使用xshell+xmanager+pycharm搭建pytorch远程调试开发环境
Posted justinzhang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用xshell+xmanager+pycharm搭建pytorch远程调试开发环境相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 相关软件版本
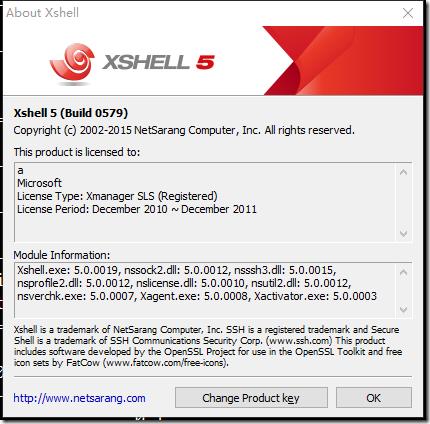
xshell:
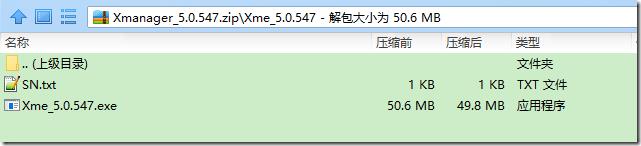
xmanager:
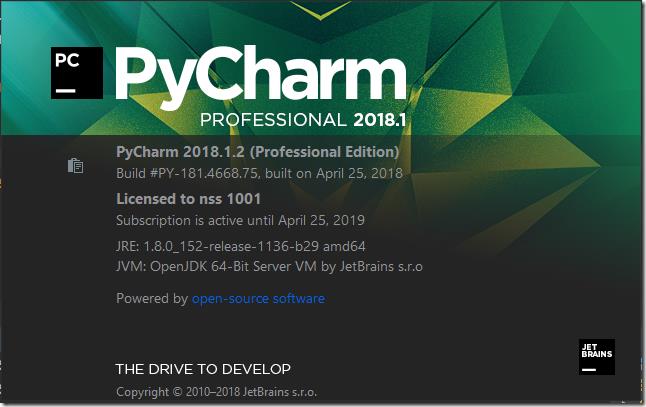
pycharm:
pycharm破解服务器:https://jetlicense.nss.im/
2. 将相应的软件安装(pojie好)
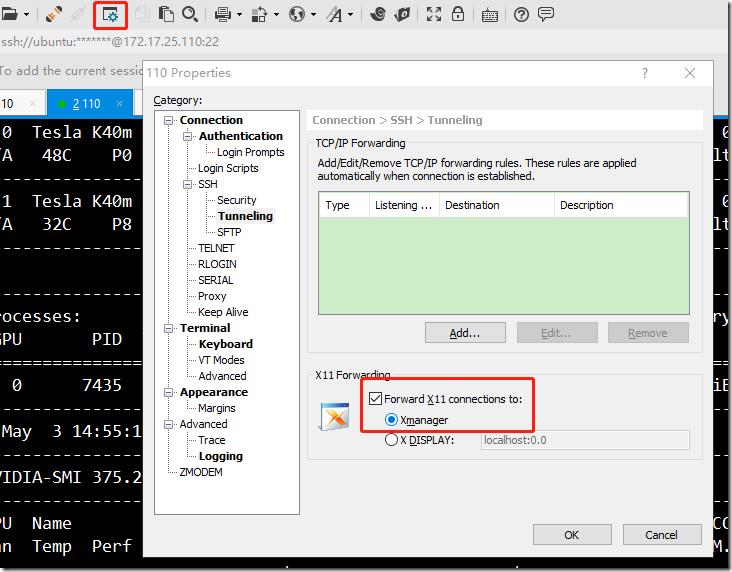
a> 启动xmanager passive,这个是用来接受linux转发过来的x11的:
