Linux学习之路--日志管理17---20180113
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux学习之路--日志管理17---20180113相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、日志介绍
日志:
历史事件:时间,地点,人物,事件
日志级别:事件的关键性程度,Loglevel系统日志服务:
sysklogd :CentOS 5之前版本
syslogd: system application 记录应用日志
klogd: linux kernel 记录内核日志
事件记录格式:
日期时间 主机 进程[pid] 事件内容
C/S架构:通过TCP或UDP协议的服务完成日志记录传送,将分布在不同主机的日志实现集中管理
1、rsyslog
rsyslog特性:CentOS6和7
多线程
UDP, TCP, SSL, TLS, RELP
mysql, PGSQL, Oracle实现日志存储
强大的过滤器,可实现过滤记录日志信息中任意部分
自定义输出格式ELK:elasticsearch, logstash, kibana
非关系型分布式数据库
基于apache软件基金会jakarta项目组的项目lucene
Elasticsearch是个开源分布式搜索引擎
Logstash对日志进行收集、分析,并将其存储供以后使用
kibana 可以提供的日志分析友好的 Web 界面
[[email protected]~]#rpm -qi rsyslog Name : rsyslog Relocations: (not relocatable) Version : 5.8.10 Vendor: CentOS Release : 10.el6_6 Build Date: Wed 17 Dec 2014 05:52:43 PM CST Install Date: Tue 23 Jan 2018 03:21:08 PM CST Build Host: c6b8.bsys.dev.centos.org Group : System Environment/Daemons Source RPM: rsyslog-5.8.10-10.el6_6.src.rpm Size : 2178098 License: (GPLv3+ and ASL 2.0) Signature : RSA/SHA1, Wed 17 Dec 2014 08:12:36 PM CST, Key ID 0946fca2c105b9de Packager : CentOS BuildSystem <http://bugs.centos.org> URL : http://www.rsyslog.com/ Summary : Enhanced system logging and kernel message trapping daemons Description : Rsyslog is an enhanced, multi-threaded syslog daemon. It supports MySQL, syslog/TCP, RFC 3195, permitted sender lists, filtering on any message part, and fine grain output format control. It is compatible with stock sysklogd and can be used as a drop-in replacement. Rsyslog is simple to set up, with advanced features suitable for enterprise-class, encryption-protected syslog relay chains. #Rsyslog是一个增强的多线程syslog守护进程。 它支持MySQL,syslog / TCP,RFC 3195,允许的发件人列表,对任何消息部分的过滤以及细粒度输出格式控制。 它与stock sysklogd兼容,可以用作替代品。 Rsyslog设置简单,具有适用于企业级加密保护系统日志中继链路的高级功能。
2、rsyslog介绍
术语,参见man logger
facility:设施,从功能或程序上对日志进行归类
auth(验证), authpriv(验证授权), cron(计划任务), daemon(守护进程), ftp, kern, lpr(打印), mail, news, security(auth)(安全), user(用户), uucp, local0-local7(自定义), syslog(系统日志)
Priority 优先级别,从低到高排序
debug(调试), info(重要事件), notice(重要通知), warn(警报), err(错误), crit(临界), alert, emerg(系统不可用)
参看帮助: man 3 syslog程序包:rsyslog
主程序:/usr/sbin/rsyslogd
CentOS 6:service rsyslog {start|stop|restart|status}
CentOS 7:/usr/lib/systemd/system/rsyslog.service
配置文件:/etc/rsyslog.conf,/etc/rsyslog.d/*.conf
库文件: /lib64/rsyslog/*.so
配置文件格式:由三部分组成
MODULES: 相关模块配置
GLOBAL DIRECTIVES: 全局配置
RULES: 日志记录相关的规则配置RULES配置格式: facility.priority; facility.priority… target
facility(设施):
*: 所有的facility
facility1,facility2,facility3,...:指定的facility列表priority(优先界别):
*: 所有级别
none:没有级别,即不记录
PRIORITY:指定级别(含)以上的所有级别
=PRIORITY:仅记录指定级别的日志信息target:
文件路径:通常在/var/log/,文件路径前的-表示异步写入
用户:将日志事件通知给指定的用户,* 表示登录的所有用户
日志服务器:@host,把日志送往至指定的远程服务器记录
管道: | COMMAND,转发给其它命令处理
[[email protected]~]#logger -p local7.info "This is a test log" [[email protected]~]#cat /var/log/boot.log Jan 29 14:08:47 Centos6-server root: This is a test log
