@AutoConfiguration注解详解
Posted 怪 咖@
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了@AutoConfiguration注解详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
@AutoConfiguration属于springboot当中autoconfigure包下的注解。springboot给我们提供了好多AutoConfiguration,例如关于缓存cache的有CacheAutoConfiguration,关于定时任务quartz的有QuartzAutoConfiguration,这些AutoConfiguration你会发现基本上都会拿@AutoConfiguration来修饰。本篇来彻底了解@AutoConfiguration到底有什么作用,以及到底如何应用他。
目录
一、观察@AutoConfiguration源码
源码当中有三个元注解:
- @Target(ElementType.TYPE): 使用范围接口、类、枚举、注解
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME): @Retention是用来修饰注解的生命周期的,RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME代表的是不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;一直有效!
- @Documented: @Documented和@Deprecated注解长得有点像,@Deprecated是用来标注某个类或者方法不建议再继续使用,@Documented只能用在注解上,如果一个注解@B,被@Documented标注,那么被@B修饰的类,生成Javadoc文档时,会显示@B。
除了元注解外还有三个注解:
- @Configuration: 这个是开发当中最常用的注解,他属于是
@Component注解的扩展注解,同@Controller、@Service等几个注解的功能是一样的,只要在类上添加了该注解,然后在springboot的扫描范围内,启动项目的时候会将该注解修饰的类通过无参构造器创建出来,然后存入spring容器当中。 - @AutoConfigureBefore: 一般都是配合着
