Nginx的基本配置
Posted xuweiweiwoaini
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Nginx的基本配置相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 nginx的配置文件总览
#设置用户 #user nobody; #设置工作进程数 worker_processes 1; #设置错误日志 #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #设置pid #pid logs/nginx.pid; #设置最大连接数 events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘ # ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘ # ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the php scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \\.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \\.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root # concurs with nginx‘s one # #location ~ /\\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { #设置pid #pid logs/nginx.pid; #设置最大连接数 events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘ #设置最大连接数 events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘ # ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘ # ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #设置gzip #gzip on; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #设置编码 #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \\.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \\.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root # concurs with nginx‘s one # #location ~ /\\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }
2 Nginx的虚拟主机配置一
2.1 配置虚拟主机的步骤
- 通常情况下,为了使每个服务器可以供更多的用户使用,可以将一根服务器分为很多虚拟的子服务器,每个子服务器都是相互独立的。
- 这些服务器是根据虚拟化技术分出来的,这样,一台服务器就可以虚拟成很多台子服务器。我们把子服务器叫虚拟主机。
- 我们搭建好Nginx服务器之后,此时只有一台Nginx服务器,这个时候如果我们对这台服务器进行虚拟主机配置,将可以将一台Nginx服务器分割为多台独立的子服务器。
- Nginx中配置虚拟主机的步骤主要有两个
- 1)配置IP地址
- 2)绑定IP地址与虚拟主机
2.2 IP地址的配置
ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.9 netmask 255.255.255.0
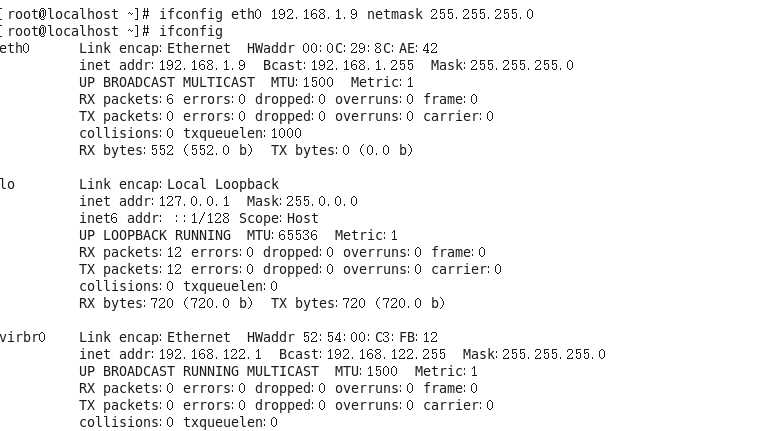
ifconfig eth0:1 192.168.1.7 broadcast 192.168.88.255 netmask 255.255.255.0
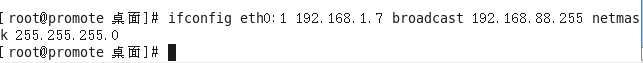
ifconfig eth0:1 192.168.1.6 broadcast 192.168.88.255 netmask 255.255.255.0
2.2 Nginx的虚拟主机的配置
- 在配置好IP地址之后,我们需要将对应的IP地址与对应的虚拟主机建立联系,这就是虚拟主机的配置。
- 编辑ngnix.conf文件
#user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘ # ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘ # ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \\.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \\.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root # concurs with nginx‘s one # #location ~ /\\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # server { listen 192.168.1.7:80; listen 192.168.1.7; access_log logs/server1.access.log combined; location / { root html/server1; index index.html index.htm; } } # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }
- 在/usr/local/nginx/html下新建server1目录,并在server1目录下新建Index.html文件
cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
touch index.html
- 使用vim编辑器,在index.html中写入一些文字信息
- 启动Nginx,然后在浏览器输入192.168.1.7你就看到你想要的啦
3 Nginx的日志文件配置
3.1 Nginx日志文件格式的配置
- Nginx服务器在运行的时候,会有各种操作,这些关键的操作信息会记录到文件中,这些文件叫做日志文件。日志文件的记录是有格式的,我们可以按系统默认的格式去记录,也可以按照我们自定义的格式去记录。我们可以使用log_format指令来设置Nginx服务器的日志文件的记录格式。
- 示例:
- 默认是关闭的,在nginx.conf文件中
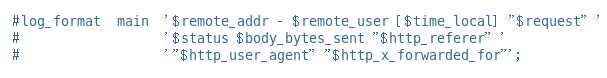
-
- 先将其开启,去掉注释
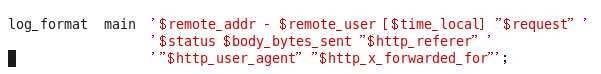
-
- 详细讲解上面红色字符的意思
- remote_addr :远程地址,就是用户访问你的IP地址
- remote_user:远程访问的用户
- request:用户访问的资源地址
- status:HTTP的状态码
- body_bytes_sent: 服务器返回客户端的数据
- http_referer:表示请求该资源来源于那个地址,即用户从哪里来
- http_user_agent:客户端浏览器的信息
