neo4j-高效的原因(节点关系属性存储)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了neo4j-高效的原因(节点关系属性存储)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A neo4j有一个节点存储文件,用来存储节点的记录,文件名为neostore.nodestore.db节点记录的长度是固定大小(9字节)
格式为:Node:inUse+nextRelld+nextPropld
对应的也有一个关系存储文件,用来存储关系的记录.文件是neostore.relationshipstore.db,长度也是固定的
关系长度(33字节)
格式为:
Relationship:inUse+firstNode+secondNode+relType+firstPrevRelId+firstNextRelId+secondPrevRelId+secondNextId+nextProId
属性记录的物理存放位置是neostore.propertystore.db文件中,属性的存储也是固定长度(不过不用担心长度不够,长度不够的时候会去申请动态存储),每个属性记录包含4个属性块和属性链中下一个属性的id.属性链是单向链表,关系链是双向链表.因为neo4j是基于java开发,所以一个属性记录中可以包含任何java虚拟机(JVM)支持的基本数据类型/字符串/数组/属性索引文件(neostore.propertystore.db.index).属性索引文件主要用于存储属性的名称,属性索引的值部分存储的是指向动态内存的记录(长度不够存储的时候会去申请动态内存,并放在动态存储文件中)或内联值.
一文高效图解二叉树面试题
二叉树,搜索二叉树,是算法面试的必面题。聊聊面试点:
一、树 & 二叉树
树的组成为节点和边,节点用来储存元素。节点组成为根节点、父节点和子节点。
如图:树深 length 为 4;根节点的值为 5 ;父子节点关系:值为 8 和 值为 3 的节点
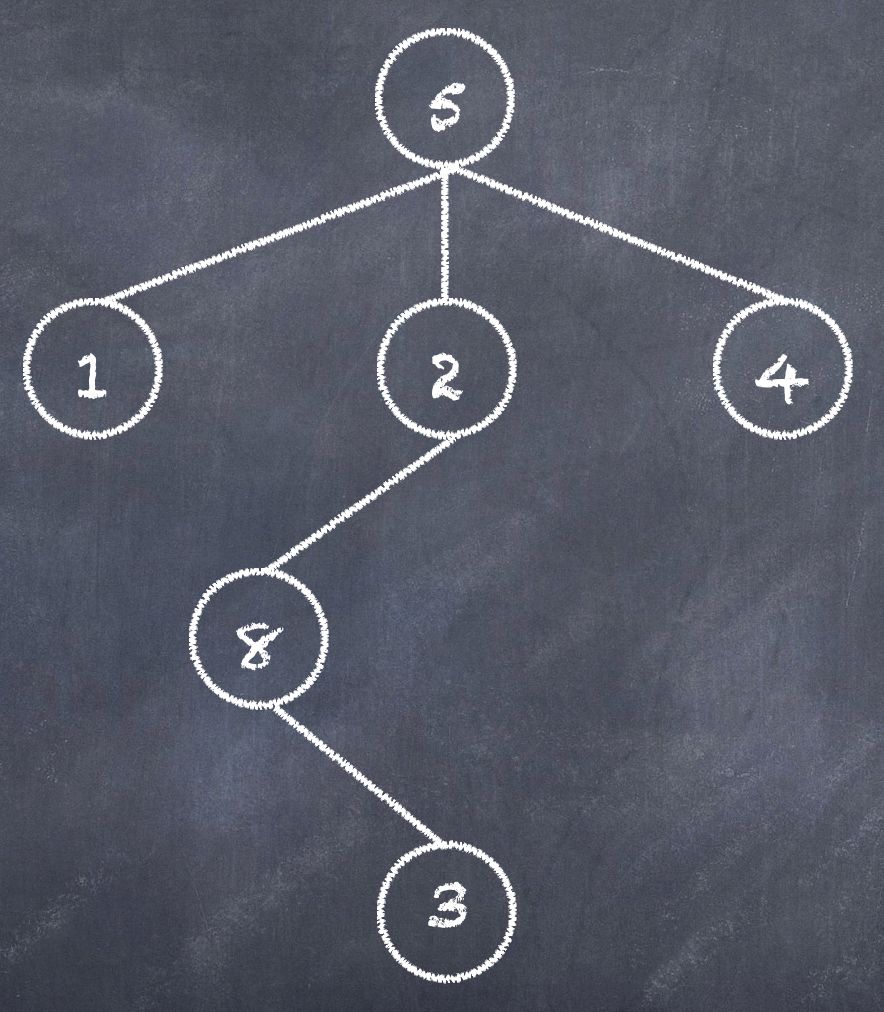
理解了树,那什么是二叉树?
