移植Linux-5.4+内核到4412开发板
Posted 心底狂像
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了移植Linux-5.4+内核到4412开发板相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
ITOP-4412开发板被Linux官方支持,所以我们在4412上学习新的内核是非常方便的,本文作者是4412精英群8群一位技术高手,接下来,我们一起来欣赏下他的表演。
环境说明
OS版本
Ubuntu 20 LTS
交叉编译环境配置
~$ sudo apt install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf
~$ sudo apt install flex
~$ sudo apt install bison
~$ sudo apt install u-boot-tools
目标开发板
CPU (Exynos4412,四核Cortex-A9,主频为1.4GHz-1.6GHz)
RAM (1GB 双通道 DDR3)
ROM (8GB EMMC)
其他请见官网链接
1. 下载源码
~$ git clone https://github.com/jason416/linux.gi
Note:移植好的源码见博主github仓库的iTop4412分支。
2. 配置内核
2.1 进入内核源码目录
~/linux-5.4$ ls
arch COPYING Documentation include Kbuild lib Makefile README security usr
block CREDITS drivers init Kconfig LICENSES mm samples sound virt
certs crypto fs ipc kernel MAINTAINERS net scripts tools
jason@jason-vm2:~/arm-develop/linux$
2.2 修改内核配置
说明:
Note: 官方提供了所有三星系列的默认配置,需要先生成一个exynos的配置为基础,再上面再修改成跟板子一致的配置选项即可。
为了避免每次都需要指定ARCH和CROSS_COMPILE变量,可以直接在顶层Makefile直接指定好,如下所示: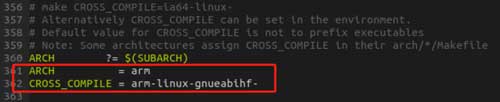
选择系统类型
System Type --->
- Samsung EXYNOS --->
--- Samsung EXYNOS
[] SAMSUNG EXYNOS3
- SAMSUNG EXYNOS4
[] SAMSUNG EXYNOS5
*** EXYNOS SoCs ***
-*- SAMSUNG EXYNOS4210
- SAMSUNG EXYNOS4412
配置调试串口 - 设置为UART2
Kernel hacking --->
- Kernel low-level debugging functions (read help!)
Kernel low-level debugging port (Use Samsung S3C UART 2 for low-level debug) --->
开启串口调试驱动
Device Drivers --->
Character devices --->
Serial drivers --->
<*> Samsung SoC serial support
- Samsung SoC serial debug
- Support for console on Samsung SoC serial port
开启DM96XX网卡驱动
Device Drivers --->
- Network device support --->
<*> USB Network Adapters --->
<*> Davicom DM96xx based USB 10/100 ethernet devices
设置内核压缩模式为LZMA(非必须,可减小文件大小)
General setup --->
() Build ID Salt
Kernel compression mode (LZMA) --->
编译内核
~/linux-5.4$ make uImage LOADADDR=0x40008000 -j$(nproc)
...
OBJCOPY arch/arm/boot/zImage
Kernel: arch/arm/boot/zImage is ready
UIMAGE arch/arm/boot/uImage
Image Name: Linux-5.4.47
Created: Sun Jun 21 22:41:40 2020
Image Type: ARM Linux Kernel Image (uncompressed)
Data Size: 5337464 Bytes = 5212.37 KiB = 5.09 MiB
Load Address: 40008000
Entry Point: 40008000
Kernel: arch/arm/boot/uImage is ready
这里需要指定LOADADDR变量,才能生成正确的uImage文件。因为在uboot启动内核时,会先解析uImage中的前64B头信息,定义如下: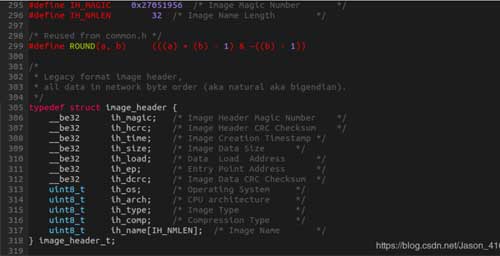 3. 修改设备树(以适配开发板)
3. 修改设备树(以适配开发板)
3.1 说明
在前面的步骤完成后,已经能够编译出可以运行的内核了,但是最后还需要根据板子的差异性,对设备树文件进行调整,以适配目标板。
3.2 修改
屏蔽掉firmware节点(安全相关,不启用,也不知道怎么用…)
修改bus_dmc 节点devfreq-events为devfreq-event
修改regulators 节点参数(参考原理图中的参数)
修改如下:
--- a/arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4412-itop-scp-core.dtsi
+++ b/arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4412-itop-scp-core.dtsi
@@ -23,10 +23,12 @@
reg = <0x40000000 0x40000000>;
};
+#if 0
