MyBatis源码阅读: MyBatis基础模块-反射模块
Posted 循环网络不循环
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MyBatis源码阅读: MyBatis基础模块-反射模块相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、概述
MyBatis在进行参数处理、结果集映射等操作时会使用到大量的反射操作,Java中的反射功能虽然强大,但是代码编写起来比较复杂且容易出错,为了简化反射操作的相关代码,MyBatis提供了专门的反射模块,该模块位于org.apache.ibatis.reflection包下,它对常见的反射操作做了进一步的封装,提供了更加简洁方便的反射API。

二、反射模块
(一)Reflector
1、属性
首先来看下Reflector中提供的相关属性的含义
// 对应的Class 类型
private final Class<?> type;
// 可读属性的名称集合 可读属性就是存在 getter方法的属性,初始值为null
private final String[] readablePropertyNames;
// 可写属性的名称集合 可写属性就是存在 setter方法的属性,初始值为null
private final String[] writablePropertyNames;
// 记录了属性相应的setter方法,key是属性名称,value是Invoker方法
// 他是对setter方法对应Method对象的封装
private final Map<String, Invoker> setMethods = new HashMap<>();
// 属性相应的getter方法
private final Map<String, Invoker> getMethods = new HashMap<>();
// 记录了相应setter方法的参数类型,key是属性名称 value是setter方法的参数类型
private final Map<String, Class<?>> setTypes = new HashMap<>();
// 和上面的对应
private final Map<String, Class<?>> getTypes = new HashMap<>();
// 记录了默认的构造方法
private Constructor<?> defaultConstructor;
// 记录了所有属性名称的集合
private Map<String, String> caseInsensitivePropertyMap = new HashMap<>();2、构造方法
在Reflector的构造器中会完成相关的属性的初始化操作
// 解析指定的Class类型 并填充上述的集合信息
public Reflector(Class<?> clazz)
type = clazz; // 初始化 type字段
addDefaultConstructor(clazz);// 设置默认的构造方法
addGetMethods(clazz);// 获取getter方法
addSetMethods(clazz); // 获取setter方法
addFields(clazz); // 处理没有getter/setter方法的字段
// 初始化 可读属性名称集合
readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
// 初始化 可写属性名称集合
writablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
// caseInsensitivePropertyMap记录了所有的可读和可写属性的名称 也就是记录了所有的属性名称
for (String propName : readablePropertyNames)
// 属性名称转大写
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
for (String propName : writablePropertyNames)
// 属性名称转大写
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
(二)ReflectorFactory
ReflectorFactory接口主要实现了对Reflector对象的创建和缓存。接口的定义如下:
public interface ReflectorFactory
// 检测该ReflectorFactory是否缓存了Reflector对象
boolean isClassCacheEnabled();
// 设置是否缓存Reflector对象
void setClassCacheEnabled(boolean classCacheEnabled);
// 创建指定了Class的Reflector对象
Reflector findForClass(Class<?> type);
然后我们来看看它的具体实现
1、DefaultReflectorFactory
MyBatis只为该接口提供了DefaultReflectorFactory这一个实现类。他与Reflector的关系如下:
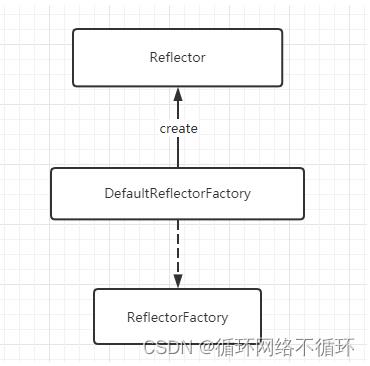
DefaultReflectorFactory中的实现,代码比较简单,我们直接贴出来
public class DefaultReflectorFactory implements ReflectorFactory
private boolean classCacheEnabled = true;
// 实现对 Reflector 对象的缓存
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Reflector> reflectorMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public DefaultReflectorFactory()
@Override
public boolean isClassCacheEnabled()
return classCacheEnabled;
@Override
public void setClassCacheEnabled(boolean classCacheEnabled)
this.classCacheEnabled = classCacheEnabled;
@Override
public Reflector findForClass(Class<?> type)
if (classCacheEnabled) // 开启缓存
// synchronized (type) removed see issue #461
return reflectorMap.computeIfAbsent(type, Reflector::new);
else
// 没有开启缓存就直接创建
return new Reflector(type);
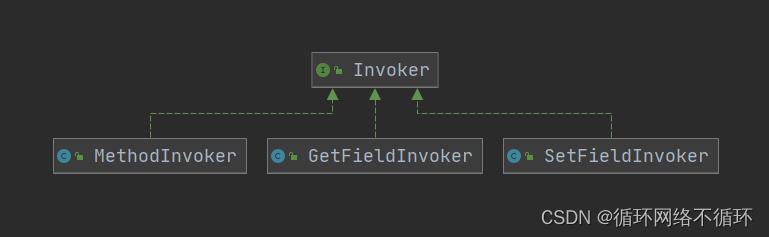
(三)Invoker
针对于Class中Field和Method的调用,在MyBatis中封装了Invoker对象来统一处理(有使用到适配器模式)
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface Invoker
// 执行Field或者Method
Object invoke(Object target, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException;
// 返回属性相应的类型
Class<?> getType();
该接口有对应的三个实现
(四)MetaClass
