MySQL读写分离中间件
Posted 港南四大炮亡
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL读写分离中间件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.什么是读写分离中间件?
就是实现当[写]的时候转发到主库,当[读]的时候转发到从库的工具。
很类似学习过的proxy,比如nginx proxy做动静分离.
2.为什么要实现读写分离?
1)让主库专注于写,因为读可以有很多从库可以干。
2)让多个从库接收并发读请求。
好处,增加读和写的并发,防止锁竞争,减轻主数据库的压力。
生产场景:读写比基本都比较大,超过10/1.
3.读写分离中间件有哪些?
1)程序实现(JAVA,php,PYTHON,SHELL)
需要读写分离的SQL语句DML语句关键字:insert,delete,update,select
读:select开头找从库,否则就找主库。
优点:少配置一个服务,降低了连接延迟以及服务宕机问题。
程序修改mysql操作,直接和数据库通信,简单快捷的读写分离和随机的方式实现的负载均衡,权限独立分配,需要开发人员协助。
2)中间件插件(对应用层透明,ip1 读,ip2写)
amoeba: 直接实现读写分离和负载均衡,不用修改代码,有很灵活的数据解决方案,自己分配账户,和后端数据库权限管理独立,权限处理不够灵活。
mysql-proxy:
直接实现读写分离和负载均衡,不用修改代码,master和slave用一样的帐号,效率低
proxySQL
Atlas
maxscale
cobar
mycat
====================
proxySQL(推荐使用)类似学习过的proxy NGINX(nginx 反向代理,代理web服务请求)
4. ProxySQL介绍
ProxySQL是一个高性能的MySQL代理软件,可以实现数据库读写分离,支持 Query路由功能,支持动态指定某个SQL进行缓存,支持动态加载配置信息(无需重启ProxySQL ),支持故障切换和SQL过滤功能。
Scale 100K+ connections
across thousands of servers
ProxySQL网站:
https://www.proxysql.com/
https://github.com/sysown/proxysql/wiki
5. 基本架构逻辑原理
见架构图。
6.检查修改主从复制环境
GTID环境:
51:Master mha node/mha management
52/53:Slave mha node
7. 安装ProxySQL插件
# 下载proxySQL
https://proxysql.com/
https://github.com/sysown/proxysql/releases
Scale 100K+ connections
across thousands of servers
# 安装proxySQL
# 理论选择哪个机器都可以,本次选择51安装。
[root@db03 ~]# rpm -ivh proxysql-2.0.10-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
[root@db03 bin]# systemctl start proxysql
[root@db03 bin]# netstat -tulnp|grep 603
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6033 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 15595/proxysql
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6032 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 15595/proxysql
注意:
#6033 对外提供服务端口,用户连接
#6032 管理员管理端口
# 登录proxySQL
[root@db03 bin]# mysql -uadmin -padmin -h127.0.0.1 -P6032
db03 [(none)]>show databases;
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| seq | name | file |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| 0 | main | |
| 2 | disk | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql.db |
| 3 | stats | |
| 4 | monitor | |
| 5 | stats_history | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql_stats.db |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
db03 [(none)]>use main
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
db03 [main]>show tables;
+----------------------------------------------------+
| tables |
+----------------------------------------------------+
| mysql_group_replication_hostgroups |
| mysql_query_rules |
| mysql_replication_hostgroups |
| mysql_servers |
| mysql_users |
| runtime_*
+----------------------------------------------------+
8. ProxySQL中管理结构自带系统库
在ProxySQL中,6032端口管理共五个库: main、disk、stats 、monitor、stats_history
核心是main库:
main:
main 库中有如下信息:
1)mysql_replication_hostgroups : 读写节点分组配置信息
db03 [main]>select * from mysql_replication_hostgroups;
+------------------+------------------+------------+---------+
| writer_hostgroup | reader_hostgroup | check_type | comment |
+------------------+------------------+------------+---------+
| 10 | 20 | read_only | proxy |
+------------------+------------------+------------+---------+
2)mysql_servers: 后端可以连接MySQL服务器的列表 ###nginx upstream池子
db03 [main]>select * from mysql_servers;
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+----------------+
| hostgroup_id | hostname | port | gtid_port | status | weight |max_connections |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+----------------+
| 20 | 10.0.0.52 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 |1000 |
| 10 | 10.0.0.51 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 |1000 |
| 20 | 10.0.0.53 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 |1000 |
| 20 | 10.0.0.51 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 |1000 |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+----------------+
3)mysql_users: 配置后端数据库的账号和监控的账号。
db03 [main]>select username,password,default_hostgroup from mysql_users;
+----------+----------+-------------------+
| username | password | default_hostgroup |
+----------+----------+-------------------+
| root | 123 | 10 |
+----------+----------+-------------------+
4)mysql_query_rules: 指定Query路由到后端不同服务器的规则列表。
db03 [main]>select rule_id,active,match_pattern,destination_hostgroup from mysql_query_rules;
+---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+
| rule_id | active | match_pattern | destination_hostgroup |
+---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+
| 1 | 1 | ^select.*for update$ | 10 |
| 2 | 1 | ^select | 20 |
+---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+
注: 表名以 runtime_开头的表示ProxySQL当前运行的配置内容,不能直接修改。
不带runtime_是下文图中Mem相关的配置。
disk :
持久化的磁盘的配置
stats:
统计信息的汇总
monitor:
监控的收集信息,比如数据库的健康状态等
stats_history:
ProxySQL收集的有关其内部功能的历史指标
9. ProxySQL管理接口的多层配置关系
见架构图。
整套配置系统分为三层:
顶层 RUNTIME
中间层 MEMORY(主要修改的配置表)
持久层 DISK和CFG FILE
RUNTIME :
代表ProxySQL当前正在使用的配置,无法直接修改此配置,必须要从下一层(MEM层)load进来。
MEMORY:
MEMORY层上面连接RUNTIME层,下面连接disk持久层。这层可以在线操作ProxySQL 配置,随便修改,不会影响生产环境。确认正常之后在加载到RUNTIME和持久化磁盘上。
修改方法: 使用SQL DML语句:insert、update、delete、select。
DISK和CONFIG FILE:
持久化配置信息。重启时,可以从磁盘快速加载回来。
10. 在不同层次间移动配置
为了将配置持久化到磁盘或者应用到 runtime,在管理接口下有一系列管理命令来实现它们。
1. user相关配置
## MEM加载到runtime
LOAD MYSQL USERS TO RUNTIME;
## runtime保存至MEM
SAVE MYSQL USERS TO MEMORY;