二叉树 (Binary Tree),二叉是分叉的意思,就是用边区分。节点最多有两个子节点,分别为左子节点和右子节点。连接节点的就是边,所以节点最多会有三条边。二叉树的场景很多,比如用来表示算术表达式等等。
如图:值为 1 或者 8 的节点是左节点;值为 2 或 3 的节点是右节点;
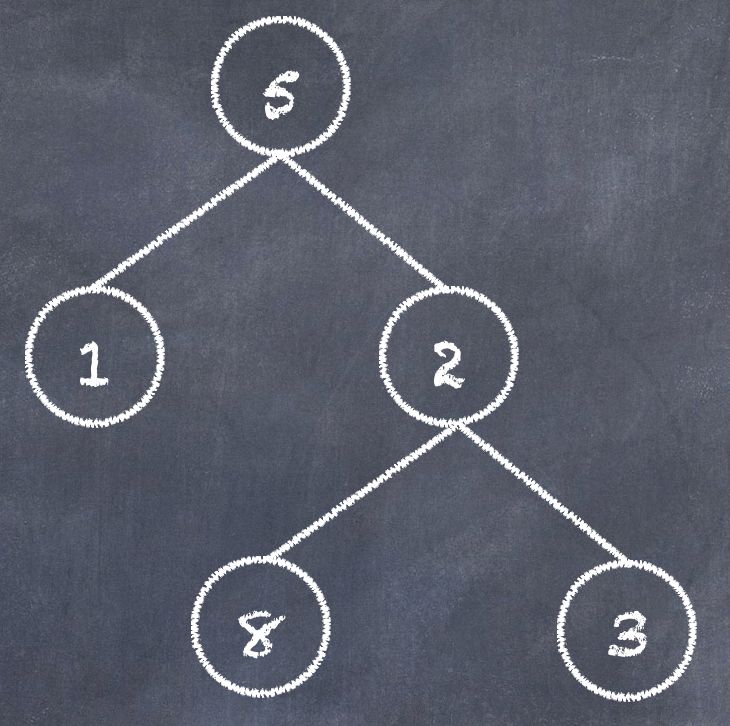
二、二叉搜索树 BST
上面理解了二叉树,那么搜索二叉树就好理解了。搜索二叉树为了搜索而设计,要求也是将无序存储变成有序。即每个节点的值要比左子树的值大,比右子树的值小。
如图:
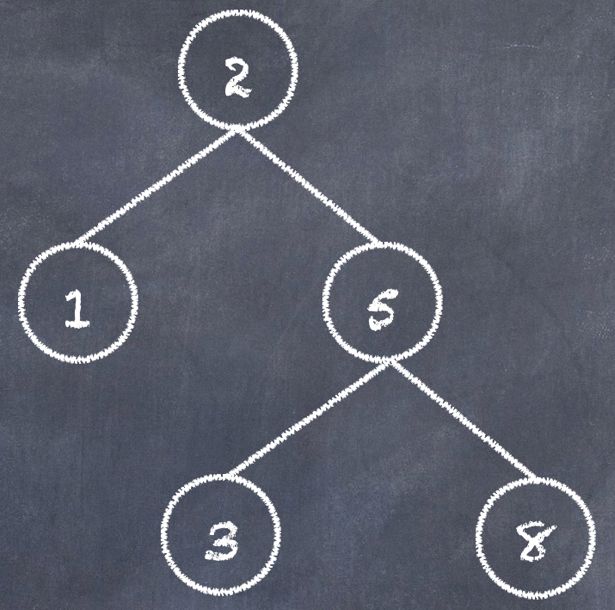
Java 实现代码如下:
public class BinarySearchTree {
/**
* 根节点
*/
public static TreeNode root;
public BinarySearchTree() {
this.root = null;
}
/**
* 查找
*/
public TreeNode search (int key) {
TreeNode current = root;
while (current != null
&& key != current.value) {
if (key < current.value )
current = current.left;
else
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
/**
* 插入
*/
public TreeNode insert (int key) {
// 新增节点
TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(key);
// 当前节点
TreeNode current = root;
// 上个节点
TreeNode parent = null;
// 如果根节点为空
if (current == null) {
root = newNode;
return newNode;
}
while (true) {
parent = current;
if (key < current.value) {
current = current.left;
if (current == null) {
parent.left = newNode;
return newNode;
}
} else {
current = current.right;
if (current == null) {
parent.right = newNode;
return newNode;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 删除节点
*/
public TreeNode delete (int key) {
TreeNode parent = root;
TreeNode current = root;
boolean isLeftChild = false;
// 找到删除节点 及 是否在左子树
while (current.value != key) {
parent = current;
if (current.value > key) {
isLeftChild = true;
current = current.left;