3、启用网络日志服务
通常的日志格式:
事件产生的日期时间 主机 进程(pid):事件内容
如: /var/log/messages,cron,secure等配置rsyslog成为日志服务器
#### MODULES ####
# Provides UDP syslog reception
$ModLoad imudp
$UDPServerRun 514
# Provides TCP syslog reception
$ModLoad imtcp
$InputTCPServerRun 514
#基于UDP远程管理日志 [[email protected]~]#ps aux | grep rsyslog root 1585 0.0 0.1 255424 1292 ? Sl Jan27 0:00 /sbin/rsyslogd -i /var/run/syslogd.pid -c 5 root 56057 0.0 0.0 103336 848 pts/0 S+ 14:11 0:00 grep rsyslog [[email protected]~]#vim /etc/rsyslog.conf # Provides UDP syslog reception $ModLoad imudp $UDPServerRun 514 [[email protected]~]#ss -nul State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port [[email protected]~]#service rsyslog restart Shutting down system logger: [ OK ] Starting system logger: [ OK ] [[email protected]~]#ss -nul State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port UNCONN 0 0 *:514 *:* UNCONN 0 0 :::514 :::* [[email protected]~]#vim /etc/rsyslog.conf *.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none @192.168.1.100 [[email protected]~]#systemctl restart rsyslog [[email protected]~]#logger "This is 2st test log" [[email protected]~]#tail -f /var/log/messages Feb 4 19:31:44 centos7mini root: This is 2st test log #基于TCP协议管理日志 [[email protected]~]#vim /etc/rsyslog.conf # Provides TCP syslog reception $ModLoad imtcp $InputTCPServerRun 514 [[email protected]~]#service rsyslog restart Shutting down system logger: [ OK ] Starting system logger: [ OK ] [[email protected]~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 25 :::514 :::* LISTEN 0 25 *:514 *:* [[email protected]~]#vim /etc/rsyslog.conf *.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none @@192.168.1.100 [[email protected]~]#systemctl restart rsyslog [[email protected]~]#logger "This is 3st test log" [[email protected]~]#tail -f /var/log/messages Feb 4 19:36:43 centos7mini root: This is 3st test log
4、其它日志
其它的日志文件
/var/log/secure(很重要):系统安装日志,文本格式,应周期性分析(用户登录、su切换等)
/var/log/btmp:当前系统上,用户的失败尝试登录相关的日志信息,二进制格式,lastb命令进行查看
/var/log/wtmp:当前系统上,用户正常登录系统的相关日志信息,二进制格式,last命令可以查看
/var/log/lastlog:每一个用户最近一次的登录信息,二进制格式,lastlog命令可以查看
/var/log/dmesg:系统引导过程中的日志信息,文本格式
文本查看工具查看
专用命令dmesg查看/var/log/messages :系统中大部分的信息
/var/log/anaconda : anaconda的日志
[[email protected]~]#cat /var/log/secure [[email protected]~]#lastb [[email protected]~]#uptime #查看开机时间命令 14:30:03 up 1 day, 19:30, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 [[email protected]~]#cat /etc/logrotate.d/syslog #查看日志滚动配置 /var/log/cron /var/log/maillog /var/log/messages /var/log/secure /var/log/spooler { sharedscripts postrotate /bin/kill -HUP `cat /var/run/syslogd.pid 2> /dev/null` 2> /dev/null || true endscript } [[email protected]~]#lastlog Username Port From Latest root pts/1 192.168.1.101 Mon Jan 29 12:58:13 +0800 2018 L **Never logged in** [[email protected]~]#cat /var/log/dmesg | wc -l 1749 [[email protected]~]#dmesg | wc -l 1838
