Linux开关机及系统进程命令
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux开关机及系统进程命令相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【一】Linux 系统启动流程
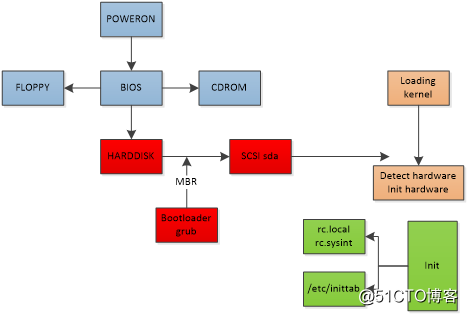
【二】关于Linux开机与关机
# Default runlevel. The runlevels used are:
# 0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
# 1 - Single user mode
# 2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking)
# 3 - Full multiuser mode
# 4 - unused
# 5 - X11
# 6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
#
id:3:initdefault:
runlevel | Active |
0 | 系统关机 |
1 | 单用户模式 |
2 | 本地多用户模式(无法使用远程网络) |
3 | 网络多用户模式 |
4 | 系统保留未定义 |
5 | 带图形界面的网络多用户模式 |
6 | 系统重启 |
init 命令:init + runlevel进行相应操作的切换
【三】Linux如何关闭和重启
Linux是一个多用户多任务的系统,关机时,需要注意一下事项:
(1)观察系统的使用状态,如谁在线,在线的用户在干什么(w)
(2)通知在线使用者关机的相关信息(可选)(wall,write)
(3)使用最安全的的关机方式(执行关机命令前执行sync将内存数据写入磁盘)
Linux系统安全关机的过程:
(1)执行sync命令将内存数据写入磁盘;
(2)关机命令下发,通知用户关机;
(3)停止系统的所有进程;
(4)卸载系统挂载的设备
【四】Linux系统关机常用命令
(1)halt :立刻关机
(2)poweroff :立刻关机
(3)shutdown -h now 立刻关机(root用户使用)
(4)shutdown -h 10 10分钟后自动关闭
注:在使用shutdown 命令设置重启的话,shutdown -c 将取消重启
【五】Linux系统开机常用命令
(1)reboot
(2)shutdown -r now 立刻重启(root用户使用)
(3)shutdown -r 10 过10分钟后重启
(4)shutdown -r 20:35 在20:35时重新启动(root用户使用)
注:在使用shutdown 命令设置重启的话,shutdown -c 将取消重启
【六】系统信息和进程类命令
命令 | 说明 |
man | 获得命令的帮助手册,如:man cp;按q键退出 |
su | 切换用户,如 su - root;"-" 表示改变用户的环境变量 |
who | 显示系统中登录的用户 |
w | 显示登录用户的详细信息 |
last | 查看最近登录系统的用户信息 |
date | 系统日期时间的设定,一般要结合参数-s使用 |
uname | 查看系统的版本 ,如uname -R |
reboot | 重启计算机,如reboot;shutdown -r now |
shutdown | 关闭计算机;如:shutdown -h now 表示停止服务后再关闭 |
free | 查看内存和swap分区情况 |
ps | 显示进程信息,参数-ux为当前用户的进程;参数-aux为所有用户的进程,参数-ef为系统所有进程信息 |
uptime | 显示当前时间,系统开机运转时间,连接数,最近1,5,15分钟的系统负载。(1个CPU 一般不超过0.8) |
top | 查看系统CPU、内存等使用情况 |
kill | 删除某个进程,进程号可用ps命令获得,如kill - 9 121 |
vmstat | 查看虚拟内存的使用情况 |
nohup | 将进程在用户退出登录后仍旧继续执行 |
jobs | 查看被挂起或后台运行的进程 |
Ctrl + Z | 进程挂起 |
Ctrl + C | 进程终止 |
fg | 进程恢复到前台继续执行 |
bg | 进程恢复到后台继续执行 |
【七】涉及到的命令操作演示
【实战一】 Linux 开关机
【关机】
halt :系统关闭,电源仍然工作
poweroff :关闭电源 icpi
shutdown -h:调用poweroff,halt命令
shutdown -h 0
shutdonw -h now
【重启】
reboot
shutdown -r
shutdown -r 10
shutdown -r 20:45
(1)shutdown --help
Options:
-r reboot after shutdown
-h halt or power off after shutdown
-H halt after shutdown (implies -h)
-P power off after shutdown (implies -h)
-c cancel a running shutdown
-k only send warnings, don't shutdown
-q, --quiet reduce output to errors only
-v, --verbose increase output to include informational messages
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
(2)
[[email protected] /]# halt
Broadcast message from [email protected]
(/dev/pts/0) at 14:27 ...
The system is going down for halt NOW!
(3)
shutdown -r now
Broadcast message from [email protected]
(/dev/pts/0) at 14:35 ...
The system is going down for reboot NOW!
(4)
[[email protected] ~]# shutdown -h 20:30
Broadcast message from [email protected]
(/dev/pts/0) at 14:36 ...
The system is going down for halt in 354 minutes!
(5)[[email protected] ~]# shutdown -c
^Hshutdown: Shutdown cancelled
(6) shutdown -k 1 "The system is going down for maintenance in 1 minute"
Broadcast message from [email protected]
(/dev/pts/0) at 14:40 ...
The system is going down for maintenance in 1 minute!
The system is going down for maintenance in 1 minute
(7)shutdown -t 60 -h now "The system is going down for maintenance in 1 minute"
Broadcast message from [email protected]
(/dev/pts/0) at 14:41 ...
The system is going down for halt NOW!