} else {
isLeftChild = false;
current = current.right;
}
if (current == null) {
return current;
}
}
// 如果删除节点左节点为空 , 右节点也为空
if (current.left == null && current.right == null) {
if (current == root) {
root = null;
}
// 在左子树
if (isLeftChild == true) {
parent.left = null;
} else {
parent.right = null;
}
}
// 如果删除节点只有一个子节点 右节点 或者 左节点
else if (current.right == null) {
if (current == root) {
root = current.left;
} else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = current.left;
} else {
parent.right = current.left;
}
}
else if (current.left == null) {
if (current == root) {
root = current.right;
} else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = current.right;
} else {
parent.right = current.right;
}
}
// 如果删除节点左右子节点都不为空
else if (current.left != null && current.right != null) {
// 找到删除节点的后继者
TreeNode successor = getDeleteSuccessor(current);
if (current == root) {
root = successor;
} else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = successor;
} else {
parent.right = successor;
}
successor.left = current.left;
}
return current;
}
/**
* 获取删除节点的后继者
* 删除节点的后继者是在其右节点树种最小的节点
*/
public TreeNode getDeleteSuccessor(TreeNode deleteNode) {
// 后继者
TreeNode successor = null;
TreeNode successorParent = null;
TreeNode current = deleteNode.right;
while (current != null) {
successorParent = successor;
successor = current;
current = current.left;
}
// 检查后继者(不可能有左节点树)是否有右节点树
// 如果它有右节点树,则替换后继者位置,加到后继者父亲节点的左节点.
if (successor != deleteNode.right) {