## disk加载到MEM
LOAD MYSQL USERS FROM DISK;
## MEM到disk
SAVE MYSQL USERS TO DISK;
## CFG到MEM
LOAD MYSQL USERS FROM CONFIG
=============================
2. server相关配置
## MEM加载到runtime
LOAD MYSQL SERVERS TO RUNTIME;
## runtime保存至MEM
SAVE MYSQL SERVERS TO MEMORY;
## disk加载到 MEM
LOAD MYSQL SERVERS FROM DISK;
## MEM 到disk
SAVE MYSQL SERVERS TO DISK;
## CFG 到 MEM
LOAD MYSQL SERVERS FROM CONFIG
===============================
3. mysql query rules配置
## MEM 加载到runtime
LOAD MYSQL QUERY RULES TO RUNTIME;
## runtime 保存至 MEM
SAVE MYSQL QUERY RULES TO MEMORY;
## disk 加载到 MEM
LOAD MYSQL QUERY RULES FROM DISK;
## MEM 到 disk
SAVE MYSQL QUERY RULES TO DISK;
## CFG 到 MEM
LOAD MYSQL QUERY RULES FROM CONFIG
=================================
4. MySQL variables配置
## MEM 加载到runtime
LOAD MYSQL VARIABLES TO RUNTIME;
## runtime 保存至 MEM
SAVE MYSQL VARIABLES TO MEMORY;
## disk 加载到 MEM
LOAD MYSQL VARIABLES FROM DISK;
## MEM 到 disk
SAVE MYSQL VARIABLES TO DISK;
## CFG 到 MEM
LOAD MYSQL VARIABLES FROM CONFIG
总结:
日常配置其实大部分时间在MEM层配置,
然后load到RUNTIME,然后SAVE到Disk。cfg很少使用。
常见命令:
使用SQL DML语句修改:insert、update、delete、select。
使用LOAD,SAVE生效和保存。
load xxx to runtime;
save xxx to disk;
XXX就是上面配置里关键字部分
注意:
所有配置保MEM或disk层时,都不会发生任何警告或错误。
只有load到runtime状态时才会验证配置。当load到 runtime时,如果出现错误,将恢复为之前保存的状态,这时可以去检查错误日志。
11. ProxySQL应用————基于SQL实现读写分离
11.1 MySQL从库要设定read_only参数
1)主从复制的从库应该禁止用户写入。
2)ProxySQL如何判断主从(根据是否有read-only=1)
read-only=1就是从,否则就是主。
将52,53设置为read-only=1,修改配置步骤略.
11.2 配置读写节点分组信息
在mysql_replication_hostgroup表中,配置读写组编号
10编号对应就是写库的组,20编号对应的就是读库的组。
[root@db01 ~]# mysql -uadmin -padmin -h127.0.0.1 -P6032
db03 [(none)]>use main
insert into mysql_replication_hostgroups(writer_hostgroup, reader_hostgroup, comment)
values (10,20,'proxy');
db01 [main]>select * from mysql_replication_hostgroups;
+------------------+------------------+------------+---------+
| writer_hostgroup | reader_hostgroup | check_type | comment |
+------------------+------------------+------------+---------+
| 10 | 20 | read_only | proxy |
+------------------+------------------+------------+---------+
db01 [main]>load mysql servers to runtime;
db01 [main]>save mysql servers to disk;
db01 [main]>select * from mysql_replication_hostgroups\\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
writer_hostgroup: 10
reader_hostgroup: 20
check_type: read_only
comment: proxy
说明:
ProxySQL会根据server的read_only的取值将服务器进行分组。
read_only=0的server,master被分到编号为10的写组,
read_only=1的server,slave则被分到编号20的读组。
所以需要将从库设置:set global read_only=1;
11.3. 添加主机到ProxySQL
insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port) values (10,'10.0.0.51',3306);
insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port) values (20,'10.0.0.52',3306);
insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port) values (20,'10.0.0.53',3306);
db01 [main]>select * from mysql_servers;
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+-----------------+
| hostgroup_id | hostname | port | gtid_port | status | weight | max_connections |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+-----------------+
| 10 | 10.0.0.51 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 | 1000 |
| 20 | 10.0.0.52 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 | 1000 |
| 20 | 10.0.0.53 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 | 1000 |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+-----------------+
load mysql servers to runtime;
save mysql servers to disk;
11.4. 创建监控用户,并开启监控
1)# 51主库创建监控用户,给ProxySQL连接。
create user monitor@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by '123';
grant replication client on *.* to monitor@'%';
# proxySQL库修改variables表,让proxySQL可以通过monitor用户和123密码去连接和监控数据库
set mysql-monitor_username='monitor';
set mysql-monitor_password='123';
或者 :
UPDATE global_variables SET variable_value='monitor'
WHERE variable_name='mysql-monitor_username';
UPDATE global_variables SET variable_value='123'
WHERE variable_name='mysql-monitor_password';
load mysql variables to runtime;
save mysql variables to disk;
2)# 查询监控日志
db01 [(none)]>select * from mysql_server_connect_log;
db01 [(none)]>select * from mysql_server_ping_log;
db01 [(none)]>select * from mysql_server_read_only_log;
db01 [(none)]>select * from mysql_server_replication_lag_log;
3)配置web节点等应用连接ProxySQL的用户
设定应用连接ProxySQL的用户为root,密码为123
# proxysql代理
insert into mysql_users(username,password,default_hostgroup) values('root','123',10);
load mysql users to runtime;
save mysql users to disk;
# 51主库创建允许proxysql代理访问的用户和密码
create user root@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by '123';
grant all on *.* to root@'%';
注意;早期版本,需要开启事务持续化。今天版本不需要,只是提及。
update mysql_users set transaction_persistent=1 where username='root';
load mysql users to runtime;
save mysql users to disk;
让事务里的所有SQL都读写同一个库:
begin;
select
update
insert
delete
commit;
4) 读写规则流程或原理
架构图
5)配置读写规则mysql_query_rules
# ProxySQL
insert into mysql_query_rules(rule_id,active,match_pattern,destination_hostgroup,apply) values (1,1,'^select.*for update$',10,1);
insert into mysql_query_rules(rule_id,active,match_pattern,destination_hostgroup,apply) values (2,1,'^select',20,1);
load mysql query rules to runtime;
save mysql query rules to disk;
注: select … for update规则的rule_id必须要小于普通的select规则的rule_id,
ProxySQL是根据rule_id的顺序进行规则匹配。
6. 模拟web测试读写分离
成功:
[root@db01 /usr/local/bin]# mysql -uroot -p123 -P6033 -h 127.0.0.1 -e "select @@server_id;"