The system is going down for maintenance in 1 minute
【实战二】 Linux 进程管理命令
常用命令:
w
(1)[[email protected] ~]# w
14:47:11 up 4 min, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.02, 0.00
USER TTY FROM [email protected] IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root pts/0 10.53.110.78 14:42 0.00s 0.05s 0.01s w
注:远程登录pts,本地登录tty
(2)[[email protected] ~]# w
14:50:10 up 7 min, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
USER TTY FROM [email protected] IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root pts/0 10.53.110.78 14:42 0.00s 0.04s 0.00s w
root pts/1 10.53.110.78 14:49 4.00s 0.02s 0.01s top
ps
ps -aux
(3)[[email protected] ~]# ps -aux|more
Warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus '-'? See /usr/share/doc/procps-3.2.8/FAQ
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.2 0.0 19364 1532 ? Ss 14:42 0:01 /sbin/init
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/0]
root 4 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
…
(4)[[email protected] ~]# ps -aux --sort time|more ## 按照时间排序
Warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus '-'? See /usr/share/doc/procps-3.2.8/FAQ
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.1 0.0 19364 1532 ? Ss 14:42 0:01 /sbin/init
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/0]
root 4 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/0]
root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [watchdog/0]
root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/1]
root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/1]
root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/1]
…
(4)[[email protected] ~]# ps -aux --sort pid|more ##按pid排序
Warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus '-'? See /usr/share/doc/procps-3.2.8/FAQ
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.1 0.0 19364 1532 ? Ss 14:42 0:01 /sbin/init
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/0]
root 4 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/0]
root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [watchdog/0]
root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/1]
【注】VSZ:使用虚拟内存大小
RSS:使用实际内存大小
TTY:终端类型
STAT: R:运行进程 S:睡眠进程 I:空闲基础 Z:僵死进程 D:不可中断进程 T:终止进程 P:交换进程
(5)[[email protected] ~]# ps -A|more ##显示所有进程
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ? 00:00:01 init
2 ? 00:00:00 kthreadd
3 ? 00:00:00 migration/0
4 ? 00:00:00 ksoftirqd/0
5 ? 00:00:00 migration/0
6 ? 00:00:00 watchdog/0
7 ? 00:00:00 migration/1
8 ? 00:00:00 migration/1
9 ? 00:00:00 ksoftirqd/1
10 ? 00:00:00 watchdog/1
11 ? 00:00:00 events/0
(6)[[email protected] ~]# ps -u root |more ##查看某个用户的进程
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ? 00:00:01 init
2 ? 00:00:00 kthreadd
3 ? 00:00:00 migration/0
4 ? 00:00:00 ksoftirqd/0
5 ? 00:00:00 migration/0
6 ? 00:00:00 watchdog/0
7 ? 00:00:00 migration/1
8 ? 00:00:00 migration/1
9 ? 00:00:00 ksoftirqd/1
10 ? 00:00:00 watchdog/1
(7)
[[email protected] ~]# ps -ef|more
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 14:42 ? 00:00:01 /sbin/init
root 2 0 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [migration/0]
root 4 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 5 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [migration/0]
root 6 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [watchdog/0]
root 7 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [migration/1]
root 8 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [migration/1]
root 9 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [ksoftirqd/1]
root 10 2 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 [watchdog/1]
UID :用户ID
PID:进程ID
PPID:父进程ID
C:0级,没有子进程
STIME:运行时间
TTY:终端类型
(8)
[[email protected] ~]# ps -ef|grep sshd
root 1508 1 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd
root 1693 1508 0 14:42 ? 00:00:00 sshd: [email protected]/1,pts/2
root 1884 1848 0 15:08 pts/2 00:00:00 grep sshd
(9)根据CPU和mem排序 (前5行)
[[email protected] ~]# ps -aux --sort -pcpu,-pmem|head -5
Warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus '-'? See /usr/share/doc/procps-3.2.8/FAQ
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1767 0.1 0.0 15036 1212 pts/1 S+ 14:50 0:01 top
root 1 0.0 0.0 19364 1532 ? Ss 14:42 0:01 /sbin/init
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 14:42 0:00 [migration/0]
(10)显示父进程和子进程
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C sshd #查看进程
PID TTY TIME CMD
1508 ? 00:00:00 sshd
1693 ? 00:00:00 sshd
[[email protected] ~]# ps -p 1508 -L #查看进程有多少线程
PID LWP TTY TIME CMD
1508 1508 ? 00:00:00 sshd
[[email protected] ~]# ps --ppid 1693 #查看进程的子进程
PID TTY TIME CMD
1737 pts/1 00:00:00 bash
1848 pts/2 00:00:00 bash
kill命令
SYNOPSIS
kill [-s signal|-p] [--] pid...
kill -l [signal]
(1)kill的信号
[[email protected] ~]# kill -l
1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
15) SIGTERM
[[email protected] ~]# ps -ef|grep top
root 2011 1984 0 15:20 pts/1 00:00:00 top
root 2015 1921 0 15:20 pts/0 00:00:00 grep top
[[email protected] ~]#
[[email protected] ~]#
[[email protected] ~]# kill -9 2011
[[email protected] ~]# ps -ef|grep top
root 2017 1921 0 15:21 pts/0 00:00:00 grep top
[[email protected] ~]#
【注】进程号为1不能kill,否则系统不能使用
nohup命令
(1)[[email protected] ~]# nohup vmstat 2>1 1.log & ##在后台运行
Ctrl + Z
jobs
Ctrl + C
以上是关于Linux开关机及系统进程命令的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章