b> 设置xshell,使用ssh隧道将x11转发到windows机器上
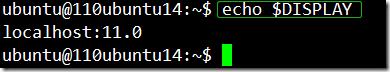
在被设置的服务器上执行echo $DISPLAY,如下:
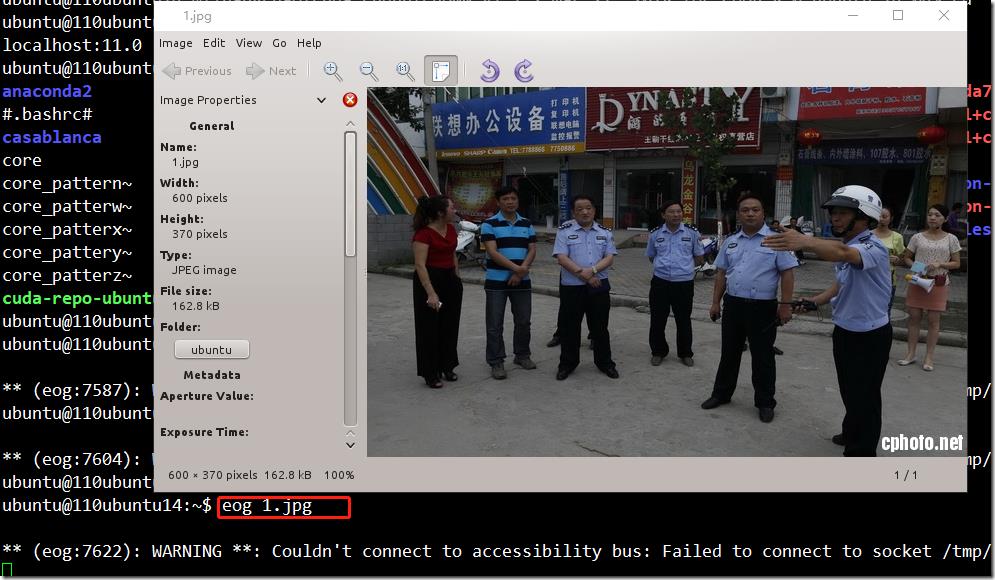
c> 通过设置后,就可以将linux中的图形界面转发到windows机器上了,例如,在linux命令行中使用eog 1.jpg可以将1.jpg显示在window系统中:
可以看到linux已经通过ssh隧道将x11成功的转发到window,而背后支撑x11的服务器正是xmanager提供的:
3. 配置pycharm,使其能够通过ssh协议远程的使用linux上的python环境,并且进行远程调试、代码同步:
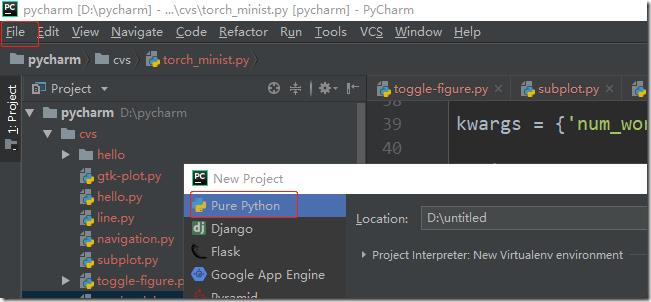
a> 新建一个pythonproject,选择好项目的位置:
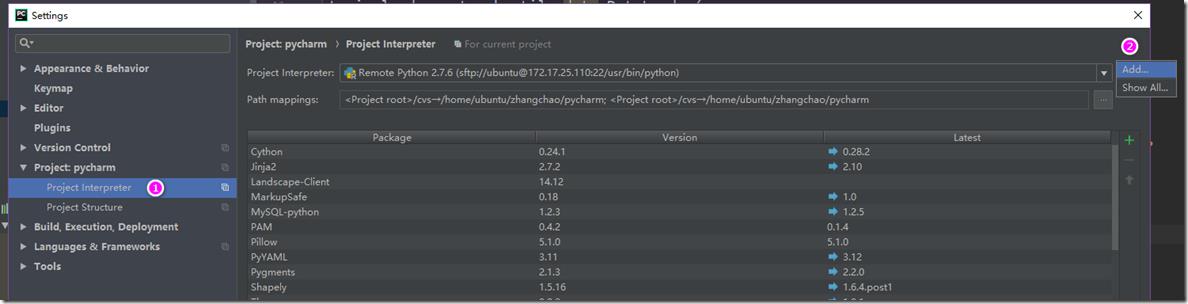
