如何看go term之间的关系
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何看go term之间的关系相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
want to go traveling on a long-term bac想长期出差吗?
packing trip but can
包装行程
重点词汇
want to要; 应该
traveling同行的; 活动的; 移动的; 带球走步,走步违例
long-term长期的; 长远
bac用绳子拖的平底渡船,酒桶
packing包装,打包; 包装材料; 填料; 压紧(pack的ing形式); 装满
trip旅游,出行; 摔倒,绊倒; 绊; 错误,过失; 旅行; 绊倒,绊; 轻快地走,跳; 使犯错误
希望对你有帮助 参考技术A Gene Ontology可分为分子功能(Molecular Function),生物过程(biological process)和细胞组成(cellular component)三个部分。
蛋白质或者基因可以通过ID对应或者序列注释的方法找到与之对应的GO号,而GO号可对于到Term,即功能类别或者细胞定位。
功能富集分析: 功能富集需要有一个参考数据集,通过该项分析可以找出在统计上显著富集的GO Term。
该功能或者定位有可能与研究的目前有关。
GO功能分类是在某一功能层次上统计蛋白或者基因的数目或组成,往往是在GO的第二层次。
此外也有研究都挑选一些Term,而后统计直接对应到该Term的基因或蛋白数。
结果一般以柱状图或者饼图表示。本回答被提问者采纳
Go 要如何才能解释的清!和 Json 之间的种种映射关系! 「含解决方案 & 代码实现,建议收藏!」
Go 解析未知类型 Json 数据 解决方案
在 Goland 开发过程中,经常会遇到解析 Json 串,把 Json 数据映射为 Go 结构体对象的场景。
Go 和 Json 两者之间存在着种种联系,要如何才能解析之间的映射关系呢!
其实很简单,总体可分为两种类型:固定数据结构 & 非固定数据结构。具体解析方案,下面进行讲解:
反解已知结构 - 固定数据结构
已知一个 Json 串,在 Go 环境中需要解析出来,如下串:
{
"layerId": 3457670478284488705,
"partitions": 1000,
"hashAlgorithm": "xxHash",
"target": "uid",
"groups": [
{
"name": "4221-g0",
"config": {},
"partitions": [],
"whiteList": [],
"blackList": [],
"masks": [],
"buckets": "UAAAAQCAAhBIAAgAAUIAYCAABAAAAEVAACABggAAAgAGAhQggQBAAAAAAAAARAgAACAACAQBgAAAAAgABEEFCgAACIAAAAAAAYhBBAAQwAAAAAEIIgIHAEEBiBQEQAAAAICQAACAEAASAAACBAUEAAEAQIAIYAEAQAAAQAI=",
"bucketBits": null
}
],
"allConfigNames": [
"ad_user_portrayal_verify_metric_item"
],
"userTraffic": true
}
可以看出这个 Json 串的结构,是固定结构,可以构造这样一结构体,进行映射,如下:
type Experiment struct {
LayerId int64 `json:"layerId"`
Partitions int64 `json:"partitions"`
HashAlgorithm string `json:"hashAlgorithm"`
Target string `json:"target"`
Groups []*Group
AllConfigNames []string `json:"allConfigNames"`
UserTraffic bool `json:"userTraffic"`
}
type Group struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Config map[string]interface{} `json:"config"`
Partitions []string `json:"partitions"`
WhiteList []string `json:"whiteList"`
BlackList []string `json:"blackList"`
Masks []string `json:"masks"`
Buckets string `json:"buckets"`
BucketBits string `json:"bucketBits"`
BucketBit []bool `json:"bucketByte"`
WhiteMap map[int64]bool `json:"whiteMap"`
BlackMap map[int64]bool `json:"blackMap"`
}
最后进行 Unmarshal 即可,如下:
var response *Experiment
jsonr.Unmarshal(str, &response)
可如果是这样的串呢?
{
"native_ad_gap": "6",
"non_progressive": "{\\n\\"enable\\": \\"false\\"\\n}",
"comment_fold": "false",
"wb_ad_fe_idx_darwin_grpc": "{\\n \\"enable_grpc\\":false\\n}",
"sfst_game_test": "{}",
"wb_ad_fe_test_abagent_uid_config": "{\\"test_abagent_icon\\": false}",
"wb_ad_dmp_tag_interest_beauty_lightGBM": "{\\n \\"replace_rules\\": [\\n {\\n \\"tag_name_en\\": \\"CATEGORY_INTEREST_V3\\",\\n \\"replace_type\\": 1001,\\n \\"target_tag_value\\": \\"116\\"\\n }\\n ]\\n}",
"lingdong": "true",
"ad_fake_1": "false",
"wb_ad_dmp_tag_interest_game_lightGBM_0721": "{\\n \\"replace_rules\\": [\\n {\\n \\"tag_name_en\\": \\"CATEGORY_INTEREST_V3\\",\\n \\"replace_type\\": 1001,\\n \\"target_tag_value\\": \\"102\\"\\n }\\n ]\\n}",
"vertical_video": "false",
"rpm_cand": "0",
"truncation_blacklist": "{\\n \\"Enable\\": false,\\n \\"TruncationSize\\": \\"2KB\\",\\n \\"ShieldTime\\": \\"24h\\"\\n}",
"feedback": "0",
"deepfilter_strategy": "{\\"cvr_minthres\\":0,\\"cvr_maxthres\\":1.0,\\"deepcvr_minthres\\":0}",
"main_cardlist": "false",
"ad_fake_gzip": "false",
"native_title": "true",
"merge_uve_idx_trace_log": "{\\n \\"enable\\":false\\n}",
"wax_service_name_list": "null",
"wb_ad_dmp_tag_score_110_abtest_0622": "{\\n\\"replace_rules\\": [\\n{\\n\\"tag_name_en\\": \\"CATEGORY_INTEREST_V3\\",\\n\\"replace_type\\": 1001,\\n\\"target_tag_value\\": 105\\n}\\n]\\n}",
"new_position_s": "false",
"fake_10": “0"
}
大概一看,就是 k - v 款的,就是 map ,可进一步,k 是 string 类型,v 的类型怎么搞呢?bool、array、int…都有….
