[LeetCode]Array主题系列
Posted Haonan Hacking
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[LeetCode]Array主题系列相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.内容介绍
开一篇文章记录在leetcode中array主题下面的题目和自己的思考以及优化过程,具体内容层次按照{题目,分析,初解,初解结果,优化解,优化解结果,反思}的格式来记录,供日后复习和反思。题目的顺序按照leetcode给出的题目顺序,有些题目在并不是按照题目本身序号顺序排列的,也不是严格按照难易程度来排列的。
因此,这篇文章并不具有很强的归类总结性,归类总结性知识将会在其他文章记录,本篇重点在记录解题过程中的思路,希望能对自己有所启发。
2.题目和解题过程
2.1 Container With Most Water
- 题目:Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an, where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
- 分析:要找到能容纳最多水的容器,等价目标是使得两条线之间面积最大(右图所示红线之间的面积),面积计算公式是:ax * |i-j|, ax是{ai,aj}中较小的一方,|i-j|是两条线之间的距离,因此可以知道面积的大小受到线的高度和两条线之间的距离的影响。
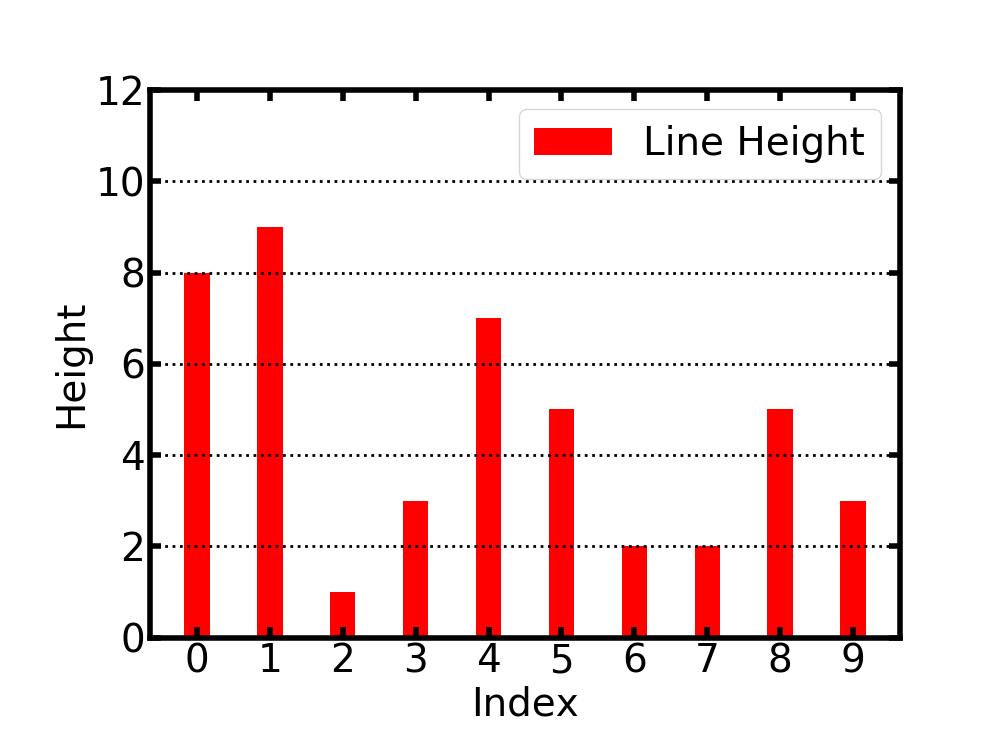
- 初解:设置一个变量初始化最大面积值为0,从最左边的一条线开始向右迭代,跳过高度为0的线,对于迭代的每条线分别计算与其右边的每一条线进行计算区域面积,跳过高度为0的线,然后与当前最大面积比较,记录下最大面积值。该解法的时间复杂度是O(n2),空间复杂度是O(1)。
class Solution { public: int maxArea(vector<int>& height) { int area = 0; int max_height = 0; for(int i = 0; i < height.size(); ++i) { while(height[i]==0 && i < height.size()) ++i; for(int j = i+1 ; j < height.size(); ++j) { while(height[j]==0 && j < height.size()) ++j; if(j < height.size()) { int a = (height[i] < height[j])? height[i]:height[j]; int tmp_area = a * (j - i); if(tmp_area > area) area = tmp_area; } } if(height[i] > max_height) max_height = height[i]; } return area; } };
- 初解结果:
- 优化解法:显然,初解的思路是对的,仅仅是效率不够高,在输入规模较大时,完全双层循环的O(n2)时间复杂度不能满足要求。但是由于目标面积受两个因素{高度,距离}的影响,因此我们可以尝试在这两个因素上做过滤检查,省去一些不必要的计算。首先,针对高度优化可以做如下考虑:在外层循环上当前线(i,ai)上做完计算后,如果后面的线(k,ak)的高度ak比ai小,那么计算出来的面积一定不会超过在ai上计算的最大面积,因此可以过滤这些线。其次,针对距离优化可以做如下考虑:每次向后移动完外层循环的线后,开始确定内层循环的起始线时,跳过在当前外层线的高度下取得最大面积必须的距离,这样的话就能省去部分计算。
class Solution { public: int maxArea(vector<int>& height) { int area = 0; int max_height = 0; for(int i = 0; i < height.size(); ) { while(height[i]==0 && i < height.size()) ++i; int j = (area == 0)?(i+1):(i + area / height[i]); for( ; j < height.size(); ++j) { while(height[j]==0 && j < height.size()) ++j; if(j < height.size()) { int a = (height[i] < height[j])? height[i]:height[j]; int tmp_area = a * (j - i); if(tmp_area > area) area = tmp_area; } } if(height[i] > max_height) max_height = height[i]; int next_index = i+1; while(next_index < height.size() && height[next_index] <= max_height) ++next_index; i = next_index; } return area; } };