二、日志管理journalctl
Systemd 统一管理所有 Unit 的启动日志。
带来的好处就是,可以只用journalctl一个命令,查看所有日志(内核日志和应用日志)。
日志的配置文件/etc/systemd/journald.conf
journalctl用法
查看所有日志(默认情况下 ,只保存本次启动的日志)
journalctl查看内核日志(不显示应用日志)
journalctl -k查看系统本次启动的日志
journalctl -b
journalctl -b -0查看上一次启动的日志(需更改设置)
journalctl -b -1查看指定时间的日志
journalctl --since="2017-10-30 18:10:30"
journalctl --since "20 min ago"
journalctl --since yesterday
journalctl --since "2017-01-10" --until "2017-01-11 03:00"
journalctl --since 09:00 --until "1 hour ago"显示尾部的最新10行日志
journalctl -n显示尾部指定行数的日志
journalctl -n 20实时滚动显示最新日志
journalctl -f查看指定服务的日志
journalctl /usr/lib/systemd/systemd查看指定进程的日志
journalctl _PID=1查看某个路径的脚本的日志
journalctl /usr/bin/bash查看指定用户的日志
journalctl _UID=33 --since today查看某个 Unit 的日志
journalctl -u nginx.service
journalctl -u nginx.service --since today实时滚动显示某个 Unit 的最新日志
journalctl -u nginx.service -f合并显示多个 Unit 的日志
journalctl -u nginx.service -u php-fpm.service --since today查看指定优先级(及其以上级别)的日志,共有8级
0: emerg
1: alert
2: crit
3: err
4: warning
5: notice
6: info
7: debug
journalctl -p err -b日志默认分页输出,--no-pager 改为正常的标准输出
journalctl --no-pager以 JSON 格式(单行)输出
journalctl -b -u nginx.service -o json以 JSON 格式(多行)输出,可读性更好
journalctl -b -u nginx.serviceqq -o json-pretty显示日志占据的硬盘空间
journalctl --disk-usage指定日志文件占据的最大空间
journalctl --vacuum-size=1G指定日志文件保存多久
journalctl --vacuum-time=1years
三、rsyslog将日志记录于MySQL中
(1) 准备MySQL Server
(2) 在mysql server上授权rsyslog能连接至当前服务器
mysql> GRANT ALL ON Syslog.* TO 'USER'@'HOST' IDENTIFIED BY 'PASSWORD';(3) 在rsyslog服务器上安装mysql模块相关的程序包
yum install rsyslog-mysql(4) 为rsyslog创建数据库及表;
mysql -uUSERNAME -hHOST -pPASSWORD < /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-7.4.7/mysql-createDB.sql(5) 配置rsyslog将日志保存到mysql中
#### MODULES ####
$ModLoad ommysql
#### RULES ####
facility.priority :ommysql:DBHOST,DBNAME,DBUSER, PASSWORD
#实验 [[email protected]~]#yum install rsyslog-mysql.x86_64 #先装包 [[email protected]~]#rpm -ql rsyslog-mysql /lib64/rsyslog/ommysql.so /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-mysql-5.8.10 /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-mysql-5.8.10/createDB.sql [[email protected]~]#scp /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-mysql-5.8.10/createDB.sql 192.168.1.101: [[email protected]~]#mysql MariaDB [(none)]> source createDB.sql Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) MariaDB [Syslog]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | Syslog | | blogdb | | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | +--------------------+ 6 rows in set (0.01 sec) MariaDB [Syslog]> show tables; +------------------------+ | Tables_in_Syslog | +------------------------+ | SystemEvents | | SystemEventsProperties | +------------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [Syslog]> grant all on Syslog.