LeetCode之Weekly Contest 92
Posted youdias
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode之Weekly Contest 92相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
第一题:转置矩阵
问题:
给定一个矩阵 A, 返回 A 的转置矩阵。
矩阵的转置是指将矩阵的主对角线翻转,交换矩阵的行索引与列索引。
示例 1:
输入:[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]]
示例 2:
输入:[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]] 输出:[[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]]
提示:
1 <= A.length <= 10001 <= A[0].length <= 1000
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/contest/weekly-contest-92/problems/transpose-matrix/
分析:
行列互换即可
AC Code:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<vector<int>> transpose(vector<vector<int>>& A) { 4 vector<vector<int>> ret; 5 vector<int> tmp; 6 if (A.size() == 0) 7 { 8 return A; 9 } 10 int m = A.size();//行 11 int n = A[0].size();//列 12 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) 13 { 14 tmp.clear(); 15 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) 16 { 17 tmp.emplace_back(A[i][j]); 18 } 19 ret.emplace_back(tmp); 20 } 21 return ret; 22 } 23 };
其他:
用时最短code(16/28):
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<vector<int>> transpose(vector<vector<int>>& A) { 4 int rows = A.size(); 5 int lines = A[0].size(); 6 7 vector<vector<int>> ans; 8 9 for(int i = 0; i < lines; i++) 10 { 11 vector<int> temp; 12 ans.push_back(temp); 13 } 14 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 15 { 16 for(int j = 0; j < lines; j++) 17 { 18 ans[j].push_back(A[i][j]); 19 } 20 } 21 return ans; 22 } 23 };
第二题:具有所有最深结点的最小子树
问题:
给定一个根为 root 的二叉树,每个结点的深度是它到根的最短距离。
如果一个结点在整个树的任意结点之间具有最大的深度,则该结点是最深的。
一个结点的子树是该结点加上它的所有后代的集合。
返回能满足“以该结点为根的子树中包含所有最深的结点”这一条件的具有最大深度的结点。
示例:
输入:[3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] 输出:[2,7,4] 解释:
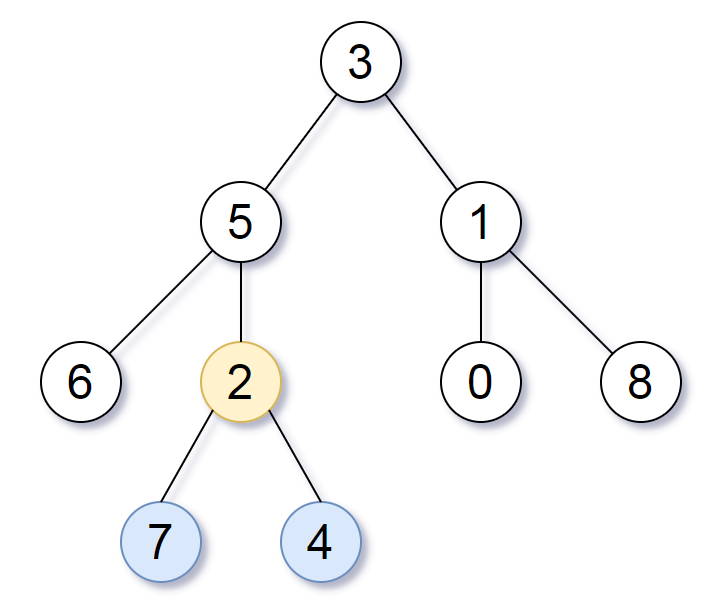
我们返回值为 2 的结点,在图中用黄色标记。 在图中用蓝色标记的是树的最深的结点。 输入 "[3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]" 是对给定的树的序列化表述。 输出 "[2, 7, 4]" 是对根结点的值为 2 的子树的序列化表述。 输入和输出都具有 TreeNode 类型。
提示:
- 树中结点的数量介于 1 和 500 之间。
- 每个结点的值都是独一无二的。
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/contest/weekly-contest-92/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/
分析:
周赛91中有一个类似的问题,按照同样做法对每个节点进行编码,根节点是0b1,下一次分别是0b10,0b11,然后将得到的数据最后一个即为最底层叶子,根据“宽度”能得到最底层所有叶子,找到公共祖先即为所求节点。
AC Code:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 //包含该节点的所有子树,最大公共部分就是 13 //包含该节点的所有子树,最大公共部分就是 14 TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) { 15 map<uint64_t, TreeNode*> data; 16 TreeNode* ret = NULL; 17 TreeNode tmp(0); 18 data = DealTreeNode(root, 1); 19 map<uint64_t, TreeNode*>::iterator it; 20 it = data.end(); 21 it--; 22 int targetvalue = (*it).first; 23 int length = GetBLength(targetvalue); 24 //uint64_t target = 0xFFFFFFFF; 25 26 set<uint64_t> sets; 27 for (map<uint64_t, TreeNode*>::reverse_iterator rit = data.rbegin(); rit != data.rend(); rit++) 28 { 29 if (GetBLength((*rit).first) == length) 30 { 31 sets.insert((*rit).first); 32 //target = !