- 优化结果:仅仅优化高度时的结果:
再加上距离优化的结果:
- 反思:求解题目时如果搜索范围较广,且不能修改搜索框架时,较好的方法是做条件过滤,去除明显不可能计算出所求结果的候选值,用于加速计算过程。
2.2 Two Sum
-
题目:Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9, Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9, return [0, 1].
- 分析:按照题目要求仅仅是找到两个不同的值然后求和,对比是否是期望值;题目的重点应该是在优化搜索空间上。
- 初解:建立双重循环,依次迭代每个数组元素并循环匹配后面的元素来进行求和,然后对比期望值,该实现的时间复杂度是O(n2)。
class Solution { public: vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<int> result; if(nums.size()<2) return result; for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); ++i) { for(int j=i+1; j<nums.size(); ++j) { if(nums[i]+nums[j]==target) { result.push_back(i); result.push_back(j); break; } } } return result; } };
- 初解结果:
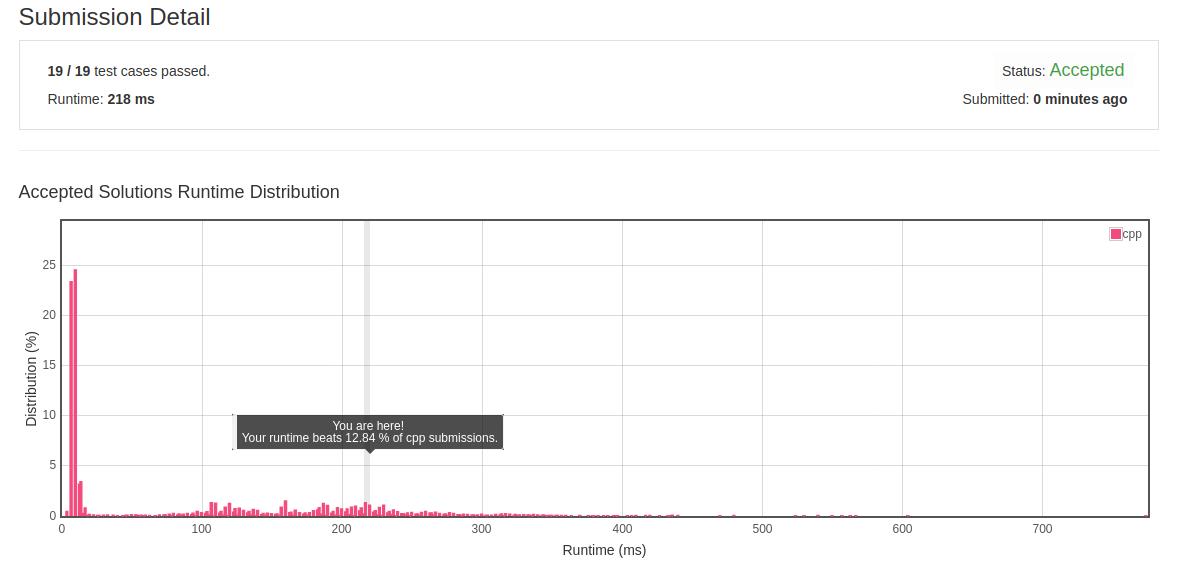
- 优化解法:想要优化时间复杂度需要更改搜索方式,由于题目所给的原始数据是无序的,也就无法给出优化,但如果假设是有序的数组,则可以利用如下关系加速搜索:两个数之和与期望值的关系只有三种情况:=,>,<。另外题目强调了两个值的索引一定是不同的,因此一定是一个索引相对大的数加上一个索引相对小的数,当数组有序时,索引的大小象征了值的大小。因此,在有序数组情况下搜索可以优化为O(n)的时间复杂度:设置两个索引分别位于数组首尾,求和对比期望值,如果偏大,移动尾指针,相反则移动首指针。加上排序的时间复杂度O(nlogn),总的时间复杂度是O(nlogn)。
class Solution { public: vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<int> result; if(nums.size()<2) return result; vector<int> cpy(nums); sort(cpy.begin(),cpy.end()); int start = 0, end = cpy.size() -1; while(start < end) { int sum = cpy[start] + cpy[end]; if(sum < target) ++start; else if(sum > target) --end; else { int a_indice = -1, b_indice = -1; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) { if(nums[i] == cpy[start] || nums[i] == cpy[end]) result.push_back(i); if(result.size() == 2) return result; } } } } };
- 优化结果:
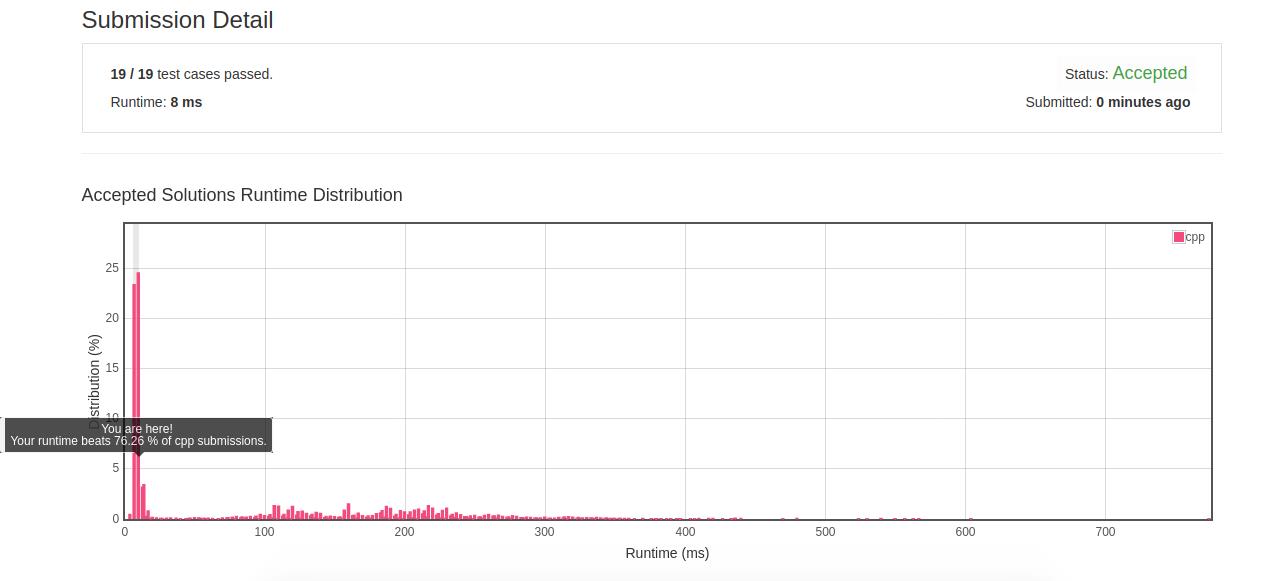
- 反思:对于无序数据的加速搜索方式之一是先排序,后搜索。
2.3 3Sum
- 题目:Given an array S of n integers, are there elements a, b, c in S such that a + b + c = 0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
For example, given array S = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4], A solution set is: [ [-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2] ]