反解未知结构 - 非固定数据结构
不用慌,我们可以用 Interface 来进行解析,设置 map[string]interface{} 类型去映射。
Interface 是一个空接口, Go 中所有的结构体都默认实现 Interface 。它在映射的时候,有一套自动的映射逻辑,如下:
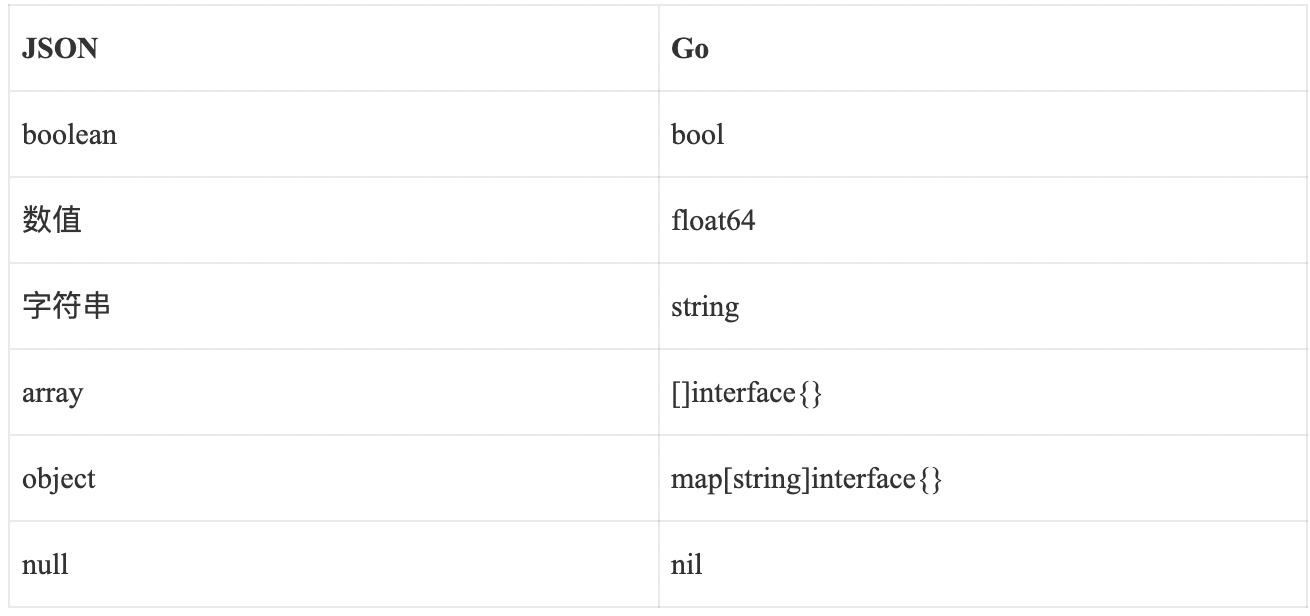
在进行解析的时候,会默认类型进行映射,实现如下:
tmp := new(interface{})
jsoniter.Unmarshal([]byte(n), &tmp)
Unmarshal
我们仔细观察 Unmarshal 方法也能发现,其参数类型就是 Interface ,如下:
// Unmarshal adapts to json/encoding Unmarshal API
//
// Unmarshal parses the JSON-encoded data and stores the result in the value pointed to by v.
// Refer to https://godoc.org/encoding/json#Unmarshal for more information
func Unmarshal(data []byte, v interface{}) error {
return ConfigDefault.Unmarshal(data, v)
}
其中主逻辑函数如下:
// ReadVal copy the underlying JSON into go interface, same as json.Unmarshal
func (iter *Iterator) ReadVal(obj interface{}) {
depth := iter.depth
cacheKey := reflect2.RTypeOf(obj)
decoder := iter.cfg.getDecoderFromCache(cacheKey)
if decoder == nil {
typ := reflect2.TypeOf(obj)
if typ == nil || typ.Kind() != reflect.Ptr {
iter.ReportError("ReadVal", "can only unmarshal into pointer")
return
}
decoder = iter.cfg.DecoderOf(typ)
}
ptr := reflect2.PtrOf(obj)
if ptr == nil {
iter.ReportError("ReadVal", "can not read into nil pointer")
return
}
decoder.Decode(ptr, iter)
if iter.depth != depth {
iter.ReportError("ReadVal", "unexpected mismatched nesting")
return
}
}
Q&A
1、为什么用 Interface 就可以解析出来呢?
见 文中 粘贴源码函数,具体源码解读「类似汇编中的词义解析,一层层的反射」 可见后续文章
附录
简单的背后,往往值的深思!
以上是关于如何看go term之间的关系的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Go 要如何才能解释的清!和 Json 之间的种种映射关系! 「含解决方案 & 代码实现,建议收藏!」
Go 要如何才能解释的清!和 Json 之间的种种映射关系! 「含解决方案 & 代码实现,建议收藏!」