firmware@203f000 {
compatible = "samsung,secure-firmware";
reg = <0x0203F000 0x1000>;
};
+#endif
fixed-rate-clocks {
xxti {
@@ -70,7 +72,7 @@
};
&bus_dmc {
- devfreq-events = <&ppmu_dmc0_3>, <&ppmu_dmc1_3>;
+ devfreq-event = <&ppmu_dmc0_3>, <&ppmu_dmc1_3>;
vdd-supply = <&buck1_reg>;
status = "okay";
};
@@ -167,8 +169,8 @@
regulators {
ldo1_reg: LDO1 {
regulator-name = "VDD_ALIVE";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1100000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <1100000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <1000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <1000000>;
regulator-always-on;
regulator-boot-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
@@ -230,8 +232,8 @@
ldo9_reg: LDO9 {
regulator-name = "VDD33_LCD";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -252,8 +254,8 @@
ldo12_reg: LDO12 {
regulator-name = "VDD33_UOTG";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
regulator-always-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -300,8 +302,8 @@
/* Used by HSIC */
ldo18_reg: LDO18 {
regulator-name = "VDDIOPERI_28";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <2800000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <2800000>;
regulator-always-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -313,15 +315,15 @@
ldo20_reg: LDO20 {
regulator-name = "VDD28_CAM";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1800000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <2800000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
ldo21_reg: LDO21 {
regulator-name = "VDD28_AF";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1800000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <2800000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -341,8 +343,8 @@
ldo24_reg: LDO24 {
regulator-name = "VDD33_A31";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <3000000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <3000000>;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
};
@@ -430,8 +432,8 @@
buck7_reg: BUCK7 {
regulator-name = "pvdd_buck7";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <750000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <2000000>;
+ regulator-min-microvolt = <2050000>;
+ regulator-max-microvolt = <2050000>;
regulator-boot-on;
regulator-always-on;
op_mode = <1>; /* Normal Mode */
3.3 编译dts
~/linux-5.4$ make dtbs
4. 启动测试
根据另一个专题《Uboot-2017-11移植DM9621网卡专题》移植的支持网络功能的uboot,和移植的ubuntu-base-20.04-base-armhf文件系统(下篇文章更新移植方法),可以直接tftp测试内核,效果如下: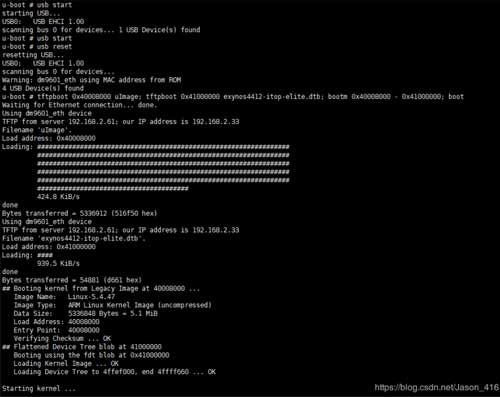
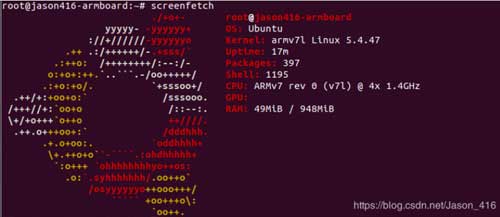
到这一步,移植工作就完成了,是不是觉得很容易呢~
更多内容关注公众号噢:
以上是关于移植Linux-5.4+内核到4412开发板的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
基于iTOP-4412开发板(精英版)的linux 4.14.2内核移植
基于iTOP-4412开发板(精英版)的linux 4.14.2内核移植
基于iTOP-4412开发板(精英版)的linux 4.14.2内核移植