蓝桥杯小白必看 —— Python
Posted 萌新的小太阳
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了蓝桥杯小白必看 —— Python相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
蓝桥杯小白必看 —— Python
文章目录
一、Python比赛规则
大赛官网比赛规则链接(可自行下载):https://dasai.lanqiao.cn/notices/846/
值得注意的是:
- 比赛编译环境:必须是Python 3.8.6的IDLE环境
- 考察的算法范围:
(1)计算机算法:枚举、排序、搜索、计数、贪心、动态规划、图论、数论、博弈论、概率论、计算几何、字符串算法等
(2) 数据结构:数组、对象/结构、字符串、队列、栈、树、图、堆、平衡树/线段树、复杂数据结构、嵌套数据结构等 - 不可用Python第三方库,只可用Python自带的标准库
- 考察方式:填空题和编程大题
- 比赛时间:4小时
二、Python3.8.6的IDLE环境
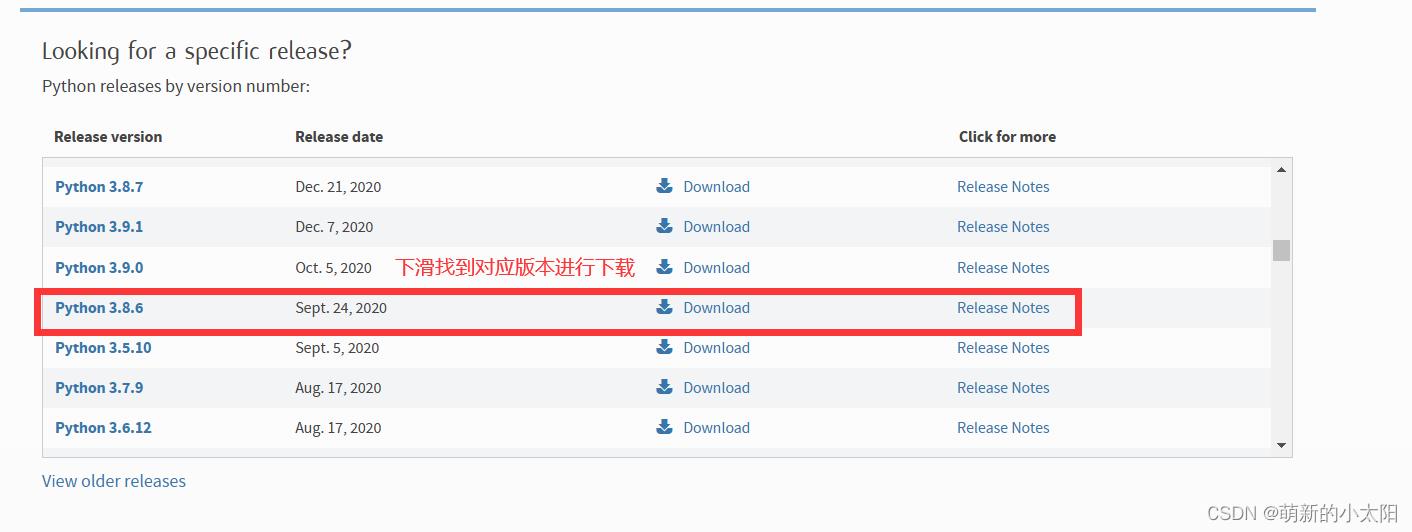
1. 官网下载地址
https://www.python.org/downloads/
2. 让编译器显示行数
打开Python编译器,点击Options下拉栏中的Configure IDLE
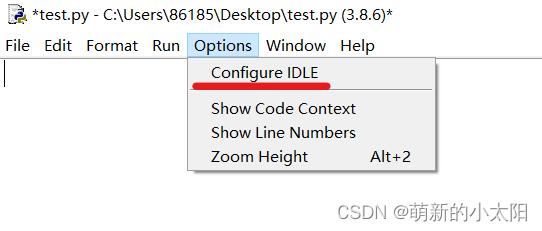
选中General,勾选Show line numbers in new windows,最后点击OK即可