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
+-------------+
| @@server_id |
+-------------+
| 51 |
+-------------+
[root@db01 /usr/local/bin]# mysql -uroot -p123 -P6033 -h 127.0.0.1 -e "select @@server_id;"
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
+-------------+
| @@server_id |
+-------------+
| 52 |
+-------------+
[root@db01 /usr/local/bin]# mysql -uroot -p123 -P6033 -h 127.0.0.1 -e "select @@server_id;"
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
+-------------+
| @@server_id |
+-------------+
| 53 |
+-------------+
[root@db01 ~]# mysql -uroot -p123 -P6033 -h 127.0.0.1 -e "begin;select @@server_id;commit;"
遇到问题:上面语句可以访问到51,52,53,原因:
db01 [main]>select * from mysql_servers;
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+-------------------------+
| hostgroup_id | hostname | port | gtid_port | status | weight max_connections |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+-------------------------+
| 10 | 10.0.0.51 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 1000 |
| 20 | 10.0.0.51 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 1000 |
| 20 | 10.0.0.53 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 1000 |
| 10 | 10.0.0.52 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 1000 |
| 10 | 10.0.0.53 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 1000 |
| 20 | 10.0.0.52 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 1000 |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+-------------------------+
从上面那内容可以发现,所有节点都在写组10里,所有节点都在读组20里。
最终罪魁祸首,没有在从库配置read_only=1;临时设置如下;
52/53上配置;
set global read_only=1; ##普通用户只读。
set global super_read_only=1; ##管理员用户只读。
返回:proxysql查看,立刻发生吧变化
db01 [main]>select * from mysql_servers;
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+---------+
| hostgroup_id | hostname | port | gtid_port | status | weight | comment |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+---------+
| 10 | 10.0.0.51 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 | |
| 20 | 10.0.0.51 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 | |
| 20 | 10.0.0.53 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 | |
| 20 | 10.0.0.52 | 3306 | 0 | ONLINE | 1 | |
+--------------+-----------+------+-----------+--------+--------+---------+
10是写组有51,20是读组,有51,52,53.
[root@db01 ~]# mysql -uroot -p123 -P 6033 -h 127.0.0.1 -e "select @@server_id;"
db01 [(none)]>select * from stats_mysql_query_digest\\G
给开发人员:
root 123
6033
10.0.0.51
自动实现读写分离,根据语句过滤select读,其他写.
8. ProxySQL应用扩展——花式路由规则
1. 基于端口实现读写分离
## 修改ProxySQL监听SQL流量的端口号,监听多端口上。
set mysql-interfaces='0.0.0.0:6033;0.0.0.0:6034';
save mysql variables to disk;
## 重启生效
systemctl restart proxysql
## 设定路由规则
delete from mysql_query_rules; # 为了测试,先清空已有规则
insert into mysql_query_rules(rule_id,active,proxy_port,destination_hostgroup,apply)
values(1,1,6033,10,1), (2,1,6034,20,1);
load mysql query rules to runtime;
save mysql query rules to disk;
说明: 除了基于端口进行分离,还可以基于监听地址(修改字段proxy_addr即可),也可以基于客户端地址(修改字段client_addr字段即可)。
给开发人员:
写:
root
123
6033
10.0.0.51
读
root
123
6034
10.0.0.51
2. 基于用户实现读写分离
insert into mysql_users(username,password,default_hostgroup)
values('writer','123',10),('reader','123',20);
load mysql users to runtime;
save mysql users to disk;
delete from mysql_query_rules; # 为了测试,先清空已有规则
insert into mysql_query_rules(rule_id,active,username,destination_hostgroup,apply)
values(1,1,'writer',10,1),(2,1,'reader',20,1);
load mysql query rules to runtime;
save mysql query rules to disk;
#最后在主库创建writer,reader用户和密码。
作业:实践基于端口和基于用户实现读写分离。
给开发人员:
写:
writer
123
6033
10.0.0.51
读:
reader
123
6033
10.0.0.51
MySQL中间件proxysql实现MySQL读写分离
1. Mysql实现读写分离的方式
mysql 实现读写分离的方式有以下几种:
- 程序修改mysql操作,直接和数据库通信,简单快捷的读写分离和随机的方式实现的负载均衡,权限独立分配,需要开发人员协助。
- amoeba,直接实现读写分离和负载均衡,不用修改代码,有很灵活的数据解决方案,自己分配账户,和后端数据库权限管理独立,权限处理不够灵活。
- mysql-proxy,直接实现读写分离和负载均衡,不用修改代码,master和slave用一样的帐号,效率低
- mycat中间件
- proxysql中间件(推荐使用)
2. ProxySQL简介
ProxySQL 是一款可以实际用于生产环境的 MySQL 中间件,它有官方版和 percona 版两种。percona版是在官方版的基础上修改的,添加了几个比较实用的工具。生产环境建议用官方版。
ProxySQL 是用 C++ 语言开发的,虽然也是一个轻量级产品,但性能很好(据测试,能处理千亿级的数据),功能也足够,能满足中间件所需的绝大多数功能,包括:
- 最基本的读/写分离,且方式有多种
- 可定制基于用户、基于schema、基于语句的规则对SQL语句进行路由。换句话说,规则很灵活。基于schema和与语句级的规则,可以实现简单的sharding(分库分表)
- 可缓存查询结果。虽然ProxySQL的缓存策略比较简陋,但实现了基本的缓存功能,绝大多数时候也够用了。此外,作者已经打算实现更丰富的缓存策略
- 监控后端节点。ProxySQL可以监控后端节点的多个指标,包括:ProxySQL和后端的心跳信息,后端节点的read-only/read-write,slave和master的数据同步延迟性(replication lag)
3. ProxySQL安装
有两种方法
一:
# 下载proxysql
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://repo.proxysql.com/ProxySQL/proxysql-1.4.x/centos/7/proxysql-1.4.15-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg proxysql-1.4.15-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install proxysql-1.4.15-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start proxysql
[root@localhost ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:6032 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 二:
//配置yum源
[root@proxysql ~]# cat <<EOF | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/proxysql.repo
[proxysql_repo]
name= ProxySQL
baseurl=http://repo.proxysql.com/ProxySQL/proxysql-1.4.x/centos/7
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://repo.proxysql.com/ProxySQL/repo_pub_key
EOF
[root@proxysql ~]# yum -y install proxysql
……下载过程略
[root@proxysql ~]# systemctl enable proxysql
proxysql.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig.