(target ^ (*rit).first); 33 } 34 else 35 { 36 break; 37 } 38 39 } 40 //到这里1知道了层次,2得到了最底层一排数据,但是1000如何确认是10的后代还是1的后代呢? 41 //向上找共同唯一祖先 42 43 44 while (sets.size()>1) 45 { 46 sets = GetUper(sets); 47 } 48 int finalcode = *(sets.begin()); 49 it = data.find(finalcode); 50 ret = (*it).second; 51 return ret; 52 } 53 set<uint64_t> GetUper(set<uint64_t> setdata) 54 { 55 std::set<uint64_t> ret; 56 for (set<uint64_t>::iterator it = setdata.begin(); it != setdata.end(); it++) 57 { 58 ret.insert((*it) / 2); 59 } 60 return ret; 61 } 62 int GetBLength(int data) 63 { 64 int ret = 0; 65 while (data) 66 { 67 ret++; 68 data /= 2; 69 } 70 return ret; 71 } 72 map<uint64_t, TreeNode*> DealTreeNode(TreeNode* root, int level) 73 { 74 map<uint64_t, TreeNode*> ret; 75 map<uint64_t, TreeNode*> left, right; 76 //TreeNode tmp(0); 77 TreeNode* tmp = NULL; 78 if (root == nullptr) 79 { 80 return ret; 81 } 82 tmp = root; 83 ret.insert(make_pair(level, tmp)); 84 left = DealTreeNode(root->left, level * 2); 85 right = DealTreeNode(root->right, level * 2 + 1); 86 for (map<uint64_t, TreeNode*>::iterator it = left.begin(); it != left.end(); it++) 87 { 88 ret.insert(*it); 89 } 90 for (map<uint64_t, TreeNode*>::iterator it = right.begin(); it != right.end(); it++) 91 { 92 ret.insert(*it); 93 } 94 return ret; 95 } 96 97 };
其他:
用时最短code(4/8):
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 int doit(TreeNode* root) 11 { 12 int tmp1,tmp2; 13 if (root==NULL) return 0; 14 tmp1=doit(root->left); 15 tmp2=doit(root->right); 16 if (tmp1>tmp2) return tmp1+1; 17 else return tmp2+1; 18 } 19 20 TreeNode* doit2(TreeNode* root,int dep) 21 { 22 if (root==NULL) return NULL; 23 if (dep==1) return root; 24 TreeNode* tmp1=doit2(root->left,dep-1); 25 TreeNode* tmp2=doit2(root->right,dep-1); 26 if (tmp1==NULL) return tmp2; 27 else if (tmp2==NULL) return tmp1; 28 else return root; 29 } 30 31 class Solution { 32 public: 33 TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) { 34 int tmp=doit(root); 35 return doit2(root,tmp); 36 } 37 };
1.doit 得到层数
2.left right中如果都含有最低一层,返回root,否则返回含有最低一层的一个
第三题:回文素数
问题:
求出大于或等于 N 的最小回文素数。
回顾一下,如果一个数大于 1,且其因数只有 1 和它自身,那么这个数是素数。
例如,2,3,5,7,11 以及 13 是素数。
回顾一下,如果一个数从左往右读与从右往左读是一样的,那么这个数是回文数。
例如,12321 是回文数。
示例 1:
输入:6 输出:7
示例 2:
输入:8 输出:11
示例 3:
输入:13 输出:101
提示:
1 <= N <= 10^8- 答案肯定存在,且小于
2 * 10^8。
链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/contest/weekly-contest-92/problems/prime-palindrome/
分析:
1.回文数比素数更稀疏
2.根据回文数特定,只需要知道一半就能构造出数据。
AC Code:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int primePalindrome(int N) { 4 if (N <= 2) 5 { 6 return 2; 7 } 8 if (N == 3) 9 { 10 return 3; 11 } 12 if (N <= 5) 13 { 14 return 5; 15 } 16 if (N <= 7) 17 { 18 return 7; 19 } 20 if (N <= 11) 21 { 22 return 11; 23 } 24 if (N <= 101) 25 { 26 return 101; 27 } 28 29 //先得到下一个回文数 30 int ret = N - 1; 31 while (true) 32 { 33 ret = GetNextPalindrome(ret); 34 //判断是否是素数,如果是,则返回,否则找到下一个回文数继续判断 35 if (isPrime(ret) == 1) 36 { 37 return ret; 38 } 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 int