实用数据结构:怎样把两个单链表A B(本身都是有序表)合并为C并且C为有序表
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了实用数据结构:怎样把两个单链表A B(本身都是有序表)合并为C并且C为有序表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
怎样把两个单链表A B(本身都是有序表)合并为C并且C为有序表
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
/* 单链表节点 */
struct node
int value;
node* next;
;
/* 给单链表添加节点 */
void insertNode(node* head, int value)
node* p = head->next;
if ( p == NULL )
p = new node;
p->value = value;
p->next = NULL;
head->next = p;
return;
while ( p->next != NULL )
p = p->next;
node* tmp = new node;
tmp->value = value;
tmp->next = NULL;
p->next = tmp;
/* 遍历输出链表节点 */
void print(node* head)
node* p = head->next;
while ( p != NULL )
cout << p->value << " ";
p = p->next;
cout << endl;
/* 利用一般的方法进行合并,形成整体递增有序 */
node* formalMerge(node* headA, node* headB)
node* head = new node;
head->next = NULL;
node* p = headA->next;
node* q = headB->next;
if ( p == NULL )
return headB;
if ( q == NULL )
return headA;
while ( (p != NULL) && (q != NULL) )
if ( p->value == q->value )
insertNode(head, p->value);
insertNode(head, q->value);
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
else if ( p->value < q->value )
insertNode(head, p->value);
p = p->next;
else if ( p->value > q->value )
insertNode(head, q->value);
q = q->next;
while ( p != NULL )
insertNode(head, p->value);
p = p->next;
while ( q != NULL )
insertNode(head, q->value);
q = q->next;
return head;
参考技术A 用两个指针,分别指向A和B;比如A和B两指针所指数据的大小(假设为升序排列)。
1。找出其中较小的,加入到C,对较小的那个指针前移一位
2。如果两指针不都不空,继续第1步;若一个指针为空,将不空的链表加到其后即可
数据结构(C语言版)严蔚敏->单链表的定义及合并两个有序单链表
头文件
linklist.h
#ifndef LINKLIST_H_INCLUDED
#define LINKLIST_H_INCLUDED
typedef struct LNode
int data;
struct LNode *next;
LNode,*LinkList;
void InitList_L(LinkList &L);
// 初始化单链表
bool ListEmpty_L(LinkList L);
// 判断单链表是否为空
int ListLength_L(LinkList L);
// 获取单链表的长度
void ClearList_L(LinkList &L);
// 清空链表
bool GetElem_L(LinkList L, int pos, int &e);
// 获取pos位置上的数据元素,用e返回
bool ListInsert_L(LinkList &L, int pos, int e);
//在L中的第pos个位置插入元素e
bool ListDelete_L(LinkList &L, int pos, int &e);
//删除L的第pos个元素,并由e返回
int LocateElem_L(LinkList L, int e);
//在L中查找与e满足关系compare()的元素,返回其在表中的位置
#endif // LINKLIST_H_INCLUDED
linklist.cpp
#include "linklist.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
// 初始化带头结点的单链表
void InitList_L(LinkList &L)
L =(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(!L)
exit(-1);
L->next = NULL;
bool ListEmpty_L(LinkList L)
return L->next == NULL;
int ListLength_L(LinkList L)
LNode *p = L->next;
int n = 0;
while(p!=NULL)
p = p->next;
n++;
return n;
// 获取单链表的长度
void ClearList_L(LinkList &L)
LNode *r = L->next,*p;
L->next = NULL;
while(r!=NULL)
p = r;
r = r->next;
free(p);
bool GetElem_L(LinkList L, int pos, int &e)
LNode *p = L->next;
int i = 1;
while(p&&i<pos)
p = p->next;
++i;
if(!p||i>pos)
return false;
e = p->data;
return true;
bool ListInsert_L(LinkList &L, int pos, int e)
LNode *p,*s;
p = L;
int i = 0;
while(p&&i<pos-1)
p = p->next;
++i;
if(!p||pos<1)
return false;
s =(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = e;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
return true;
bool ListDelete_L(LinkList &L, int pos, int &e)
LNode *p,*q;
p = L;
int i = 0;
while(p->next&&i<pos-1)
p = p->next;
++i;
if(pos<1||!(p->next))
return false;
// p为删除节点的前驱节点
q = p->next;
// q为删除的节点
p->next = q->next;
e = q->data;
free(q);
return true;
int LocateElem_L(LinkList L, int e)
LNode *p;
p = L;
int i = 1;
while(p->next)
p = p->next;
++i;
if(p->data == e)
return i;
return -1;
主文件
main.cpp 【注】不是main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "linklist.h"
void PrintList_L(LinkList L)
LNode *p = L->next;
while(p)
printf("%d->",p->data);
p = p->next;
// 合并有序链表函数
void MerageLinkList(LinkList La,LinkList Lb,LinkList &Lc)
LNode *pa,*pb,*pc;
int a,b;
pa = La->next;
pb = Lb->next;
Lc = pc = La;
while(pa&&pb)
a = pa->data;
b = pb->data;
if(a>b)
pc->next = pb;
pc = pb;
pb = pb->next;
else
pc->next = pa;
pc = pa;
pa = pa->next;
pc->next=pa?pa:pb;
int main()
LinkList la,lb,lc;
int a[] = 1,3,5,7,9,b[]=2,4,6,8,10,12;
InitList_L(la);
InitList_L(lb);
InitList_L(lc);
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
ListInsert_L(la,i,a[i-1]);
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
ListInsert_L(lb,i,b[i-1]);
printf("la:");
PrintList_L(la);
printf("NULL\\n");
printf("lb:");
PrintList_L(lb);
printf("NULL\\n");
MerageLinkList(la,lb,lc);
printf("lc:");
PrintList_L(lc);
printf("NULL\\n");
return 0;
运行结果如下:
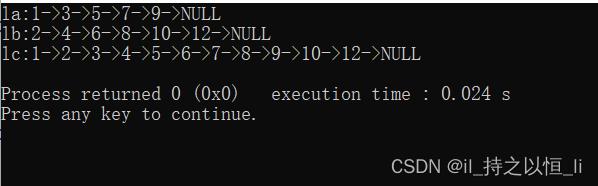
以上是关于实用数据结构:怎样把两个单链表A B(本身都是有序表)合并为C并且C为有序表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章