Springboot 多线程分批切割处理 大数据量List集合 ,实用示例
Posted 小目标青年
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Springboot 多线程分批切割处理 大数据量List集合 ,实用示例相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
哲学提问镇贴:

不了解异步怎么使用的看官, 可阅:
SpringBoot 最简单的使用异步线程案例 @Async_小目标青年的博客-CSDN博客
Springboot Async异步扩展使用 结合 CompletableFuture_小目标青年的博客-CSDN博客
想了解更多关于批量list处理操作的看官,可阅:
Java List数据量大, 需要分片批次操作_小目标青年的博客-CSDN博客
Mybatis 批量插入 采用分批处理一次500条_小目标青年的博客-CSDN博客
Springboot 手动分页查询,分批批量插入数据_小目标青年的博客-CSDN博客
正文
话不多说,本篇核心介绍的是日常毕竟常遇到的一些处理点。
首先list数据量大,需要切割操作 :
//模拟拿到的数据量大的list
List<Product> products = getBatchListTest();
//直接用Lists.partition 按照100条一次切割
List<List<Product>> allList = Lists.partition(products, 100);
//循环分批处理切割的list
for (List<Product> batchProducts :allList)
productService.batchDealList(batchProducts);
但是往往有时候 数据量是真大,切割完循环处理 还嫌慢 。
是的,因为循环处理是串行的, 也就是,比如500条数据的list,切割成5个 batchList。
如果每次处理一个barchList要1秒钟,那么循环串行处理5次,就是 1X5=5 秒。
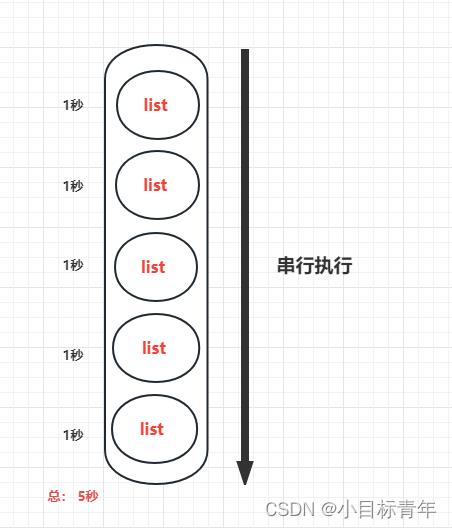
所以我们分批切割这样串行处理完,觉得慢, 如果业务场景合适,我们可以试着改 并行 处理。
开袋及食:
① 配置一个线程池,交给spring管理的 线程池,用起来才放心、安心:
ThreadConfig.java
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class ThreadConfig
/**
* 执行需要依赖线程池,这里就来配置一个线程池
* @return
*/
// 当池子大小小于corePoolSize,就新建线程,并处理请求
// 当池子大小等于corePoolSize,把请求放入workQueue(QueueCapacity)中,池子里的空闲线程就去workQueue中取任务并处理
// 当workQueue放不下任务时,就新建线程入池,并处理请求,如果池子大小撑到了maximumPoolSize,就用RejectedExecutionHandler来做拒绝处理
// 当池子的线程数大于corePoolSize时,多余的线程会等待keepAliveTime长时间,如果无请求可处理就自行销毁
@Bean("MyExecutor")