GetNextPalindrome(int data) 44 { 45 //100以内的数字已经特殊考虑过,不存在差值1的两个回文数 46 //首先得到长度,如果是奇数,取前一半+中间值构造,如果是偶数,取前一半构造 47 int tmpdata=data; 48 int length = 0; 49 while (tmpdata) 50 { 51 tmpdata /= 10; 52 length++; 53 } 54 //到这里得到数据长度,根据奇偶判断 55 if (length % 2 == 0) 56 { 57 //偶数长度 58 int highhalf = data / (pow(10, length / 2)); //得到前一半 59 int lowhalf = data % (int)(pow(10, length / 2)); //低一半 60 int tmphigh = GetPallindrom(highhalf); 61 if (tmphigh > lowhalf) 62 { 63 //只需要将高一般构建结果即可 64 return data + (tmphigh - lowhalf); 65 } 66 else 67 { 68 highhalf += 1; 69 int tmplength = 0; 70 tmpdata = highhalf; 71 while (tmpdata) 72 { 73 tmpdata /= 10; 74 tmplength++; 75 } 76 if (tmplength == length / 2) 77 { 78 //没产生进位 79 return highhalf*pow(10, tmplength) + GetPallindrom(highhalf); 80 } 81 else 82 { 83 //返回奇数个的10X01 84 return highhalf*pow(10, tmplength-1) + GetPallindrom(highhalf); 85 } 86 87 } 88 } 89 else 90 { 91 //奇数长度中间+1即可,如果原来是9,变为10XX01 92 int highhalf = data / (int)(pow(10, length / 2)); 93 int mid = highhalf % 10; 94 highhalf /= 10; 95 int lowhalf = data % (int)(pow(10, length / 2)); 96 int tmphighhalf = GetPallindrom(highhalf); 97 98 //不需要动到中间位置数组 99 if (tmphighhalf > lowhalf) 100 { 101 return data + (tmphighhalf - lowhalf); 102 } 103 104 //需要更新中间数字 105 if (mid < 9) 106 { 107 return (highhalf * 10 + mid + 1)*pow(10, length / 2) + tmphighhalf; 108 } 109 else 110 { 111 //高一半+1不进位,只需要高一半+1,该位变0即可,比如191 -> 202 112 //如果高位+1后需要进位,如99X,则需要变为1001,即最小的高一位 113 mid = 0; 114 highhalf += 1; 115 tmphighhalf = GetPallindrom(highhalf); 116 int tmplength = 0; 117 tmpdata = highhalf; 118 while (tmpdata) 119 { 120 tmpdata /= 10; 121 tmplength++; 122 } 123 if (tmplength == length / 2) 124 { 125 //没产生进位 126 return (highhalf * 10 + mid)*pow(10, length / 2) + tmphighhalf; 127 } 128 else 129 { 130 //产生了进位 比如999应该变为1001 131 return highhalf*pow(10, tmplength) + tmphighhalf; 132 } 133 } 134 135 } 136 } 137 int isPrime(int data) 138 { 139 if (data == 2 || data == 3) 140 { 141 return 1; 142 } 143 for (int i = 2; i*i <= data; i++) 144 { 145 if (data%i == 0) 146 { 147 return 0; 148 } 149 } 150 return 1; 151 } 152 int GetPallindrom(int data) 153 { 154 int ret = 0; 155 while (data>0) 156 { 157 ret = ret * 10 + data % 10; 158 data = data / 10; 159 } 160 //cout << "debug:" << data << " -> " << ret << endl;; 161 return ret; 162 } 163 164 };
其他:
用时最短code(0/12)
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int primePalindrome(int N) { 4 if (N<=2) return 2; 5 string s = to_string(N); 6 int base = stoi(s.substr(0, (s.size()+1)/2)); 7 int flag = (s.size()%2==0?2:1); 8 while (true) { 9 int n = base; 10 for (int k = (flag==1?n/10:n); k>0; k/=10) n = n*10+k%10; 11 if (n>=N && isPrime(n)) 12 return n; 13 base ++; 14 if ((base==10 || base==100 || base==1000 || base==10000)) { 15 if (flag==1) base /= 10; 16 flag = (flag==1?2:1); 17 } 18 } 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 bool isPrime(int n) { 23 if (n==2) return true; 24 if (n%2==0) return false; 25 for (int i=3; i*i<=n; i+=2) { 26 if (n%i==0) 27 return false; 28 } 29 return true; 30 } 31 };