* to [email protected]'192.168.1.100' identified by 'centos'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) [[email protected]~]#vim /etc/rsyslog.conf #### MODULES #### $ModLoad ommysql *.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none :mmysql:92.168.1.101,Syslog,syslog,centos [[email protected]~]#service rsyslog restart Shutting down system logger: [ OK ] Starting system logger: [ OK ] MariaDB [Syslog]> select * from SystemEvents\G; *************************** 9. row *************************** ID: 9 CustomerID: NULL ReceivedAt: 2018-02-04 21:18:42 DeviceReportedTime: 2018-02-04 21:18:42 Facility: 1 Priority: 5 FromHost: localhost Message: Hello mysql
四、通过loganalyzer展示数据库中的日志
(1) 在rsyslog服务器上准备amp或nmp组合
yum install httpd php php-mysql php-gd(2) 安装LogAnalyzer
tar xf loganalyzer-4.1.5.tar.gz
cp -a loganalyzer-4.1.5/src /var/www/html/loganalyzer
cd /var/www/html/loganalyzer
touch config.php
chmod 666 config.php(3)配置loganalyzer
systemctl start httpd.service
http://HOST/loganalyzer
MySQL Native, Syslog Fields, Monitorware(4) 安全加强
cd /var/www/html/loganalyzer
chmod 644 config.php
#实验loganalyzer(日志的分析器) [[email protected]~]#service mysqld start [[email protected]~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 50 *:3306 *:* [[email protected]~]#yum install httpd php php-mysql php-gd [[email protected]]#tar xvf loganalyzer-4.1.6.tar.gz [[email protected]]#cp -r src/ /app/httpd24/htdocs/log/ [[email protected]]#cd /app/httpd24/htdocs/log/ [[email protected]]#ls admin classes details.php include lang search.php userchange.php asktheoracle.php convert.php export.php index.php login.php statistics.php BitstreamVeraFonts cron favicon.ico install.php reportgenerator.php templates chartgenerator.php css images js reports.php themes [[email protected]]#cat /app/src/loganalyzer-4.1.6/contrib/configure.sh #!/bin/sh touch config.php chmod 666 config.php [[email protected]]#cat /app/src/loganalyzer-4.1.6/contrib/secure.sh #!/bin/sh chmod 644 config.php [[email protected]]#cd - [[email protected]]#bash -x configure.sh [[email protected]]#ll -rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 0 Feb 4 21:44 config.php [[email protected]]#chmod 644 config.php

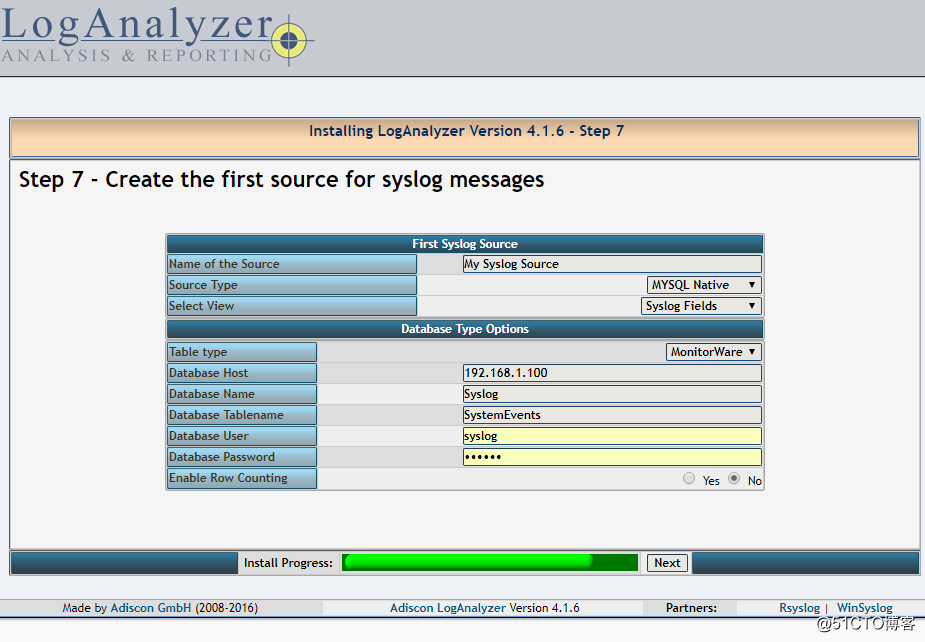
五、Logrotate日志存储
logrotate 程序是一个日志文件管理工具。用来把旧的日志文件删除,并创建新的日志文件,称为日志转储或滚动。可以根据日志文件的大小,也可以根据其天数来转储,这个过程一般通过 cron 程序来执行
配置文件是 /etc/logrotate.conf
主要参数如下
compress 通过gzip 压缩转储以后的日志
nocompress 不需要压缩时,用这个参数
copytruncate 用于还在打开中的日志文件,把当前日志备份并截断
nocopytruncate 备份日志文件但是不截断
create mode owner group 转储文件,使用指定的文件模式创建新的日志文件
nocreate 不建立新的日志文件
delaycompress 和 compress 一起使用时,转储的日志文件到下一次转储时才压缩
nodelaycompress 覆盖 delaycompress 选项,转储并压缩
errors address 专储时的错误信息发送到指定的Email 地址
ifempty 即使是空文件也转储,是缺省选项。
notifempty 如果是空文件的话,不转储
mail address 把转储的日志文件发送到指定的E-mail 地址
nomail 转储时不发送日志文件
olddir directory 转储后的日志文件放入指定的目录,必须和当前日志文件在同一个文件系统
noolddir 转储后的日志文件和当前日志文件放在同一个目录下
prerotate/endscript 在转储以前需要执行的命令可以放入这个对,这两个关键字必须单独成行