在Reflector中可以针对普通的属性操作,但是如果出现了比较复杂的属性,比如 private Person person; 这种,我们要查找的表达式 person.userName.针对这种表达式的处理,这时就可以通过MetaClass来处理了。我们来看看主要的属性和构造方法。
/**
* 通过 Reflector 和 ReflectorFactory 的组合使用 实现对复杂的属性表达式的解析
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class MetaClass
// 缓存 Reflector
private final ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory;
// 创建 MetaClass时 会指定一个Class reflector会记录该类的相关信息
private final Reflector reflector;
private MetaClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory)
this.reflectorFactory = reflectorFactory;
this.reflector = reflectorFactory.findForClass(type);
// ....
(五)MetaObject
我们可以通过MetaObject对象解析复杂的表达式来对提供的对象进行操作。具体的通过案例来演示会更直观些
@Test
public void shouldGetAndSetField()
RichType rich = new RichType();
MetaObject meta = SystemMetaObject.forObject(rich);
meta.setValue("richField", "foo");
System.out.println(meta.getValue("richField"));
@Test
public void shouldGetAndSetNestedField()
RichType rich = new RichType();
MetaObject meta = SystemMetaObject.forObject(rich);
meta.setValue("richType.richField", "foo");
System.out.println(meta.getValue("richType.richField"));
@Test
public void shouldGetAndSetMapPairUsingArraySyntax()
RichType rich = new RichType();
MetaObject meta = SystemMetaObject.forObject(rich);
meta.setValue("richMap[key]", "foo");
System.out.println(meta.getValue("richMap[key]"));
以上三个方法的输出结果都是foo
三、反射模块的应用
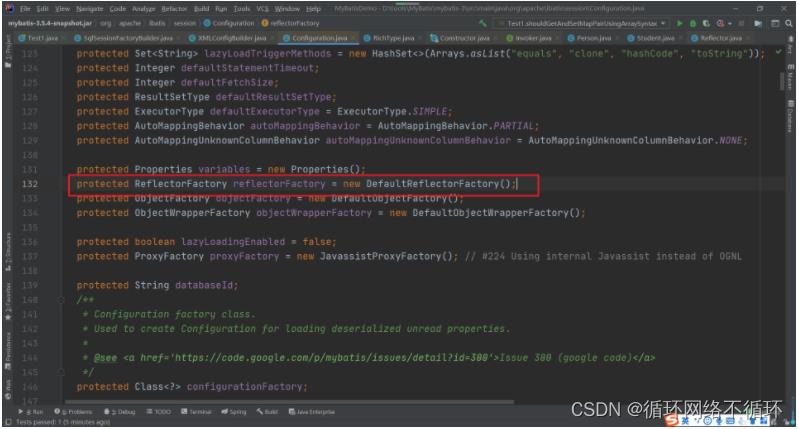
(一)SqlSessionFactory
在创建SqlSessionFactory操作的时候会完成Configuration对象的创建,而在Configuration中默认定义的ReflectorFactory的实现就是DefaultReflectorFactory对象。然后在解析全局配置文件的代码中,给用户提供了ReflectorFactory的扩展,也就是我们在全局配置文件中可以通reflectorFactory标签来使用我们自定义的ReflectorFactory。
(二)执行SQL
在Statement获取结果集后,在做结果集映射的使用有使用到,在DefaultResultSetHandler的createResultObject方法中。
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException
this.useConstructorMappings = false; // reset previous mapping result 标识是否使用 构造函数创建对象
// 记录构造函数的参数类型
final List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes = new ArrayList<>();
// 记录构造函数的实参
final List<Object> constructorArgs = new ArrayList<>();
// 创建该行记录对应的结果对象,核心步骤
Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
if (resultObject != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType()))
final List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings)
// 如果有嵌套查询且配置了延迟加载,则创建代理对象
if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null && propertyMapping.isLazy())
resultObject = configuration.getProxyFactory().createProxy(resultObject, lazyLoader, configuration, objectFactory, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs);
break;
this.useConstructorMappings = resultObject != null && !constructorArgTypes.isEmpty(); // set current mapping result
return resultObject;
然后在DefaultResultSetHandler的getRowValue方法中在做自动映射的时候
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, CacheKey combinedKey, String columnPrefix, Object partialObject) throws SQLException
final String resultMapId = resultMap.getId();
Object rowValue = partialObject;
if (rowValue != null)
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue);
putAncestor(rowValue, resultMapId);
applyNestedResultMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix, combinedKey, false);
ancestorObjects.remove(resultMapId);
else
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
rowValue = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
if (rowValue != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType()))
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue);
