Java使用不同方式获取两个集合List的交集补集并集(相加)差集(相减)
Posted 吳名氏
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java使用不同方式获取两个集合List的交集补集并集(相加)差集(相减)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 明确概念
首先知道几个单词的意思:
并集 = union
交集 = intersection
补集 = complement
析取 = disjunction
减去 = subtract
1.1 并集
对于两个给定集合A、B,由两个集合所有元素构成的集合,叫做A和B的并集。
记作:AUB 读作“A并B”
例:3,5U2,3,4,6= 2,3,4,5,6
1.2 交集
对于两个给定集合A、B,由属于A又属于B的所有元素构成的集合,叫做A和B的交集。
记作: A∩B 读作“A交B”
例:A=1,2,3,4,5,B=3,4,5,6,8,A∩B=3,4,5
1.3 补集
一般地,设S是一个集合,A是S的一个子集,由S中所有不属于A的元素组成的集合,叫做子集A在S中的绝对补集。
记作:∁UA,包括三层含义:
1)A是U的一个子集,即A⊊U;
2)∁UA表示一个集合,且∁UA⊊U;
3)∁UA是由U中所有不属于A的元素组成的集合,∁UA与A没有公共元素,U中的元素分布在这两个集合中。
2 使用apache工具包
2.1 导入依赖
<!-- apache 集合工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.1</version>
</dependency>2.2 代码如下:
public static final List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", null);
public static final List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "D", "E", "F", null);
/**
* apache测试方法
*/
@Test
public void apacheTest()
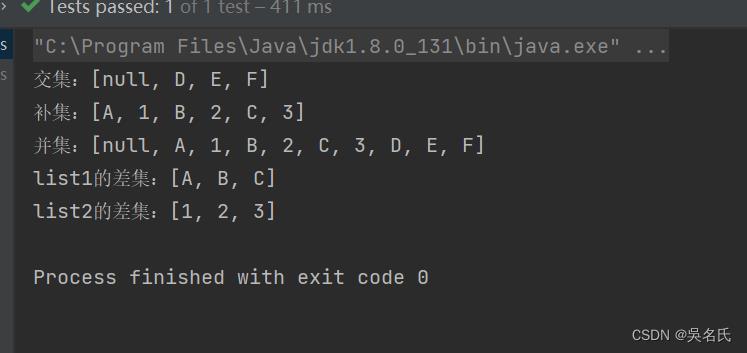
System.out.println("交集:" + CollectionUtils.intersection(list1, list2)); // 交集
System.out.println("补集:" + CollectionUtils.disjunction(list1, list2)); // 补集
System.out.println("并集:" + CollectionUtils.union(list1, list2)); // 并集
System.out.println("list1的差集:" + CollectionUtils.subtract(list1, list2)); // list1的差集
System.out.println("list2的差集:" + CollectionUtils.subtract(list2, list1)); // list2的差集
输出:
3 使用hutool工具包
3.1 导入依赖
<!-- hutool工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.12</version>
</dependency>3.2 代码如下:
public static final List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", null);
public static final List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "D", "E", "F", null);
/**
* hutool工具类
*/
@Test
public void hutoolTest()
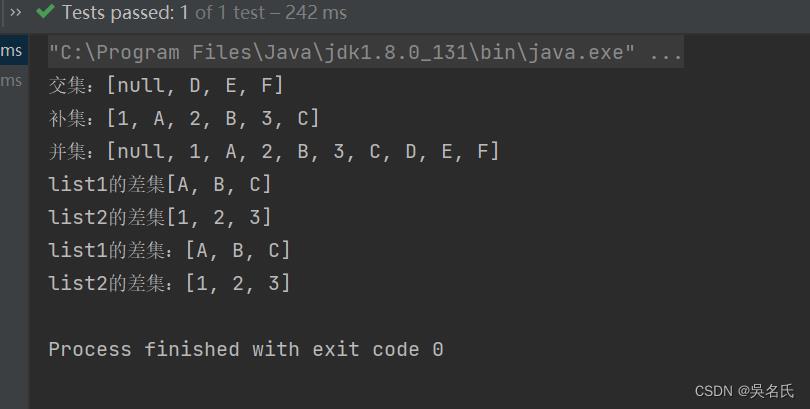
System.out.println("交集:" + CollectionUtil.intersection(list1, list2)); // 交集
System.out.println("补集:" + CollectionUtil.disjunction(list1, list2)); // 补集
System.out.println("并集:" + CollectionUtil.union(list1, list2)); //并集
System.out.println("list1的差集"+CollectionUtil.subtract(list1,list2));
System.out.println("list2的差集"+CollectionUtil.subtract(list2,list1));
System.out.println("list1的差集:" + CollectionUtil.subtractToList(list1, list2));
System.out.println("list2的差集:" + CollectionUtil.subtractToList(list2, list1));
输出:
3.3 注意
subtract()和subtractToList()作用一样,不过处理方式不同,使用subtract()时,参数不能是Arrays.asList()的结果,否则会报异常,因为Arrays.asList()返回的对象是Arrays.ArrayList,在方法实现里面调用的是AbstractList抽象类里面的removeAll()方法,该方法代码如下:
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E>
// ....
public E remove(int index)
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
// ....
