Linux硬件资源管理与外设设备使用系统运行机制及用户管理
Posted 成平艺君
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux硬件资源管理与外设设备使用系统运行机制及用户管理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Linux硬件资源管理
PCI设备
显卡
$>>dmesg |grep -i vga
[ 0.000000] Console: colour VGA+ 80x25
[ 0.262267] vgaarb: device added: PCI:0000:00:0f.0,decodes=io+mem,owns=io+mem,locks=none
[ 0.262271] vgaarb: loaded
[ 0.262272] vgaarb: bridge control possible 0000:00:0f.0
[ 1.969021] fbcon: svgadrmfb (fb0) is primary device
网卡
$>>lscpi |grep -i eth
02:01.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82545EM Gigabit Ethernet Controller (Copper) (rev 01)
声卡
$>>lspci |grep -i vga
00:0f.0 VGA compatible controller: VMware SVGA II Adapter
CPU信息
通过/proc文件系统查看 $>> cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0 vendor_id : GenuineIntel cpu family : 6 model : 94 model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700HQ CPU @ 2.60GHz stepping : 3 microcode : 0x6a cpu MHz : 2601.000 cache size : 6144 KB physical id : 0 siblings : 1 core id : 0 cpu cores : 1 apicid : 0 initial apicid : 0 fpu : yes fpu_exception : yes cpuid level : 22 wp : yes flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc aperfmperf eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch ida arat epb pln pts dtherm hwp hwp_noitfy hwp_act_window hwp_epp fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid rtm rdseed adx smap xsaveopt bogomips : 5202.00 clflush size : 64 cache_alignment : 64 address sizes : 42 bits physical, 48 bits virtual power management:
内存信息
$>>free -m 或 cat /proc/meminfo
total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1824 713 300 10 810 912 Swap: 2047 0 2047 total //内存总数 used //已经使用的内存数 free //空闲的内存数 shared //多个进程共享的内存总额 page cache //磁盘缓存的大小
磁盘分区信息
$>>fdisk -l //分区情况
$>>df -h //大小情况
$>>du -h //使用情况
[root@ ~]# fdisk -l Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x000ab2c2 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sda1 * 2048 1026047 512000 83 Linux /dev/sda2 1026048 41943039 20458496 8e Linux LVM Disk /dev/mapper/centos-root: 18.8 GB, 18756927488 bytes, 36634624 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/mapper/centos-swap: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes [root@ ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/centos-root 18G 4.2G 14G 24% / devtmpfs 898M 0 898M 0% /dev tmpfs 913M 100K 913M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 913M 9.0M 904M 1% /run tmpfs 913M 0 913M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 497M 157M 341M 32% /boot tmpfs 183M 20K 183M 1% /run/user/1000 tmpfs 183M 0 183M 0% /run/user/0
外部设备使用
在Linux系统中硬件设备都以文件的形式存在;不同的硬件设备具有不同的文件类型;设备文件在/dev目录下
[root@ ~]# cd /dev/ [root@ dev]# ls agpgart crash initctl mqueue rfkill stdin tty18 tty3 tty41 tty53 tty8 vcs1 vfio autofs disk input net rtc stdout tty19 tty30 tty42 tty54 tty9 vcs2 vga_arbiter block dm-0 kmsg network_latency rtc0 tty tty2 tty31 tty43 tty55 ttyS0 vcs3 vhost-net bsg dm-1 log network_throughput sda tty0 tty20 tty32 tty44 tty56 ttyS1 vcs4 vmci btrfs-control dmmidi loop-control null sda1 tty1 tty21 tty33 tty45 tty57 ttyS2 vcs5 vsock bus dri lp0 nvram sda2 tty10 tty22 tty34 tty46 tty58 ttyS3 vcs6 zero cdrom fb0 lp1 oldmem sg0 tty11 tty23 tty35 tty47 tty59 uhid vcsa centos fd lp2 port sg1 tty12 tty24 tty36 tty48 tty6 uinput vcsa1 char full lp3 ppp shm tty13 tty25 tty37 tty49 tty60 urandom vcsa2 console fuse mapper ptmx snapshot tty14 tty26 tty38 tty5 tty61 usbmon0 vcsa3 core hidraw0 mcelog pts snd tty15 tty27 tty39 tty50 tty62 usbmon1 vcsa4 cpu hpet mem random sr0 tty16 tty28 tty4 tty51 tty63 usbmon2 vcsa5 cpu_dma_latency hugepages midi raw stderr tty17 tty29 tty40 tty52 tty7 vcs vcsa6
系统运行机制
系统启动过程
开机自检->MBR引导->GRUB菜单->加载内核->init进程初始化->登录系统

