OS第1次实验报告:熟悉使用Linux命令和剖析ps命令
Posted 霓袅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OS第1次实验报告:熟悉使用Linux命令和剖析ps命令相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- 姓名:李瑶
- 学号:201821121002
- 班级:计算1811
1. 实验环境介绍
- 操作系统:Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.18362.657]
- 平台:Cygwin
- 用户名:LiYao
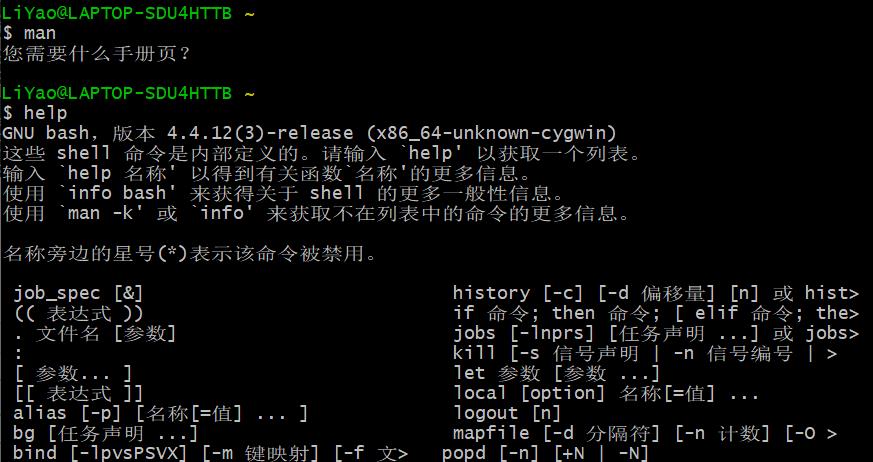
2. 常用命令使用
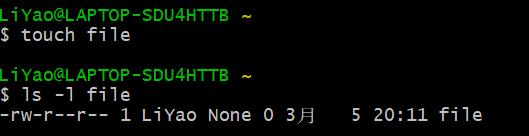
3. 剖析ps命令
(1)运行man ps:
SYNOPSIS
ps [−aA] [−defl] [−g grouplist] [−G grouplist]
[−n namelist] [−o format]... [−p proclist] [−t termlist]
[−u userlist] [−U userlist]
DESCRIPTION
The ps utility shall write information about processes, subject to
having appropriate privileges to obtain information about those pro‐
cesses.
By default, ps shall select all processes with the same effective user
ID as the current user and the same controlling terminal as the in‐
voker.
OPTIONS
The ps utility shall conform to the Base Definitions volume of
POSIX.1‐2008, Section 12.2, Utility Syntax Guidelines.
The following options shall be supported:
−a Write information for all processes associated with termi‐
nals. Implementations may omit session leaders from this
list.
−A Write information for all processes.
−d Write information for all processes, except session leaders.
−e Write information for all processes. (Equivalent to −A.)
−f Generate a full listing. (See the STDOUT section for the
contents of a full listing.)
−g grouplist
Write information for processes whose session leaders are
given in grouplist. The application shall ensure that the
grouplist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or
<comma>-separated list.
−G grouplist
Write information for processes whose real group ID numbers
are given in grouplist. The application shall ensure that
the grouplist is a single argument in the form of a <blank>
or <comma>-separated list.
−l Generate a long listing. (See STDOUT for the contents of a
long listing.)
−n namelist
Specify the name of an alternative system namelist file in
place of the default. The name of the default file and the
format of a namelist file are unspecified.
−o format Write information according to the format specification given
in format. This is fully described in the STDOUT section.
Multiple −o options can be specified; the format specifica‐
tion shall be interpreted as the <space>-separated concate‐
nation of all the format option-arguments.
−p proclist
Write information for processes whose process ID numbers are
given in proclist. The application shall ensure that the
proclist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or
<comma>-separated list.
−t termlist
Write information for processes associated with terminals
given in termlist. The application shall ensure that the
termlist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or
<comma>-separated list. Terminal identifiers shall be given
in an implementation-defined format. On XSI-conformant sys‐
tems, they shall be given in one of two forms: the device\'s
filename (for example, tty04) or, if the device\'s filename
starts with tty, just the identifier following the characters
tty (for example, "04").
−u userlist
Write information for processes whose user ID numbers or lo‐
gin names are given in userlist. The application shall en‐
sure that the userlist is a single argument in the form of a
<blank> or <comma>-separated list. In the listing, the nu‐
merical user ID shall be written unless the −f option is
used, in which case the login name shall be written.
−U userlist
Write information for processes whose real user ID numbers or
login names are given in userlist. The application shall
ensure that the userlist is a single argument in the form of
a <blank> or <comma>-separated list.
(2)运行ps -ef命令
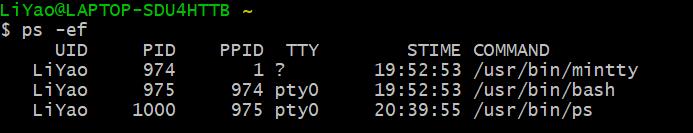
解释命令中参数的含义:
-e:显示系统所有进程信息
-f:显示UID,PPIP,C与STIME栏位。
解释返回结果每个字段的含义:
UID:用户ID PID:进程ID PPID:父进程ID C: CPU使用的资源百分比 STIME:系统启动时间 TTY:登入者的终端机位置 COMMAND:所下达的指令
(3)运行ps -aux命令

解释命令中参数的含义:
-a:显示现行终端机下的所有进程,包括其他用户的进程; -u:以用户为主的进程状态 ; -x:通常与 a 这个参数一起使用,可列出较完整信息。
4. 通过该实验产生新的疑问及解答
(1)关于如何修改用户名为自己名字的拼音
使用写字板或其他文本编辑器打开cygwin目录下的/etc/passwd文件;
刚开始找不到passwd文件,需要使用用mkpasswd -l > /etc/passwd 语句创建,然后再更改用户名为自己名字的拼音;
接着在home目录下建立相应的名字拼音。这样用户名就修改好了。
以上是关于OS第1次实验报告:熟悉使用Linux命令和剖析ps命令的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章