- 分析:这是一个在给定无序数据范围内搜索满足函数条件的三个变量值,并且不重复,因此搜索方式和查重方式会影响程序的效率。
- 初解:设置一个三重循环,分别对变量a,b,c的可能值进行迭代,设置一个集合来存储满足条件的结果实现自动去重,该方法的时间复杂度是O(n4logn)。
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; if(nums.size()<=2) return res; set<vector<int>> tmp_res; for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); ++i) for(int j=i+1; j<nums.size(); ++j) for(int k=j+1; k<nums.size(); ++k) { if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]==0) { vector<int> val{nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]}; sort(val.begin(),val.end()); tmp_res.insert(val); } } res.insert(res.end(), tmp_res.begin(), tmp_res.end()); return res; } };
- 初解结果:
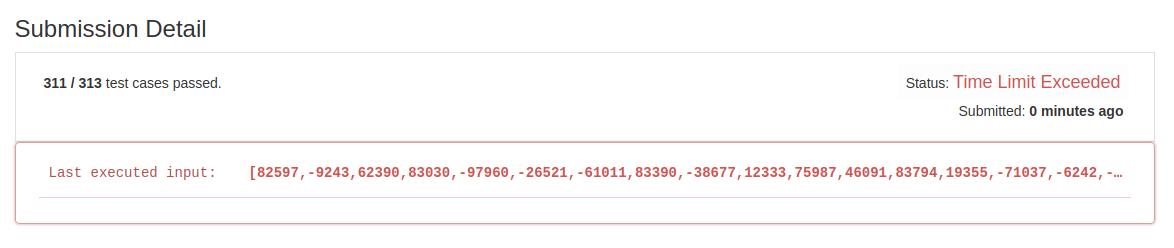
- 优化解法:根据初解结果来看求解的思路是正确的,问题出在搜索方式和查重方式的效率上,考虑优化搜索方式:本题在本质上与TwoSum一致,在给定范围内搜索几个数使得求和与期望值相同,不同之处在于本题的期望值是固定的0,利用TwoSum的优化思想(对数据进行排序),可以将初解的搜索时间复杂度从O(n3)降到O(n2)。考虑优化查重方式:在前一步优化搜索的基础上,数据已经是有序的,因此相同的值会被放置在相邻的位置,因此查重方式仅仅是判断后一个值是否与当前值相同即可。整体的时间复杂度是O(nlogn + n2)。
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> result; int sz = nums.size(); sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); for (int i = 0; i < sz - 2; ++i){ twoSum(nums, i + 1, 0 - nums[i], result); while(nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) ++i;//这一步要注意,防止得出重复的vector } return result; } void twoSum(vector<int> & nums, int start, int value, vector<vector<int>> & ret) { int beg = start; int end = nums.size()-1; while (beg < end){ int sum = nums[beg] + nums[end]; if (sum < value) beg++; else if (sum > value) end--; else{ ret.push_back(vector<int>{nums[start - 1], nums[beg], nums[end]}); while (nums[beg + 1] == nums[beg]) beg++;//这一步的处理应该注意,防止出现相同的vector while (nums[end - 1] == nums[end]) end--; beg++, end--; } } } };
- 优化结果:
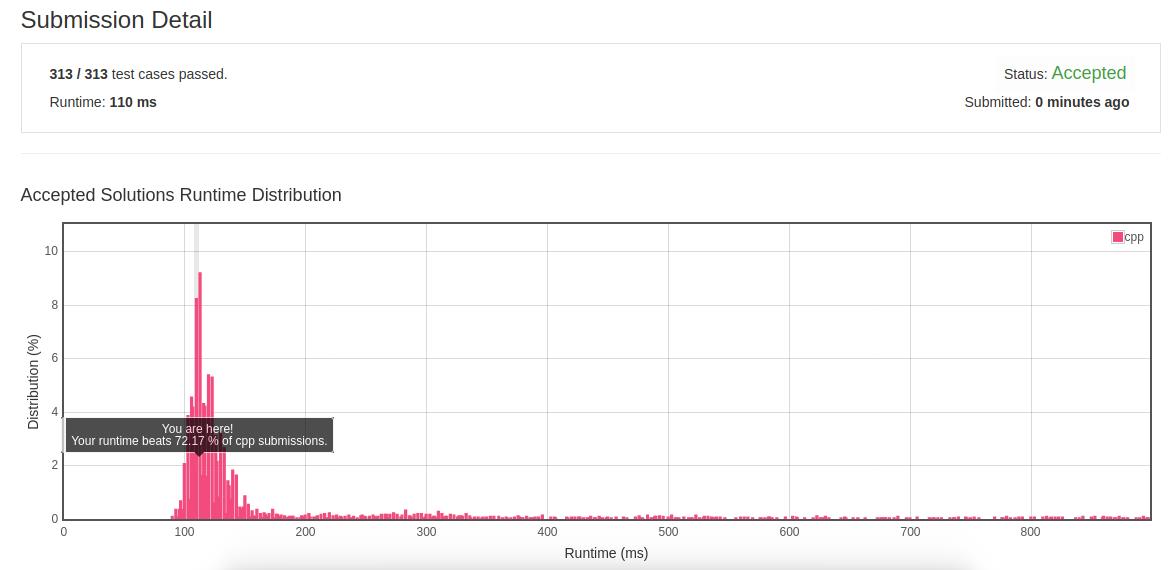
- 反思:在无序数据中做搜索一定要先排序,对于给定条件函数求解通过排序原始数据后可以将搜索的时间复杂度降一个量级。
2.4 3Sum Closest
- 题目:Given an array S of n integers, find three integers in S such that the sum is closest to a given number, target. Return the sum of the three integers. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution. For example, given array S = {-1 2 1 -4}, and target = 1. The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
