WEB框架
Posted hpython
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了WEB框架相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
WEB框架本质
通常为B/S架构,浏览器作为客户端,服务器为服务端。优点:升级维护方便。
浏览器
功能:发送/解析请求(request)
请求格式
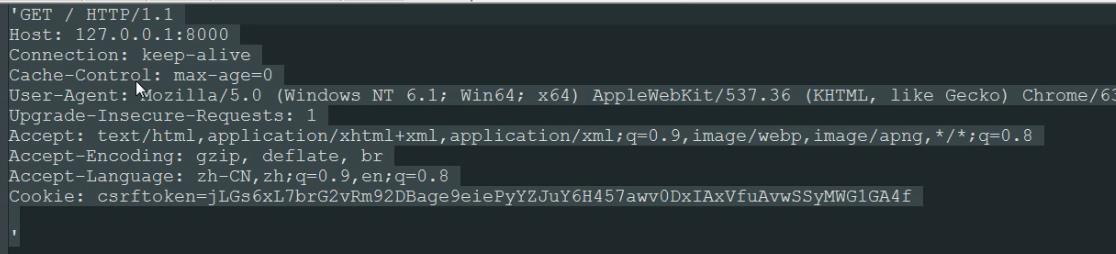
1)GET

GET请求格式
“GET / HTTP/1.1 \\r\\n”
k1:v1\\r\\n
k2:v2\\r\\n
只有请求头,没有请求体
响应
特点:
- 没有请求体
- 数据必须在1K之内!
- GET请求数据会暴露在浏览器的地址栏中 —— 缺点
GET请求常用的操作:
- 在浏览器的地址栏中直接给出URL,那么就一定是GET请求
- 点击页面上的超链接也一定是GET请求
- 提交表单时,表单默认使用GET请求,但可以设置为POST
2) POST

POST:请求格式
“POST / HTTP/1.1 \\r\\n”
k1:v1\\r\\n
k2:v2\\r\\n
有请求头和请求体
POST /index HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/44.0.2403.89 Safari/537.36
HTTPS: 1
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, sdch
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8
Cookie: csrftoken=hNmu2JOtntGMN0hSRSPmMQk2newEb3o8zb6pXW5Cc3m54IaA5VlTkUvqWsFezpni

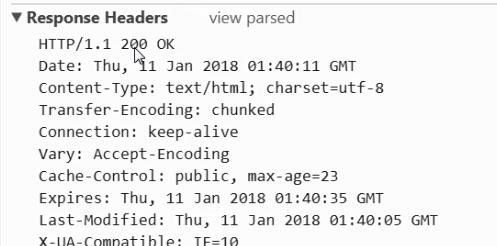
200 OK
Cache-Control:public, max-age=15
Connection:keep-alive
Content-Encoding:gzip
Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8
Date:Wed, 14 Jun 2017 01:21:17 GMT
Expires:Wed, 14 Jun 2017 01:21:33 GMT
Last-Modified:Wed, 14 Jun 2017 01:21:03 GMT
Transfer-Encoding:chunked
Vary:Accept-Encoding
X-Frame-Options:SAMEORIGIN
X-UA-Compatible:IE=10
注意: 用户在页面看到的内容“字符串”(看到页面效果,由于浏览器解析)
响应:
Header
Body
HTTP
上面的GET、POST请求属于HTTP请求,浏览器和WEB服务端通信需要一个规则,这个规则就是HTTP协议:简单理解为规定消息格式。
特点:是无状态、短连接
自定义WEB框架
流程
A)自定义soket服务端,处理请求相关的数据 ——Wsgiref / uWSGI / Gunicorn
B)通过URL——>函数——>根据函数的逻辑(取数据)
C)把数据填充到HTML页面(字符串替换)
WEB框架分类
1.a、b、c都是自己的 Tornado
2.a用别人的,b、c用自己的 Django
3.a、c用别人的,b用自己的 Flask
对于所有的Web应用,本质上其实就是一个socket服务端,用户的浏览器其实就是一个socket客户端
import socket
def handle_request(client):
buf = client.recv(1024)
client.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n\\r\\n")
client.send("Hello, Seven")
def main():
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.bind((\'localhost\',8000))
sock.listen(5)
while True:
connection, address = sock.accept()
handle_request(connection)
connection.close()
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
main()
上述通过socket来实现了其本质,而对于真实开发中的python web程序来说,一般会分为两部分:服务器程序和应用程序。服务器程序负责对socket服务器进行封装,并在请求到来时,对请求的各种数据进行整理。应用程序则负责具体的逻辑处理。为了方便应用程序的开发,就出现了众多的Web框架,例如:Django、Flask、web.py 等。不同的框架有不同的开发方式,但是无论如何,开发出的应用程序都要和服务器程序配合,才能为用户提供服务。这样,服务器程序就需要为不同的框架提供不同的支持。这样混乱的局面无论对于服务器还是框架,都是不好的。对服务器来说,需要支持各种不同框架,对框架来说,只有支持它的服务器才能被开发出的应用使用。这时候,标准化就变得尤为重要。我们可以设立一个标准,只要服务器程序支持这个标准,框架也支持这个标准,那么他们就可以配合使用。一旦标准确定,双方各自实现。这样,服务器可以支持更多支持标准的框架,框架也可以使用更多支持标准的服务器。
WSGI(Web Server Gateway Interface)是一种规范,它定义了使用python编写的web app与web server之间接口格式,实现web app与web server间的解耦。我们需要在WSGI接口之上能进一步抽象,让我们专注于用一个函数处理一个URL,至于URL到函数的映射,就交给Web框架来做。
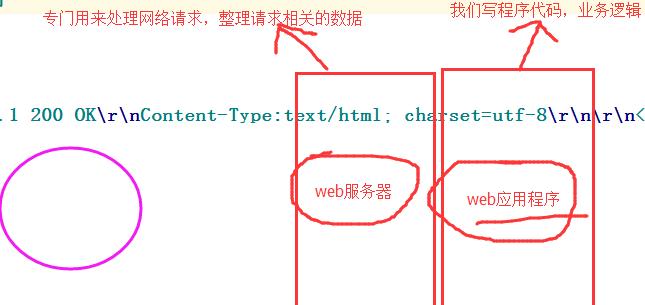
python标准库提供的独立WSGI服务器称为wsgiref。
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server def RunServer(environ, start_response): start_response(\'200 OK\', [(\'Content-Type\', \'text/html\')]) return [bytes(\'<h1>Hello, web!</h1>\', encoding=\'utf-8\'), ] if __name__ == \'__main__\': httpd = make_server(\'\', 8000, RunServer) print("Serving HTTP on port 8000...") httpd.serve_forever()
web请求生命周期
自定义web框架