@Configuration使用,主要用于修饰在类上,然后可以指定该类 在 某类之前进行加载到容器。 - @AutoConfigureAfter: 同
@AutoConfigureBefore功能一样,他是指定该类 在 某类 之后进行加载到容器当中。
具体的用法请看下面的示例!
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@AutoConfigureBefore
@AutoConfigureAfter
public @interface AutoConfiguration
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
String value() default "";
@AliasFor(
annotation = AutoConfigureBefore.class,
attribute = "value"
)
Class<?>[] before() default ;
@AliasFor(
annotation = AutoConfigureBefore.class,
attribute = "name"
)
String[] beforeName() default ;
@AliasFor(
annotation = AutoConfigureAfter.class,
attribute = "value"
)
Class<?>[] after() default ;
@AliasFor(
annotation = AutoConfigureAfter.class,
attribute = "name"
)
String[] afterName() default ;
@AutoConfiguration其实就是一个组合注解。因为一个自动配置类往往需要加很多注解,于是乎springboot就将一些经常用到的注解,给组合到一块,这样就可以做到一个注解拥有三个注解的功能。具体他是如何做到注解聚合到一块的呢,原因是依赖于@AliasFor注解,@AliasFor注解就是起到一个注解传值的作用。想深入了解@AliasFor可以看我的这一篇文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43888891/article/details/126962698?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