- 分析:本题与上一题相似,仅仅是求解目标不同,但仅仅涉及到搜索,而没有查重过程。
- 初解:设置三重循环分别用于搜索a,b,c三个变量的可能值,然后比较求和结果与期望值的距离,记录下最短距离和求和值,时间复杂度为O(n3)。
class Solution { public: int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) { if(nums.size()<3) return 0; int sum = 0, dis = 99999; for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); ++i) for(int j=i+1; j<nums.size(); ++j) for(int k=j+1; k<nums.size(); ++k) { int tmp_sum = nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]; int tmp_dis = 0; if(target >= 0) { if(tmp_sum >= 0) tmp_dis = (target >= tmp_sum)? (target-tmp_sum):(tmp_sum-target); else tmp_dis = target - tmp_sum; } else { if(tmp_sum >= 0) tmp_dis = tmp_sum - target; else tmp_dis = (target < tmp_sum)? (tmp_sum - target):(target - tmp_sum); } if(tmp_dis < dis) { dis = tmp_dis; sum = tmp_sum; } if(dis==0) break; } return sum; } };
- 初解结果:
- 优化解法:本题的效率瓶颈主要出现在三重循环,因此需要对搜索方式进行优化,同样,对于无序数据的查找加速最好方式是先排序后搜索,搜索方式为固定一个变量,然后对其他两个变量从有序数据的首尾展开逼近搜索,首尾指针的移动条件是与期望值进行相比,如果大于期望值,则移动尾指针,如果小于期望值则移动首指针,时间复杂度为O(n2)。
class Solution { public: int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) { sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); int res = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2]; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++){ int j = i + 1, k = nums.size() - 1; while(j < k){ int num = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]; if(abs(num - target) < abs(res - target)) res = num; if(num < target) j++; else k--; } } return res; } };
- 优化结果:
- 反思:搜索无序数据时先排序。
2.5 4Sum
- 题目:Given an array S of n integers, are there elements a, b, c, and d in S such that a + b + c + d = target? Find all unique quadruplets in the array which gives the sum of target. Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate quadruplets. For example, given array S = [1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2], and target = 0. A solution set is: [ [-1, 0, 0, 1], [-2, -1, 1, 2], [-2, 0, 0, 2] ]
- 分析:本题与3Sum相同,涉及搜索方式和查重方式。
- 初解:设置四重循环,分别用于迭代搜索a,b,c,d所有可能的值,然后将满足条件的值的列表放入到一个不重复的集合中,该方法的时间复杂度为O(n5logn)。