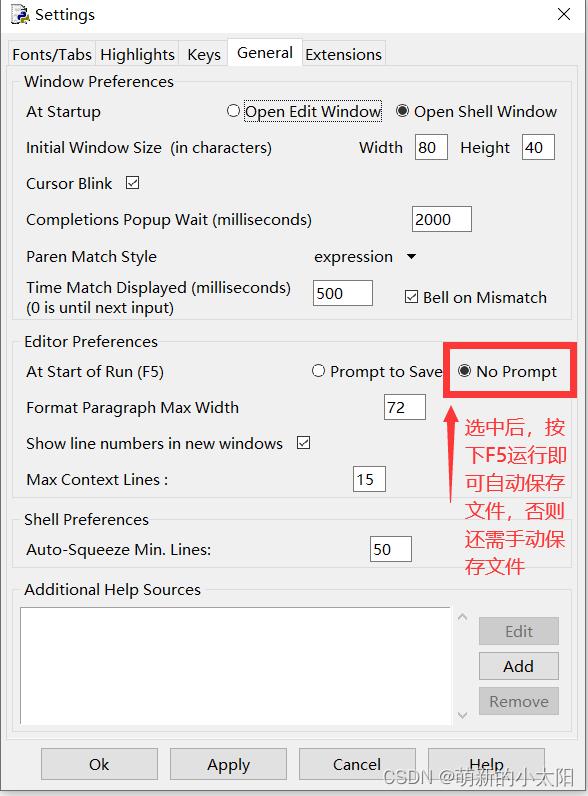
3. 设置自动保存
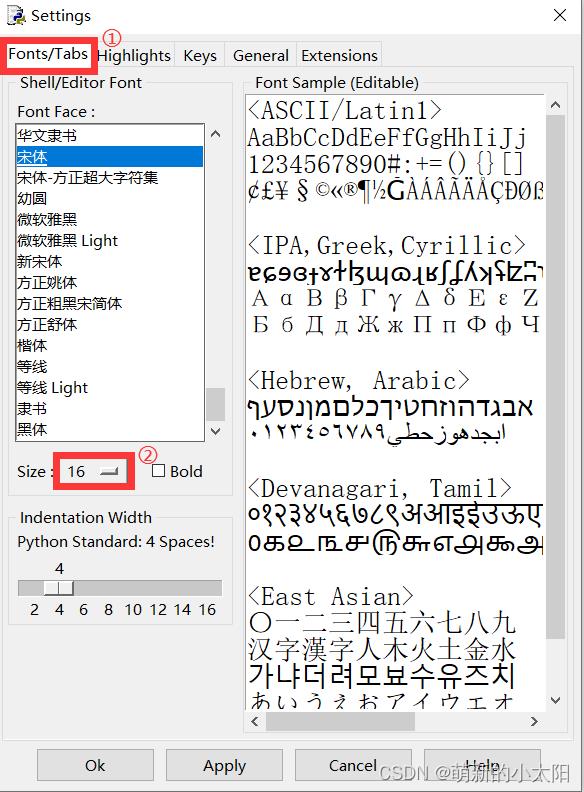
4. 设置页面字体大小
选中Fonts/Tabs后,可根据自己的喜好设置字体样式和字体大小
5. 快捷键的使用
(1)自动补齐代码: Tab键
(2)运行: F5
(3)加注释: Alt + 3
(4)去注释: Alt + 4
(5)撤回上一步: Clt +Z
(6)加缩进: Clt + [
(7)去缩进: Clt + ]
(8)查看用户手册: F1
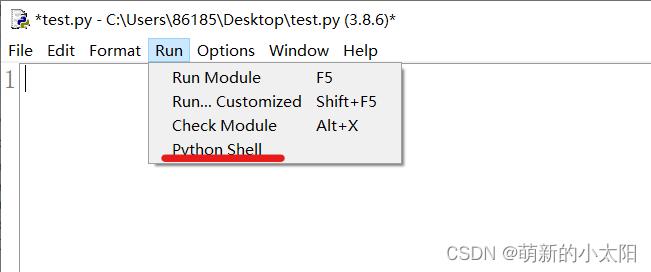
**注:**另外我们可以在Python shell中进行代码的调试,可以在Run中打开
其中有也有两种常用的快捷键是:
(1)调换上一条命令: Alt + p
(2)调换下一条命令: Alt + N
三、备赛建议
1. 第一阶段(Python小白)
对于初次参加比赛的Python小白来说,建议可以先去中国慕课学习北京理工的Python课程,以及菜鸟教程中,所有Python的关键字、函数、标准库的使用。
快速学习一遍即可,可以适当记录一些笔记备于后续刷题时使用。
2. 第二阶段(Python初学)
再推荐到微信搜索 “Python小屋”,获取刷题软件,每天刷至少10道题,刷至少一个月,积累题感。
3. 第三阶段(Python进阶)
到蓝桥官网刷真题,学习不懂的数据结构和算法
推荐学习视频: b站Python数据结构(清华大学)
后续还有更多有关蓝桥Python备赛的文章会发布哦!!!