import socket sk = socket.socket() sk.bind(("127.0.0.1", 8000)) sk.listen(5) while True: conn, addr = sk.accept() data = conn.recv(8096) print(data) # data是浏览器传过来的请求信息,bytes类型 data_str = str(data, encoding="utf8") l1 = data_str.split("\\r\\n") l2 = l1[0].split() url = l2[1] # 根据url的不同,返回不同的内容 if url == "/index/": body = "这是index页面" elif url == "/home/": body = "这是home页面" else: body = "404找不到" # 服务端回复消息 conn.send(bytes("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\nContent-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8\\r\\n\\r\\n<h1>{}</h1>".format(body), encoding="utf8")) conn.close()

from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server def index(): with open("index.html", encoding="utf8") as f: data = f.read() # 连接数据库 import pymysql # 连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost", user="root", password="root1234", database="s8", charset="utf8") # 没有- # 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 写sql语句 sql = "select name, pwd from userinfo where id =1;" cursor.execute(sql) ret = cursor.fetchone() print(ret) # 将数据库中的数据填充到HTML页面 new1_data = data.replace("@@2@@", ret[0]) new2_data = new1_data.replace("##3##", ret[1]) return new2_data def home(): return "这是home页面" def login(): with open("login.html", encoding="utf8") as f: data = f.read() import time time_str = str(time.time()) new_data = data.replace("@@2@@", time_str) return new_data URL_FUNC = [ ("/index/", index), ("/home/", home), ("/login/", login), ] def run_server(environ, start_response): start_response(\'200 OK\', [(\'Content-Type\', \'text/html;charset=utf8\')]) # 设置HTTP响应的状态码和头信息 url = environ[\'PATH_INFO\'] # 取到用户输入的url print("--->url:", url) # 根据url的不同,返回不同的内容 func_name = None for i in URL_FUNC: if url == i[0]: # 如果能找到对应关系,就把函数名拿到 func_name = i[1] break # 拿到可以执行的函数,执行函数拿到结果 if func_name: body = func_name() else: body = "404找不到这个页面" return [bytes("<h1>{}</h1>".format(body), encoding="utf8"),] if __name__ == \'__main__\': httpd = make_server(\'\', 8000, run_server) print("Serving HTTP on port 8000...") httpd.serve_forever()

from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server import jinja2 def index(): with open("index.html", encoding="utf8") as f: data = f.read() # 连接数据库 import pymysql # 连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost", user="root", password="root1234", database="s8", charset="utf8") # 没有- # 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 写sql语句 sql = "select name, pwd from userinfo where id =1;" cursor.execute(sql) ret = cursor.fetchone() print(ret) # 将数据库中的数据填充到HTML页面 new1_data = data.replace("@@2@@", ret[0]) new2_data = new1_data.replace("##3##", ret[1]) return new2_data def home(): return "这是home页面" def userlist(): with open("userlist.html", encoding="utf8") as f: data = f.read() # 生成了一个jinja2的模板对象 template = jinja2.Template(data) # 相当于字符串替换 new_data = template.render({ "user_list": [ {"name": "jianchao", "pwd": "1234"}, {"name": "liyan", "pwd": "5678"} ] }) return new_data def login(): with open("login.html", encoding="utf8") as f: data = f.read() import time time_str = str(time.time()) new_data = data.replace("@@2@@", time_str) return new_data URL_FUNC = [ ("/index/", index), ("/home/", home), ("/login/", login), ("/userlist/", userlist), ] def run_server(environ, start_response): start_response(\'200 OK\', [(\'Content-Type\', \'text/html;charset=utf8\')]) # 设置HTTP响应的状态码和头信息 url = environ[\'PATH_INFO\'] # 取到用户输入的url print("--->url:", url) # 根据url的不同,返回不同的内容 func_name = None for i in URL_FUNC: if url == i[0]: # 如果能找到对应关系,就把函数名拿到 func_name = i[1] break # 拿到可以执行的函数,执行函数拿到结果 if func_name: body = func_name() else: body = "404找不到这个页面" return [bytes("<h1>{}</h1>".format(body), encoding="utf8"),] if __name__ == \'__main__\': httpd = make_server(\'\', 9000, run_server) print("Serving HTTP on port 8000...") httpd.serve_forever()

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>index</title> </head> <body> <h1>姓名:@@2@@</h1> <h1>密码:##3##</h1> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap-3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <form action=""> <p>姓名<input type="text"></p> <p>密码<input type="password"></p> <p><input type="submit" value="登录"></p> </form> @@2@@ <script src="jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <ul> {% for user in user_list %} <li>{{user.name}}|{{user.pwd}}</li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html>
以上是关于WEB框架的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