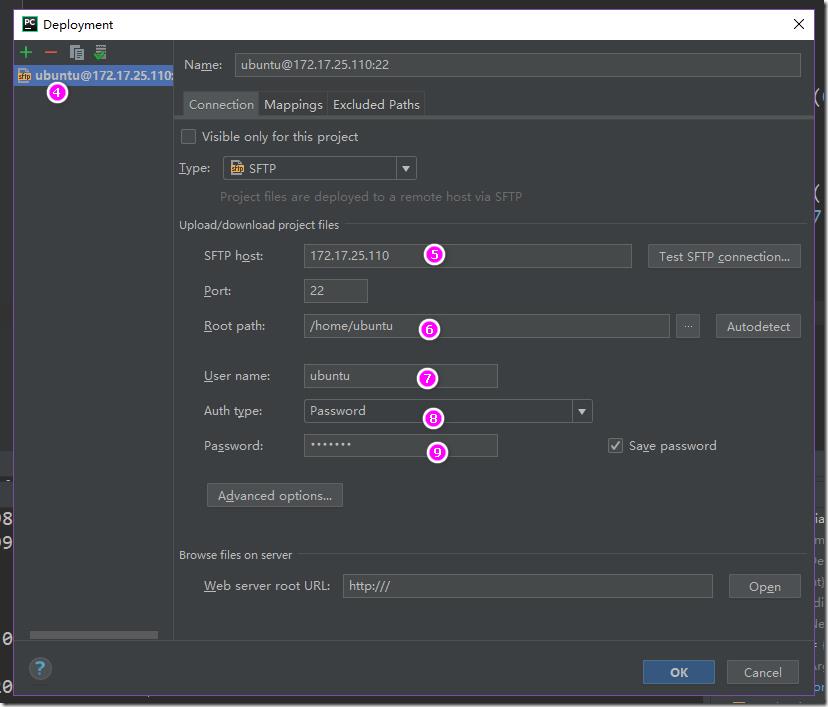
b> 在File->settings中,设置远程linux服务器:
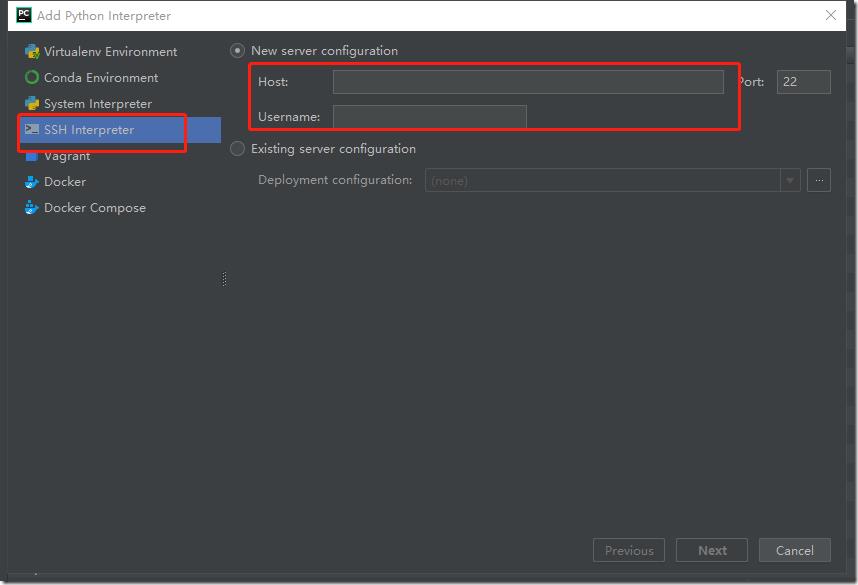
选择Add..,然后填写好远程服务器的ip地址以及用户名和密码:
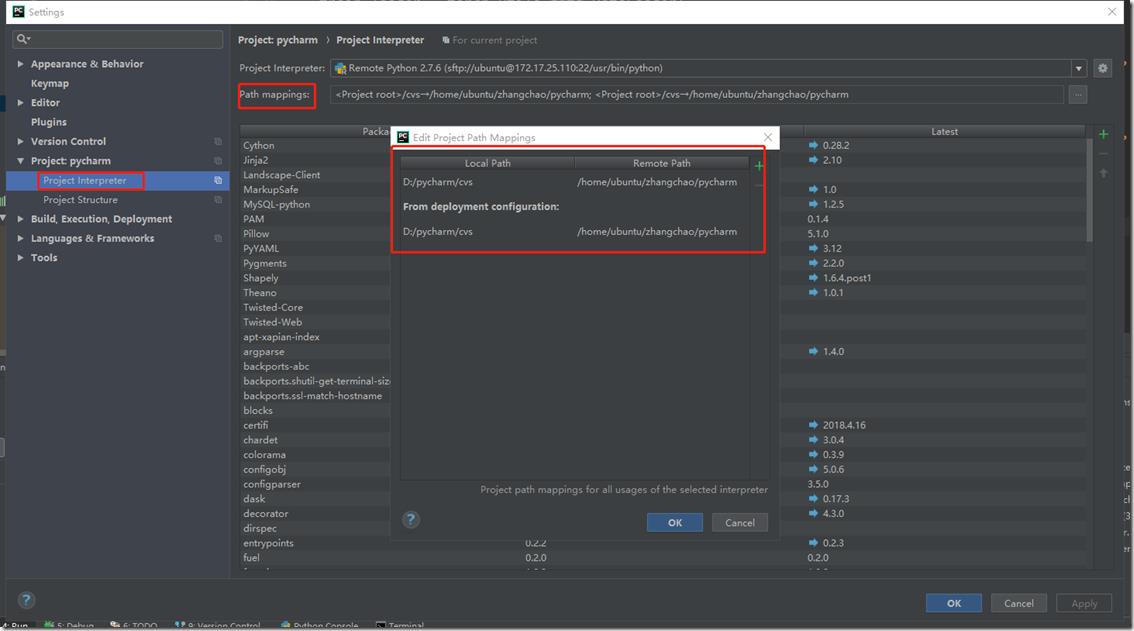
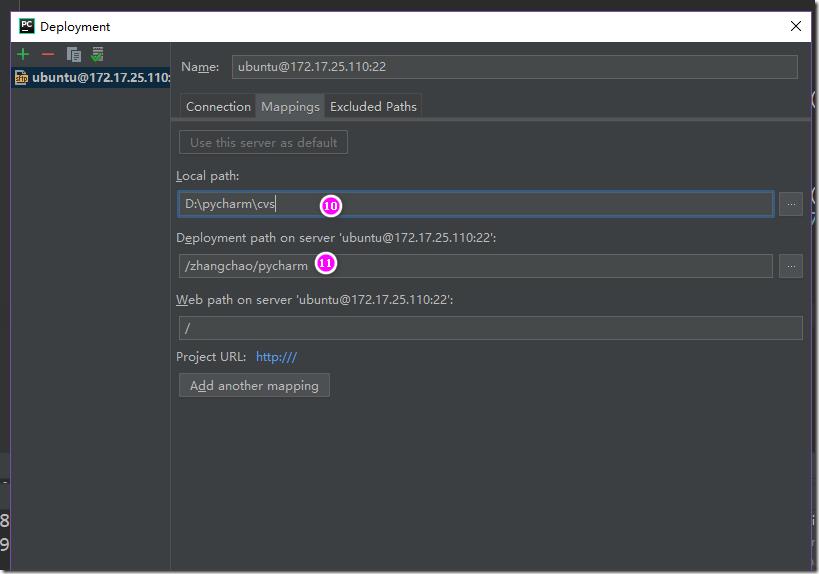
在path mapping中设置windows目录和linux目录的映射关系,这样方便进行windows和linux之间进行代码同步:
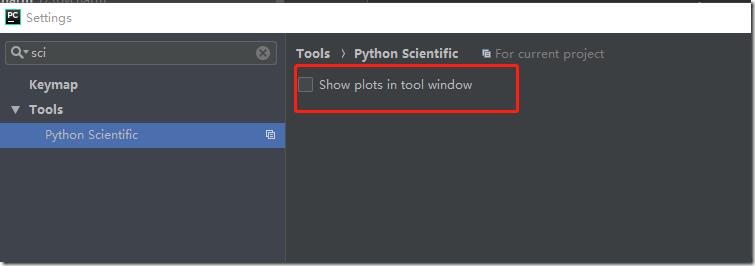
在settings=>Tools=>python Scientific页面中,将show plots in tool window关闭,这样是为了使pycharm能够正常的将linux的中的x11协议转发到xmanger中:
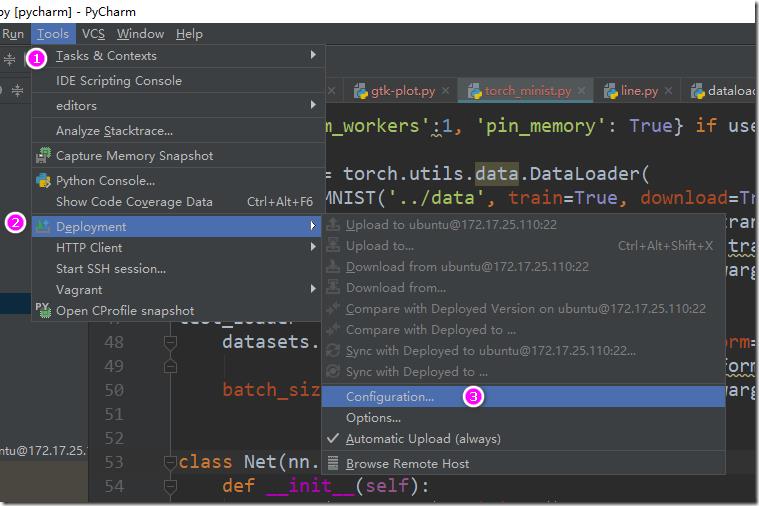