successorParent.left = successor.right;
successor.right = deleteNode.right;
}
return successor;
}
public void toString(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
toString(root.left);
System.out.print("value = " + root.value + " -> ");
toString(root.right);
}
}
}
/**
* 节点
*/
class TreeNode {
/**
* 节点值
*/
int value;
/**
* 左节点
*/
TreeNode left;
/**
* 右节点
*/
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
面试点一:理解 TreeNode 数据结构
节点数据结构,即节点、左节点和右节点。如图

面试点二:如何确定二叉树的最大深度或者最小深度
答案:简单的递归实现即可,代码如下:
int maxDeath(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return 0;
}
int left = maxDeath(node.left);
int right = maxDeath(node.right);
return Math.max(left,right) + 1;
}
int getMinDepth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return getMin(root);
}
int getMin(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if(root.left == null&&root.right == null){
return 1;
}
return Math.min(getMin(root.left),getMin(root.right)) + 1;
}
面试点三:如何确定二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
答案:简单的递归实现即可,代码如下:
boolean isBalanced(TreeNode node){
return maxDeath2(node)!=-1;
}
int maxDeath2(TreeNode node){
if(node == null){
return 0;
}
int left = maxDeath2(node.left);
int right = maxDeath2(node.right);
if(left==-1||right==-1||Math.abs(left-right)>1){
return -1;
}
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
前面面试点是 二叉树 的,后面面试点是 搜索二叉树 的。先运行搜搜二叉树代码:
public class BinarySearchTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree b = new BinarySearchTree();
