IEnumerable和IEnumerator的区别
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了IEnumerable和IEnumerator的区别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A IEnumerable接口和IEnumerator接口是.NET中非常重要的接口,二者有何区别?1. 简单来说IEnumerable是一个声明式的接口,声明实现该接口的类就是“可迭代的enumerable”,但并没用说明如何实现迭代器(iterator).其代码实现为:
public interface IEnumerable
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
2. 而IEnumerator接口是实现式接口,它声明实现该接口的类就可以作为一个迭代器iterator.其代码实现为:
public interface IEnumerator
object Current get;
bool MoveNext();
void Reset();
3.一个collection要支持Foreach进行遍历,就必须实现IEnumerable,并一某种方式返回迭代器对象:IEnumerator.
那么又如何实现这两个接口呢? 其代码如下:
假设有一个Person类,其有两个属性FirstName和LastName
public class Person
public string FirstName get; set;
public string LastName get; set;
public Person(string firstName, string lastName)
this.FirstName = firstName;
this.LastName = lastName;
另外通过People类来实现IEnumerable和IEnumerator接口.
//实现IEnumerable接口
public class People :IEnumerable
public Person [] pers;
public People(Person [] ps)
this.pers = ps;
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
//foreach(Person p in pers)
//
// yield return p;
//
return new People1(pers);
//实现IEnumerator接口
public class People1 : IEnumerator
public Person[] pers;
public People1(Person[] per)
this.pers = per;
int position = -1;
public bool MoveNext()
position++;
return position < pers.Length;
public void Reset()
position=-1;
public object Current
get
try
return pers[position];
catch(IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
throw new InvalidOperationException();
C# IEnumerator IEnumerable接口
前言
使用linq的时候大家应该都知道IEnumerable和IEnumerator接口!
解释一下
IEnumerable 它利用 GetEnumerator() 返回 IEnumerator 集合访问器,声明实现该接口的class是“可枚举(enumerable)”的 通俗点说就是可进行迭代操作的类型。
IEnumerator解释:它是一个的集合访问器,使用foreach语句遍历集合或数组时,就是调用 Current、MoveNext()的结果。
例子
今天给大家讲讲迭代器的原理 我们自己实现一个UserInforMationList
我这里定义一个UserInforMationModel和UserInforMationList类
public class UserInforMationList
public UserInforMation[] _UserInforMations;
public void Add(UserInforMation[] userInforMations)
_UserInforMations = new UserInforMation[userInforMations.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < userInforMations.Length; i++)
_UserInforMations[i] = userInforMations[i];
public class UserInforMation
public string UserName get; set;
public string Sex get; set;
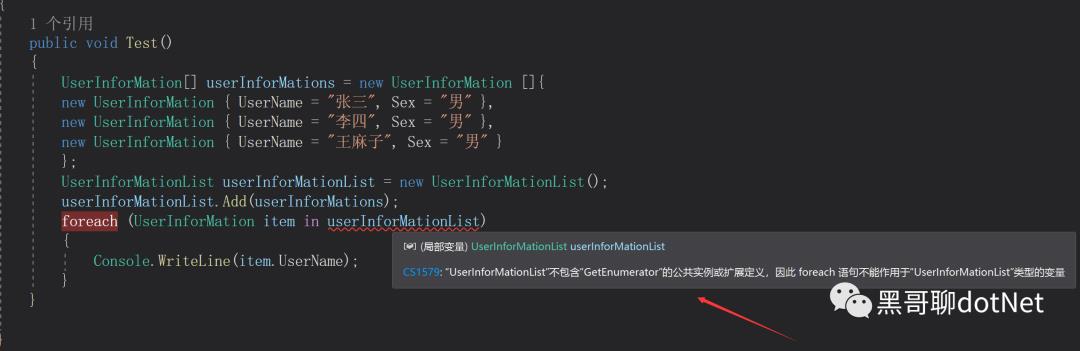
使用我们的测试方法,发现我们的代码报错了UserInforMationList不包含 GetEnumerator的公共实例,因此不能使用ForEach.
那么我们要怎么实现Foreach了那就要用到IEnumerator、IEnumerable!
提示告诉我们缺少一个GetEnumerator的公共实例
我们看下IEnumerable接口
public interface IEnumerable
[DispId(-4)]
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
Enumerable接口刚好返回一个GetEnumerator 然后再看一下IEnumerator
IEnumerator接口为类内部的集合提供了迭代方式, IEnumerator 要求你实现三个方法:
public interface IEnumerator
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
object Current
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
get;
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
bool MoveNext();
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
void Reset();
看了这两个接口就可以知道我们的UserInforMationList:要继承这个IEnumerable接口 这个接口返回的是一个GetEnumerator。观察这方法,
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
throw new NotImplementedException();
需要返回一个叫做IEnumerator的接口,因此,一个类要想可迭代,还需要进一步实现IEnumerator类,这个才是真正获取到的迭代器,
那我们再定义一个UserInforMationEnumerator继承于GetEnumerator然后实现这三个方法,
MoveNext方法:该方法将集合索引加1,并返回一个bool值,指示是否已到达集合的末尾。
Reset方法:它将集合索引重置为其初始值-1,这会使枚举数无效。
Current方法: 返回position位置的当前对象
public class UserInforMationEnumerator : IEnumerator
public UserInforMation[] _userInforMations;
public int _Index = -1;
public UserInforMationEnumerator(UserInforMation[] userInforMations)
_userInforMations = userInforMations;
public object Current => _userInforMations[_Index];
public bool MoveNext()
_Index++;
return _Index < _userInforMations.Length;
public void Reset()
_Index = -1;
这样我们就实现了自己的迭代器。
然后我们跑一下代码

我们调用GetEnumerator的时候,看似里面for循环了一次,其实这个时候没有做任何操作。只有调用MoveNext的时候才会对应调用for循环:
现在我想可以回答你为什么Linq to Object中要返回IEnumerable?:
因为IEnumerable是延迟加载的,每次访问的时候才取值。也就是我们在Lambda里面写的where、select并没有循环遍历(只是在组装条件),只有在ToList或foreache的时候才真正去集合取值了。这样大大提高了性能。
最后大家如果喜欢我的文章,还麻烦给个关注并点个赞, 希望net生态圈越来越好!
以上是关于IEnumerable和IEnumerator的区别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章