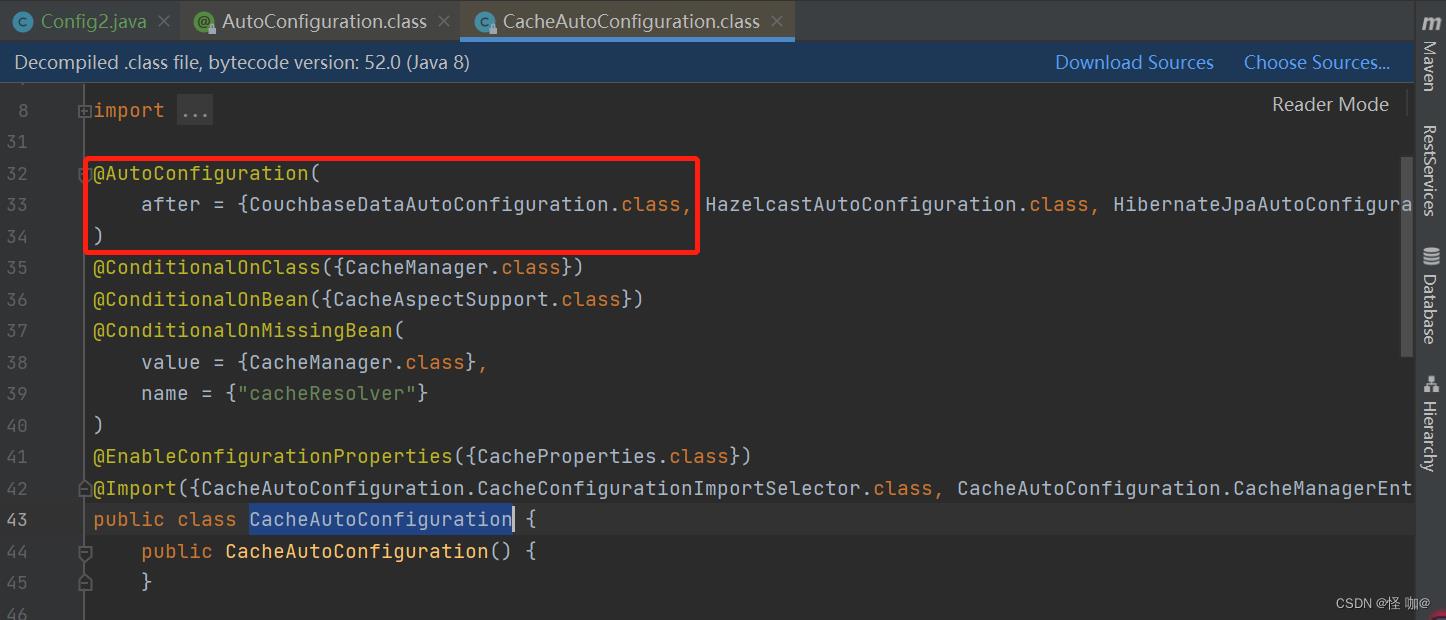
二、@Configuration
@Configuration注解我们经常用,但是我们很少这样用@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false),这里的proxyBeanMethods默认是true,但是这里却设置为了false,那么这个属性到底有什么作用?
@Configuration属于spring当中的注解,感兴趣的可以看一下spring源码当中的解释:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/blob/main/spring-context/src/main/java/org/springframework/context/annotation/Configuration.java
源码当中解释不是中文,再者一般的也看不懂,我们直接通过代码试验来得出结论:
当他为true的时候,我们在容器中获取到的对象总是同一个,即便是我们调用了创建对象的方法,那获取到的还是同一个。但是当是多例的时候,如果我们调用了创建对象的方法,那就不是同一个了。
(1)自定义一个类,用于测试
public class TestBean1
@Override
public String toString()
return super.toString() + "--我是TestBean1";
public TestBean1()
System.out.println("TestBean1构造器执行了");
(2)添加配置类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)
public class Myconfig
@Bean
public TestBean1 testBean1()
return new TestBean1();
(3)添加测试类
@RestController
public class CommonController
@Autowired
private Myconfig myconfig;
@Autowired
private TestBean1 testBean1;
@RequestMapping("/import")
public void printImportBeanInfo()
System.out.println(testBean1);