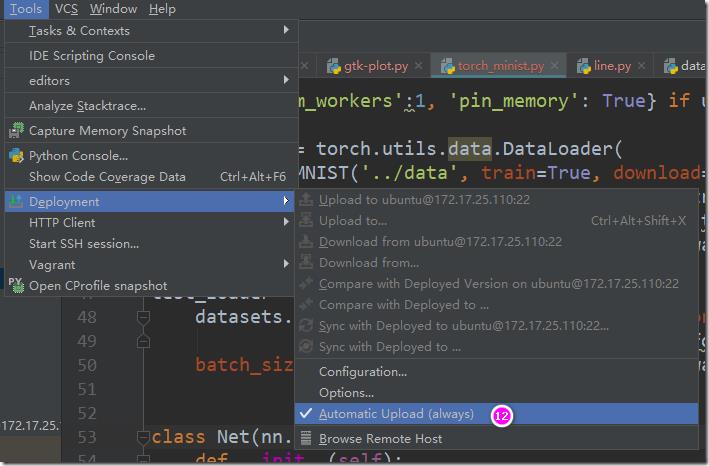
c> 设置源代码同步:
到此,已经设置好了pycharm、xshell、xmanager相互交互的环境。下面在pycharm中写一段测试代码,这个测试代码通过pycharm提交到linux机器上,然后linux通过x11协议转发到windows上,在windows上显示一张图片,line.py代码如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np plt.plot(range(5), linestyle=\'--\', linewidth=3, color=\'purple\') plt.ylabel(\'Numbers from 1-5\') plt.xlabel(\'Love yohanna\') plt.show() #plt.clf() #plt.close() N = 1000 x = np.random.randn(N) y = np.random.randn(N) z = np.random.randn(N) plt.scatter(z, y, color=\'yellow\', linewidths=0.05) plt.scatter(x, y, color=\'green\', linewidths=0.2) plt.axis([-4, 4, -4, 4]) plt.show()
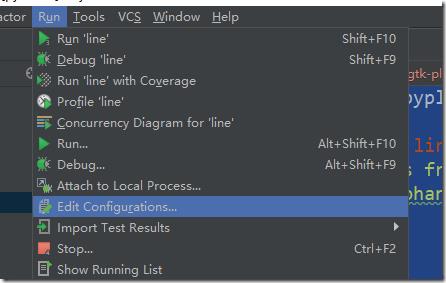
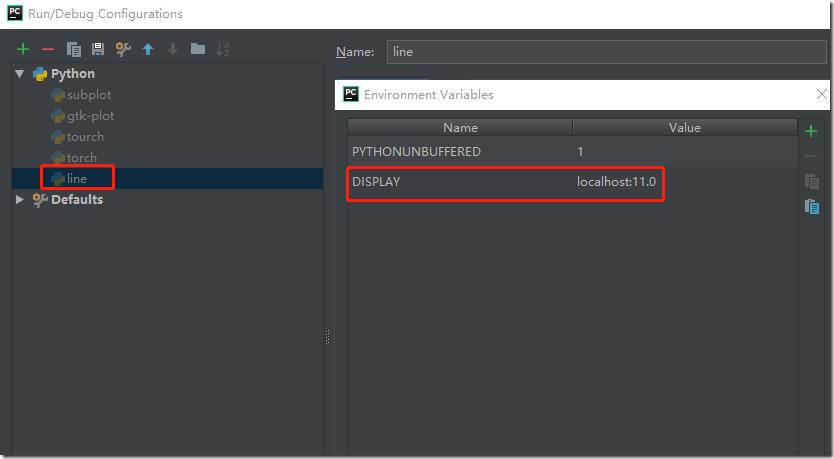
设置pycharm运行line.py的环境变量:
在环境变量列表中加入DISPLAY变量,值为localhost:11.0(具体值,在设置好xshell x11转发规则后,通过linux shell中的echo $DISPLAY获得)
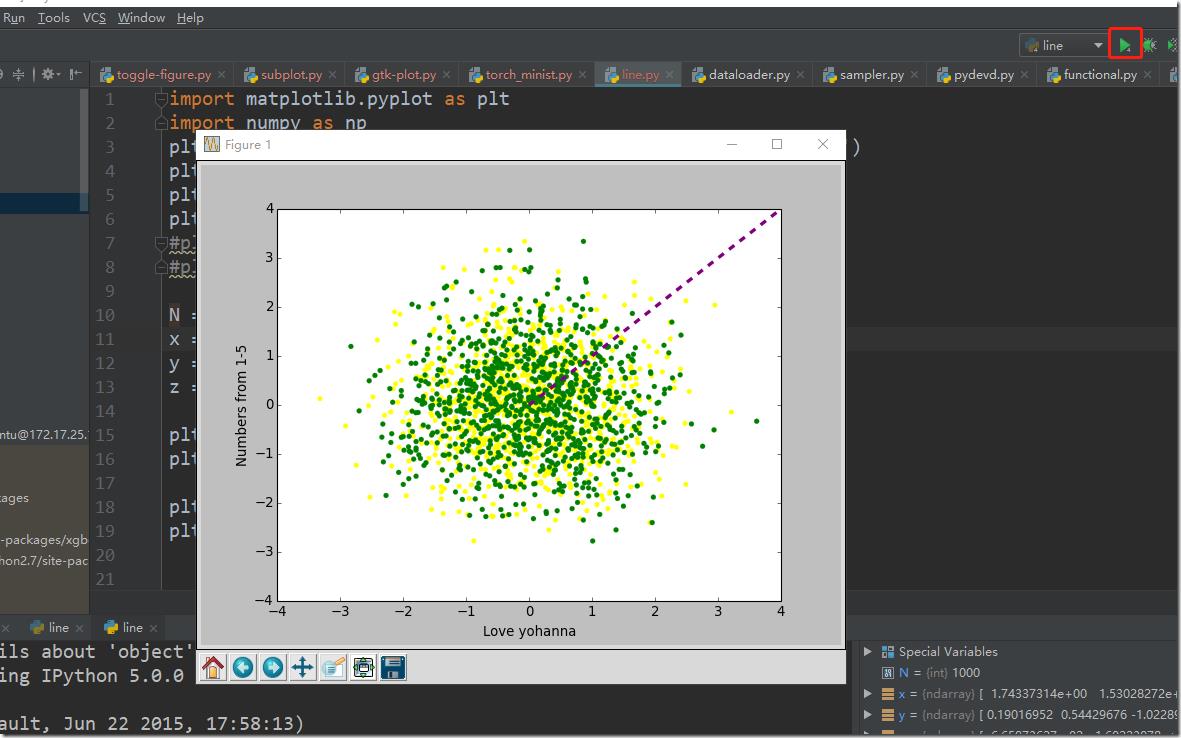
点击运行按钮,可以看到在windows中显示了画图的效果:
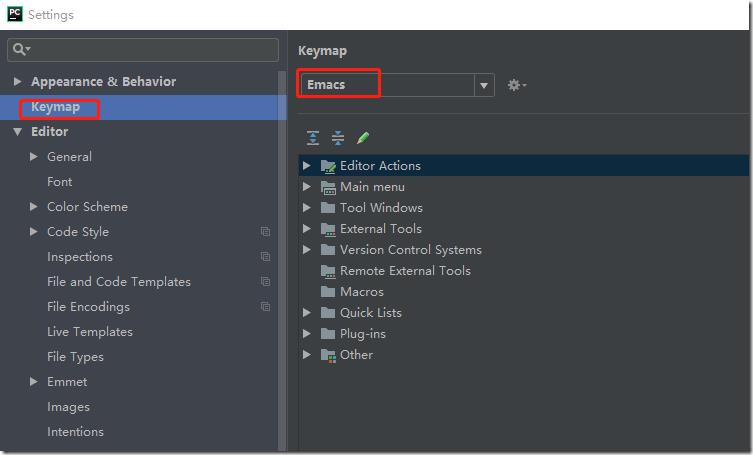
4. 设置pycharm使用emacs方式编辑:File->settings->keyMap->Emacs