4 使用stream方式
4.1 代码如下:
public static final List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", null);
public static final List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "D", "E", "F", null);
/**
* stream方式
*/
@Test
public void streamTest()
List<Object> intersection = list1.stream().filter(list2::contains).collect(Collectors.toList());
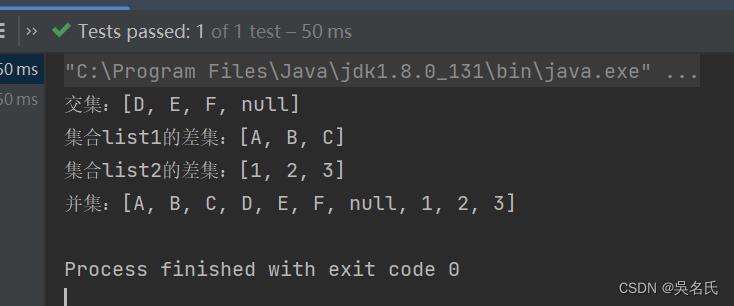
System.out.println("交集:" + intersection);
List<String> subtract1 = list1.stream().filter(s -> !list2.contains(s)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("集合list1的差集:" + subtract1);
List<String> subtract2 = list2.stream().filter(s -> !list1.contains(s)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("集合list2的差集:" + subtract2);
List<String> union1 = list1.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> union2 = list2.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toList());
union1.addAll(union2);
List<String> union3 = union1.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("并集:" + union3);
输出:
5 使用Collection接口中的方法
5.1 代码如下:
public static String[] attr1 = new String[]"A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", null;
public static String[] attr2 = new String[]"1", "2", "3", "D", "E", "F", null;
/**
* 使用Collection接口中的方法
*/
@Test
public void collectionTest()
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr1));
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr2));
list1.retainAll(list2);
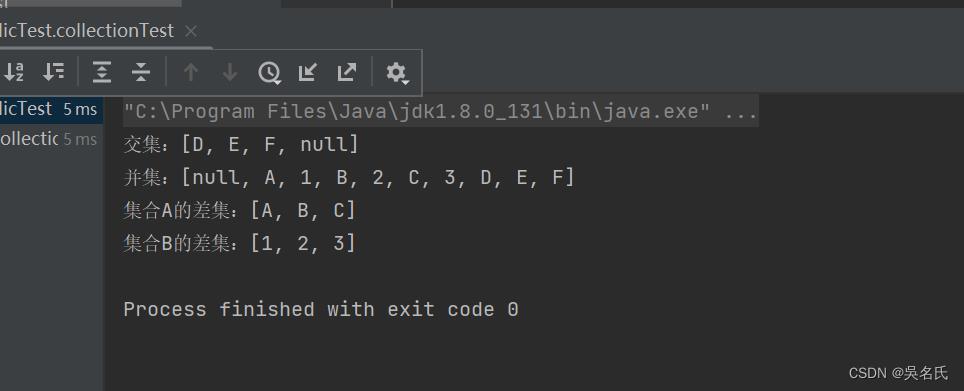
System.out.println("交集:" + list1);
ArrayList<String> list3 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr1));
ArrayList<String> list4 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr2));
Set<Object> set = new HashSet<>();
set.addAll(list3);
set.addAll(list4);
System.out.println("并集:" + set);
ArrayList<String> list5 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr1));
ArrayList<String> list6 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr2));
list5.removeAll(list6);
System.out.println("集合A的差集:" + list5);
ArrayList<String> list7 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr1));
ArrayList<String> list8 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(attr2));
list8.removeAll(list7);
System.out.println("集合B的差集:" + list8);
输出:
Python求两个list的交集并集补集对称差集的两种方法
1、使用set集合运算符
a = [0,1,2,3,4]
b = [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
list(set(a) & set(b)) # 使用 "&" 运算求a与b的交集,输出:[3, 4]
list(set(a) | set(b)) # 使用 "|" 运算求a与b的并集,输出:[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
list(set(b) - set(a)) # 使用 "-" 运算求a与b的差(补)集: 求b中有而a中没有的元素,输出:[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
list(set(a) - set(b)) # 使用 "-" 运算求a与b的差(补)集: 求a中有而b中没有的元素,输出: [0, 1, 2]
list(set(a) ^ set(b)) # 使用 "^" 运算求a与b的对称差集,输出:[0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
结果:
求交集: list(set(a) & set(b)) 输出 -> [3, 4]
求并集: list(set(a) | set(b)) 输出 -> [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
求差(补)集: list(set(b) - set(a)) 输出 -> [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
求差(补)集: list(set(a) - set(b)) 输出 -> [0, 1, 2]
求对称差集: list(set(a) ^ set(b)) 输出 -> [0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
2、 使用set集合的方法 (高效率)
a = [0,1,2,3,4]
b = [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
print(list(set(a).intersection(set(b)))) # 使用 intersection 求a与b的交集,输出:[3, 4]
print(list(set(a).union(b)) ) # 使用 union 求a与b的并集,输出:[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(list(set(b).difference(set(a)))) # 使用 difference 求a与b的差(补)集:求b中有而a中没有的元素,输出: [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(list(set(a).difference(set(b))) ) # 使用 difference 求a与b的差(补)集:求a中有而b中没有的元素,输出:[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(list(set(a).symmetric_difference(b))) # 使用 symmetric_difference 求a与b的对称差集,输出:[0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
结果:
[3, 4]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
[0, 1, 2]
[0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
以上是关于Java使用不同方式获取两个集合List的交集补集并集(相加)差集(相减)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章