System.out.println(myconfig.testBean1());
(4)访问接口,得出从容器里面取和直接访问testBean1方法得出来的对象是一个对象,这就是所谓的被代理了
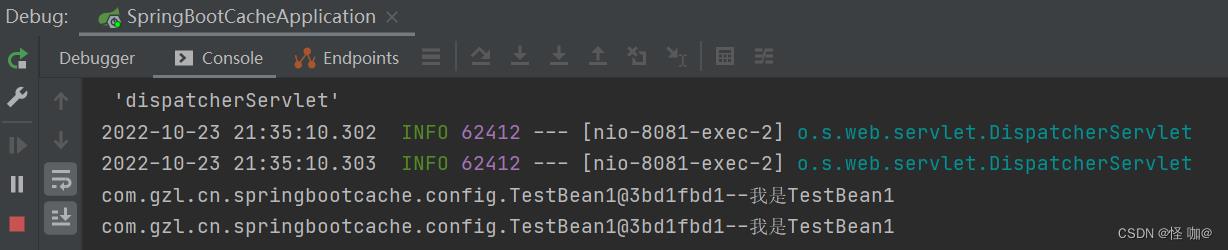
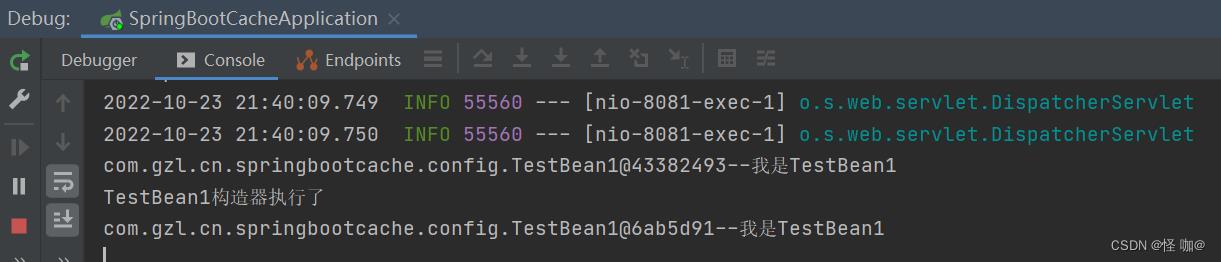
(5)设置为false@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
很显然已经不是一个对象了
三、@AutoConfigureBefore
(1)自定义两个配置类
@Configuration
public class Config1
public Config1()
System.out.println("Config1构建了");
@Configuration
public class Config2
public Config2()
System.out.println("Config2构建了");
(2)启动项目测试:默认是先创建的Config1后创建的Config2
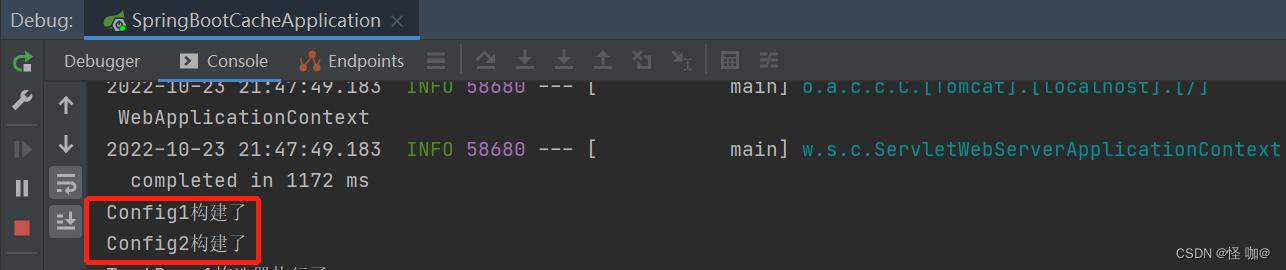
现在是有个需求要求让@Config2先加载,可能这时候有人该说了@Order注解不就可以了吗,其实不是的,@Order值可能会影响注入点的优先级,但请注意,它不会影响单例启动顺序。关于@order我专门整理了一篇文章,供参考学习!
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43888891/article/details/127481825
(3)使用@AutoConfigure相关注解的前提是必须是自动配置类,可能有时候走了狗屎运给你一种错觉还真的配置成功了。
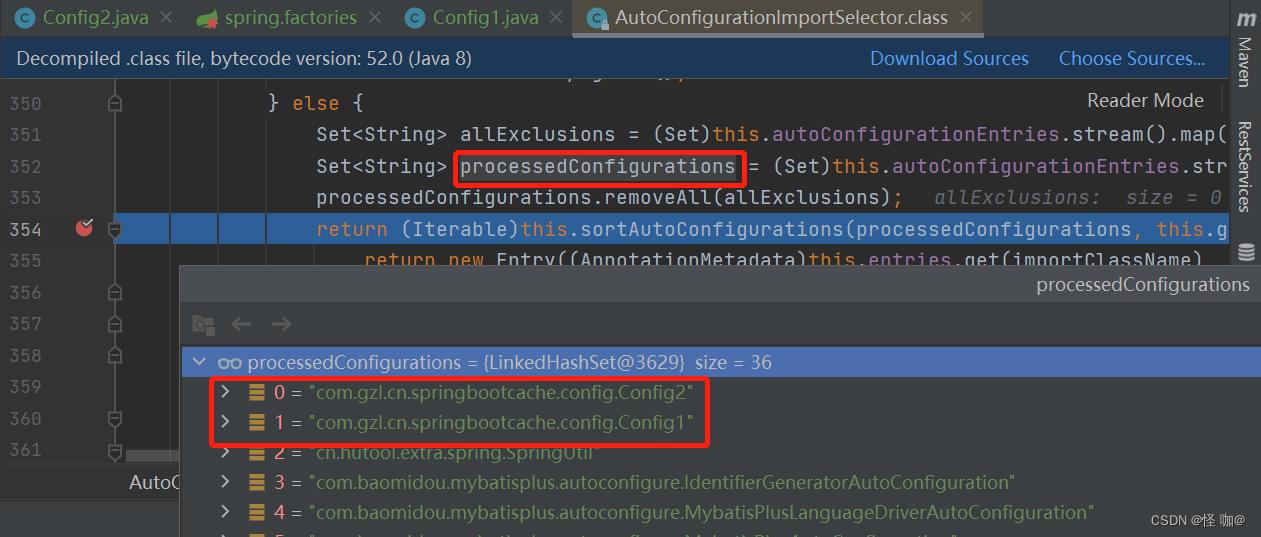
在autoconfigure包下就有spring.factories,这个文件配置了自动配置类,springboot会读取这个文件的,我们也可以在自己项目上定义spring.factories,这样我们的配置类对于@AutoConfigureAfter注解就可以生效了。
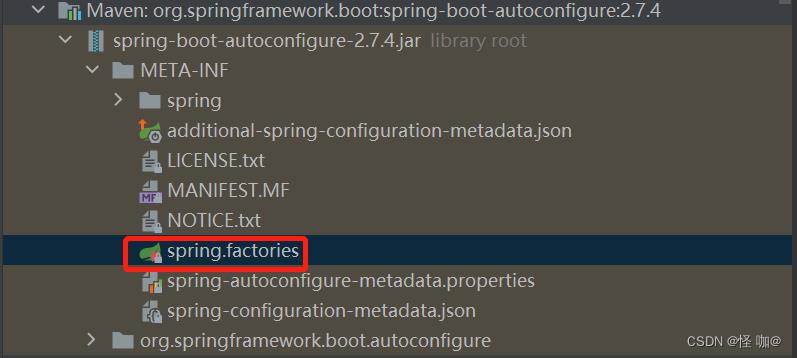
(4)自定义spring.factories
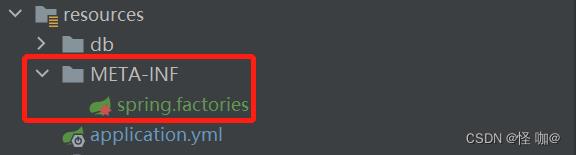