- http_x_forwarded_for:客户端的地址
- 详细讲解上面红色字符的意思
3.2 Nginx日志文件存储路径的配置
- 日志文件在记录的时候,需要存储在磁盘上,存储的路径是可以配置的,我们通常通过access_log指令来配置nginx的日志文件的存储路径。
- 默认情况下是关闭的

- 开启就很简单啦,让注释去死吧,就是下面这个样子

- 如果你不想让nginx记录日志文件,可以使用如下的指令,但是你觉得实际开发中谁这样干?
access_log off;
3.3 Nginx日志文件的切割
- 为了让Nginx的日志文件存储的更为合理、有序,我们需要将日志文件进行分开存储,比如我们按照时间来分开,今天的日志文件存储到一个文件中,明天的日志文件存储到另外一个文件中等等。这个时候,我们就需要用到日志文件的切割。
- 手动切割
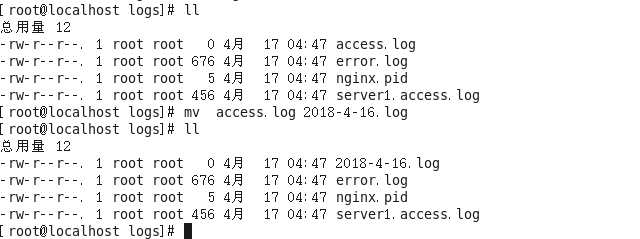
- ①将原来的access.log通过mv重新命名
-
-
- ②通过USR1这个控制信号来实现
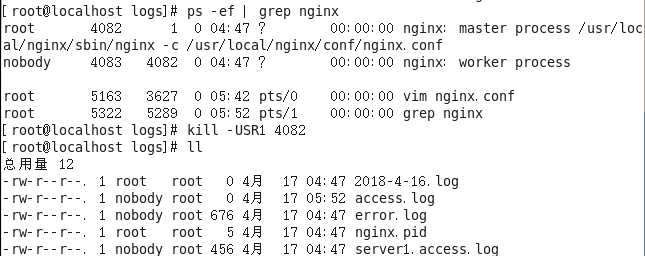
- 自动切割
- ①新建一个批处理文件,在logs文件夹下
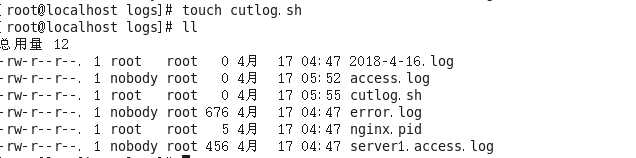
-
- ②使用vim编辑器,去编辑此批处理文件
D=$(date +%Y%m%d)
mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log ${D}.log
kill -USR1 $(cat /usr/local/nginx/nginx.pid)
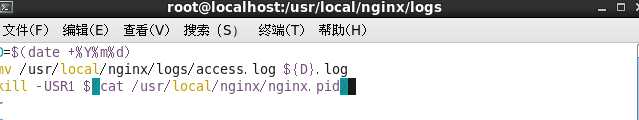
-
- ③使用crontab -e
- 输入crontab -e ,然后空格
- 输入如下的指令
- ③使用crontab -e
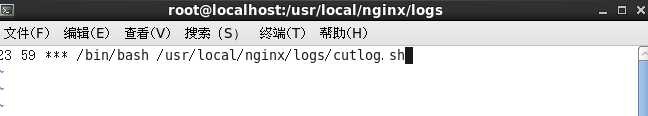
-
-
- 退出保存,然后y
-
4 Nginx的缓存配置和其他配置
4.1 Nginx的缓存配置
- 当我们在浏览器中浏览某个网页的时候,我们会把该网页上的一些信息存储到本地,当我们第二次浏览该网页的时候,这个网页上的某些信息就可以从本地加载,这样速度就会快很多。
- 存储到本地的这些信息我们就称为缓存。但是,缓存并不是越多越好,缓存文件过大,会影响我们正常的上网,所以,缓存需要定期清理。
- 在location /{}下面配置
location ~ .*\\.(jpg|png)$ { expires 2d; }

4.2 压缩功能
- 通过gzip压缩技术,可以使原来的网页的内容大小压缩成原来的30%,这样,用户在访问网页的时候,由于传输的内容比原来的内容小很多,所以访问的速度会快很多。Nginx服务器支持gzip压缩技术,但是,使需要配置的。
- 默认情况下,gzip是关闭的
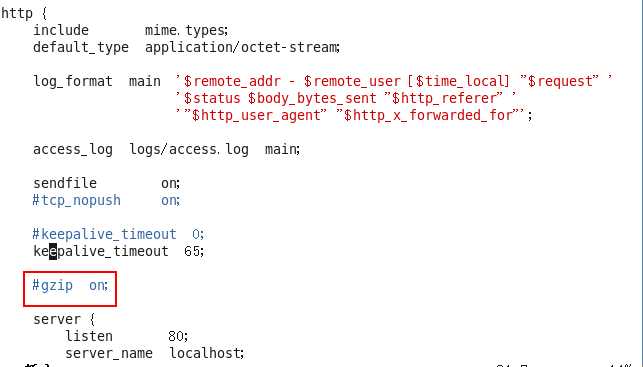
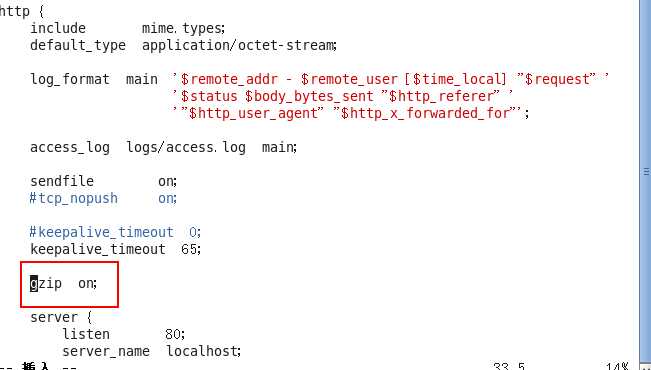
- 开启,很简单哦,直接干死注释,让注释去死
- 当然,一些文件很小,就不需要进行压缩了,比如最低的临界值就是1k
gzip_min_length 1k;

- 当然,这些文件都放在缓存中,所以需要配置缓存了
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
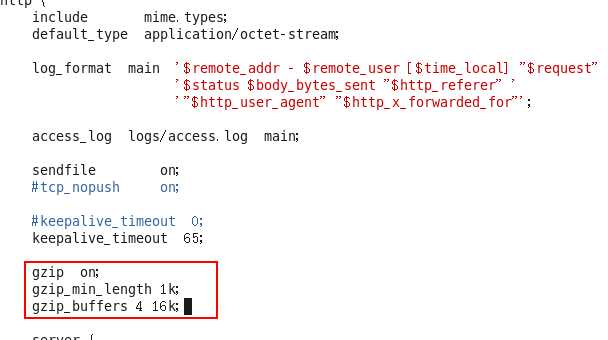
- 设置gzip的HTTP协议的版本是1.1
gzip_http_version 1.1;
- 开启判断客户端是否支持gzip。
gzip_vary on;
以上是关于Nginx的基本配置的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章