java编程,txt文件整合到一起。
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java编程,txt文件整合到一起。相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这样,我有一个文件夹,叫做data
这个文件夹里呢,有不定量的文件夹,比如data1,data2。。。
每个文件夹里,有不定量的txt文件,1.txt,2.txt。。。
也就是说,文件夹 - 文件夹 - txt文件,这样一个层次关系。
我想把所有的txt文件内容,都整合到一个txt文件all.txt里面。
请大侠们帮忙写个简单的程序,谢谢啦~~~
C:\data\StudentInfo.txt
--------
C:\data\新建 文本文档.txt
(该文件内容为空!)
C:\data\新建文件夹\1.txt
第一行
第二行
代码如下:
import java.io.*;
public class AllTxt
public static void main(String[] args)
moveAllContentToOne("C:\\data\\", "C:\\all.txt");
public static void moveAllContentToOne(String path, String target)
File source = new File(path);
File targetfile = new File(target);
moveAllContentToOne(source, targetfile);
public static void moveAllContentToOne(File source, File targetfile)
File[] files = null;
if(source.isDirectory())
files = source.listFiles();
for(int i=0; i<files.length; i++)
moveAllContentToOne(files[i], targetfile);
return;
if(source.getName().matches(".*\\.[tT][xX][tT]$"))
System.out.println(source.getName());
try
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(source));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(targetfile, true));
bw.write(source.getPath());
bw.newLine();
String str = br.readLine();
if(str == null)
bw.write("(该文件内容为空!)");
bw.newLine();
else
while(str != null)
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
str = br.readLine();
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
参考技术A java调用DOS命令。 参考技术B 我可以给你一个思路吧,
就是用IO流迭代地读取每个文件夹下的内容是文件就把它里面的内容读出来,加到你是合成的文件里面,是文件夹就进行迭代。最后就完成了。
不过你是注意,好像有的流是写文件的时候会把原来 的内容给删了,有的不会,具体我不记得了。你自己还是去网上找下吧。 参考技术C package com;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test
private String path = "E:\\workspace\\test\\src\\com\\all.txt";// all.txt路径
private String tempPath = "E:\\workspace\\test\\src\\com\\temp.txt";
private File finalFile = new File(path);
private File tempFile = new File(tempPath);// 临时文件,完成后请删除
public static void main(String[] args)
Test t = new Test();
File file = new File("E:\\workspace\\test\\src\\com\\");// 指定目录
t.writeAll(file);
// Runtime run = Runtime.getRuntime();
// String cmd = "del E:\\workspace\\test\\src\\com\\temp.txt";
// try
// Process p = run.exec(cmd);
// p.waitFor();
// catch (Exception e)
// e.printStackTrace();
//
public void writeAll(File file)
if (file.isDirectory())
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++)
writeAll(files[i]);
else if (file.isFile())
writeFile(file);
public void writeFile(File file)
FileReader fr;
BufferedReader br;
FileReader fr1;
BufferedReader br1;
FileWriter fw;
BufferedWriter bw;
String line;
try
fr = new FileReader(finalFile);
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
fw = new FileWriter(tempFile);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
line = br.readLine();
while (line != null)
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
line = br.readLine();
br.close();
bw.close();
fr = new FileReader(file);
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
fr1 = new FileReader(tempFile);
br1 = new BufferedReader(fr1);
fw = new FileWriter(finalFile);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
line = br1.readLine();
while (line != null)
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
line = br1.readLine();
bw.newLine();
bw.write(file.getName());
bw.newLine();
bw.newLine();
line = br.readLine();
while (line != null)
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
line = br.readLine();
tempFile.deleteOnExit();
br.close();
bw.close();
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
java面试第四弹(算法和编程)思路
1、编写一个程序,将a.txt文件中的单词与b.txt文件中的单词交替合并到c.txt文件中,a.txt文件中的单词用回车符分隔,b.txt文件中用回车或空格进行分隔.