Executing /sbin/chkconfig proxysql on
[root@proxysql ~]# chkconfig proxysql on
[root@proxysql ~]# systemctl start proxysql
//端口号为6032和6033
[root@proxysql ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:6032 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 4. ProxySQL的Admin管理接口
当 ProxySQL 启动后,将监听两个端口:
- admin管理接口,默认端口为6032。该端口用于查看、配置ProxySQL
- 接收SQL语句的接口,默认端口为6033,这个接口类似于MySQL的3306端口
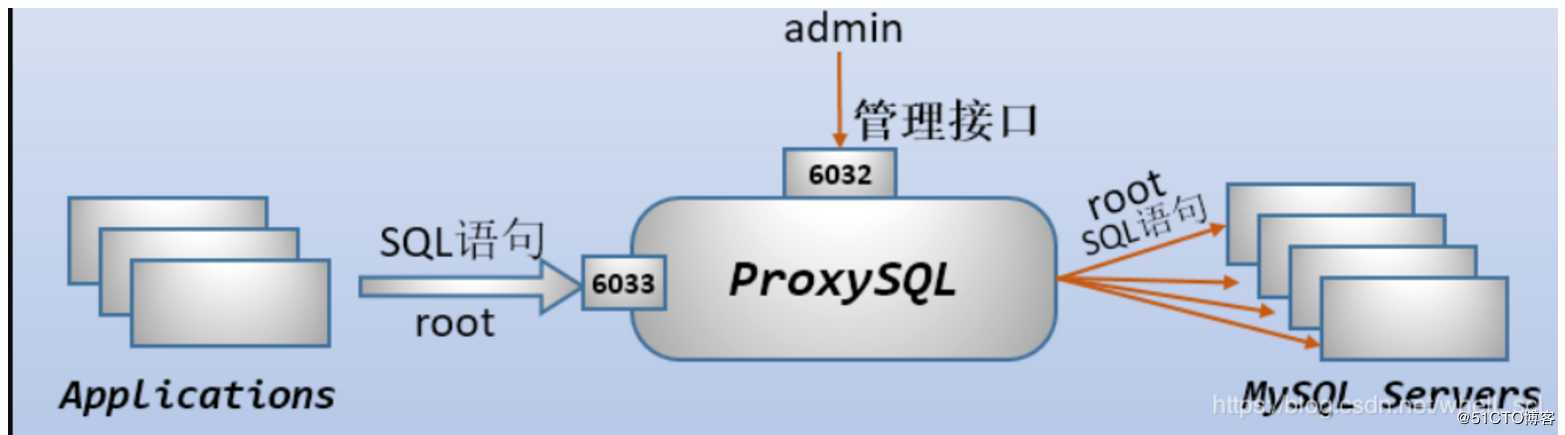
ProxySQL 的 admin 管理接口是一个使用 MySQL 协议的接口,所以,可以直接使用 mysql 客户端、navicat 等工具去连接这个管理接口,其默认的用户名和密码均为 admin
例如,使用 mysql 客户端去连接 ProxySQL 的管理接口:[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uadmin -padmin -h127.0.0.1 -P6032 Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MySQL connection id is 6 Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL Admin Module)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| seq | name | file |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| 0 | main | |
| 2 | disk | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql.db |
| 3 | stats | |
| 4 | monitor | |
| 5 | stats_history | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql_stats.db |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
由于 ProxySQL 的配置全部保存在几个自带的库中,所以通过管理接口,可以非常方便地通过发送一些SQL命令去修改 ProxySQL 的配置。 ProxySQL 会解析通过该接口发送的某些对ProxySQL 有效的特定命令,并将其合理转换后发送给内嵌的 SQLite3 数据库引擎去运行
ProxySQL 的配置几乎都是通过管理接口来操作的,通过 Admin 管理接口,可以在线修改几乎所有的配置并使其生效。只有两个变量的配置是必须重启 ProxySQL 才能生效的,它们是:
**mysql-threads 和 mysql-stacksize**
# 5. 和admin管理接口相关的变量
# 5.1 admin-admin_credentials
admin-admin_credentials 变量控制的是admin管理接口的管理员账户。默认的管理员账户和密码为admin:admin,但是这个默认的用户只能在本地使用。如果想要远程连接到ProxySQL,例如用windows上的navicat连接Linux上的ProxySQL管理接口,必须自定义一个管理员账户。
**添加管理员帐户**MySQL [(none)]> select @@admin-admin_credentials; ## 查看当前的用户名密码
+---------------------------+
| @@admin-admin_credentials |
+---------------------------+
| admin:admin |
+---------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
设置管理员帐号myadmin,密码scl666
MySQL [(none)]> set admin-admin_credentials=‘admin:admin;myadmin:scl666‘;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> select @@admin-admin_credentials;
+----------------------------+
| @@admin-admin_credentials |
+----------------------------+
| admin:admin;myadmin:scl666 |
+----------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
MySQL [(none)]>
MySQL [(none)]> load admin variables to runtime; ## 使修改立即生效
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> save admin variables to disk; ## 使修改永久保存到磁盘
Query OK, 31 rows affected (0.00 sec)
**修改后,就可以使用该用户名和密码连接管理接口**[root@localhost ~]# mysql -umyadmin -pscl666 -h127.0.0.1 -P6032
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 5
Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL Admin Module)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [(none)]>
**所有的配置操作都是在修改main库中对应的表**MySQL [(none)]> select * from global_variables where variable_name=‘admin-admin_credentials‘;
+-------------------------+----------------------------------+
| variable_name | variable_value |
+-------------------------+----------------------------------+
| admin-admin_credentials | admin:admin;myadmin:wangqing123! |
+-------------------------+----------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
**必须要区分admin管理接口的用户名和mysql_users中的用户名**
* admin管理接口的用户是连接到管理接口(默认端口6032)上用来管理、配置ProxySQL的
* mysql_users表中的用户名是应用程序连接ProxySQL(默认端口6033),以及ProxySQL连接后端MySQL Servers使用的用户。它的作用是发送、路由SQL语句,类似于MySQL Server的3306端口。所以,这个表中的用户必须已经在后端MySQL Server上存在且授权了
admin管理接口的用户必须不能存在于mysql_users中,这是出于安全的考虑,防止通过admin管理接口用户猜出mysql_users中的用户
# 5.2 admin-stats_credentials
admin-stats_credentials 变量控制admin管理接口的普通用户,这个变量中的用户没有超级管理员权限,只能查看monitor库和main库中关于统计的数据,其它库都是不可见的,且没有任何写权限
默认的普通用户名和密码均为 stats ,与admin一样,它默认也只能用于本地登录,若想让人远程查看则要添加查看的专有用户MySQL [(none)]> select @@admin-stats_credentials;
+---------------------------+
| @@admin-stats_credentials |
+---------------------------+
| stats:stats |
+---------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
添加专有的查看用户
MySQL [main]> set admin-stats_credentials=‘stats:stats;mystats:scl777‘;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [main]> select @@admin-stats_credentials;
+----------------------------+
| @@admin-stats_credentials |
+----------------------------+
| stats:stats;mystats:scl777 |
+----------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [main]>
