oracle查询表用for in loop循环出来更新
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了oracle查询表用for in loop循环出来更新相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
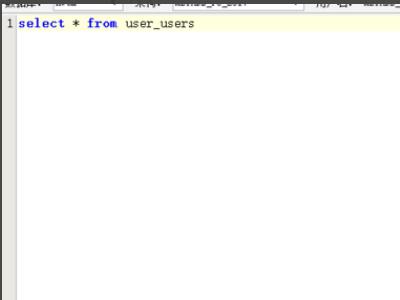
参考技术A1、查看当前用户使用的表空间情况,使用命令select * from user_users即可,其中username标识用户名,default_tablespace表示默认的表空间。
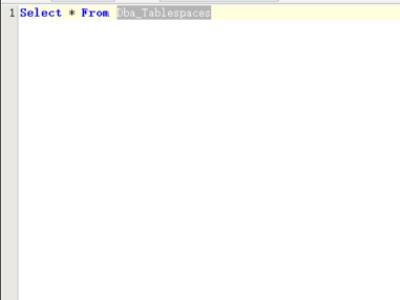
2、查看oracle下面所有的表空间,使用命令select * from Dba_Tablespaces即可,呈现的信息包括表空间名称以及表空间的大小。
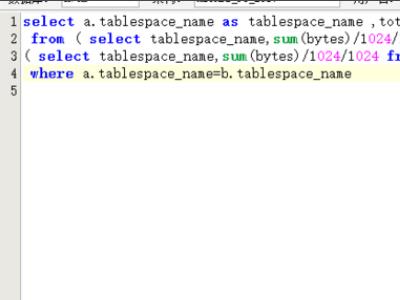
3、表空间是非常重要的资源,如果我们想查看表空间的使用情况,比如表空间利用率等指标,首先我们查询的用户必须有dba权限,使用如下的命令查询即可。
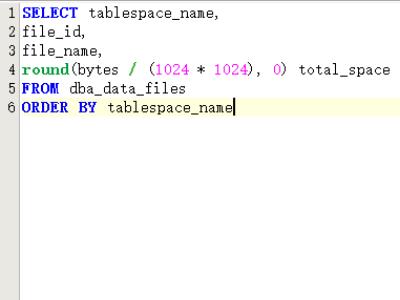
4、查看表空间物理文件的名称、位置及大小信息,表空间文件通常以dbf的后缀方式存储。
5、有些查询表空间的语句需要执行用户需要高的权限,使用命令select * from user_role_privs即可。
6、在查询到表空间的信息之后,我们有时需要删除没用的表空间,使用命令drop tablespace xxx including contents and datafiles;即可。
oracle in和exists的区别
参考技术A in 和 exists区别in 是把外表和内表作hash join,而exists是对外表作loop,每次loop再对内表进行查询。
一直以来认为exists比in效率高的说法是不准确的。
如果查询的两个表大小相当,那么用in和exists差别不大。
如果两个表中一个较小,一个是大表,则子查询表大的用exists,子查询表小的用in:
例如:表A(小表),表B(大表)
1:
select * from A where cc in (select cc from B)
效率低,用到了A表上cc列的索引;
select * from A where exists(select cc from B where cc=A.cc)
效率高,用到了B表上cc列的索引。
相反的
2:
select * from B where cc in (select cc from A)
效率高,用到了B表上cc列的索引;
select * from B where exists(select cc from A where cc=B.cc)
效率低,用到了A表上cc列的索引。
带in的关联子查询是多余的,因为in子句和子查询中相关的操作的功能是一样的。如:
select staff_name from staff_member where staff_id in
(select staff_id from staff_func where staff_member.staff_id=staff_func.staff_id);
为非关联子查询指定exists子句是不适当的,因为这样会产生笛卡乘积。如:
select staff_name from staff_member where staff_id
exists (select staff_id from staff_func);
not in 和not exists
如果查询语句使用了not in 那么内外表都进行全表扫描,没有用到索引;
而not extsts 的子查询依然能用到表上的索引。
所以无论哪个表大,用not exists都比not in要快。
尽量不要使用not in子句。使用minus 子句都比not in 子句快,虽然使用minus子句要进行两次查询:
select staff_name from staff_member where staff_id in (select staff_id from staff_member minus select staff_id from staff_func where func_id like '81%');
in 与 "=" 的区别
select name from student where name in ('zhang','wang','li','zhao');
与
select name from student where name='zhang' or name='li' or name='wang' or name='zhao'
的结果是相同的。
以上是关于oracle查询表用for in loop循环出来更新的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章