求所有不重复路径, Unique Paths, LeetCode题解
Posted import_SOBER
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了求所有不重复路径, Unique Paths, LeetCode题解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
求所有不重复的路径问题
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked \'Start\' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked \'Finish\' in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?

Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Example 1:
Input: m = 3, n = 2 Output: 3 Explanation: From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner: 1. Right -> Right -> Down 2. Right -> Down -> Right 3. Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:
Input: m = 7, n = 3 Output: 28
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 100- It\'s guaranteed that the answer will be less than or equal to
2 * 10 ^ 9.
递归解法
求所有不相同的路径,从左上角走到右下角。走法只能是向下或者向右。
题目中给示例是3 X 2的输入,就是两行三列,走法共3种。
容易看出,所有的步骤可以用一个二叉树存储。例如
1. Right -> Right -> Down
2. Right -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> Right
画成二叉树就是:
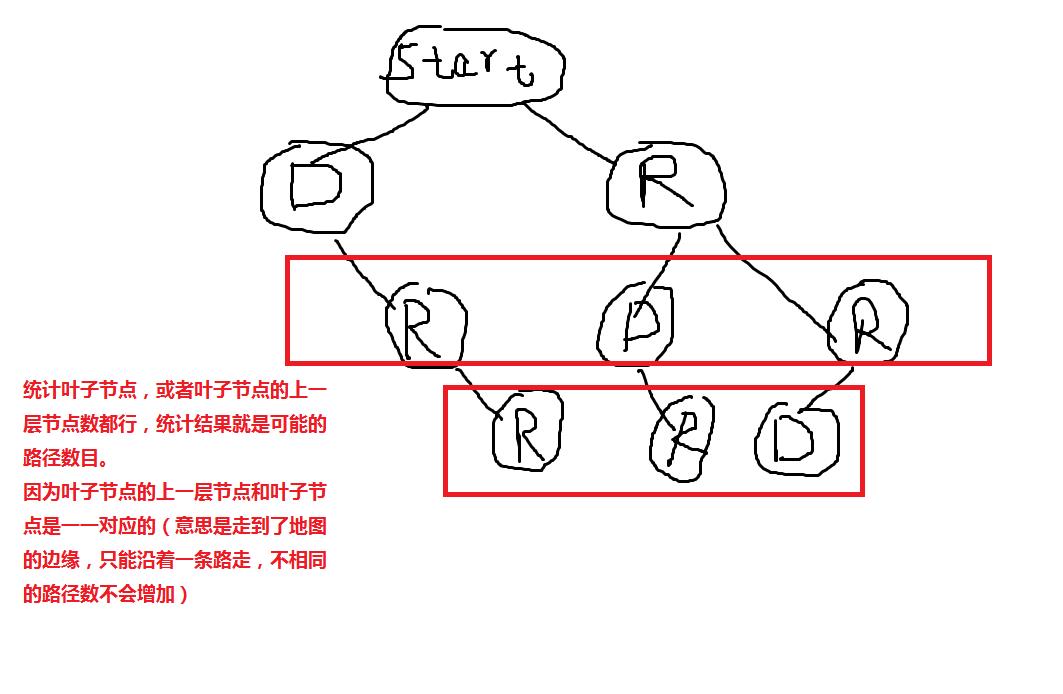
所以问题转化为构建二叉树和统计二叉树叶子节点个数的问题。
class Node:
def __init__(self, left=None, right=None):
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def uniquePaths(self, m, n):
"""
:type m: int
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
def recursive(m, n):
root = Node()
if m == 1 and n == 1:
return None
elif m > 1 and n > 1:
root.right = recursive(m-1, n)
root.left = recursive(m, n-1)
elif m > 1:
root.right = recursive(m - 1, n)
elif n > 1:
root.left = recursive(m, n-1)
return root
def count_leaves(root):
count = 0
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
count += 1
if root.left is not None:
count += count_leaves(root.left)
if root.right is not None:
count += count_leaves(root.right)
return count
root = recursive(m, n)
if not root:
return 1
return count_leaves(root)
a = Solution()
b = a.uniquePaths(1, 1)
print(b)
不过很遗憾,这种算法leetcode OJ跑到 37 / 62 个测试样例时就超时了。可以尝试在这个想法上进行改进,比如不建二叉树,直接在m=1和n=1时进行计数+1。但由于是递归,重复计算太多。
m行n列的数据,时间复杂度是O(m!)*O(n!)