MySQL [(none)]> load admin variables to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> save admin variables to disk;
Query OK, 31 rows affected (0.00 sec)
**同样,这个变量中的用户必须不能存在于mysql_users表中
使用mystats用户远程连接查看**[root@localhost ~]# mysql -umystats -pscl777 -h192.168.100.99 -P6032
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 7
Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL Admin Module)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [(none)]>
MySQL [(none)]> show tables from main;
+--------------------------------------+
| tables |
+--------------------------------------+
| global_variables |
| stats_memory_metrics |
| stats_mysql_commands_counters |
| stats_mysql_connection_pool |
| stats_mysql_connection_pool_reset |
| stats_mysql_global |
| stats_mysql_prepared_statements_info |
| stats_mysql_processlist |
| stats_mysql_query_digest |
| stats_mysql_query_digest_reset |
| stats_mysql_query_rules |
| stats_mysql_users |
| stats_proxysql_servers_checksums |
| stats_proxysql_servers_metrics |
| stats_proxysql_servers_status |
+--------------------------------------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]>
# 5.3 admin-mysql_ifaces
admin-mysql_ifaces 变量指定admin接口的监听地址,格式为冒号分隔的hostname:port列表。默认监听在 0.0.0.0:6032
注意,允许使用UNIX的domain socket进行监听,这样本主机内的应用程序就可以直接被处理。
例如:MySQL [(none)]> SET admin-mysql_ifaces=‘0.0.0.0:6032;/tmp/proxysql_admin.sock‘;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> load admin variables to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> save admin variables to disk;
Query OK, 31 rows affected (0.00 sec)
##修改端口号6032为3306
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> SET admin-mysql_ifaces=‘0.0.0.0:6032;/tmp/proxysql_admin.sock‘;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> load admin variables to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> save admin variables to disk;
Query OK, 31 rows affected (0.05 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> select @@admin-mysql_ifaces;
+---------------------------------------+
| @@admin-mysql_ifaces |
+---------------------------------------+
| 0.0.0.0:6032;/tmp/proxysql_admin.sock |
+---------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.05 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> set admin-mysql_ifaces=‘0.0.0.0:3306‘;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> select @@admin-mysql_ifaces;
+----------------------+
| @@admin-mysql_ifaces |
+----------------------+
| 0.0.0.0:3306 |
+----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> load admin variables to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> save admin variables to disk;
Query OK, 31 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> exit
Bye
[root@40 ~]# systemctl restart proxysql
[root@40 ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 :3306 :
LISTEN 0 128 :111 :
LISTEN 0 128 :6033 :
LISTEN 0 128 :6033 :
LISTEN 0 128 :6033 :
LISTEN 0 128 :6033 :
LISTEN 0 128 :22 :
LISTEN 0 128 :10050 :
LISTEN 0 128 :::111 :::
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::
[root@40 ~]# mysql -uadmin -padmin -h127.0.0.1 -P3306
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1
Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL Admin Module)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
(admin@127.0.0.1:3306) [(none)]>
# 6. 多层配置系统
# 6.1 proxysql中的库使用ProxySQL的Admin管理接口连上ProxySQL,可查看ProxySQL拥有的库
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -umyadmin -pscl666 -h127.0.0.1 -P6032
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 9
Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL Admin Module)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| seq | name | file |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| 0 | main | |
| 2 | disk | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql.db |
| 3 | stats | |
| 4 | monitor | |
| 5 | stats_history | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql_stats.db |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]>
其中:
* main库是ProxySQL最主要的库,是需要修改配置时使用的库,它其实是一个内存数据库系统。所以,修改main库中的配置后,必须将其持久化到disk上才能永久保存
* disk库是磁盘数据库,该数据库结构和内存数据库完全一致。当持久化内存数据库中的配置时,其实就是写入到disk库中。磁盘数据库的默认路径为 $DATADIR/proxysql.db
* stats库是统计信息库。这个库中的数据一般是在检索其内数据时临时填充的,它保存在内存中。因为没有相关的配置项,所以无需持久化
* monitor库是监控后端MySQL节点相关的库,该库中只有几个log类的表,监控模块收集到的监控信息全都存放到对应的log表中
* stats_history库是1.4.4版新增的库,用于存放历史统计数据。默认路径为$DATADIR/proxysql_stats.db