public Executor getExecutor()
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//设置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
//设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(100);
//线程池所使用的缓冲队列
executor.setQueueCapacity(250);
//设置线程名
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("JcTest-Async");
//设置多余线程等待的时间,单位:秒
//executor.setKeepAliveSeconds();
// 初始化线程
executor.initialize();
return executor;

看看我们并行的写法:
@Autowired
ThreadConfig threadConfig;
@PostMapping("doBatchParallelTes")
public void doBatchParallelTes()
List<Product> products = getBatchListTest();
List<List<Product>> allList = Lists.partition(products, 100);
int batchNum = allList.size();
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
Executor threadConfigExecutor = threadConfig.getExecutor();
List<CompletableFuture> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Product> batchProducts :allList)
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
productService.batchDealList(batchProducts);
return "";
, threadConfigExecutor);
results.add(future);
CompletableFuture.allOf(results.toArray(results.toArray(new CompletableFuture[batchNum]))).join();
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("总用时"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()+"毫秒");
代码简析: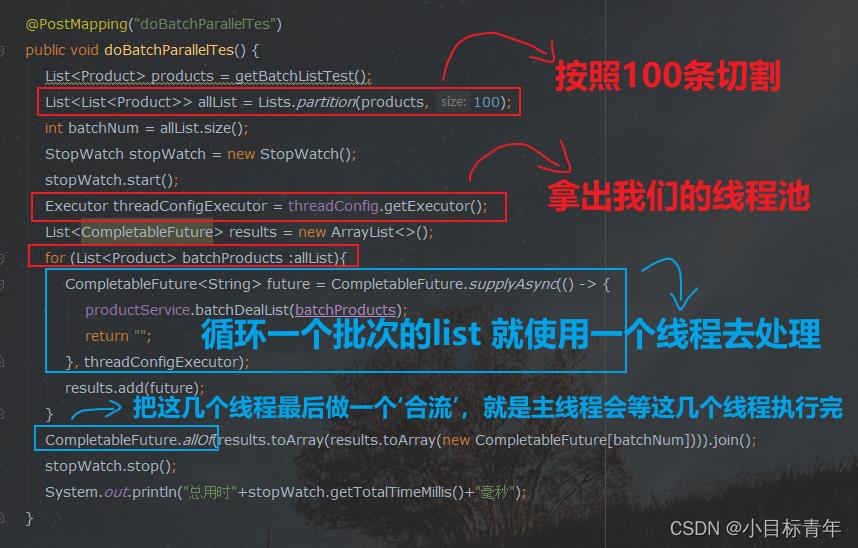
并行图解: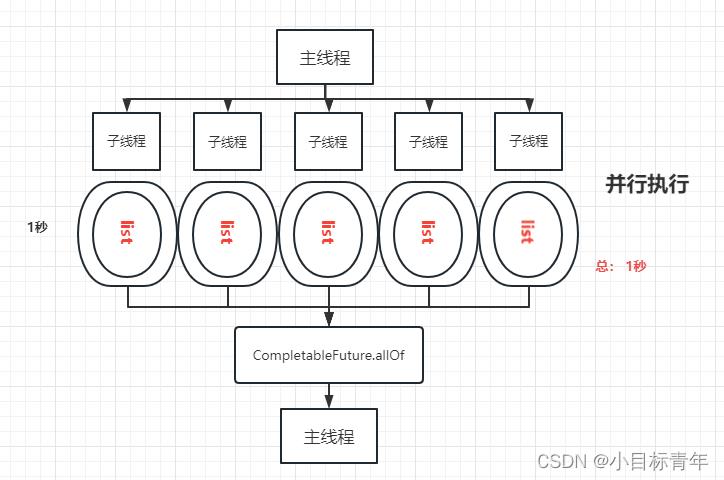
看看执行效果:
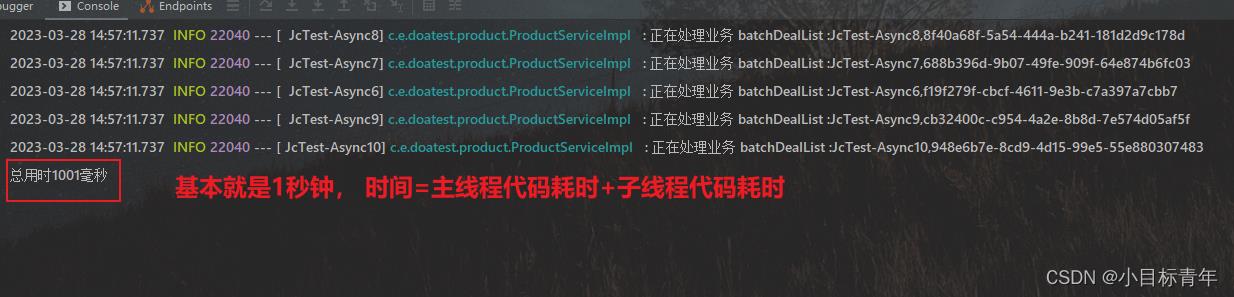
那么看到这里,大家一定注意到了那个 ‘合流’ , 是不是每个业务都需要这样所谓的‘合流’?