b.insert(3);b.insert(8);b.insert(1);b.insert(4);b.insert(6);
b.insert(2);b.insert(10);b.insert(9);b.insert(20);b.insert(25);
// 打印二叉树
b.toString(b.root);
System.out.println();
// 是否存在节点值10
TreeNode node01 = b.search(10);
System.out.println("是否存在节点值为10 => " + node01.value);
// 是否存在节点值11
TreeNode node02 = b.search(11);
System.out.println("是否存在节点值为11 => " + node02);
// 删除节点8
TreeNode node03 = b.delete(8);
System.out.println("删除节点8 => " + node03.value);
b.toString(b.root);
}
}
结果如下:
value = 1 -> value = 2 -> value = 3 -> value = 4 -> value = 6 -> value = 8 -> value = 9 -> value = 10 -> value = 20 -> value = 25 ->
是否存在节点值为10 => 10
是否存在节点值为11 => null
删除节点8 => 8
value = 1 -> value = 2 -> value = 3 -> value = 4 -> value = 6 -> value = 9 -> value = 10 -> value = 20 -> value = 25 ->
面试点四:搜索二叉树如何实现插入
插入,还是比较容易理解的。就按照要求,插入到指定的位置。如果插入到叉搜索树的中间节点,那么会引起节点的动态变化。如图插入的逻辑:
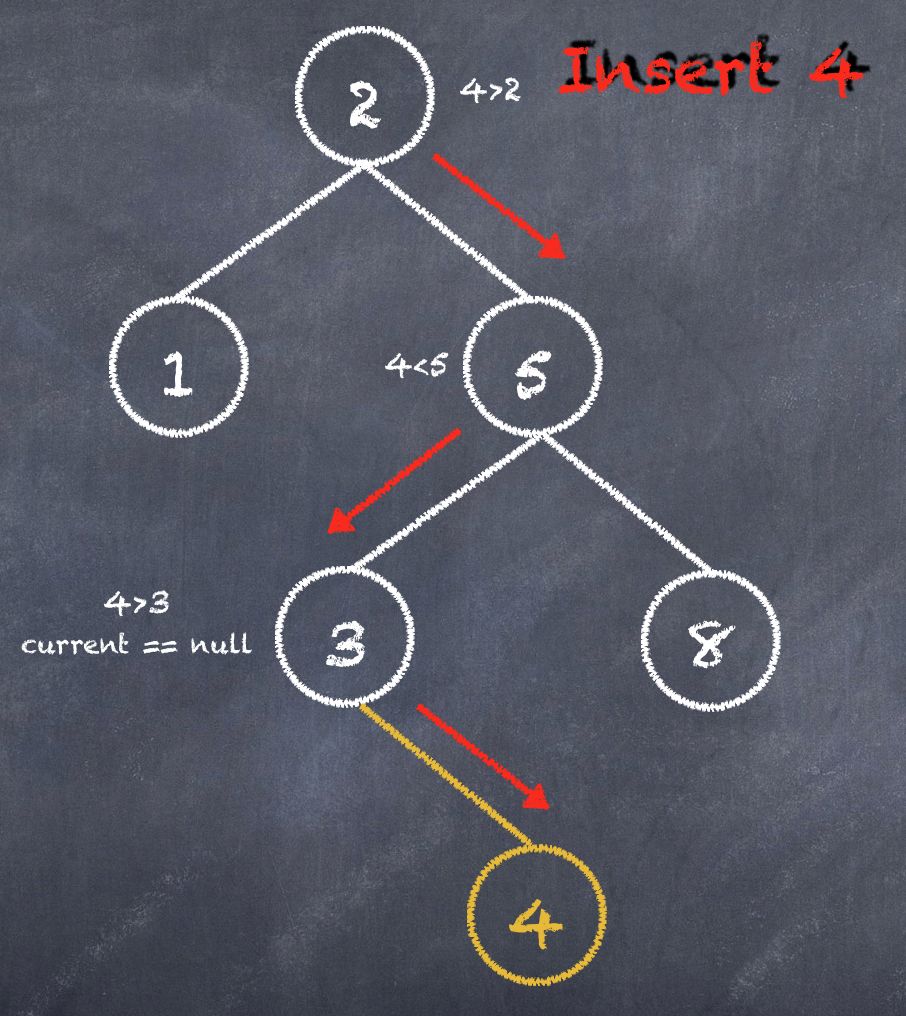
值为 2 的节点开始判断
如果为空,则插入该节点
循环下面节点:
节点当前值大于,继续循环左节点
节点当前值小于,继续循环右节点
面试点五:搜索二叉树如何实现查找
算法复杂度 : O(lgN)。如图搜索及查找逻辑:
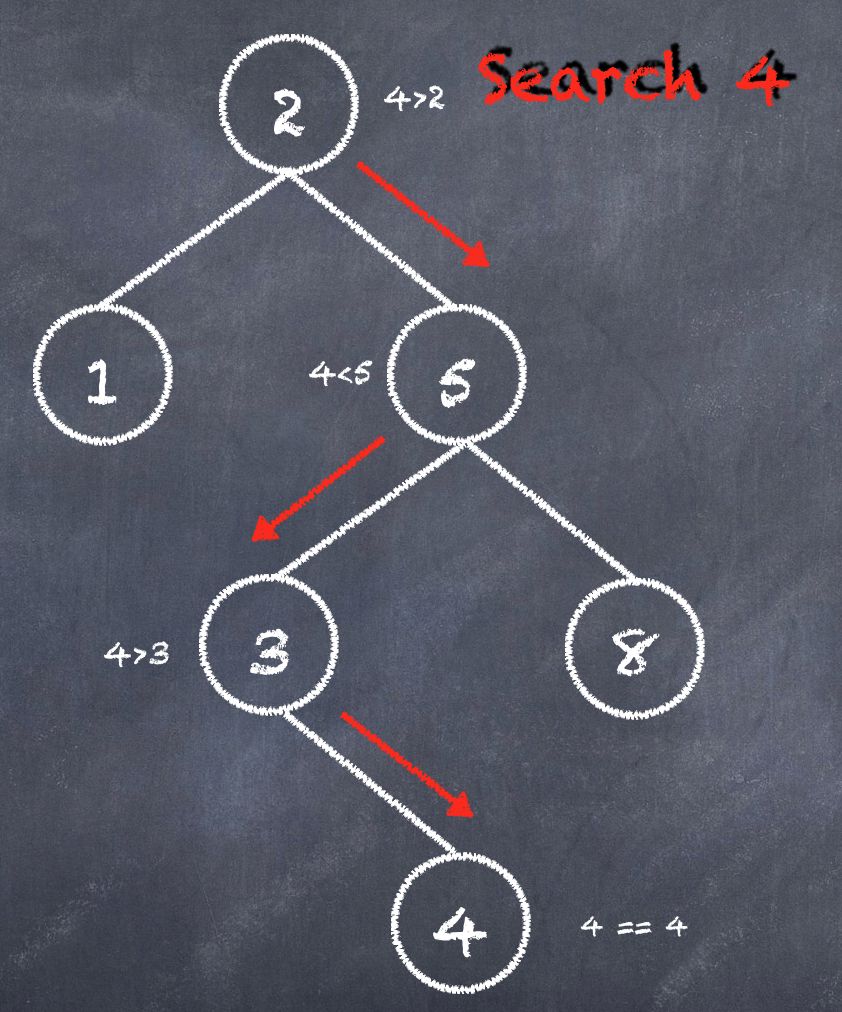
值为 2 的节点开始判断
节点当前值大于,继续循环左节点
节点当前值小于,继续循环右节点
如果值相等,搜索到对应的值,并返回
如果循环完毕没有,则返回未找到
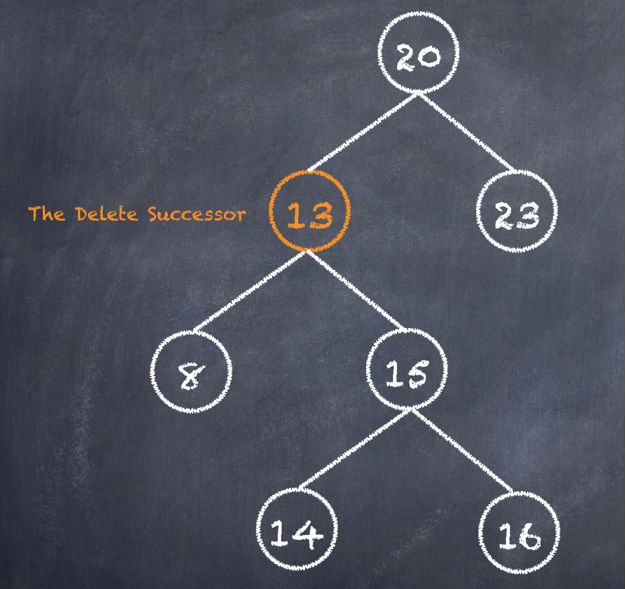
面试点五:搜索二叉树如何实现删除
比较复杂了。相比新增、搜搜,删除需要将树重置。逻辑为:删除的节点后,其替代的节点为,其右节点树中值最小对应的节点。如图:

结果为:
三、小结
就像码出高效面试的程序媛偶尔吃一碗“老坛酸菜牛肉面”一样的味道,品味一个算法,比如 BST 的时候,总是那种说不出的味道。
面试必备小结:
树,二叉树的概念
BST 算法
最后安利一下小灰创建的免费知识星球,
每天都有许多有趣的抢答活动和各种奖品,
关键是不要钱!欢迎大家扫码加入:
以上是关于neo4j-高效的原因(节点关系属性存储)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章