PyTorch中的matmul函数详解
Posted 旅途中的宽~
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了PyTorch中的matmul函数详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
PyTorch中的两个张量的乘法可以分为两种:
-
两个张量对应的元素相乘(element-wise),在PyTorch中可以通过
torch.mul函数(或者 ∗ * ∗运算符)实现 -
两个张量矩阵相乘(Matrix product),在PyTorch中可以通过
torch.matmul函数实现
本文主要介绍两个张量的矩阵相乘。
语法为:
torch.matmul(input, other, out = None)
函数对input和other两个张量进行矩阵相乘。为了方便后续的讲解,将input记为a,将other记为b。
点积在数学中,又称数量积,是指接受在实数R上的两个1D张量并返回一个实数值0D张量的二元运算。
若1D张量a=[1,2],1D张量b=[3,4],则:
a ⋅ \\cdot ⋅b=1 × \\times × 3 + 2 × \\times × 4 = 11
- 若a为1D张量,b为1D张量,则返回两个张量的点积,则返回两个张量的点积(此时的torch.matmul不支持out参数)
举例如下:
import torch
a = torch.tensor([1, 2])
b = torch.tensor([3, 4])
result = torch.matmul(a, b)
print(result)
结果为:
(PyTorch) D:\\Code Project>D:/Anaconda/envs/PyTorch/python.exe "d:/Code Project/demo.py"
tensor(11)
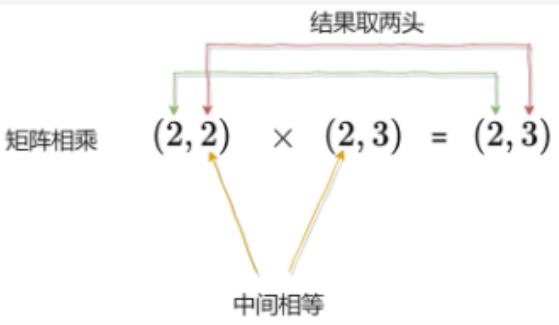
- 若a为2D张量,b为2D张量,则返回两个张量的矩阵乘积。
矩阵相乘最重要的方法是一般矩阵乘积,它只有在第一个2D张量(矩阵)的列数(column)和第二个2D张量(矩阵)的行数(row)相同时才有意义。
若2D张量a=[[1,2],[3,4]],2D张量b=[[5,6,7],[8,9,10]],则:
a × \\times × b=[[21,24,27],[47,54,61]],2D张量a的形状为(2,2),而2D张量b的形状(2,3)。矩阵乘积的运算规则:
举例为:
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2],[3,4]])
b = torch.tensor([[5,6,7],[8,9,10]])
result = torch.matmul(a, b)
print(result)
结果展示为:
(PyTorch) D:\\Code Project>D:/Anaconda/envs/PyTorch/python.exe "d:/Code Project/demo.py"
tensor([[21, 24, 27],
[47, 54, 61]])
- 若a为1D张量,b为2D张量,torch.matmul函数:
首先,在1D张量a的前面插入一个长度为1的新维度变成2D张量;
然后,在满足第一个2D张量(矩阵)的列数(column)和第二个2D张量(矩阵)的行数(row)相同的条件下,两个2D张量矩阵乘积,否则会抛出错误;
最后,将矩阵乘积结果中长度为1的维度(前面插入的长度为1的新维度)删除作为最终torch.matmul函数返回的结果。
import torch
a = torch.tensor([1, 2])
b = torch.tensor([[5, 6, 7],[8, 9, 10]])
result = torch.matmul(a, b)
print(result, result.shape)
结果为:
(PyTorch) D:\\Code Project>D:/Anaconda/envs/PyTorch/python.exe "d:/Code Project/demo.py"
tensor([21, 24, 27]) torch.Size([3])
简单来说,先将1D张量a扩展成2D张量,满足矩阵乘积的条件下,将两个2D张量进行矩阵乘积的运算。
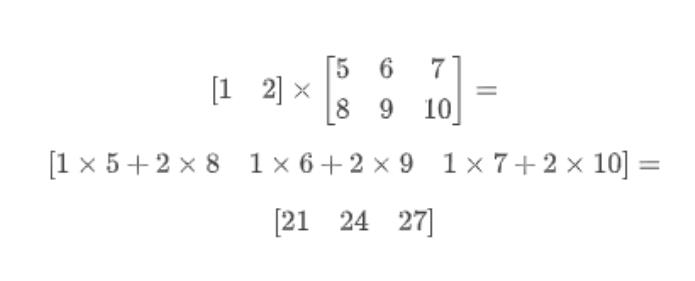
此时得到的形状是(1,3)的2D张量,最后将前面插入长度为1的新维度删除即为最终torch.matmul(a, b)函数返回的结果。
- 若a为2D张量,b为1D张量,torch.matmul函数:
首先,在1D张量b的后面插入一个长度为1的新维度变成2D张量;
然后,在满足第一个2D张量(矩阵)的列数(column)和第二个2D张量(矩阵)的行数(row)相同的条件下,两个2D张量矩阵乘积,否则会抛出错误;
最后,将矩阵乘积结果中长度为1的维度(后面插入的长度为1的新维度)删除作为最终torch.matmul函数返回的结果;
import torch
b = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
a = torch.tensor([[5, 6, 7],[8, 9, 10]])
result = torch.matmul(a, b)
print(result, result.shape)
结果展示为:
(PyTorch) D:\\Code Project>D:/Anaconda/envs/PyTorch/python.exe "d:/Code Project/demo.py"
tensor([38, 56]) torch.Size([2])
其中:
38 = 15+26+3*7
56 = 18+29+3*10
每天讲解一点PyTorch torch.matmul
每天讲解一点PyTorch——函数torch.matmul
torch.matmul
今天我们学习函数torch.matmul:Tensor的乘法
// An highlighted block
>>> import torch
>>> x = torch.rand(2,2)
>>> x
tensor([[0.7834, 0.5647],
[0.2723, 0.6277]])
>>> y = torch.rand(2,2)
>>> y
tensor([[0.3738, 0.1724],
[0.3732, 0.3012]])
>>>
>>> z = torch.rand(1,2)
>>> z
tensor([[0.8670, 0.3807]])
>>>
>>> torch.mul(x,y)
tensor([[0.2928, 0.0973],
[0.1016, 0.1891]])
>>> m = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
>>> m
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
>>>
>>> n = torch.tensor([[2,3],[4,5]])
>>> n
tensor([[2, 3],
[4, 5]])
>>>
>>> torch.mul(m,n)
tensor([[ 2, 6],
[12, 20]])
>>>
>>> torch.mul(m,m)
tensor([[ 1, 4],
[ 9, 16]])
>>>
>>> torch.mul(n,n)
tensor([[ 4, 9],
[16, 25]])
>>>
实现点乘功能:对应位相乘
以上是关于PyTorch中的matmul函数详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章