ProxySQL 内部使用的是 SQLite3 数据库,无论是内存数据库还是磁盘数据库,都是通过SQLite3引 擎进行解析、操作的。它和 MySQL 的语法可能稍有不同,但ProxySQL会对不兼容的语法自动进行调整,最大程度上保证MySQL语句的有效率。
上面描述main库的时候,只是说了内存数据库需要持久化到disk库才能永久保存配置。但实际上,修改了main库中的配置后,并不会立即生效,它还需要load到runtime的数据结构中才生效,只有在runtime数据结构中的配置才是对ProxySQL当前有效的配置
# 6.2 ProxySQL多层配置系统
ProxySQL 的配置系统非常强大,它能在线修改几乎所有配置(仅有的两个需要重启才能生效的变量为 mysql-threads 和 mysql-stacksize ),并在线生效、持久化保存。这得益于它采用的多层配置系统。
多层配置系统结构如下:
> +-------------------------+
> | RUNTIME |
> +-------------------------+
> /| |
> | |
> [1] | [2] |
> | |/
> +-------------------------+
> | MEMORY |
> +-------------------------+ _
> /| | |> | | > [3] | [4] | [5]
> | |/ > +-------------------------+ +---------------+
> | DISK | | CONFIG FILE |
> +-------------------------+ +---------------+
>
最底层的是 disk 库和 config file 。这里需要注意,这里的 config file 就是传统的配置文件,默认为 /etc/proxysql.cnf , ProxySQL 启动时,主要是从 disk 库中读取配置加载到内存并最终加载到 runtime 生效,只有极少的几个特定配置内容是从 config file 中加载的,除非是第一次初始化 ProxySQL 运行环境(或者disk库为空)。
中间层的是 memory ,表示的是内存数据库,其实就是 main 库。通过管理接口修改的所有配置,都保存在内存数据库(main)中。当 ProxySQL 重启或者崩溃时,这个内存数据库中的数据会丢失,所以需要 save 到 disk 库中。
最上层的是 runtime ,它是 ProxySQL 有关线程运行时读取的数据结构。换句话说,该数据结构中的配置都是已生效的配置。所以,修改了 main 库中的配置后,必须 load 到 runtime 数据结构中才能使其生效。
在上面的多层配置系统图中,标注了[1]、[2]、[3]、[4]、[5]的序号。每个序号都有两个操作方向from/to,其实只是所站角度不同而已。以下是各序号对应的操作:
> [1] :将内存数据库中的配置加载到RUNTIME数据结构中
> LOAD XXX FROM MEMORY
> LOAD XXX TO RUNTIME
>
> [2] :将RUNTIME数据结构中的配置持久化到内存数据库中
> SAVE XXX FROM RUNTIME
> SAVE XXX TO MEMORY
>
> [3] :将磁盘数据库中的配置加载到内存数据库中
> LOAD XXX FROM DISK
> LOAD XXX TO MEMORY
>
> [4] :将内存数据库中的配置持久化到磁盘数据库中
> SAVE XXX FROM MEMORY
> SAVE XXX TO DISK
>
> [5] :从传统配置文件中读取配置加载到内存数据库中
> LOAD XXX FROM CONFIG
**DISK/MEMORY/RUNTIME/CONFIG 可以缩写,只要能识别即可。例如MEMORY可以缩写为MEM,runtime可以缩写为run**
另外,上面的XXX是什么?这表示要加载/保存的是哪类配置。目前的ProxySQL支持以下几种:
* mysql users
* mysql servers
* mysql variables
* mysql query rules
* admin variables
* scheduler
* proxysql_servers:目前ProxySQL集群功能还处于实验阶段,所以该类配置不应该去使用
这些从main库或disk库中就可以查看到MySQL [(none)]> show tables from disk;
+------------------------------------+
| tables |
+------------------------------------+
| global_variables | # (1)
| mysql_collations | # (N)
| mysql_group_replication_hostgroups | # (2)
| mysql_query_rules | # (3)
| mysql_query_rules_fast_routing | # (4)
| mysql_replication_hostgroups | # (5)
| mysql_servers | # (6)
| mysql_users | # (7)
| proxysql_servers | # (8)
| scheduler | # (9)
+------------------------------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
**上面的结果中我给这些表都标注了一些序号,其所对应的表的内容有以下讲究:**
* (1)中包含两类变量,以amdin-开头的表示admin variables,以mysql-开头的表示mysql variables。修改哪类变量,前文的XXX就代表哪类
* (2,5,6)对应的都是mysql servers
* (3,4)对应的是mysql query rules
* (7)对应的mysql users
* (9)对应的scheduler
* (N)只是一张表,保存的是ProxySQL支持的字符集和排序规则,它是不用修改的
* (8)是ProxySQL的集群配置表,该功能目前还处于实验阶段。如果想要配置该功能,则load/save proxysql_servers to/from …
# 6.3 启动ProxySQL时如何加载配置
如果 ProxySQL 是刚安装的,或者磁盘数据库文件为空(甚至不存在),或者启动 ProxySQL 时使用了选项 --initial,这几种情况启动 ProxySQL 时,都会从传统配置文件 config file 中读取配置加载到内存数据库,并自动 load 到 runtime 数据结构、save到磁盘数据库,这是初始化 ProxySQL 运行环境的过程。
如果不是第一次启动 ProxySQL ,由于已经存在磁盘数据库文件,这时 ProxySQL 会从磁盘数据库中读取几乎所有的配置(即使传统配置文件中配置了某项,也不会去解析),但有3项是必须从传统配置文件中读取,它们分别是:
* datadir:ProxySQL启动时,必须从配置文件中确定它的数据目录,因为磁盘数据库文件、日志以及其它一些文件是存放在数据目录下的。如果使用/etc/init.d/proxysql管理ProxySQL,则除了修改/etc/proxysql.cnf的datadir,还需要修改该脚本中的datadir。
* restart_on_missing_heartbeats:MySQL线程丢失多少次心跳,就会杀掉这个线程并重启它。默认值为10。
* execute_on_exit_failure:如果设置了该变量,ProxySQL父进程将在每次ProxySQL崩溃的时候执行已经定义好的脚本。建议使用它来生成一些崩溃时的警告和日志。注意,ProxySQL的重启速度可能只有几毫秒,因此很多其它的监控工具可能无法探测到ProxySQL的一次普通故障,此时可使用该变量
# 7. 不同类型的读写分离方案解析
数据库中间件最基本的功能就是实现读写分离, ProxySQL 当然也支持。而且 ProxySQL 支持的路由规则非常灵活,不仅可以实现最简单的读写分离,还可以将读/写都分散到多个不同的组,以及实现分库 sharding (分表sharding的规则比较难写,但也能实现)。
本文只描述通过规则制定的语句级读写分离,不讨论通过 ip/port, client, username, schemaname 实现的读写分离。
下面描述了ProxySQL能实现的常见读写分离类型
# 7.1 最简单的读写分离

这种模式的读写分离,严格区分后端的master和slave节点,且slave节点必须设置选项read_only=1
在ProxySQL上,分两个组,一个写组HG=10,一个读组HG=20。同时在ProxySQL上开启monitor模块的read_only监控功能,让ProxySQL根据监控到的read_only值来自动调整节点放在HG=10(master会放进这个组)还是HG=20(slave会放进这个组)
这种模式的读写分离是最简单的,只需在mysql_users表中设置用户的默认路由组为写组HG=10,并在mysql_query_rules中加上两条简单的规则(一个select for update,一个select)即可
这种读写分离模式,在环境较小时能满足绝大多数需求。但是需求复杂、环境较大时,这种模式就太过死板,因为一切都是monitor模块控制的
# 7.2 多个读组或写组的分离模式
前面那种读写分离模式,是通过 monitor 模块监控 read_only 来调整的,所以每一个后端集群必须只能分为一个写组,一个读组。
但如果想要区分不同的 select ,并将不同的 select 路由到不同的节点上。例如有些查询语句的开销非常大,想让它们独占一个节点/组,其它查询共享一个节点/组,怎么实现?