蓝桥杯BFS从此搞懂搜索题的套路! | 入门必看
目录
注意的点:题目地图范围是从(1,1)~(n,n),我们是从(0,0)~(n+1,n+1),即扩大一圈最外圈全部为0,这样当我们搜索(bfs)即可满足将外围的0全部标记
BFS可用于解决2类问题:
1.从A点出发是否存在到达B的路径;DFS也可以
2.从A点出发到达B的最短路径;数据小于20以内的话,DFS也不是不可以
整体思路
其思路为从图上一个节点出发,先访问其直接相连的子节点,若子节点不符合,再问其他子节点,按级别顺序(一层一层)依次访问,直到访问到目标节点。
步骤
- 起始:将起点(源点,树的根节点)放入队列中
- 扩散:从队列中取出队头的节点,将它相邻节点放入队列中,不断重复这一步
- 终止:当队列为空时,说明我们遍历了所有的能到的结点,整个图能到的点都被搜索了一遍
贴一个非常详细的学习视频
简单热身题
第一题:走迷宫-BFS
题目描述
给定一个 n×m 的二维整数数组,用来表示一个迷宫,数组中只包含 0 或 1,其中 0 表示可以走的路,11 表示不可通过的墙壁。最初,有一个人位于左上角 (1,1) 处,已知该人每次可以向上、下、左、右任意一个方向移动一个位置。
请问,该人从左上角移动至右下角 (n,m) 处,至少需要移动多少次。
数据保证 (1,1) 处和 (n,m) 处的数字为 0,且一定至少存在一条通路。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 n 和 m。
接下来 n 行,每行包含 m 个整数(0 或 1),表示完整的二维数组迷宫。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示从左上角移动至右下角的最少移动次数。
数据范围
1≤n,m≤100
输入样例:
5 5 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
输出样例:8
题目分析
难点
- 方向坐标:4连通
static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0;用队列存每一个位置的坐标
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();//存坐标 q.offer(new Pair(1, 1));//将起始位置坐标放入队头坐标用一个类来存取
class Pair int x, y; public Pair(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;边界是什么
if (a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > m) continue;//越界,需要换一个方向 if (map[a][b] ==1 || dist[a][b] > 0) continue;//障碍,遍历过的点就不搜索了
题目代码
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.generic.IF_ACMPEQ; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Scanner; public class 走迷宫_bfs static int n, m, res=0; static int[][] map = new int[110][110];//地图 static int[][] dist = new int[110][110];//存起始位置到每一个坐标的移动次数 static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0; public static void main(String[] args) Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); n = sca.nextInt(); m = sca.nextInt(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) map[i][j] = sca.nextInt(); res = bfs(); System.out.println(res); static int bfs() Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();//存坐标 q.offer(new Pair(1, 1));//将起始位置坐标放入队头 while (!q.isEmpty()) //队列不为空 Pair pair = q.poll();//取出队头 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) int a = pair.x + dx[i], b = pair.y + dy[i]; if (a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > m) continue;//越界,需要换一个方向 if (map[a][b] ==1 || dist[a][b] > 0) continue;//障碍,遍历过的点就不搜索了 q.offer(new Pair(a, b));//将此位置加入队列 dist[a][b] = dist[pair.x][pair.y] + 1;//移动次数+1 if (pair.x==n&&pair.y==m) return dist[n][m]; return dist[n][m]; class Pair int x, y; public Pair(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;
第二题:离开中山路
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
3 001 101 100 1 1 3 3输出 #1复制
4说明/提示
对于 20% 数据,满足 1≤n≤100。
对于 100%数据,满足 1≤n≤1000。
题目分析
思路和第一题一样
难点
方向坐标:4连通
static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0;用队列存每一个位置的坐标
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();//存坐标 q.offer(new Pair(x1-1, y1-1));//将起始位置坐标放入队头坐标用一个类来存取
class Pair int x, y; public Pair(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;边界是什么
if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= n) continue; if (map[a][b] == '1' || dist[a][b] > 0) continue;- 终止条件是什么
if (pair2.x == x2 - 1 && pair2.y == y2 - 1) return dist[x2 - 1][y2 - 1];
题目代码