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<vector<int>> res; if(nums.size()<4) return res; set<vector<int>> tmp_res; for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); ++i) for(int j=i+1; j<nums.size(); ++j) for(int k=j+1; k<nums.size(); ++k) for(int m=k+1; m<nums.size(); ++m) { if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]+nums[m]==target) { vector<int> val{nums[i],nums[j],nums[k],nums[m]}; sort(val.begin(),val.end()); tmp_res.insert(val); } } res.insert(res.end(), tmp_res.begin(), tmp_res.end()); return res; } };
- 初解结果:
- 优化解法:根据初解的结果可以看出求解思路正确但是搜索效率很低,因此为了优化搜索效率,采取和3Sum相同的方式(先排序后搜索)来降低时间复杂度。最终时间复杂度为O(n3)。
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<vector<int>> result; if(nums.size() < 4) return result; sort(nums.begin(),nums.end()); for(int i = 0; i < nums.size()-3; ++i) { threeSum(nums, i+1, target - nums[i], result, nums[i]); while(nums[i]==nums[i+1]) ++i; } return result; } void threeSum(vector<int>& nums, int start, int value, vector<vector<int>>& result, int pre_value) { for(int i = start; i < nums.size() - 2; ++i) { twoSum(nums, i+1, value - nums[i], result, pre_value); while(nums[i]==nums[i+1]) ++i; } } void twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int start, int value, vector<vector<int>>& result, int pre_value) { int begin = start; int end = nums.size() - 1; while(begin < end) { int sum = nums[begin] + nums[end]; if(sum < value) ++begin; else if(sum > value) --end; else { result.push_back(vector<int>{pre_value, nums[start-1], nums[begin], nums[end]}); while(nums[begin+1]==nums[begin]) ++begin; while(nums[end-1]==nums[end]) --end; ++begin; --end; } } } };
- 优化结果:
- 反思:在无序数据中搜索时先排序后搜索可以加速搜索和查重。
2.6 Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- 题目:Given a sorted array, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appears only once and return the new length.Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.Example: Given nums = [1,1,2], Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively. It doesn\'t matter what you leave beyond the new length.
- 分析:题目考察对数组本身的原址去重操作效率,需要能识别重复元素和去除重复元素。
- 初解:最简单的方法是遇到一个重复的元素就将后面全部数据向前移动一个位置,这样的时间复杂度是O(n2),工作量较大,在此基础上的小小优化解法是遇到所有重复元素后再将后面所有的元素向前移动重复元素数目的位置。