第一行是固定的,后面的就是全类名,虽然只有Config2使用了注解,但是需求是和Config1进行排序,所以这两个都得加。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\\
com.gzl.cn.springbootcache.config.Config2,\\
com.gzl.cn.springbootcache.config.Config1
(5)测试,成功解决
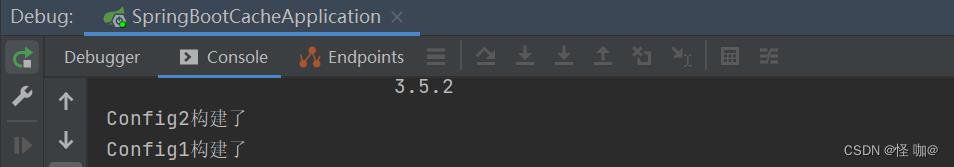
四、@AutoConfigureAfter
@AutoConfigureAfter和@AutoConfigureBefore其实是一样的,我这里就不演示了哈,感兴趣的可以自己参照上面进行练习一下。
五、@AutoConfigureOrder
这种也是可以的!当然前提也是需要配置spring.factories
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureOrder(2)
public class Config1
public Config1()
System.out.println("Config1构建了");
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureOrder(1)
public class Config2
public Config2()
System.out.println("Config2构建了");
六、源码分析
其实关键的代码还是在AutoConfigurationImportSelector中,将自动配置类从spring.factories加载出来之后会根据条件排序,在selectImports()方法中最后一行代码如下:
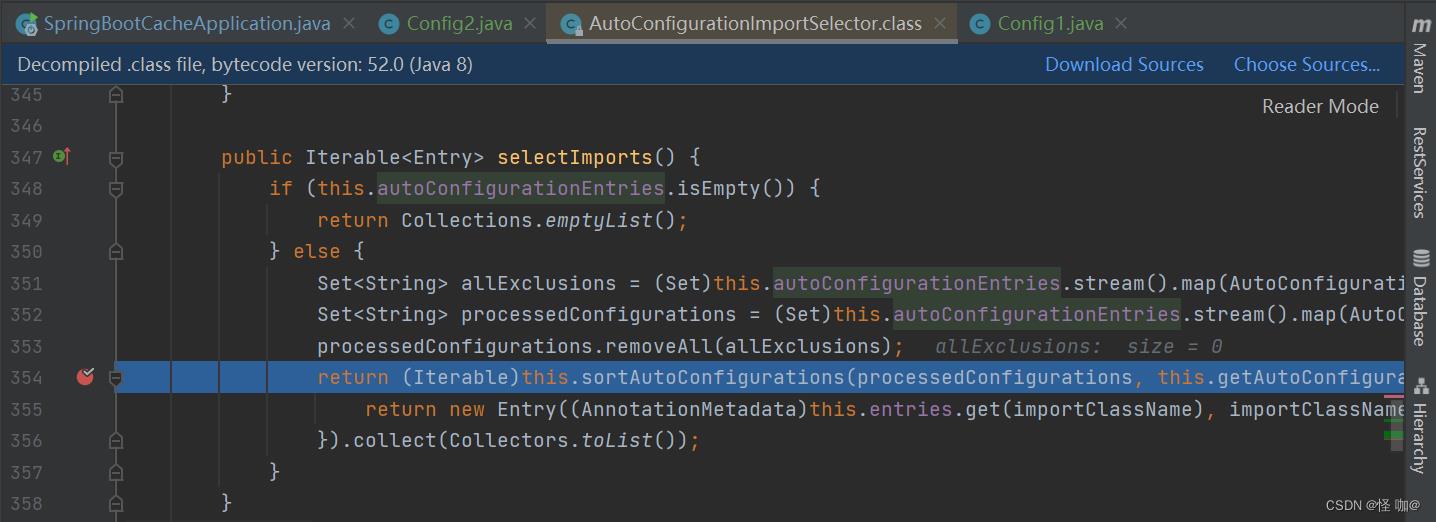
紧接着会走到这个地方,实际上是分了三步排序:
- 先按照字母排序
- 按照@AutoConfigureOrder进行排序
- 按照 @AutoConfigureBefore和@AutoConfigureAfter排序
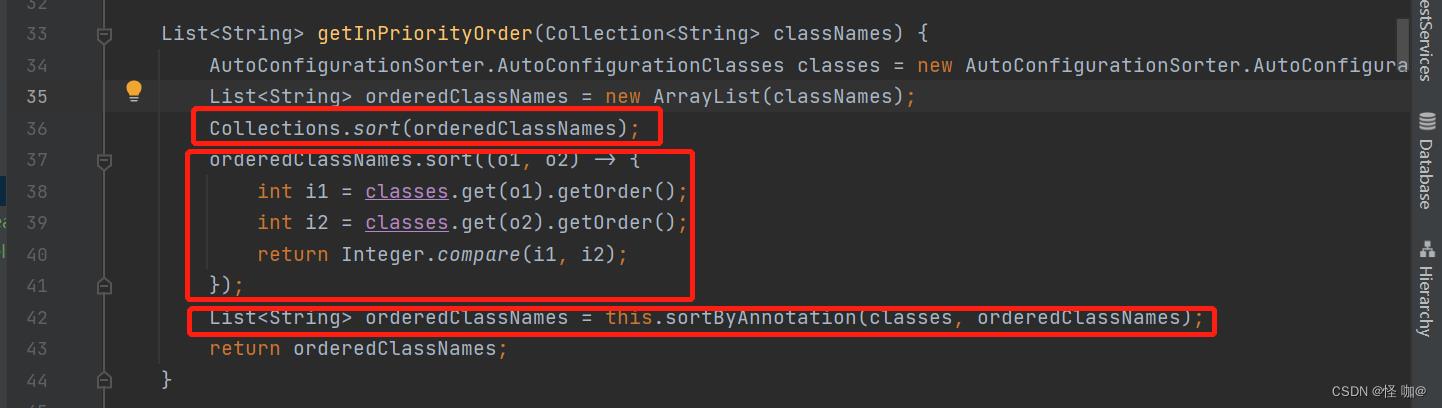
从上面配置的顺序可以知道,最终决定权还是在@AutoConfigureAfter、@AutoConfigureBefore这两个注解。
当我们不设置spring.factories的时候,这里面压根都没有这两个类!