boolean foundValues = this.useConstructorMappings;
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, true))
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix) || foundValues;
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, columnPrefix) || foundValues;
putAncestor(rowValue, resultMapId);
foundValues = applyNestedResultMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix, combinedKey, true) || foundValues;
ancestorObjects.remove(resultMapId);
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
rowValue = foundValues || configuration.isReturnInstanceForEmptyRow() ? rowValue : null;
if (combinedKey != CacheKey.NULL_CACHE_KEY)
nestedResultObjects.put(combinedKey, rowValue);
return rowValue;
继续跟踪,在createAutomaticMappings方法中
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException
// 获取ResultSet中存在,但在ResultMap中没有明确映射的列
List<UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (!autoMapping.isEmpty())
for (UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping)
// 使用TypeHandler 获取自定映射的列值
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null)
foundValues = true;
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !mapping.primitive))
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
// 将自动映射的属性值设置到结果对象中
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
return foundValues;
MyBatis源码分析-基础支持层反射模块Reflector/ReflectorFactory
本文主要介绍MyBatis的反射模块是如何实现的。
MyBatis 反射的核心类Reflector,下面我先说明它的构造函数和成员变量。具体方法下面详解。
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector public class Reflector { private final Class<?> type; //对应的Class 类型 //可读属性的名称集合,可读属性就是存在相应getter 方法的属性,初始值为空数纽 private final String[] readablePropertyNames; //可写属性的名称集合,可写属性就是存在相应setter 方法的属性,初始值为空数纽 private final String[] writeablePropertyNames; //记录了属性相应的setter 方法, key 是属性名称, value 是Invoker 对象,它是对setter 方法对应 private final Map<String, Invoker> setMethods = new HashMap<>(); //记录了属性相应的getter 方法, key 是属性名称, value 是Invoker 对象,它是对setter 方法对应 private final Map<String, Invoker> getMethods = new HashMap<>(); //记录了属性相应的setter 方法的参数值类型, ke y 是属性名称, value 是setter 方法的参数类型 private final Map<String, Class<?>> setTypes = new HashMap<>(); //记录了属性相应的getter 方法的返回位类型, key 是属性名称, value 是getter 方法的返回位类型 private final Map<String, Class<?>> getTypes = new HashMap<>(); //记录了默认构造方法 private Constructor<?> defaultConstructor; //记录了所有属性名称的集合 private Map<String, String> caseInsensitivePropertyMap = new HashMap<>(); public Reflector(Class<?> clazz) { type = clazz; //查找clazz的无参构造方法,通过反射遍历所有构造方法,找到构造参数集合长度为0的。 addDefaultConstructor(clazz); //处理clazz 中的getter 方法,填充getMethods 集合和getTypes 集合 addGetMethods(clazz); //处理clazz 中的set ter 方法,填充setMethods 集合和set Types 集合 addSetMethods(clazz); //处理没有get/set的方法字段 addFields(clazz); //初始化可读写的名称集合 readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[getMethods.keySet().size()]); writeablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[setMethods.keySet().size()]); //初始化caseInsensitivePropertyMap ,记录了所有大写格式的属性名称 for (String propName : readablePropertyNames) { caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName); } for (String propName : writeablePropertyNames) { caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName); } } 。。。。。。。。。。。。具体代码先忽略,通过构造函数的调用慢慢渗透。 }
1:addDefaultConstructor() // 查找clazz的无参构造方法,通过反射遍历所有构造方法,找到构造参数集合长度为0的。
主要实现的思想是,通过clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();获取所有构造方法集合,然后循环遍历 判断参数长度为0的,并且构造函数权限可控制的设为默认构造方法。