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Scanner; public class 离开中山路_bfs static int n; static char map[][]; static int dist[][]; static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0; static int x1, y1, x2, y2; public static void main(String[] args) Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); n = sca.nextInt(); sca.nextLine(); map = new char[n][n]; dist = new int[n][n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //特别注意这里给第i行数组赋值是从下表0开始的,所以下面起始和结束的位置下标都要-1 这个地方卡了我好久..... map[i] = sca.next().toCharArray(); x1 = sca.nextInt(); y1 = sca.nextInt(); x2 = sca.nextInt(); y2 = sca.nextInt(); System.out.println(bfs()); static int bfs() Queue<Pair2> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.offer(new Pair2(x1 - 1, y1 - 1)); while (!q.isEmpty()) Pair2 pair2 = q.poll(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) int a = pair2.x + dx[i], b = pair2.y + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= n) continue; if (map[a][b] == '1' || dist[a][b] > 0) continue; q.offer(new Pair2(a, b)); dist[a][b] = dist[pair2.x][pair2.y] + 1; if (pair2.x == x2 - 1 && pair2.y == y2 - 1) return dist[x2 - 1][y2 - 1]; return dist[x2 - 1][y2 - 1]; class Pair2 int x, y; public Pair2(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;
第三题: 马的遍历
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
3 3 1 1输出 #1复制
0 3 2 3 -1 1 2 1 4说明/提示
数据规模与约定
对于全部的测试点,保证 1≤x≤n≤400,1≤y≤m≤400。
题目分析
难点
- 方向坐标:8连通
static int dx[] = 2, 2, 1, 1, -1, -1, -2, -2; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2, 1, -1;用队列存每一个位置的坐标
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();//存坐标 q.offer(new Pair(1, 1));//将起始位置坐标放入队头坐标用一个类来存取
class Pair int x, y; public Pair(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;边界是什么
if (a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > m) continue; if (map[a][b] >= 0) continue;//走过就不走了
题目代码
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Scanner; public class 马的遍历_bfs static int n, m, x, y; static int map[][]; static int dx[] = 2, 2, 1, 1, -1, -1, -2, -2; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2, 1, -1; public static void main(String[] args) Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); n = sca.nextInt(); m = sca.nextInt(); x = sca.nextInt(); y = sca.nextInt(); map = new int[n + 1][m + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) map[i][j] = -1; bfs(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) System.out.printf("%-4d",map[i][j]); System.out.println(); static void bfs() Queue<Pair3> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.offer(new Pair3(x, y)); map[x][y] = 0;//给起点赋值 while (!q.isEmpty()) Pair3 pair3 = q.poll(); for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) //8连通 int a = pair3.x + dx[i], b = pair3.y + dy[i]; if (a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > m) continue; if (map[a][b] >= 0) continue;//走过就不走了 q.offer(new Pair3(a, b)); map[a][b] = map[pair3.x][pair3.y] + 1; class Pair3 int x, y; public Pair3(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;
多源BFS
第四题: 血色先锋队
输入格式
第 1 行:四个整数 n,m,a,b,表示军团矩阵有 n 行 m 列。有 a 个感染源,b 为血色敢死队中领主的数量。
接下来 a 行:每行有两个整数 x,y,表示感染源在第 x 行第 y 列。
接下来 b 行:每行有两个整数 x,y,表示领主的位置在第 x 行第 y 列。
输出格式
第 1 至 b 行:每行一个整数,表示这个领主感染瘟疫的时间,输出顺序与输入顺序一致。如果某个人的位置在感染源,那么他感染瘟疫的时间为 0。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
5 4 2 3 1 1 5 4 3 3 5 3 2 4输出 #1复制
3 1 3说明/提示
输入输出样例 1 解释
如下图,标记出了所有人感染瘟疫的时间以及感染源和领主的位置。
数据规模与约定
对于 100% 的数据,保证 1≤n,m≤500,1≤a,b≤105。
题目分析
思路和前面不同的是:本题从多个位置开始进行BFS
难点
如何处理多个位置同时进行BFS:
while (a-- > 0) //先将感染源放入队列成为队头 int x1 = sca.nextInt(); int y1 = sca.nextInt(); q.offer(new Pair4(x1, y1)); map[x1][y1] = 0;方向坐标:4连通
static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0;用队列存取每一个位置的坐标
while (!q.isEmpty()) Pair4 pair4 = q.poll();//队头出队坐标用一个类来存取
class Pair4 int x, y; public Pair4(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;边界是什么
if (a1 < 1 || a1 > n || b1 < 1 || b1 > m) continue; if (map[a1][b1] >= 0) continue;//感染过的就跳过- 终止条件是什么