创建两个FileManager分别是a.txt和b.txt 参数需要创建一个char数组来进行回车符分割和空格分割
FileManager a = new FileManager("a.txt",new char[]{\'\\n\'});
FileManager b = new FileManager("b.txt",new char[]{\'\\n\',\' \'});
创建一个FileWriter写入流 为c.txt
FileWriter c = new FileWriter("c.txt");
声明两个String来存储a.txt和b.txt里面的 单词
String aWord = null; String bWord = null;
使用while循环遍历
while((aWord = a.nextWord()) !=null ){
c.write(aWord + "\\n");
bWord = b.nextWord();
if(bWord != null)
c.write(bWord + "\\n");
}
如果a.txt和b.txt中的单词不为空,写入到c.txt
while((bWord = b.nextWord()) != null){
c.write(bWord + "\\n");
}
c.close();
这里不明白为什么要写入两次。
然后关闭写入流
创建一个FileManager的类
public class FileManager(){
}
声明一个类型为string的单词数组
String[] words = null;
然后就懵逼了
int pos = 0;
public FileManager(String filename,char[] seperators) throws Exception{
File f = new File(filename);
FileReader reader = new FileReader(f);
char[] buf = new char[(int)f.length()];
int len = reader.read(buf);
String results = new String(buf,0,len);
String regex = null;
if(seperators.length >1 ){
regex = "" + seperators[0] + "|" + seperators[1];
}else{
regex = "" + seperators[0];
}
words = results.split(regex);
}
public String nextWord(){
if(pos == words.length)
return null;
return words[pos++];
}
}
2、编写一个程序,将d:\\java目录下的所有.java文件复制到d:\\jad目录下,并将原来文件的扩展名从.java改为.jad。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CopyFolderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 封装数据源和目的地
File file1 = new File("d:\\\\Java");
File file2 = new File("d:\\\\jad");
// 文件过滤器封装目录下String数组对象,匿名对象
String[] strArr = file1.list(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
// 判断条件文件和后缀
return new File(dir, name).isFile() && name.endsWith(".java");
}
});
// 遍历
for (String str : strArr) {
// 输入流,封装符合条件的数据源
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
new File(file1, str)));
// 输出流,改名并封装要装入的目的地
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(
new File(file2, str.replace(".java", ".jad"))));
// 遍历读写文件
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
}
整体思路:
得到某个目录下的所有的java文件集合-----》得到目录下的所有java文件合-----》只想得到.java的文件-----》遍历-----》输入流,封装符合条件的数据源-----》输出流,改名并封装要装入的地方-----》 遍历读写文件
3、编一个截取字符串的函数,输入为一个字符串和字节数,输出为按字节截取的字符串,要保证汉字不被截取半个,如“我ABC”,4,应该截取“我AB”,输入“我ABC汉DEF”,6,应该输出“我ABC”,而不是“我ABC+汉的半个”。
首先要了解中文字符有多种编码及各种编码的特征。
假设n为要截取的字节数。
// main方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ String str = "我a爱中华abc我爱传智def\'; //定义了两个字符串 String str = "我ABC汉"; int num = trimGBK(str.getBytes("GBK"),5); System.out.println(str.substring(0,num) ); }
// 测试类 public static int trimGBK(byte[] buf,int n){ int num = 0; boolean bChineseFirstHalf = false;
/**
输出输入的字符串格式化buf[]数组后前个5字符中不为中文的个数
程序中前七个字符应该为我a爱中华
默认bChineseFirstHalf为false,如果是汉字的话,buf[i]就会返回的是负数,所以当输入第一个字符“我”的时候,bChineseFirstHalf = true;
继续循环,输入a的时候,buf[1]>0,则进入else, bChineseFirstHalf = false,同时num++
*/
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
if(buf[i]<0 && !bChineseFirstHalf) {
bChineseFirstHalf = true;
} else {
num++; bChineseFirstHalf = false;
}
}
return num;
}
4、有一个字符串,其中包含中文字符、英文字符和数字字符,请统计和打印出各个字符的个数。
String s = "aaaabbc中国1512";
int zh = 0 ; //中文字数
int en = 0; //英文字数
int num = 0; //数字字数
for(int i = 0; i< s.length() ;i++){
char c = s.charAt(i); //下标
if((c >= \'a\' && c <= \'z\')||(c >= \'A\' && c <= \'Z\')){
en++;
}else if(c >= \'0\' && c <= \'9\'){
num++;
}else{
zh++;
}
}