**例如,下面这种模式**

看上去非常简单。但是却能适应各种需求。例如,后端做了分库,对某库的查询要路由到特定的主机组
至于各个主机组是同一个主从集群(下图左边),还是互相独立的主从集群环境(下图右边),要看具体的需求,不过这种读写分离模式都能应付

在实现这种模式时,前提是不能开启monitor模块的read_only监控功能,也不要设置mysql_replication_hostgroup 表
例如,下面的配置实现的是上图左边的结构:写请求路由给HG=10,对test1库的select语句路由给HG=20,其它select路由给HG=30mysql_servers:
+--------------+----------+------+--------+--------+
| hostgroup_id | hostname | port | status | weight |
+--------------+----------+------+--------+--------+
| 10 | host1 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 |
| 20 | host2 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 |
| 30 | host3 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 |
+--------------+----------+------+--------+--------+
mysql_users:
+----------+-------------------+
| username | default_hostgroup |
+----------+-------------------+
| root | 10 |
+----------+-------------------+
mysql_query_rules:
+---------+-----------------------+----------------------+
| rule_id | destination_hostgroup | match_digest |
+---------+-----------------------+----------------------+
| 1 | 10 | ^SELECT.FOR UPDATE$ |
| 2 | 20 | ^SELECT.test1..* |
| 3 | 30 | ^SELECT |
+---------+-----------------------+----------------------+
**查看表结构的方式:**
> PRAGMA table_info("表名");
# 8. ProxySQL实现读写分离示例
**环境说明:**
| IP | 角色 | 应用 |系统平台
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
| 192.168.100.99 | 读写分离解析主机 | proxysql |rhel7.4
|192.168.100.98|master|mysql5.7|rhel7.4
|192.168.100.96|slave1|mysql5.7|rhel7.4
|192.168.100.100|slave2|mysql5.7|rhel7.4
**准备工作:**
* 关闭防火墙
* 关闭SELINUX
* 安装mysql并配置主从(这里就不做演示了)
# 8.1 安装ProxySQL下载proxysql
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://repo.proxysql.com/ProxySQL/proxysql-1.4.x/centos/7/proxysql-1.4.15-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg proxysql-1.4.15-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install proxysql-1.4.15-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
启动proxysql并设置开机自动启动
//proxysql默认只提供了sysv风格的启动脚本,所以想设置开机自启则需借助于chkconfig工具
[root@proxysql ~]# systemctl start proxysql
[root@proxysql ~]# chkconfig proxysql on
# 8.2 配置ProxySQL
# 8.2.1 mysql主库添加proxysql可以增删改查的账号mysql> grant all on . to ‘proxysql‘@‘192.168.100.99‘ identified by ‘pwproxysql‘;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql>
# 8.2.2 登录proxysql管理端[root@proxysql ~]# yum -y install mariadb
[root@proxysql ~]# export MYSQL_PS1="(u@h:p) [d]> "
[root@proxysql ~]# mysql -uadmin -padmin -h127.0.0.1 -P6032
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 10
Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL Admin Module)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> show databases;
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| seq | name | file |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
| 0 | main | |
| 2 | disk | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql.db |
| 3 | stats | |
| 4 | monitor | |
| 5 | stats_history | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql_stats.db |
+-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
**数据库说明:**
* main 内存配置数据库,表里存放后端db实例、用户验证、路由规则等信息。表名以 runtime开头的表示proxysql当前运行的配置内容,不能通过dml语句修改,只能修改对应的不以 runtime 开头的(在内存)里的表,然后 LOAD 使其生效, SAVE 使其存到硬盘以供下次重启加载
* disk 是持久化到硬盘的配置,sqlite数据文件
* stats 是proxysql运行抓取的统计信息,包括到后端各命令的执行次数、流量、processlist、查询种类汇总/执行时间等等
* monitor 库存储 monitor 模块收集的信息,主要是对后端db的健康/延迟检查
* stats_history 统计信息历史库
# 8.2.3 Proxysql管理端添加后端连接mysql主从数据库的配置(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> show tables from main;
+--------------------------------------------+
| tables |
+--------------------------------------------+
| global_variables | # ProxySQL的基本配置参数,类似与MySQL
| mysql_collations | # 配置对MySQL字符集的支持
| mysql_group_replication_hostgroups | # MGR相关的表,用于实例的读写组自动分配
| mysql_query_rules | # 路由表
| mysql_query_rules_fast_routing | # 存储MySQL实例的信息
| mysql_replication_hostgroups | # 主从复制相关的表,用于实例的读写组自动分配
| mysql_servers | # 存储MySQL用户
| mysql_users | # 存储ProxySQL的信息,用于ProxySQL Cluster同步
| proxysql_servers | # 运行环境的存储校验值
| runtime_checksums_values |
| runtime_global_variables |
| runtime_mysql_group_replication_hostgroups |
| runtime_mysql_query_rules |
| runtime_mysql_query_rules_fast_routing |
| runtime_mysql_replication_hostgroups | # 与上面对应,但是运行环境正在使用的配置
| runtime_mysql_servers |
| runtime_mysql_users |
| runtime_proxysql_servers |
| runtime_scheduler |
| scheduler | # 定时任务表
+--------------------------------------------+
20 rows in set (0.00 sec)
runtime_ 开头的是运行时的配置,这些是不能修改的。要修改 ProxySQL 的配置,需要修改了非 runtime_ 表,修改后必须执行 LOAD … TO RUNTIME 才能加载到 RUNTIME 生效,执行 save … to disk 才能将配置持久化保存到磁盘
下面语句中没有先切换到 main 库也执行成功了,因为 ProxySQL 内部使用的 SQLite3 数据库引擎,和 MySQL 的解析方式是不一样的。即使执行了 USE main 语句也是无任何效果的,但不会报错
使用 insert 语句添加 mysql 主机到 mysql_servers 表中,其中:hostgroup_id 10 表示写组,20,30表示读组(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port,weight,comment) values(10,‘192.168.100.98‘,3306,1,‘Write Group‘);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port,weight,comment) values(20,‘192.168.100.96‘,3306,1,‘Read Group‘);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]>
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port,weight,comment) values(30,‘192.168.100.100‘,3306,1,‘Read Group‘);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> select * from mysql_servers;
+--------------+-----------------+------+--------+--------+-------------+-----------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+-------------+
| hostgroup_id | hostname | port | status | weight | compression | max_connections | max_replication_lag | use_ssl | max_latency_ms | comment |
+--------------+-----------------+------+--------+--------+-------------+-----------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+-------------+
| 10 | 192.168.100.98 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 | 0 | 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Write Group |
| 20 | 192.168.100.96 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 | 0 | 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Read Group |
| 30 | 192.168.100.100 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 | 0 | 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Read Group |
+--------------+-----------------+------+--------+--------+-------------+-----------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+-------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]>
**修改后,需要加载到RUNTIME,并保存到disk**(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> load mysql servers to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> save mysql servers to disk;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
在 proxysql 主机的 mysql_users 表中添加刚才在 master 上创建的账号 proxysql,proxysql 客户端需要使用这个账号来访问数据库
default_hostgroup 默认组设置为写组,也就是10;