本题是将整个地图上的全部位置赋值,即感染时间,所以当队列为空时终止
题目代码
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Scanner; public class 血色先锋队_多源bfs static int n, m, a, b; static int map[][]; static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0; static Queue<Pair4> q = new LinkedList(); public static void main(String[] args) Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); n = sca.nextInt(); m = sca.nextInt(); a = sca.nextInt(); b = sca.nextInt(); map = new int[n + 1][m + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) //预处理 for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) map[i][j] = -1; while (a-- > 0) //先将感染源放入队列 int x1 = sca.nextInt(); int y1 = sca.nextInt(); q.offer(new Pair4(x1, y1)); map[x1][y1] = 0; bfs(); while (b-- > 0) //在输入领主时就输出 int x2 = sca.nextInt(); int y2 = sca.nextInt(); System.out.println(map[x2][y2]); static void bfs() while (!q.isEmpty()) Pair4 pair4 = q.poll();//队头出队 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) int a1 = pair4.x + dx[i], b1 = pair4.y + dy[i]; if (a1 < 1 || a1 > n || b1 < 1 || b1 > m) continue; if (map[a1][b1] >= 0) continue;//感染过的就跳过 q.offer(new Pair4(a1, b1));//入队 map[a1][b1] = map[pair4.x][pair4.y] + 1; class Pair4 int x, y; public Pair4(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;
染色问题
第五题:填涂颜色
题目描述
由数字 0 组成的方阵中,有一任意形状闭合圈,闭合圈由数字 1 构成,围圈时只走上下左右 4 个方向。现要求把闭合圈内的所有空间都填写成 2。例如:6×6 的方阵(n=6),涂色前和涂色后的方阵如下:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1输入格式
每组测试数据第一行一个整数 n(1≤n≤30)。
接下来 n 行,由 0 和 1 组成的 n×n 的方阵。
方阵内只有一个闭合圈,圈内至少有一个 0。
//感谢黄小U饮品指出本题数据和数据格式不一样. 已修改(输入格式)
输出格式
已经填好数字 2 的完整方阵。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1输出 #1复制
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1说明/提示
对于 100%的数据,1≤n≤30。
题目分析
思路:类似于灌溉问题
本题只需要将没标记过的0染色为2
因为围起来的难标记,所以换一个方向将外围的0标记即可。
注意的点:题目地图范围是从(1,1)~(n,n),我们是从(0,0)~(n+1,n+1),即扩大一圈最外圈全部为0,这样当我们搜索(bfs)即可满足将外围的0全部标记
难点
方向坐标:4连通
static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0;用队列存取每一个位置的坐标
q.offer(new Pair5(0, 0));//将队头入队列坐标用一个类来存取
class Pair5 int x, y; public Pair5(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;边界是什么
if (a1 < 1 || a1 > n || b1 < 1 || b1 > m) continue; if (map[a1][b1] >= 0) continue;//感染过的就跳过- 终止条件是什么
当队列为空时终止
题目代码
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Scanner; public class 填涂颜色_染色问题bfs static int n; static int map[][]; static boolean st[][]; static int dx[] = 0, 0, 1, -1; static int dy[] = 1, -1, 0, 0; static Queue<Pair5> q = new LinkedList(); public static void main(String[] args) Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); n = sca.nextInt(); map = new int[n + 2][n + 2]; st = new boolean[n + 2][n + 2]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) //输入 for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) map[i][j] = sca.nextInt(); st[0][0] = true; bfs(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) //输出 for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) if (map[i][j] == 0 && !st[i][j]) System.out.print(2 + " "); else System.out.print(map[i][j] + " "); System.out.println(); static void bfs() q.offer(new Pair5(0, 0));//将队头入队列 while (!q.isEmpty()) Pair5 pair5 = q.poll();//将队头出队列 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) int a = pair5.x + dx[i], b = pair5.y + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a > n + 1 || b < 0 || b > n + 1) continue; if (map[a][b] == 1 || st[a][b]) continue;//值为1和标记过的跳过 q.offer(new Pair5(a, b)); st[a][b] = true;//做标记 class Pair5 int x, y; public Pair5(int x, int y) this.x = x; this.y = y;
以上是关于蓝桥杯小白必看 —— Python的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章