private void addDefaultConstructor(Class<?> clazz) { Constructor<?>[] consts = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors(); for (Constructor<?> constructor : consts) { if (constructor.getParameterTypes().length == 0) { //判断反射对象的控制权限 为true是可控制 if (canControlMemberAccessible()) { try { //设置Accessible为true后,反射可以访问私有变量。 constructor.setAccessible(true); } catch (Exception e) { // Ignored. This is only a final precaution, nothing we can do. } } if (constructor.isAccessible()) { this.defaultConstructor = constructor; } } } }
2:addGetMethods(clazz)// 处理clazz 中的getter 方法,填充getMethods 集合和getTypes 集合
private void addGetMethods(Class<?> cls) { Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters = new HashMap<>(); //获取当前类以及父类中定义的所有方法的唯一签名以及相应的Method对象。 Method[] methods = getClassMethods(cls); for (Method method : methods) { if (method.getParameterTypes().length > 0) { continue; } String name = method.getName(); //判断如果方法明是以get开头并且方法名长度大于3 或者 方法名是以is开头并且长度大于2 if ((name.startsWith("get") && name.length() > 3) || (name.startsWith("is") && name.length() > 2)) { //将方法名截取,如果是is从第二位截取,如果是get或者set从第三位开始截取 name = PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(name); //addMethodConflict 方法内部很简单只有两行代码: //1:List<Method> list=conflictingGetters.computeIfAbsent(name,K->new ArrayList<>()); 这句话的意思是,在conflictingGetters 的Map中 如果key中存在name,name什么都不做,将value返回,如果name不存在,则返回一个新的ArrayList. //2:list.add(method); 将方法对象添加到list对象中。 addMethodConflict(conflictingGetters, name, method); } } resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters); }
2-1:getClassMethods(cls);//获取当前类以及父类中定义的所有方法的唯一签名以及相应的Method对象。
private Method[] getClassMethods(Class<?> cls) { Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods = new HashMap<>(); Class<?> currentClass = cls; while (currentClass != null && currentClass != Object.class) { //currentClass.getDeclaredMethods(),获取当前类的所有方法 //addUniqueMethods 为每个方法生成唯一签名,并记录到uniqueMethods集合中 addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, currentClass.getDeclaredMethods()); // we also need to look for interface methods - // because the class may be abstract Class<?>[] interfaces = currentClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) { addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, anInterface.getMethods()); } currentClass = currentClass.getSuperclass(); } Collection<Method> methods = uniqueMethods.values(); return methods.toArray(new Method[methods.size()]); }
2-1-1: addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, currentClass.getDeclaredMethods()); 为每个方法生成唯一签名,并记录到uniqueMethods集合中
private void addUniqueMethods(Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods, Method[] methods) { for (Method currentMethod : methods) { //判断是不是桥接方法, 桥接方法是 JDK 1.5 引入泛型后,为了使Java的泛型方法生成的字节码和 1.5 版本前的字节码相兼容,由编译器自动生成的方法 if (!currentMethod.isBridge()) { //获取签名 // 签名格式为:方法返回参数#方法名:参数名 ps:多个参数用,分割 签名样例:String#getName:User String signature = getSignature(currentMethod); // check to see if the method is already known // if it is known, then an extended class must have // overridden a method //如果签名存在,则不做处理,表示子类已经覆盖了该方法。 //如果签名不存在,则将签名作为Key,Method作为value 添加到uniqueMethods中 if (!uniqueMethods.containsKey(signature)) { if (canControlMemberAccessible()) { try { currentMethod.setAccessible(true); } catch (Exception e) { // Ignored. This is only a final precaution, nothing we can do. } } uniqueMethods.put(signature, currentMethod); } } } }