postrotate/endscript 在转储以后需要执行的命令可以放入这个对,这两个关键字必须单独成行
daily 指定转储周期为每天
weekly 指定转储周期为每周
monthly 指定转储周期为每月
size 大小 指定日志超过多大时,就执行日志转储
rotate count 指定日志文件删除之前转储的次数,0 指没有备份,5 指保留5 个备份
Missingok 如果日志不存在,提示错误
Nomissingok如果日志不存在,继续下一次日志,不提示错误
[[email protected]~]#rpm -qf /usr/sbin/logrotate logrotate-3.7.8-28.el6.x86_64 [[email protected]~]#rpm -qi logrotate Name : logrotate Relocations: (not relocatable) Version : 3.7.8 Vendor: CentOS Release : 28.el6 Build Date: Wed 22 Mar 2017 05:11:03 AM CST Install Date: Tue 23 Jan 2018 03:20:37 PM CST Build Host: c1bm.rdu2.centos.org Group : System Environment/Base Source RPM: logrotate-3.7.8-28.el6.src.rpm Size : 89448 License: GPL+ Signature : RSA/SHA1, Thu 23 Mar 2017 11:03:45 PM CST, Key ID 0946fca2c105b9de Packager : CentOS BuildSystem <http://bugs.centos.org> URL : https://fedorahosted.org/logrotate/ Summary : Rotates, compresses, removes and mails system log files Description : The logrotate utility is designed to simplify the administration of log files on a system which generates a lot of log files. Logrotate allows for the automatic rotation compression, removal and mailing of log files. Logrotate can be set to handle a log file daily, weekly, monthly or when the log file gets to a certain size. Normally, logrotate runs as a daily cron job. Install the logrotate package if you need a utility to deal with the log files on your system. #logrotate实用程序旨在简化对生成大量日志文件的系统上日志文件的管理。 Logrotate允许自动旋转压缩,删除和邮寄日志文件。 Logrotate可以设置为每天,每周,每月或当日志文件达到一定的大小时处理日志文件。 通常,logrotate作为日常的cron作业运行。如果需要一个实用程序来处理日志文件在您的系统上。 [[email protected]~]#rpm -ql logrotate /etc/cron.daily/logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf /etc/logrotate.d /usr/sbin/logrotate /usr/share/doc/logrotate-3.7.8 /usr/share/doc/logrotate-3.7.8/CHANGES /usr/share/doc/logrotate-3.7.8/COPYING /usr/share/man/man5/logrotate.conf.5.gz /usr/share/man/man8/logrotate.8.gz /var/lib/logrotate.status [[email protected]~]#cat /etc/cron.daily/logrotate #!/bin/sh /usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf EXITVALUE=$? if [ $EXITVALUE != 0 ]; then /usr/bin/logger -t logrotate "ALERT exited abnormally with [$EXITVALUE]" fi exit 0 [[email protected]~]#cat /etc/logrotate.conf # see "man logrotate" for details # rotate log files weekly weekly # keep 4 weeks worth of backlogs rotate 4 # create new (empty) log files after rotating old ones create # use date as a suffix of the rotated file dateext # uncomment this if you want your log files compressed #compress # RPM packages drop log rotation information into this directory include /etc/logrotate.d # no packages own wtmp and btmp -- we'll rotate them here /var/log/wtmp { monthly create 0664 root utmp minsize 1M rotate 1 } /var/log/btmp { missingok monthly create 0600 root utmp rotate 1 } # system-specific logs may be also be configured here.
以上是关于Linux学习之路--日志管理17---20180113的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章