System.out.println("中文个数" + zh);
System.out.println("英文个数" + en);
System.out.println("数字个数" + num);
}
}
5、说明生活中遇到的二叉树,用java实现二叉树
这是组合设计模式
假如我们有很多条数据需要保存起来,以后还需要从保存的数据中检索某条数据是否存在。假如我们使用数组,而碰巧要找的是99999,那么就需要从1依次往后取,然后进行比较。速度会特别慢平衡二叉树(构建平衡二叉树需要先排序,我们这里就不作考虑了)可以很好地解决这个问题,但二叉树的遍历(前序,中序,后序)效率要比数组低很多。原理如下图:
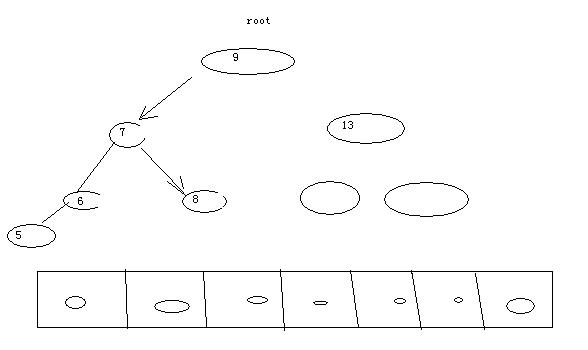
JAVA代码实现:
package tree;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 功能:把一个数组的值存入二叉树中,然后进行3种方式的遍历
*
* 参考资料0:数据结构(C语言版)严蔚敏
*
* 参考资料1:http://zhidao.baidu.com/question/81938912.html
*
* 参考资料2:http://cslibrary.stanford.edu/110/BinaryTrees.html#java
*
* @author ocaicai@yeah.net @date: 2011-5-17
*
*/
public class BinTreeTraverse2 {
private int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
private static List<Node> nodeList = null;
/**
* 内部类:节点
*
* @author ocaicai@yeah.net @date: 2011-5-17
*
*/
private static class Node {
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
int data;
Node(int newData) {
leftChild = null;
rightChild = null;
data = newData;
}
}
public void createBinTree() {
nodeList = new LinkedList<Node>();
// 将一个数组的值依次转换为Node节点
for (int nodeIndex = 0; nodeIndex < array.length; nodeIndex++) {
nodeList.add(new Node(array[nodeIndex]));
}
// 对前lastParentIndex-1个父节点按照父节点与孩子节点的数字关系建立二叉树
for (int parentIndex = 0; parentIndex < array.length / 2 - 1; parentIndex++) {
// 左孩子
nodeList.get(parentIndex).leftChild = nodeList
.get(parentIndex * 2 + 1);
// 右孩子
nodeList.get(parentIndex).rightChild = nodeList
.get(parentIndex * 2 + 2);
}
// 最后一个父节点:因为最后一个父节点可能没有右孩子,所以单独拿出来处理
int lastParentIndex = array.length / 2 - 1;
// 左孩子
nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).leftChild = nodeList
.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 1);
// 右孩子,如果数组的长度为奇数才建立右孩子
if (array.length % 2 == 1) {
nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).rightChild = nodeList
.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 2);
}
}
/**
* 先序遍历
*
* 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已
*
* @param node
* 遍历的节点
*/
public static void preOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
preOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
preOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*
* 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已
*
* @param node
* 遍历的节点
*/
public static void inOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
}
/**
* 后序遍历
*
* 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已
*
* @param node
* 遍历的节点
*/
public static void postOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
postOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
postOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinTreeTraverse2 binTree = new BinTreeTraverse2();
binTree.createBinTree();
// nodeList中第0个索引处的值即为根节点
Node root = nodeList.get(0);
System.out.println("先序遍历:");
preOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
inOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("后序遍历:");
postOrderTraverse(root);
}
因为理解能力有限直接用Iteye上的一个案例copy下来了。 注释还挺详细
6、从类似如下的文本文件中读取出所有的姓名,并打印出重复的姓名和重复的次数,并按重复次数排序:
1,张三,28
2,李四,35
3,张三,28
4,王五,35
5,张三,28
6,李四,35
7,赵六,28
8,田七,35
import java.io.BufferedReader;
2 import java.io.IOException;
3 import java.io.InputStream;
4 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
5 import java.util.Comparator;