2-2: resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters);;//在2-1中返回的方法可能存在,两个相同的方法名称,因为当子类实现父类方法时且参数不同,此时2-1生成的签名是不同的生成签名的规则是 方法返回值#方法名#参数名,那么就会返回两个相同的方法名。 resolveGetterConflicts方法会对这种覆写的情况进行处理,同时将处理后的getter方法记录到getMethods集合中,将其返回值类型填充到getTypes集合中。 内部实现主要是两个for循环,循环比较方法名称相同的情况下,返回值不同的情况下,拿第二个当最终想要的Method。
private void resolveGetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters) { for (Entry<String, List<Method>> entry : conflictingGetters.entrySet()) { Method winner = null; String propName = entry.getKey(); for (Method candidate : entry.getValue()) { if (winner == null) { winner = candidate; continue; } Class<?> winnerType = winner.getReturnType(); Class<?> candidateType = candidate.getReturnType(); if (candidateType.equals(winnerType)) { if (!boolean.class.equals(candidateType)) { throw new ReflectionException( "Illegal overloaded getter method with ambiguous type for property " + propName + " in class " + winner.getDeclaringClass() + ". This breaks the JavaBeans specification and can cause unpredictable results."); } else if (candidate.getName().startsWith("is")) { winner = candidate; } } else if (candidateType.isAssignableFrom(winnerType)) { // OK getter type is descendant } else if (winnerType.isAssignableFrom(candidateType)) { winner = candidate; } else { throw new ReflectionException( "Illegal overloaded getter method with ambiguous type for property " + propName + " in class " + winner.getDeclaringClass() + ". This breaks the JavaBeans specification and can cause unpredictable results."); } } addGetMethod(propName, winner); } }
总结一下addGetMethods(clazz)方法和addSetMethods(clazz)大致相同:
首先创建:
Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters = new HashMap<>();
1:获取子类和父类的所有方法。 获取方法是:先生成唯一签名,唯一签名规则是方法返回值#方法名:方法参数1,方法参数2 。 根据签名作为key,method对象作为value生成Map,通过签名进行过滤,将此Map转换为List返回。
2:循环遍历Map,找到符合条件的方法名,is开头或者get开头的,将方法名截取,截取后的方法名作为key,List<Method>作为value,放入到conflictingGetters中。
3:由于子类存在实现父类方法,且返回值不同的情况,导致用一方法名可能有不同的Method ,第三步 resolveGetterConflicts方法会对这种覆写的情况进行处理,同时将处理后的getter方法记录到getMethods集合中,将其返回值类型填充到getTypes集合中。
Reflector Factory 接口主要实现了对Reflector对象的创建和缓存,有三个方法:该接口定义如下:
public interface ReflectorFactory { boolean isClassCacheEnabled(); //检测该ReflectorFactory对象是否会缓存Reflector对象 void setClassCacheEnabled(boolean classCacheEnabled);//设置是否缓存Reflector对象 Reflector findForClass(Class<?> type); //创建指定class对应的Reflector对象 }
Reflector Factory的实现是DefaultReflectorFactory,具体实现如下:
public class DefaultReflectorFactory implements ReflectorFactory { private boolean classCacheEnabled = true; private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Reflector> reflectorMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public DefaultReflectorFactory() { } @Override public boolean isClassCacheEnabled() { return classCacheEnabled; } @Override public void setClassCacheEnabled(boolean classCacheEnabled) { this.classCacheEnabled = classCacheEnabled; } @Override public Reflector findForClass(Class<?> type) { //如果开启缓存,Reflector对象从ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Reflector> 取出。 if (classCacheEnabled) { // synchronized (type) removed see issue #461 return reflectorMap.computeIfAbsent(type, Reflector::new); } else {//没开启缓存,重新创建。 return new Reflector(type); } } }
DefaultReflectorFactory 的缓存是通过ConcurrentMap来实现的,如果开启了缓存,那么就从ConcurrentMap取Reflector,如果没有开启,就新建Reflector.
除了使用MyBatis提供的DefaultReflectorFactory实现,我们还可以在mybatis-config.xml中配置自定义的ReflectorFactory 实现类,从而实现功能上的扩展。
以上是关于MyBatis源码阅读: MyBatis基础模块-反射模块的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章