当读写分离的路由规则不符合时,会访问默认组的数据库;(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> insert into mysql_users(username,password,default_hostgroup,transaction_persistent)values(‘proxysql‘,‘pwproxysql‘,10,1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> select * from mysql_users G
1. row
username: proxysql # 后端mysql实例的用户名
password: pwproxysql # 后端mysql实例的密码
active: 1 # active=1表示用户生效,0表示不生效
use_ssl: 0
default_hostgroup: 10 # 用户默认登录到哪个hostgroup_id下的实例
default_schema: NULL # 用户默认登录后端mysql实例时连接的数据库,这个地方为NULL的话,则由全局变量mysql-default_schema决定,默认是information_schema
schema_locked: 0
transaction_persistent: 1 # 如果设置为1,连接上ProxySQL的会话后,如果在一个hostgroup上开启了事务,那么后续的sql都继续维持在这个hostgroup上,不论是否会匹配上其它路由规则,直到事务结束。虽然默认是1
fast_forward: 0 # 忽略查询重写/缓存层,直接把这个用户的请求透传到后端DB。相当于只用它的连接池功能,一般不用,路由规则 .* 就行了
backend: 1
frontend: 1
max_connections: 10000 # 该用户允许的最大连接数
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> load mysql users to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> save mysql users to disk;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 8.2.4 添加健康检测的帐号
**在mysql的 master 端添加属于proxysql的只读账号**mysql> GRANT SELECT ON . TO ‘monitor‘@‘192.168.100.%‘ IDENTIFIED BY ‘monitor‘;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql>
**在proxysql主机端修改变量设置健康检测的账号**(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> set mysql-monitor_username=‘monitor‘;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> set mysql-monitor_password=‘monitor‘;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> load mysql variables to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> save mysql variables to disk;
Query OK, 97 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]>
# 8.2.5 添加读写分离的路由规则
**需求:**
* 将 select 查询语句全部路由至 hostgroup_id=20 的组(也就是读组)
* 将 show 查询语句全部路由至 hostgroup_id=30 的组(也就是另一个读组)
* 但是 select * from tb for update 这样的语句是会修改数据的,所以需要单独定义,将它路由至 hostgroup_id=10 的组(也就是写组)
* 其他没有被规则匹配到的组将会被路由至用户默认的组(mysql_users 表中的 default_hostgroup)(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> insert into mysql_query_rules(rule_id,active,match_digest,destination_hostgroup,apply)values(1,1,‘^SELECT.*FOR UPDATE$‘,10,1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> insert into mysql_query_rules(rule_id,active,match_digest,destination_hostgroup,apply)values(2,1,‘^SELECT‘,20,1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> insert into mysql_query_rules(rule_id,active,match_digest,destination_hostgroup,apply)values(3,1,‘^SHOW‘,30,1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> select rule_id,active,match_digest,destination_hostgroup,apply from mysql_query_rules;
+---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+-------+
| rule_id | active | match_digest | destination_hostgroup | apply |
+---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+-------+
| 1 | 1 | ^SELECT.*FOR UPDATE$ | 10 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | ^SELECT | 20 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | ^SHOW | 30 | 1 |
+---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]>
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> load mysql query rules to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> load admin variables to runtime;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> save mysql query rules to disk;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> save admin variables to disk;
Query OK, 31 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]>
# 8.3 验证读写分离
# 8.3.1 登录 proxysql 客户端
**登录用户是刚才我们在 mysql_user 表中创建的用户,端口为6033**[root@proxysql ~]# mysql -uproxysql -ppwproxysql -h127.0.0.1 -P6033
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 11
Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
(proxysql@127.0.0.1:6033) [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
| test | ## test数据库是在主从上面创建的
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.05 sec)
(proxysql@127.0.0.1:6033) [(none)]>
# 8.3.2 尝试修改数据库和查询
**创建2个数据库并查询一下表**(proxysql@127.0.0.1:6033) [(none)]> create database xiaobai;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)
(proxysql@127.0.0.1:6033) [(none)]> create database xiaohong;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
(proxysql@127.0.0.1:6033) [(none)]> select user,host from mysql.user;
+---------------+----------------+
| user | host |
+---------------+----------------+
| proxysql | 172.16.12.99 |
| monitor | 192.168.100.% |
| proxysql | 192.168.100.99 |
| mysql.session | localhost |
| mysql.sys | localhost |
| root | localhost |
+---------------+----------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(proxysql@127.0.0.1:6033) [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
| test |
| xiaobai |
| xiaohong |
+--------------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(proxysql@127.0.0.1:6033) [(none)]>
# 8.3.3 验证读写分离是否成功
> proxysql有个类似审计的功能,可以查看各类SQL的执行情况,其需要在proxysql管理端执行[root@proxysql ~]# mysql -uadmin -padmin -h127.0.0.1 -P6032
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 12
Server version: 5.5.30 (ProxySQL Admin Module)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;‘ or ‘h‘ for help. Type ‘c‘ to clear the current input statement.
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]> select * from stats_mysql_query_digest;
+-----------+--------------------+----------+--------------------+----------------------------------+------------+------------+------------+----------+----------+----------+
| hostgroup | schemaname | username | digest | digest_text | count_star | first_seen | last_seen | sum_time | min_time | max_time |
+-----------+--------------------+----------+--------------------+----------------------------------+------------+------------+------------+----------+----------+----------+
| 20 | information_schema | proxysql | 0x0F02B330C823D739 | select user,host from mysql.user | 1 | 1568035114 | 1568035114 | 720 | 720 | 720 |
| 10 | information_schema | proxysql | 0x826FE2FC8066B91B | create database xiaohong | 1 | 1568035047 | 1568035047 | 2472 | 2472 | 2472 |
| 10 | information_schema | proxysql | 0xA1FBCC498BD4A9EA | create database xiaobai | 1 | 1568035042 | 1568035042 | 51438 | 51438 | 51438 |
| 30 | information_schema | proxysql | 0x02033E45904D3DF0 | show databases | 2 | 1568034912 | 1568035126 | 52731 | 1234 | 51497 |
+-----------+--------------------+----------+--------------------+----------------------------------+------------+------------+------------+----------+----------+----------+
7 rows in set (0.05 sec)
(admin@127.0.0.1:6032) [(none)]>
从上面的 hostgroup 和 digest_text 值来看,所有的写操作都被路由至10组,读操作都被路由至20组,30组,其中10组为写组,20,30组为读组!
由此可见,读写分离成功!!!以上是关于MySQL读写分离中间件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章