6 import java.util.HashMap;
7 import java.util.Iterator;
8 import java.util.Map;
9 import java.util.TreeSet;
10
11
12 public class GetNameTest {
13
14 /**
15 * @param args
16 */
17 public static void main(String[] args) {
18 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
19 //InputStream ips = GetNameTest.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/huawei/interview/info.txt");
20 //用上一行注释的代码和下一行的代码都可以,因为info.txt与GetNameTest类在同一包下面,所以,可以用下面的相对路径形式
21
22 Map results = new HashMap();
23 InputStream ips = GetNameTest.class.getResourceAsStream("info.txt");
24 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ips));
25 String line = null;
26 try {
27 while((line=in.readLine())!=null)
28 {
29 dealLine(line,results);
30 }
31 sortResults(results);
32 } catch (IOException e) {
33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
34 e.printStackTrace();
35 }
36 }
37
38 static class User
39 {
40 public String name;
41 public Integer value;
42 public User(String name,Integer value)
43 {
44 this.name = name;
45 this.value = value;
46 }
47
48 @Override
49 public boolean equals(Object obj) {
50 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
51
52 //下面的代码没有执行,说明往treeset中增加数据时,不会使用到equals方法。
53 boolean result = super.equals(obj);
54 System.out.println(result);
55 return result;
56 }
57 }
58
59 private static void sortResults(Map results) {
60 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
61 TreeSet sortedResults = new TreeSet(
62 new Comparator(){
63 public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
64 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
65 User user1 = (User)o1;
66 User user2 = (User)o2;
67 /*如果compareTo返回结果0,则认为两个对象相等,新的对象不会增加到集合中去
68 * 所以,不能直接用下面的代码,否则,那些个数相同的其他姓名就打印不出来。
69 * */
70
71 //return user1.value-user2.value;
72 //return user1.value<user2.value?-1:user1.value==user2.value?0:1;
73 if(user1.value<user2.value)
74 {
75 return -1;
76 }else if(user1.value>user2.value)
77 {
78 return 1;
79 }else
80 {
81 return user1.name.compareTo(user2.name);
82 }
83 }
84
85 }
86 );
87 Iterator iterator = results.keySet().iterator();
88 while(iterator.hasNext())
89 {
90 String name = (String)iterator.next();
91 Integer value = (Integer)results.get(name);
92 if(value > 1)
93 {
94 sortedResults.add(new User(name,value));
95 }
96 }
97
98 printResults(sortedResults);
99 }
100 private static void printResults(TreeSet sortedResults)
101 {
102 Iterator iterator = sortedResults.iterator();
103 while(iterator.hasNext())
104 {
105 User user = (User)iterator.next();
106 System.out.println(user.name + ":" + user.value);
107 }
108 }
109 public static void dealLine(String line,Map map)
110 {
111 if(!"".equals(line.trim()))
112 {
113 String [] results = line.split(",");
114 if(results.length == 3)
115 {
116 String name = results[1];
117 Integer value = (Integer)map.get(name);
118 if(value == null) value = 0;
119 map.put(name,value + 1);
120 }
121 }
122 }
123
124 }
整体思路:
使用HashMap<String,Integer> 来存储每次获取到的姓名。 每次存储之前判断 hashmap中是否存在当前获取到的名字,如果已经存在则在其基础上加1,如果不存在 则 put(name,1);
7、写一个Singleton出来。
Singleton模式主要作用是保证在Java应用程序中,一个类Class只有一个实例存在。
一般Singleton模式通常有几种种形式:
第一种形式: 定义一个类,它的构造函数为private的,它有一个static的private的该类变量,在类初始化时实例话,通过一个public的getInstance方法获取对它的引用,继而调用其中的方法。
public class Singleton {
private Singleton(){}
//在自己内部定义自己一个实例,是不是很奇怪?