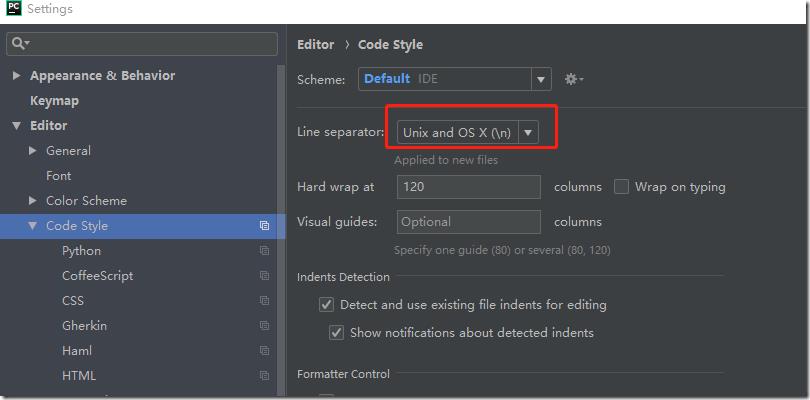
设置文件结尾为unix格式:
5. 搭建pytorch+cuda的环境:
a> 安装pytorch使用,sudo pip install pytorch
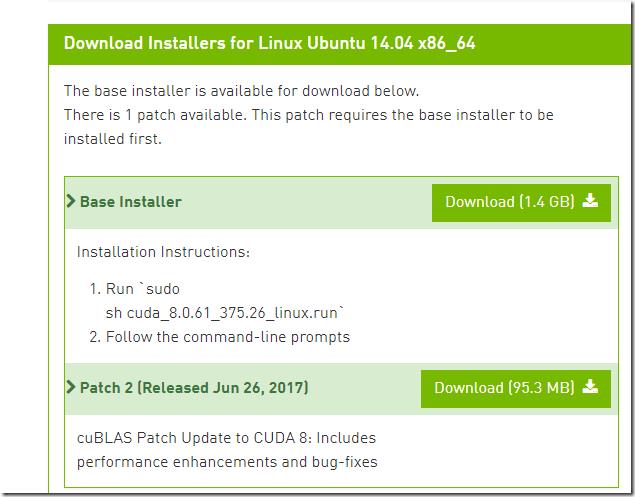
b> 下载和安装cuda:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
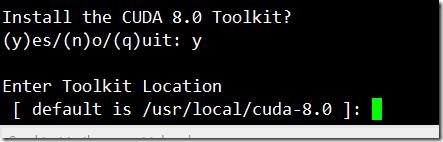
cuda的默认安装位置:/usr/local/cuda-8.0
在安装的过程中如果遇到X dispaly的问题,
It appears that an X server is running. Please exit X before installation. If you\'re sure that X is not running, but are getting this error, please delete any X lock files in /tmp.