Spring Boot AutoConfiguration注解@ConditionalXXXX之前生今世
1.注解@Conditional的定义
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface Conditional { /** * All {@link Condition}s that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match} * in order for the component to be registered. */ Class<? extends Condition>[] value(); }
注解@Conditional标识一个组件时,该组件只有全面满足value()指定的所有条件时才可以注册到容器中。
注解@Conditional的使用场景如下:
. 作为类型级别的注解,作用在一个直接或者间接@Component注解(包括@Configuration作为元注解的类)的类上,目标是组成自定义的steretype注解。
. 作为方法级别的注解,作用在任意的@Bean 方法上
如果一个标注了@Configuration的类,也标注了@Conditional,所有的@Bean方法,@Import和@ComponentScan注解关联的类将也满足这些Conditions。
注意,@Conditional注解不能继承,从父类或者重写方法的condition是不起作用的。
其中,一个Condition是要注册的Bean定义之前可以编程决定的状态。详细信息如下:
2 前生 Condition定义
public interface Condition { /** * Determine if the condition matches. * @param context the condition context * @param metadata metadata of the {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata class} * or {@link org.springframework.core.type.MethodMetadata method} being checked. * @return {@code true} if the condition matches and the component can be registered * or {@code false} to veto registration. */ boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata); }
一个单独的condition是一个组件为注册为bean时必须满足matches()方法。
Conditions在要注册的组件变成bean definition之前必须检查立即检查所有的matches方法。
Condition也必须和BeanFactoryPostProcessor一样满足同样的限制条件。更细粒度的控制可以考虑使用ConfigurationCondition。
3.后世
spring-boot-autoconfigure condition相关的类如下:
3.1 ConditionalOnBean定义
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnBean { /** * The class type of bean that should be checked. The condition matches when all of * the classes specified are contained in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class types of beans to check */ Class<?>[] value() default {}; /** * The class type names of bean that should be checked. The condition matches when all * of the classes specified are contained in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class type names of beans to check */ String[] type() default {}; /** * The annotation type decorating a bean that should be checked. The condition matches * when all of the annotations specified are defined on beans in the * {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class-level annotation types to check */ Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {}; /** * The names of beans to check. The condition matches when all of the bean names * specified are contained in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the name of beans to check */ String[] name() default {}; /** * Strategy to decide if the application context hierarchy (parent contexts) should be * considered. * @return the search strategy */ SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
ConditionalOnBean作用:当指定bean的类名或者名称已经在BeanFactory中存在时才算满足条件。
其实现类为OnBeanCondition,检查指定的bean是存在还是不存在。
@Order(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE) class OnBeanCondition extends SpringBootCondition implements ConfigurationCondition { /** * Bean definition attribute name for factory beans to signal their product type (if * known and it can‘t be deduced from the factory bean class). */ public static final String FACTORY_BEAN_OBJECT_TYPE = BeanTypeRegistry.FACTORY_BEAN_OBJECT_TYPE; @Override public ConfigurationPhase getConfigurationPhase() { return ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN; } @Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty(); if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnBean.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new BeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnBean.class); MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (!matchResult.isAllMatched()) { String reason = createOnBeanNoMatchReason(matchResult); return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnBean.class, spec).because(reason)); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnBean.class, spec) .found("bean", "beans") .items(Style.QUOTE, matchResult.getNamesOfAllMatches()); } if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new SingleCandidateBeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class); MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (!matchResult.isAllMatched()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .didNotFind("any beans").atAll()); } else if (!hasSingleAutowireCandidate(context.getBeanFactory(), matchResult.getNamesOfAllMatches(), spec.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.ALL)) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .didNotFind("a primary bean from beans") .items(Style.QUOTE, matchResult.getNamesOfAllMatches())); } matchMessage = matchMessage .andCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .found("a primary bean from beans") .items(Style.QUOTE, matchResult.namesOfAllMatches); } if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new BeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnMissingBean.class); MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (matchResult.isAnyMatched()) { String reason = createOnMissingBeanNoMatchReason(matchResult); return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class, spec) .because(reason)); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class, spec) .didNotFind("any beans").atAll(); } return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage); } }
3.2 ConditionalOnClass
当指定的类在classpath下认定满足条件,实现类为:OnClassCondition。
定义如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnClassCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnClass { /** * The classes that must be present. Since this annotation parsed by loading class * bytecode it is safe to specify classes here that may ultimately not be on the * classpath. * @return the classes that must be present */ Class<?>[] value() default {}; /** * The classes names that must be present. * @return the class names that must be present. */ String[] name() default {}; }
3.3 ConditionalOnCloudPlatform
指定的云平台激活时满足条件。实现类为:OnCloudPlatformCondition
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnCloudPlatformCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnCloudPlatform { /** * The {@link CloudPlatform cloud platform} that must be active. * @return the expected cloud platform */ CloudPlatform value(); }