//注意这是private 只供内部调用
private static Singleton instance = new Singleton();
//这里提供了一个供外部访问本class的静态方法,可以直接访问
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
第二种形式:
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance = null;
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() {
//这个方法比上面有所改进,不用每次都进行生成对象,只是第一次
//使用时生成实例,提高了效率!
if (instance==null)
instance=new Singleton();
return instance; }
}
其他形式:
定义一个类,它的构造函数为private的,所有方法为static的。
一般认为第一种形式要更加安全些
8、递归算法题1
一个整数,大于0,不用循环和本地变量,按照n,2n,4n,8n的顺序递增,当值大于5000时,把值按照指定顺序输出来。
例:n=1237
则输出为:
1237,
2474,
4948,
9896,
9896,
4948,
2474,
1237,
提示:写程序时,先致谢按递增方式的代码,写好递增的以后,再增加考虑递减部分。
public static void doubleNum(int n) {
System.out.println(n);
if(n<=5000)
doubleNum(n*2);
System.out.println(n);
}
9、递归算法题2
第1个人10,第2个比第1个人大2岁,依次递推,请用递归方式计算出第8个人多大?
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(computeAge(8)); } public static int computeAge(int n) { if (n == 1) { return 10; } else { return computeAge(n - 1) + 2; } }}
10、排序都有哪几种方法?请列举。用JAVA实现一个快速排序。
本人只研究过冒泡排序、选择排序和快速排序,下面是快速排序的代码:
public class QuickSort {
/**
* 快速排序
*
* @param strDate
* @param left
* @param right
*/
public void quickSort(String[] strDate, int left, int right) {
String middle, tempDate;
int i, j;
i = left;
j = right;
middle = strDate[(i + j) / 2];
do {
while (strDate[i].compareTo(middle) < 0 && i < right)
i++; // 找出左边比中间值大的数
while (strDate[j].compareTo(middle) > 0 && j > left)
j--; // 找出右边比中间值小的数
if (i <= j) { // 将左边大的数和右边小的数进行替换
tempDate = strDate[i];
strDate[i] = strDate[j];
strDate[j] = tempDate;
i++;
j--;
}
} while (i <= j); // 当两者交错时停止
if (i < right) {
quickSort(strDate, i, right);// 从
}
if (j > left) {
quickSort(strDate, left, j);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] strVoid = new String[] { "11", "66", "22", "0", "55", "22",
"0", "32" };
QuickSort sort = new QuickSort();
sort.quickSort(strVoid, 0, strVoid.length - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < strVoid.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strVoid[i] + " ");
}
}
}
11、有数组a[n],用java代码将数组元素顺序颠倒
public class Test {
public static void reverse(int[] a, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right)
return;
int temp;
temp = a[left];
a[left] = a[right];
a[right] = temp;
reverse(a, ++left, --right);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
reverse(a, 0, a.length - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
12.金额转换,阿拉伯数字的金额转换成中国传统的形式如:(¥1011)->(一千零一拾一元整)输出。
去零的代码:
public class RenMingBi {
private static final char[] data = new char[] { \'零\', \'壹\', \'贰\', \'叁\', \'肆\', \'伍\', \'陆\', \'柒\', \'捌\', \'玖\' };
private static final char[] units = new char[] { \'元\', \'拾\', \'佰\', \'仟\', \'万\', \'拾\', \'佰\', \'仟\', \'亿\' };
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(convert(135689123));
}
public static String convert(int money) {
StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer();
int unit = 0;
while (money != 0) {
sbf.insert(0, units[unit++]);
int number = money % 10;
sbf.insert(0, data[number]);
money /= 10;
}
return sbf.toString();
}
}
以上是关于java编程,txt文件整合到一起。的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章