那么可以尝试使用/etc/init.d/lightdm stop
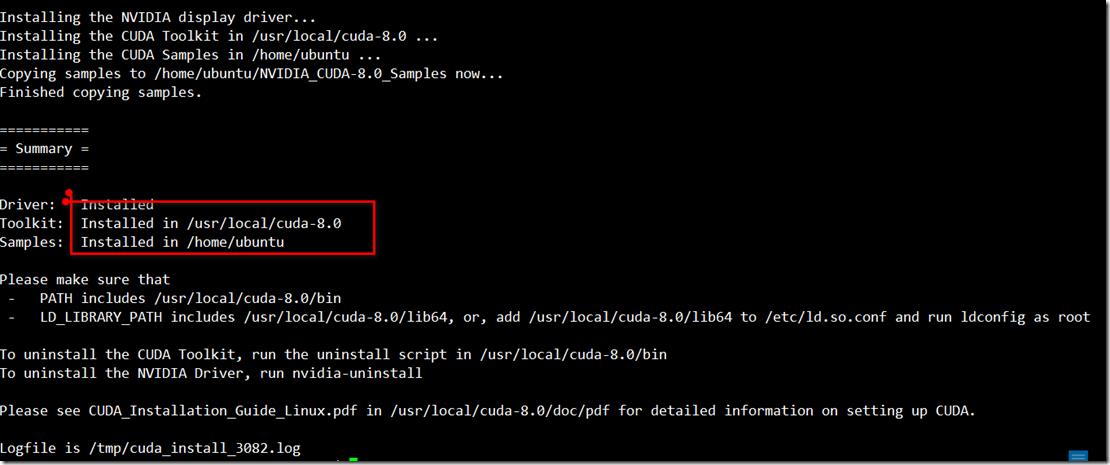
然后在尝试安装,安装成功后日志如下:
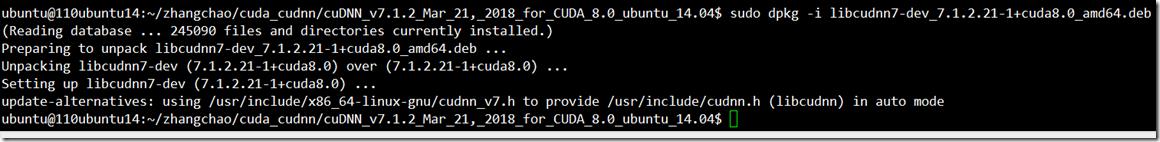
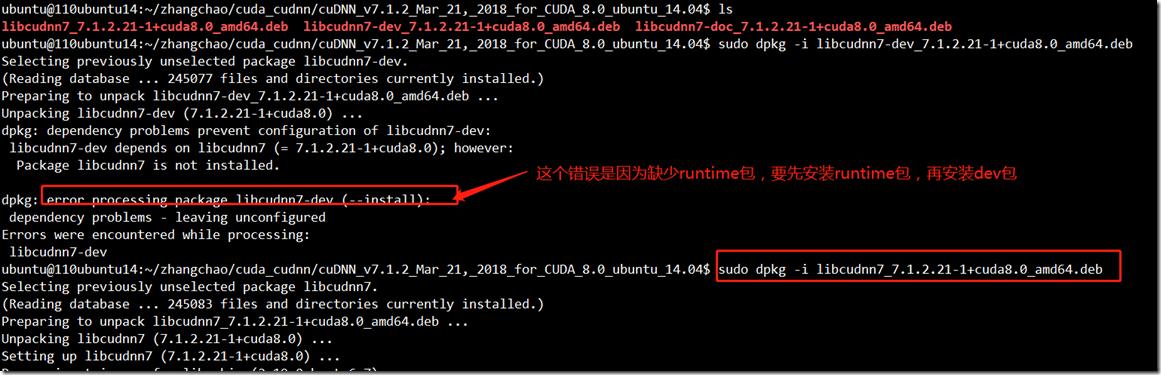
c> 下载和安装cudnn:
https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-download
libcudnn的安装,先安装runtime,然后再安装dev包。
d>
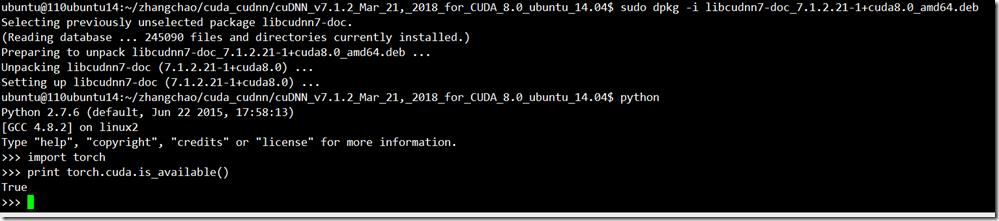
将cuda和cudnn安装成功后,发现torch已经支持cuda了:torch.cuda.is_available() --> true
6. 现在pytorch+cuda的环境已经搭建好,可以跑一个简单的minst例子了,首先将代码下载好torch_minist.py:
# This file will train minist dataset , using pytorch from __future__ import print_function import argparse import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms import pdb # Training settings parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=\'PyTorch MNIST Example\') parser.add_argument(\'--batch-size\', type=int, default=64, metavar=\'N\', help=\'input batch size for training(default: 64)\') parser.add_argument(\'--test-batch-size\', type=int, default=1000, metavar=\'N\', help=\'input batch size for testing (default: 1000)\') parser.add_argument(\'--epochs\', type=int, default=10, metavar=\'N\', help=\'number of epochs to train (default: 10)\') parser.add_argument(\'--lr\', type=float, default=0.01, metavar=\'LR\', help=\'learning rate(default: 0.01)\') parser.add_argument(\'--momentum\', type=float, default=0.5, metavar=\'M\', help=\'SGD momentum (default: 0.5)\') parser.add_argument(\'--no-cuda\', action=\'store_true\', default=False, help=\'disables CUDA training\') parser.add_argument(\'--seed\', type=int, default=1, metavar=\'S\', help=\'random seed (default: 1)\') parser.add_argument(\'--log-interval\', type=int, default=10, metavar=\'N\', help=\'how many batches to wait before logging training status\') args = parser.parse_args() use_cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available() torch.manual_seed(args.seed) device = torch.device(\'cuda\' if use_cuda else \'cpu\') kwargs = {\'num_workers\':1, \'pin_memory\': True} if use_cuda else {} train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( datasets.MNIST(\'../data\', train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,),(0.3081,))])), batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs) test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( datasets.MNIST(\'../data\', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,),(0.3081,))])), batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs) class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5) self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10) def