def uniquePaths2(self, m, n):
"""
:type m: int
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
def recursive(m, n):
count = 0
if m == 1 and n == 1:
count = 1
elif m > 1 and n > 1:
count = recursive(m - 1, n) + recursive(m, n - 1)
elif m > 1:
count = recursive(m - 1, n)
elif n > 1:
count = recursive(m, n - 1)
return count
count = recursive(m, n)
return count
动态规划解法
然而如果画出一张二维表,表中每个点表示,到当前位置的所有路径数,问题就可用成动态规划求解,时间、空间复杂度均O(m*n)
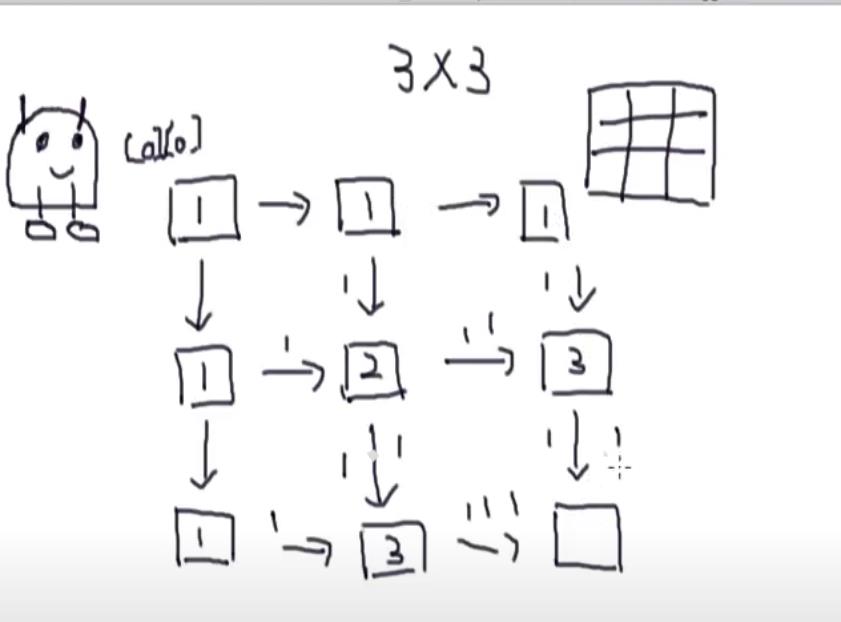
class Solution(object):
def uniquePaths(self, m, n):
road_map = [[1]*m]*n
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(1, m):
road_map[i][j] = road_map[i-1][j] + road_map[i][j-1]
return road_map[n-1][m-1]
换硬币问题,给定零钱集合与固定金额,求有多少种换零钱的方法
Example 1:
Input: amount = 5, coins = [1, 2, 5] Output: 4 Explanation: there are four ways to make up the amount: 5=5 5=2+2+1 5=2+1+1+1 5=1+1+1+1+1
Example 2:
Input: amount = 3, coins = [2] Output: 0 Explanation: the amount of 3 cannot be made up just with coins of 2.
Example 3:
Input: amount = 10, coins = [10] Output: 1
同样,这个问题是类似的,也可以用递归方法求解。
为什么用递归?因为首先想到的是缩减问题规模,本来5块钱,用了一个1块钱的硬币,那么就剩下4块钱了,问题规模也就缩减至4块钱换零钱的问题。
但是递归就意味着重复计算,时间复杂度太高,只能解决超小规模问题(稍微大点就不行了)。
那么还是需要用动态规划求解。

动态规划相当于(1)问题规模缩小+(2)寻找子问题,这两个都考虑到并转化为公式,还是有一定难度(思想上)。
思路(对于示例中的问题,金额=5,零钱集=[1, 2, 5]):
(1)零钱集为空[],那么对任何金额都无解,即换零钱的方法为0种;
(2)金额为0时,对于任何零钱集,换零钱的方法都是一种,即不给任何硬币,就能完成问题;
(3)零钱集逐次增加一种类型的硬币;
(4)金额的粒度为整数1,因此可以让金额从0开始每次+1,一直增长到金额5.
(5)画出矩阵,矩阵中元素含义为:使用当前的零钱集,有多少种方法换到当前的金额?
(6)矩阵中元素的计算:
我是否应该使用零钱集中新加入的那种类型的硬币?如果我不使用,那么我相当于使用的是上一步(上一行)中的零钱集来求解当前位置的金额的换硬币方法,而这个方法已经计算出来了,就在当前元素的上一行正上方。
如果我使用了零钱集中新加入的那种类型的硬币一次,假如新加入的那种类型的硬币面值x,当前的金额是y,由于我使用了x,那么金额就会变成y-x。所以如果我知道当金额是y-x时,使用当前的零钱集有多少种换法,就知道了问题的解。这里相当于在矩阵当前元素的同一行的左边(因为金额减少了,y-x<y)去寻找答案。
class Solution(object):
def change(self, amount, coins):
"""
:type amount: int
:type coins: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
sub_problem_table = [[0 for i in range(amount + 1)] for j in range(len(coins) + 1)]
sub_problem_table[0][0] = 1 # 相当于0元用空零钱集[]去换,共有1种换法
for row_id in range(1, len(coins) + 1):
sub_problem_table[row_id][0] = 1 # 相当于0元钱用各种硬币换,换法只有一种那就是什么也不换
for coins_type in range(1, len(coins) + 1):
for money in range(1, amount + 1):
not_using_ways = sub_problem_table[coins_type - 1][money]
if coins[coins_type - 1] > money:
using_ways = 0
else:
using_ways = sub_problem_table[coins_type][money - coins[coins_type - 1]]
sub_problem_table[coins_type][money] = not_using_ways + using_ways
return sub_problem_table[-1][-1]
以上是关于求所有不重复路径, Unique Paths, LeetCode题解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章