class Solution { public: int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) { if(nums.size()<2) return nums.size(); int tail = nums.size(); for(int i=1; i<tail; ) { int moved_nums = 0; while(nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&i<tail) { ++moved_nums; ++i; } tail -= moved_nums; if(moved_nums!=0) { move(nums,i,moved_nums); i = i-moved_nums; } else ++i; } return tail; } void move(vector<int>& nums, int start, int offset) { for(int j=start; j < nums.size(); ++j) nums[j-offset]=nums[j]; } };
- 初解结果:
- 优化解法:根据初解的结果可以看出解题思路正确但是搜索方式的时间复杂度过高,初解的搜索方式是遇到单个值的所有重复值后将后面所有数据整体向前移动来覆盖重复值,这涉及到后面整体数据,工作量大,时间耗费高,所以优化的目标是减少每次移动的数据量和总的移动次数,换句话说就是每次移动后面的数据时只移动不重复的数据即可,因为这些数据是求解必要的数据,为了知道后面哪些是必要的数据,首先需要对整个数组进行依次遍历和标记以实现筛选数据,然后从前向后遍历数据,遇到被标记的位置A说明该位置需要被覆盖,因此向后寻找第一个没有被标记的位置B,并将这个位置的值向前移动到被标记的位置A,再将B置为已标记。为了减少每次遇到被标记位置向后查找的长度,应该记录上一次找到没有被标记数据的位置,然后下一次查找时从记录的位置向后查找即可。该方法的时间复杂度是O(n)。
#include<climits> class Solution { public: int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) { if(nums.size() <= 1) return nums.size(); int counter = 0; int max_val = 0x7fffffff; int last_pos = 0; for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) { if(nums[i]==nums[i-1]) { nums[i-1]=max_val; ++counter; } } if(counter!=0) { for(int i = 0; i < nums.size()-counter; ++i) { if(nums[i]==max_val) { if(last_pos < i) last_pos = i; last_pos = findNonNull(nums, last_pos, max_val); if(last_pos < nums.size()) { nums[i] = nums[last_pos]; nums[last_pos] = max_val; } else break; } } }return nums.size()-counter; } int findNonNull(vector<int>& nums, int start, int& max_val) { while(start < nums.size()) { if(nums[++start]!=max_val) return start; } return start; } };
- 优化结果:
- 反思:涉及到重复多次移动冗余数据的优化方式是提前对冗余数据进行标记,然后不予移动以减少工作量。
2.7 Remove Element
- 题目:Given an array and a value, remove all instances of that value in-place and return the new length.Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.The order of elements can be changed. It doesn\'t matter what you leave beyond the new length.Example: Given nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3, Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
- 分析:本题目涉及到对数组的检索与移动,实际效果等同于紧凑操作。