3.4 ConditionalOnExpression
/** * Configuration annotation for a conditional element that depends on the value of a SpEL * expression. * * @author Dave Syer */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Documented @Conditional(OnExpressionCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnExpression { /** * The SpEL expression to evaluate. Expression should return {@code true} if the * condition passes or {@code false} if it fails. * @return the SpEL expression */ String value() default "true"; }
3.5 ConditionalOnJava
/** * {@link Conditional} that matches based on the JVM version the application is running * on. * * @author Oliver Gierke * @author Phillip Webb * @author Andy Wilkinson * @since 1.1.0 */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnJavaCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnJava { /** * Configures whether the value configured in {@link #value()} shall be considered the * upper exclusive or lower inclusive boundary. Defaults to * {@link Range#EQUAL_OR_NEWER}. * @return the range */ Range range() default Range.EQUAL_OR_NEWER; /** * The {@link JavaVersion} to check for. Use {@link #range()} to specify whether the * configured value is an upper-exclusive or lower-inclusive boundary. * @return the java version */ JavaVersion value(); /** * Range options. */ enum Range { /** * Equal to, or newer than the specified {@link JavaVersion}. */ EQUAL_OR_NEWER, /** * Older than the specified {@link JavaVersion}. */ OLDER_THAN } /** * Java versions. */ enum JavaVersion { /** * Java 1.9. */ NINE(9, "1.9", "java.security.cert.URICertStoreParameters"), /** * Java 1.8. */ EIGHT(8, "1.8", "java.util.function.Function"); private final int value; private final String name; private final boolean available; JavaVersion(int value, String name, String className) { this.value = value; this.name = name; this.available = ClassUtils.isPresent(className, getClass().getClassLoader()); } /** * Determines if this version is within the specified range of versions. * @param range the range * @param version the bounds of the range * @return if this version is within the specified range */ public boolean isWithin(Range range, JavaVersion version) { Assert.notNull(range, "Range must not be null"); Assert.notNull(version, "Version must not be null"); switch (range) { case EQUAL_OR_NEWER: return this.value >= version.value; case OLDER_THAN: return this.value < version.value; } throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown range " + range); } @Override public String toString() { return this.name; } /** * Returns the {@link JavaVersion} of the current runtime. * @return the {@link JavaVersion} */ public static JavaVersion getJavaVersion() { for (JavaVersion candidate : JavaVersion.values()) { if (candidate.available) { return candidate; } } return EIGHT; } } }
3.6 ConditionalOnJndi
/** * {@link Conditional} that matches based on the availability of a JNDI * {@link InitialContext} and the ability to lookup specific locations. * * @author Phillip Webb * @since 1.2.0 */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnJndiCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnJndi { /** * JNDI Locations, one of which must exist. If no locations are specific the condition * matches solely based on the presence of an {@link InitialContext}. * @return the JNDI locations */ String[] value() default {}; }
3.7 ConditionalOnMissingBean
/** * {@link Conditional} that only matches when the specified bean classes and/or names are * not already contained in the {@link BeanFactory}. * <p> * The condition can only match the bean definitions that have been processed by the * application context so far and, as such, it is strongly recommended to use this * condition on auto-configuration classes only. If a candidate bean may be created by * another auto-configuration, make sure that the one using this condition runs after. * * @author Phillip Webb * @author Andy Wilkinson */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnMissingBean { /** * The class type of bean that should be checked. The condition matches when each * class specified is missing in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class types of beans to check */ Class<?>[] value() default {}; /** * The class type names of bean that should be checked. The condition matches when * each class specified is missing in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class type names of beans to check */ String[] type() default {}; /** * The class type of beans that should be ignored when identifying matching beans. * @return the class types of beans to ignore * @since 1.2.5 */ Class<?>[] ignored() default {}; /** * The class type names of beans that should be ignored when identifying matching * beans. * @return the class type names of beans to ignore * @since 1.2.5 */ String[] ignoredType() default {}; /** * The annotation type decorating a bean that should be checked. The condition matches * when each annotation specified is missing from all beans in the * {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class-level annotation types to check */ Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {}; /** * The names of beans to check. The condition matches when each bean name specified is * missing in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the name of beans to check */ String[] name() default {}; /** * Strategy to decide if the application context hierarchy (parent contexts) should be * considered. * @return the search strategy */ SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
3.8 ConditionalOnMissingClass
/** * {@link Conditional} that only matches when the specified classes are not on the * classpath. * * @author Dave Syer */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnClassCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnMissingClass { /** * The names of the classes that must not be present. * @return the names of the classes that must not be present */ String[] value() default {}; }
3.9 ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