当然不是,如果说这批list处理完完事了,不需要考虑回到主线程去做其余操作,那么我们就不需要‘合流’操作。
不需要合流,主线程走主线程逻辑,子线程自己玩自己的:
@PostMapping("doBatchTestNew2")
public void doBatchTestNew2()
List<Product> products = getBatchListTest();
List<List<Product>> allList = Lists.partition(products, 100);
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
Executor threadConfigExecutor = threadConfig.getExecutor();
for (List<Product> batchProducts :allList)
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() ->
productService.batchDealList(batchProducts);
, threadConfigExecutor);
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("总用时"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()+"毫秒");
效果,其实就是异步执行:

那如果说是基于@Async 的方式去实现呢,当然也是可以的,示例:
基于@Async 就不多说了,这个在文章开头有介绍相关文章,之前写的,介绍过玩法,就是这两篇:
SpringBoot 最简单的使用异步线程案例 @Async_小目标青年的博客-CSDN博客
Springboot Async异步扩展使用 结合 CompletableFuture_小目标青年的博客-CSDN博客
好了,该篇就到这。
线程池和CountDownLatch配合使用,大数据量批量多次处理
前言
我们在日常开发的时候经常会使用线程池来分批处理大数据,但是有时候我们需要主线程等待所有的子线程处理完大数据才往下走,那么这个时候我们就需要使用线程池配合CountDownLatch,完成这个需求
代码如下
private void multiThreadHandle(List<User> cachedDataList)
//单次分批落库条数
int subList = 1000;
//计算执行次数
int count = cachedDataList.size() % subList > 0 ? (cachedDataList.size() / subList) + 1 : cachedDataList.size() / subList;
//临时集合
List<User> tempList;
// 定义CountDownLatch
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(cachedDataList.size() / subList);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
//截取集合
tempList = cachedDataList.stream().skip((long) subList * i).limit(subList).collect(Collectors.toList());
//多线程执行数据处理
List<User> finalTempList = tempList;
// 这里就是线程池,这里会开count个线程去分段处理大集合
EventManagerExecutor.execute(() ->
saveData(finalTempList, countDownLatch);
);
try
// 主线程等待
countDownLatch.await();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
// 操作数据,并且减countDownLatch
private void saveData(List<User> cachedDataList, CountDownLatch countDownLatch)
try
// 操作数据
finally
// 在这里进行countDownLatch.countDown(); 减countDownLatch
countDownLatch.countDown();
// 我的线程池
package com.xiangzheng.gmcmember.util.easyExcel;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
*
*
* @author xusj
* @date 2021.12.17 23:32
**/
public class EventManagerExecutor
public static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
static
executor.setCorePoolSize(20);
// 配置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(50);
// 配置缓存队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
// 空闲线程存活时间
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(15);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("event-executor-thread-");
// 线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略:这里采用了CallerRunsPolicy策略,当线程池没有处理能力的时候,该策略会直接在execute方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务;如果执行程序已关闭,则会丢弃该任务
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 等待所有任务结束后再关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 设置线程池中任务的等待时间,如果超过这个时候还没有销毁就强制销毁,以确保应用最后能够被关闭,而不是被没有完成的任务阻塞
executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
executor.initialize();
public static void execute(Runnable task)
executor.execute(task);
3.总结
这样就使用了countDownLatch去等待子线程全部完成之后,再继续跑主线程
以上是关于Springboot 多线程分批切割处理 大数据量List集合 ,实用示例的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章