- 初解:先对数组进行一次检索和对要抹除的数据进行标记,然后从头开始遍历,遇到一个需要抹除的数据就将后面的数据整体向前移动,直到当前遍历过的数组元素数等于紧凑过后的数据总量。该方法的时间复杂度是O(n2)。
class Solution { public: int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) { int tail = nums.size(); for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); ++i) { if(nums[i]==val) { nums[i]=0x7fffffff; --tail; } } for(int i=0; i<tail; ) { if(nums[i]==0x7fffffff) { for(int j=i+1; j<nums.size(); ++j) nums[j-1]=nums[j]; } else ++i; } return tail; } };
- 初解结果:
- 优化解法1:初解中移动的方式比较初级但效率低,因为每次需要移动后面的整体数据,因此优化目标是减少每次移动的数据量,由于题目不考虑移动后的数据顺序,因此每次在移动后面整体数据时就没有必要保持前后之间的顺序性,也就是说如果将最后一个数据移动到最前面也是可以的,因此具体的优化方式是设置一个游标指向从后逆序第一个没有被标记的数据位置,每次从前向后遇到一个需要填充的位置时就将尾部的游标数据向前填充,并重新将游标指向下一个没有被标记的位置。该方法的时间复杂度是O(n)。
class Solution { public: int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) { int counter = 0; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) { if(nums[i]==val) { ++counter; nums[i] = 0x7fffffff; } } if(counter!=0) { int tail = nums.size()-1; while(nums[tail]==0x7fffffff) --tail; for(int i=0; i<tail; ++i) { if(nums[i]==0x7fffffff) { nums[i]=nums[tail]; nums[tail]=0x7fffffff; while(nums[tail]==0x7fffffff) --tail; } } } return nums.size()-counter; } };
- 优化结果1:
- 优化解法2:题目的要求是移除特定的值,对于此有两种做法,一种是上面的解法:填充式,另一种则是排序式,意思是将需要移除的值设置为最大值,然后对整体进行排序,则可以将移除的值放在数组尾部,而前面的数据就是所求的结果。该方法的时间复杂度是O(nlogn)。
class Solution { public: int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) { int max = 0x7fffffff; int counter = 0; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) { if(nums[i]==val) { ++counter; nums[i] = max; } } if(counter != 0) sort(nums.begin(),nums.end()); return nums.size()-counter; } };
- 优化结果2:

- 反思:排序是一种快速简单的工具...
2.8 Next Permutation
- 题目:Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.If such arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (ie, sorted in ascending order).The replacement must be in-place, do not allocate extra memory.Here are some examples. Inputs are in the left-hand column and its corresponding outputs are in the right-hand column.
1,2,3→1,3,23,2,1→1,2,31,1,5→1,5,1以上是关于[LeetCode]Array主题系列的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章