/** * {@link Conditional} that only matches when the application context is a not a web * application context. * * @author Dave Syer */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnWebApplicationCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnNotWebApplication { }
3.10 ConditionalOnProperty
/** * {@link Conditional} that checks if the specified properties have a specific value. By * default the properties must be present in the {@link Environment} and * <strong>not</strong> equal to {@code false}. The {@link #havingValue()} and * {@link #matchIfMissing()} attributes allow further customizations. * * <p> * The {@link #havingValue} attribute can be used to specify the value that the property * should have. The table below shows when a condition matches according to the property * value and the {@link #havingValue()} attribute: * * <table summary="having values" border="1"> * <tr> * <th>Property Value</th> * <th>{@code havingValue=""}</th> * <th>{@code havingValue="true"}</th> * <th>{@code havingValue="false"}</th> * <th>{@code havingValue="foo"}</th> * </tr> * <tr> * <td>{@code "true"}</td> * <td>yes</td> * <td>yes</td> * <td>no</td> * <td>no</td> * </tr> * <tr> * <td>{@code "false"}</td> * <td>no</td> * <td>no</td> * <td>yes</td> * <td>no</td> * </tr> * <tr> * <td>{@code "foo"}</td> * <td>yes</td> * <td>no</td> * <td>no</td> * <td>yes</td> * </tr> * </table> * * <p> * If the property is not contained in the {@link Environment} at all, the * {@link #matchIfMissing()} attribute is consulted. By default missing attributes do not * match. * * @author Maciej Walkowiak * @author Stephane Nicoll * @author Phillip Webb * @since 1.1.0 */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Documented @Conditional(OnPropertyCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnProperty { /** * Alias for {@link #name()}. * @return the names */ String[] value() default {}; /** * A prefix that should be applied to each property. The prefix automatically ends * with a dot if not specified. * @return the prefix */ String prefix() default ""; /** * The name of the properties to test. If a prefix has been defined, it is applied to * compute the full key of each property. For instance if the prefix is * {@code app.config} and one value is {@code my-value}, the fully key would be * {@code app.config.my-value} * <p> * Use the dashed notation to specify each property, that is all lower case with a "-" * to separate words (e.g. {@code my-long-property}). * @return the names */ String[] name() default {}; /** * The string representation of the expected value for the properties. If not * specified, the property must <strong>not</strong> be equals to {@code false}. * @return the expected value */ String havingValue() default ""; /** * Specify if the condition should match if the property is not set. Defaults to * {@code false}. * @return if should match if the property is missing */ boolean matchIfMissing() default false; /** * If relaxed names should be checked. Defaults to {@code true}. * @return if relaxed names are used */ boolean relaxedNames() default true; }
3.11 ConditionalOnResource
/** * {@link Conditional} that only matches when the specified resources are on the * classpath. * * @author Dave Syer */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnResourceCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnResource { /** * The resources that must be present. * @return the resource paths that must be present. */ String[] resources() default {}; }
3.12 ConditionalOnSingleCandidate
/** * {@link Conditional} that only matches when the specified bean class is already * contained in the {@link BeanFactory} and a single candidate can be determined. * <p> * The condition will also match if multiple matching bean instances are already contained * in the {@link BeanFactory} but a primary candidate has been defined; essentially, the * condition match if auto-wiring a bean with the defined type will succeed. * <p> * The condition can only match the bean definitions that have been processed by the * application context so far and, as such, it is strongly recommended to use this * condition on auto-configuration classes only. If a candidate bean may be created by * another auto-configuration, make sure that the one using this condition runs after. * * @author Stephane Nicoll * @since 1.3.0 */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnSingleCandidate { /** * The class type of bean that should be checked. The condition match if the class * specified is contained in the {@link ApplicationContext} and a primary candidate * exists in case of multiple instances. * <p> * This attribute may <strong>not</strong> be used in conjunction with {@link #type()} * , but it may be used instead of {@link #type()}. * @return the class type of the bean to check */ Class<?> value() default Object.class; /** * The class type name of bean that should be checked. The condition matches if the * class specified is contained in the {@link ApplicationContext} and a primary * candidate exists in case of multiple instances. * <p> * This attribute may <strong>not</strong> be used in conjunction with * {@link #value()}, but it may be used instead of {@link #value()}. * @return the class type name of the bean to check */ String type() default ""; /** * Strategy to decide if the application context hierarchy (parent contexts) should be * considered. * @return the search strategy */ SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
3.13 ConditionalOnWebApplication
/** * {@link Conditional} that matches when the application is a web application. By default, * any web application will match but it can be narrowed using the {@link #type()} * attribute. * * @author Dave Syer * @author Stephane Nicoll */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnWebApplicationCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnWebApplication { /** * The required type of the web application. * @return the required web application type */ Type type() default Type.ANY; /** * Available application types. */ enum Type { /** * Any web application will match. */ ANY, /** * Only servlet-based web application will match. */ SERVLET, /** * Only reactive-based web application will match. */ REACTIVE } }
以上是关于@AutoConfiguration注解详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章