forward(self, x): x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2)) x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2)) x = x.view(-1, 320) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training) x = self.fc2(x) return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1) model = Net().to(device) optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr, momentum=args.momentum) def train(epoch): #pdb.set_trace() model.train() for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader): data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) optimizer.zero_grad() output = model(data) loss = F.nll_loss(output, target) loss.backward() optimizer.step() if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0: print(\'Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\\tLoss: {:.6f}\'.format( epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset), 100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item() )) def test(): model.eval() test_loss = 0 correct = 0 with torch.no_grad(): for data, target in test_loader: data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) output = model(data) test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, size_average=False).item() # sum up batch loss pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1] # get the index of the max log-probability correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item() test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset) print(\'\\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\\n\'.format( test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset), 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset) )) for epoch in range(1, args.epochs+1): train(epoch) test()
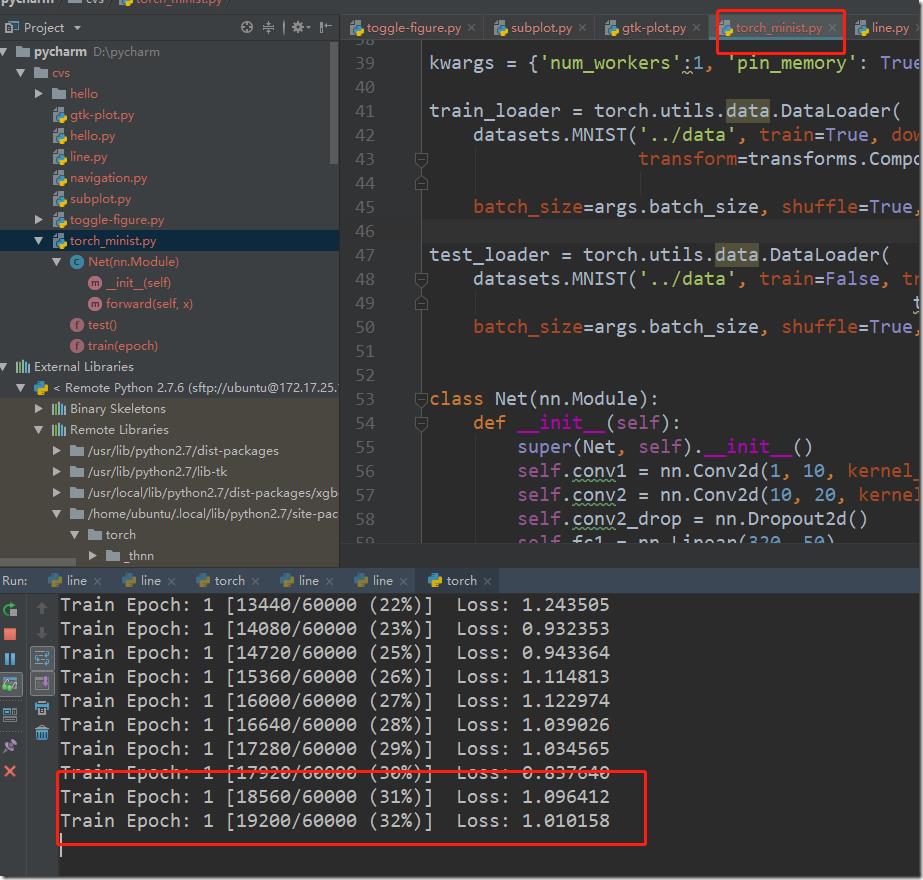
然后设置torch_minst.py运行时的环境变量DISPLAY=localhost:11.0,点击run按钮可以看到运行效果:
图终于截完。
以上是关于使用xshell+xmanager+pycharm搭建pytorch远程调试开发环境的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Xmanager Enterprise 4 xshell的使用