系统运行级别
$>>cat /etc/inittab
# 0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this) //关机 # 1 - Single user mode //单用户模式 # 2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking)//无网络支持的多用户模式 # 3 - Full multiuser mode //有网络支持的多用户模式 # 4 - unused //保留,未使用 # 5 - X11 //有网络支持的X-Windows支持的多用户模式 # 6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this) //重新引导,重启 # id:5:initdefault: eg:切换到第3运行级别 $>>systemctl isolate multi-user.target 或 systemctl isolate runlevel3.target eg:切换到第5运行级别 $>>systemctl isolate graphical.target 或 systemctl isolate runlevel5.target eg:设置默认第三启动级别 $>>systemctl set-default multi-user.target $>>systemctl get-default //查看当前运行启动级别 eg:设置默认第五启动级别 $>>systemctl set-default graphical.target
系统用户管理
用户账号分类

用户账号密码配置文件

/etc/passwd 每个字段的作用
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
用户名:密码占位符:UID:GID:用户描述:用户主目录:登录后使用的shell
系统中的伪用户
Linux中任何一个命令的操作都必须有一个用户的身份。伪用户一般和系统或者程序服务相关
bin,daemon,shutdown,halt,linux默认都有这些伪用户,伪用户通常不需要或无法登陆系统,可以没有宿主目录
eg:/etc/passwd文件中常见的伪用户Nobody
添加系统用户
[root@ dev]# useradd
-d, --home-dir HOME_DIR home directory of the new account //目录,创建用户时指定用户主目录
-g, --gid GROUP name or ID of the primary group of the new account//用户组,指定用户所属组
-G, --groups GROUPS list of supplementary groups of the new account//用户组,指定用户所属的附加组
faillog databases
-m, --create-home create the user\'s home directory //不创建用户宿主目录
-s, --shell SHELL login shell of the new account //指定用户的登录shell
-u, --uid UID user ID of the new account //指定用户号
eg:创建一个用户名称为sam,指定宿主目录为/opt/sam,登录的shell为/bin/sh.
[root@ dev]# useradd -d /opt/sam -s /bin/sh sam
[root@ dev]# tail -1 /etc/passwd
sam:x:1001:1001::/opt/sam:/bin/sh
eg:创建一个用户名为test,UID为2010,指定起始组为root,附加组为ftp,登录shell为/bin/sh
[root@ dev]# useradd -u 2010 -g root -G ftp -s /bin/sh test
[root@ dev]# tail -1 /etc/passwd
test:x:2010:0::/home/test:/bin/sh
注:当所创建用户无法正常显示时!将/etc/skel/下的所有文件拷贝到新建用户的宿主目录下
[root@ skel]# cd /etc/skel/
[root@ skel]# ls
[root@ skel]# ls -a
. .. .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .mozilla
[root@ skel]# ls -a /opt/sam/
. .. .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .mozilla
删除用户
如果一个用户的账号不再使用,可以从系统中删除,删除用户账号就是要/etc/passwd等系统文件中的该用户记录删除,必要时删除用户宿主目录
[root@ skel]# userdel -r, --remove remove home directory and mail spool //把用户的主目录一起删除 eg:删除用户sam [root@ skel]# userdel sam [root@ skel]# tail -1 /etc/passwd test:x:2010:0::/home/test:/bin/sh [root@ skel]# ls /opt/ //不加-r ,其主目录还是存在 rh sam eg:删除用户test,并删除宿主目录 [root@ skel]# userdel -r test [root@ skel]# tail -1 /etc/passwd enmoedu:x:1000:1000:enmoedu:/home/enmoedu:/bin/bash [root@ skel]# ls /home/ enmoedu
修改用户信息
根据实际情况更改用户的相关属性,如用户号、主目录、用户组等,跟useradd差不多
[root@ skel]# usermod -d, --home HOME_DIR new home directory for the user account -g, --gid GROUP force use GROUP as new primary group -G, --groups GROUPS new list of supplementary GROUPS -a, --append append the user to the supplemental GROUPS -s, --shell SHELL new login shell for the user account -u, --uid UID new UID for the user account
用户密码管理
eg:交互式配置用户密码 [root@ skel]# useradd sam Creating mailbox file: File exists [root@ skel]# passwd sam Changing password for user sam. New password: BAD PASSWORD: The password is shorter than 8 characters Retype new password: passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. eg:无交互式配置用户密码 [root@ skel]# echo 123456 | passwd --stdin sam Changing password for user sam. passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
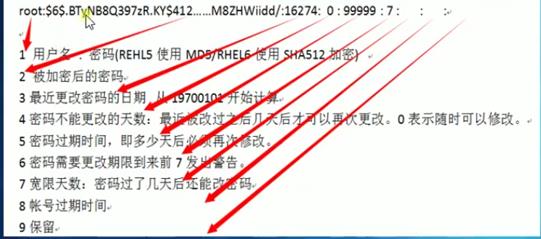
密码配置文件
/etc/shadow [root@ skel]# cat /etc/shadow|grep root root:$6$hvU.3oadtx9DHSDw $Qq27h05p4y2KlIa5BTeu0y7U3plXmPQJqBCQWwvsi1E6hJ27JflijHHnLTH/HyDgacxip76PoAFJ.G7mKyLRj/::0:99999:7:::
以上是关于Linux硬件资源管理与外设设备使用系统运行机制及用户管理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章