第四题:获取所有钥匙的最短路径
问题:
- 用户通过次数0
- 用户尝试次数4
- 通过次数0
- 提交次数6
- 题目难度Hard
给定一个二维网格 grid。 "." 代表一个空房间, "#" 代表一堵墙, "@" 是起点,("a", "b", ...)代表钥匙,("A", "B", ...)代表锁。
我们从起点开始出发,一次移动是指向四个基本方向之一行走一个单位空间。我们不能在网格外面行走,也无法穿过一堵墙。如果途经一个钥匙,我们就把它捡起来。除非我们手里有对应的钥匙,否则无法通过锁。
假设 K 为钥匙/锁的个数,且满足 1 <= K <= 6,字母表中的前 K 个字母在网格中都有自己对应的一个小写和一个大写字母。换言之,每个锁有唯一对应的钥匙,每个钥匙也有唯一对应的锁。另外,代表钥匙和锁的字母互为大小写并按字母顺序排列。
返回获取所有钥匙所需要的移动的最少次数。如果无法获取所有钥匙,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:["@.a.#","###.#","b.A.B"] 输出:8
示例 2:
输入:["@..aA","..B#.","....b"] 输出:6
提示:
1 <= grid.length <= 301 <= grid[0].length <= 30grid[i][j]只含有‘.‘,‘#‘,‘@‘,‘a‘-‘f‘以及‘A‘-‘F‘- 钥匙的数目范围是
[1, 6],每个钥匙都对应一个不同的字母,正好打开一个对应的锁。
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/contest/weekly-contest-92/problems/shortest-path-to-get-all-keys/
分析:
最开始做法是记录每一条路径,从起点开始,得到接下来可能的下一步,如果是#不可达,如果是门但是没有对应钥匙,不可达,如果已经存储在路径中不可达,如果是.或者钥匙,或者是门但有对应钥匙,视为道路,
并存储到路径中。如果拿到了一把新钥匙,清空已经记录的路径,因为原来不可达的位置也许现在能够到达了,运行走回头路。可惜超时了。折腾一周都没搞出来,参考https://blog.csdn.net/yanglingwell/article/details/80984968。
感觉比较巧妙的地方有:
1,同一起点的接下来不同走法采用同一个地图,同时走过的路都设为#,不需要记录就可以避免回头。
2,BFS中当前位置存储在一个队列中,通过{-1,-1}来隔离下一步能够到达的位置。
AC Code:
1 pair<int, int> BFS(const vector<string>& grid, int x, int y, string keysearched, char key, int& len) 2 { 3 if (x<0 || x>=grid.size() || y<0 || y>=grid[0].size()) 4 { 5 return{-1,-1}; 6 } 7 vector<string> localgrid(grid); 8 localgrid[x][y] = ‘#‘; 9 queue<pair<int, int>> que; 10 que.push({ x, y }); 11 que.push({ -1, -1 }); 12 int directions[][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } }; 13 while (!que.empty()) 14 { 15 int curx = que.front().first; 16 int cury = que.front().second; 17 18 que.pop(); 19 if (curx == -1 && que.empty()) 20 { 21 continue; 22 } 23 else if (cury == -1 && !que.empty()) 24 { 25 que.push({ -1, -1 }); 26 ++len; 27 continue; 28 } 29 30 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 31 { 32 int tx = curx + directions[i][0]; 33 int ty = cury + directions[i][1]; 34 if (tx < 0 || tx >= grid.size() || ty < 0 || ty >= grid[0].size()) 35 { 36 continue; 37 } 38 if (localgrid[tx][ty] == ‘#‘) 39 { 40 continue; 41 } 42 if (isupper(localgrid[tx][ty]) && keysearched.find(tolower(localgrid[tx][ty])) == keysearched.npos) 43 { 44 continue; 45 } 46 47 //找到了目标key 48 if (localgrid[tx][ty]==key && keysearched.find(tolower(localgrid[tx][ty])) == keysearched.npos) 49 { 50 return{ tx, ty }; 51 } 52 53 localgrid[tx][ty] = ‘#‘; 54 que.push({ tx, ty }); 55 } 56 } 57 return{ -1, -1 }; 58 } 59 //返回 60 int DFS(const vector<string>& grid, int x, int y, string keysearched, string keysearching) 61 { 62 //起点越界 63 if (x<0 || x>=grid.size() || y<0 || y>=grid[0].size()) 64 { 65 return -1; 66 } 67 if (keysearching.empty()) 68 { 69 return 0; 70 } 71 72 int ans = -1; 73 //逐个找key 74 for (int i = 0; i < keysearching.size(); i++) 75 { 76 int nextLen = 1; 77 pair<int,int> nextpos = BFS(grid, x, y, keysearched, keysearching[i],nextLen); 78 if (nextpos.first == -1) 79 { 80 continue; 81 } 82 string tmpkeysearched(keysearched); 83 string tmpkeysearching(keysearching); 84 tmpkeysearched.push_back(grid[nextpos.first][nextpos.second]); 85 tmpkeysearching.erase(keysearching.find(grid[nextpos.first][nextpos.second]), 1); //find不是在新的string里面? 