一个 FOR、WHILE 或 UNTIL 循环。如果指定了N,则打破N重
循环
退出状态:
退出状态为0除非 N 不大于或等于 1。
测试脚本内容
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..5}
do
if [ $i -eq 3 ]
then
break
fi
echo $i
done
echo "ok"
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn scripts]# sh break.sh 1 2 ok
1.5.2 continue命令说明
[root@clsn scripts]# help continue
continue: continue [n]
继续 for、while、或 until 循环。
继续当前 FOR、WHILE 或 UNTIL 循环的下一步。
如果指定了 N, 则继续当前的第 N 重循环。
退出状态:
退出状态为 0 除非 N 不大于或等于1。
测试脚本内容
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..5}
do
if [ $i -eq 3 ]
then
continue
fi
echo $i
done
echo "ok"
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn scripts]# sh continue.sh 1 2 4 5 ok
1.5.3 exit命令说明
[root@clsn scripts]# help exit
exit: exit [n]
退出shell。
以状态 N 退出 shell。 如果 N 被省略,则退出状态
为最后一个执行的命令的退出状态。
测试脚本内容
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..5}
do
if [ $i -eq 3 ]
then
exit
fi
echo $i
done
echo "ok"
脚本执行结果
[root@clsn scripts]# sh exit.sh 1 2
1.5.4 return命令说明
[root@clsn tuichu]# help return
return: return [n]
从一个 shell 函数返回。
使一个函数或者被引用的脚本以指定的返回值 N 退出。
如果 N 被省略,则返回状态就是
函数或脚本中的最后一个执行的命令的状态。
退出状态:
返回 N,或者如果 shell 不在执行一个函数或引用脚本时,失败。
1.6 shell中的数组
1.6.1 为什么会产生Shell数组
通常在开发Shell脚本时,定义变量采用的形式为“a=l;b=2;C=3”,可如果有多个 变量呢?这时再逐个地定义就会很费劲,并且要是有多个不确定的变量内容,也会难以 进行变量定义,此外,快速读取不同变量的值也是一件很痛苦的事情,于是数组就诞生 了,它就是为了解决上述问题而出现的。
1.6.2 什么是Shell数组
Shell的数组就是一个元素集合,它把有限个元素(变量或字符内容)用一个名字来 命名,然后用编号对它们进行区分。这个名字就称为数组名,用于区分不同内容的编 号就称为数组下标。组成数组的各个元素(变量)称为数组的元素,有时也称为下标变量。
1.6.3 数组中的增删改查
数组的定义
# 定义数组
[root@clsn scripts]# stu=(001 002 003)
# 打印数组
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[@]}
001 002 003
# 显示数组长度
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${#stu}
3
查: 遍历数组的内容
# 打印数组内容(通过数组下标或索引)
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[0]}
001
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[1]}
002
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[2]}
003
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[3]}
# 遍历数组
方法一
[root@clsn scripts]# for i in ${stu[@]};do echo $i ;done
001
002
003
# 方法二
[root@clsn scripts]# array=(1 2 3 4 5)
[root@clsn scripts]# for i in `eval echo {1..${#array[@]}}`;do echo ${array[i-1]};done
1
2
3
4
5
增:数组添加
[root@clsn scripts]# stu[3]=004
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[@]}
001 002 003 004
改:数组修改
[root@clsn scripts]# stu[2]=000
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[@]}
001 002 000 004
删:数组删除
[root@clsn scripts]# unset stu[2]
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${#stu[@]}
3
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${stu[@]}
001 002 004
1.6.4 将命令的结果赋值给数组
dir=(`ls`) dir=($(ls))
命令定义数组
[root@clsn scripts]# COM=(`ls`)
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${COM[@]}
bianliang.sh case cfb.sh chanshu.sh check check_url.sh
clsn.sh clsn_test.sh daojishi.sh ddos_check.sh echo.sh for for2 fruits.sh
function fz.sh html jingdutiao.sh jishuanqi2.sh jishuanqi.sh lamp.sh lnmp.sh
memcache_check.sh menu.sh nginx.sh panduan panduan1 play quanju.sh rsync_check.sh
rsyncd system6 tuichu web_check.sh web_view.sh while xiugaizhuji.sh yhk.sh yunshuan.sh
zhuajiu.sh
1.6.1 数组定义格式
[root@clsn scripts]# a=(1 2 3 )
[root@clsn scripts]# b=(1
> 2
> 3
> 4
> )
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${a[@]}
1 2 3
[root@clsn scripts]# echo ${b[@]}
1 2 3 4
1.6.2 数组的本质就是一个变量,只是这个变量存了多个值
在shell 常用的功能是查
array=(valuel value2 value3 ...)
打印数组格式
${array[@]} 所有元素
${#array[@]} 数组长度
${array[i]} 单个元素,i是下标
1.6.3 【练习题】批量检查多个网站地址是否正常
要求:
1、使用shell数组方法实现,检测策略尽量模拟用户访问。
2、每10秒钟做一次所有的检测,无法访问的输出报警。
3、待检测的地址如下
http://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/
http://blog.znix.top
http://blog.nmtui.com
http://10.0.0.7
脚本内容:
[root@clsn scripts]# cat check_url.sh
#!/bin/bash
#############################################################
# File Name: check_url.sh
# Version: V1.3
# Author: clsn
# Organization: http://blog.znix.top
# Created Time : 2017-12-12 10:44:39
# Description:
#############################################################
url=(
http://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/
http://blog.znix.top
http://blog.nmtui.com
http://10.0.0.7
)
while true
do
for i in ${url[@]}
do
#curl $i &>/dev/null
a=$(curl -I -w "%{http_code}\\n" -o /dev/null -s $i)
if [ $a -ne 200 ]
then
echo "$url 异常"
fi
done
sleep 10
done
1.7 Shell 函数
shell一个非常重要的特性是它可作为一种编程语言来使用。因为shell是一个解释器,所以它不能对为它编写的程序进行编译,而是在每次从磁盘加载这些程序时对它们进行解释。而程序的加载和解释都是非常耗时的。
针对此问题,许多shell(如BourneAgainShell)都包含shell函数,shell把这些函数放在内存中,这样每次需要执行它们时就不必再从磁盘读入。shell还以一种内部格式来存放这些函数,这样就不必耗费大量的时间来解释它们。
函数的作用就是把程序里多次调用相同代码的部分定义成一份,然后起个名字,所有的调用都 只用这名字就可以了,修改代码时,只需要改变函数体内的代码即可。
1.7.1 使用函数的优势
以上是关于Shell编程进阶篇(完结)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