86 //tmpkeysearching.erase(tmpkeysearching.find(grid[nextpos.first][nextpos.second]), 1); //find不是在新的string里面? 87 88 int ret = DFS(grid, nextpos.first, nextpos.second, tmpkeysearched, tmpkeysearching); 89 if (ret == -1) 90 { 91 continue; 92 } 93 if (ans == -1 || ans > ret + nextLen) 94 { 95 ans = ret + nextLen; 96 } 97 98 } 99 return ans; 100 } 101 //找到起始点坐标,各个钥匙坐标 102 //通过 二维数组jil 103 //https://blog.csdn.net/yanglingwell/article/details/80984968 104 int shortestPathAllKeys(vector<string>& grid) { 105 //参考网络编写code 106 //首先得到起点位置 107 int location_x, location_y=-1; 108 string keys; 109 for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) 110 { 111 for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].size(); j++) 112 { 113 if (grid[i][j] == ‘@‘) 114 { 115 location_x = i; 116 location_y = j; 117 } 118 if (islower(grid[i][j])) 119 { 120 keys.push_back(grid[i][j]); 121 } 122 } 123 124 } 125 126 return DFS(grid, location_x, location_y, "", keys); 127 128 129 }
其他:
用时最短code(8/272)
1 int t[32][32][1 << 6]; 2 int dr[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dc[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; 3 class Solution { 4 5 public: 6 vector<string> g; 7 int m, n; 8 int shortestPathAllKeys(vector<string>& grid) { 9 g = grid; 10 m = grid.size(); 11 if(m == 0) return -1; 12 n = grid[0].size(); 13 if (n == 0) return -1; 14 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ 15 for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ 16 if(grid[i][j] == ‘@‘) return go(i, j); 17 } 18 } 19 return -1; 20 } 21 int go(int r, int c){ 22 int all = 0; 23 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ 24 for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ 25 if(‘a‘ <= g[i][j] && g[i][j] <= ‘z‘) 26 all |= (1 <<(g[i][j] - ‘a‘)); 27 } 28 } 29 memset(t, 0xff, sizeof(t)); 30 t[r][c][0] = 0; 31 deque<int> que; 32 que.push_back((r << 12) + (c << 6) + 0); 33 while(!que.empty()){ 34 int key = que.front(); 35 que.pop_front(); 36 r = key >> 12; 37 c = (key >> 6) & 0x3f; 38 int k = key & 0x3f; 39 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ 40 int r1 = r + dr[i]; 41 int c1 = c + dc[i]; 42 if(r1 < 0 || c1 < 0 || r1 >= m || c1 >=n) continue; 43 char ch = g[r1][c1]; 44 if(ch == ‘#‘) continue; 45 if(‘A‘ <= ch && ch <=‘Z‘){ 46 int x = 1 << (ch - ‘A‘); 47 if( !(x&k)) continue; 48 } 49 int k1 = k; 50 if(‘a‘ <=ch && ch <=‘z‘){ 51 k1 |= (1 <<(ch - ‘a‘)); 52 } 53 if (t[r1][c1][k1] < 0){ 54 t[r1][c1][k1] = t[r][c][k] + 1; 55 if(k1 == all) return t[r1][c1][k1]; 56 que.push_back((r1 << 12) + (c1 << 6) + k1); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 return -1; 61 62 } 63 };
以上是关于LeetCode之Weekly Contest 92的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章