Linux学习:输入子系统 input
Posted LeeAaron
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux学习:输入子系统 input相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、输入子系统
针对输入设备设计:触摸屏、键盘、按键、传感器、鼠标......
二、每种设备都属于字符设备驱动,程序的写法步骤也相同
1、实现入口函数 xxx_init() 和卸载函数 xxx_exit()
2、申请设备号 register_chrdev() --- 与内核相关
3、创建设备文件(节点) class_create() 和 device_create() --- 与内核相关
4、硬件初始化
GPIO操作 --- 与硬件相关
注册中断 --- 与硬件相关
初始化等待队列 --- 与内核相关
初始化定时器 --- 与内核相关
5、构建 file_operations 结构,实现操作硬件方法 xxx_open/xxx_read... --- 与硬件相关
三、引入输入子系统:
1、不需要每个步骤都编写,只需要编写部分代码即可
2、不同类的输入设备,编写驱动的方式是一样的
3、应用程序读取输入设备的数据结构是统一的
输入设备按照产生的数据的类型进行分类:
1、产生按键数据 --- 每个按键都是一个整数
按键、键盘
2、产生绝对数据 --- 每个数据都有最大值和最小值
触摸屏、传感器
3、产生相对数据 --- 某个收据是相对另一个数据的
鼠标
四、输入子系统的框架
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
应用层:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
input handler 层:
知道如何将数据交给用户,不知道如何从硬件获取数据
driver/input/evdev.c
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
input core 层:
维护两个链表,和上下两层交互
/driver/input/input.c
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
input device 层:
知道如何从硬件获取数据,不知道如何将数据交给用户
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
硬件:
触摸屏、键盘、鼠标、按键......
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
五、输入子系统的驱动编程方法:
1、构建 input device 对象
2、初始化 input device 对象
3、注册 input device 对象
4、硬件初始化
六、描述一个具体的输入设备对象常用的参数:
struct input_dev { const char *name; // 设备名称 const char *phys; // 物理路径 const char *uniq; // 设备唯一的识别码 struct input_id id; // 设备id,如果有多个输入设备,可以通过此id找到需要的设备 __u16 bustype; // 总线类型 __u16 vendor; // VID __u16 product; // PID __u16 version; // 版本号 unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)]; // 设备支持的事件类型 unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)]; // 此设备具有哪些按键 unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)]; // 此设备具有相对坐标 unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)]; // 此设备具有相对坐标 ... ... struct device dev; //父类 struct list_head h_list; struct list_head node; //节点 };
evbit 是只有 1 个元素的 long 型数组,总共占 32 位,每种类型占一位,存在的就将对应位置 1
unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)];
keybit 是含 24 个元素的 long 型数组,总共 768 位,最大支持 768 种按键,每一种按键占一位,存在的就将对应位置 1
unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
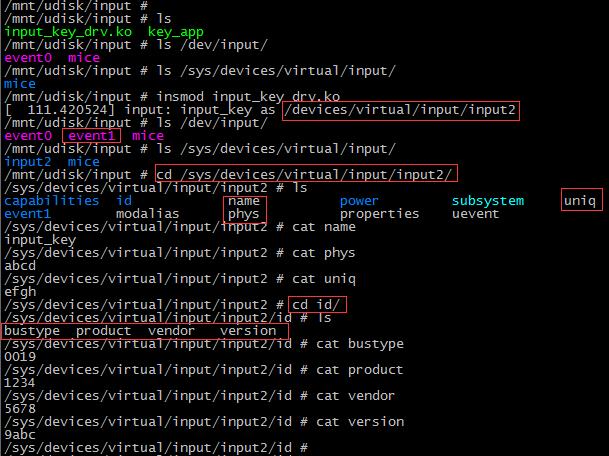
七、常用函数
// 上报按键数据
void input_report_key(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
// 上报相对坐标
void input_report_rel(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
// 上报绝对坐标
void input_report_abs(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
// 同步 (唤醒等待队列 /driver/input/evdev.c -> evdev_event -> wake_up_interruptible(&evdev->wait);)
input_sync(input_key);
input_key_drv.c
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/input.h> #include <linux/interrupt.h> #include <linux/gpio.h> #include <linux/irq.h> static struct input_dev *input_key; static int irqno; irqreturn_t input_key_handler(int irqno, void *dev_id) { int value; printk("---%s---\\n", __FUNCTION__); value = gpio_get_value(EXYNOS4_GPX1(1)); // value = gpio_direction_input(EXYNOS4_GPX1(1)); printk("---<DRV>--- %d\\n", value); input_report_key(input_key, KEY_HOME, !value); input_sync(input_key); return IRQ_HANDLED; } static int __init input_key_drv_init(void) { int ret; input_key = input_allocate_device(); if (input_key == NULL) { printk("input_allocate_device fail!\\n"); return -ENOMEM; } input_key->name = "input_key"; input_key->phys = "abcd"; input_key->uniq = "efgh"; input_key->id.bustype = BUS_HOST; input_key->id.product = 0x1234; input_key->id.vendor = 0x5678; input_key->id.version = 0x9ABC; input_key->evbit[BIT_WORD(EV_KEY)] |= BIT_MASK(EV_KEY); input_key->keybit[BIT_WORD(KEY_HOME)] |= BIT_MASK(KEY_HOME); ret = input_register_device(input_key); if (ret != 0) { printk("input_register_device fail!\\n"); ret = -ENOMEM; goto input_free; } irqno = gpio_to_irq(EXYNOS4_GPX1(1)); ret = request_irq(irqno, input_key_handler, IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_BOTH, "input_eint9", NULL); if (ret < 0) { printk("request_irq fail!\\n"); ret = -EBUSY; goto input_unregister; } return 0; input_unregister: input_unregister_device(input_key); input_free: input_free_device(input_key); return ret; } static void __exit input_key_drv_exit(void) { free_irq(irqno, NULL); input_unregister_device(input_key); input_free_device(input_key); } module_init(input_key_drv_init); module_exit(input_key_drv_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("Aaron Lee");
key_app.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <linux/input.h> struct input_event key_info; int main(void) { int fd; int ret; fd = open("/dev/input/event1", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { perror("open"); exit(1); } while (1) { read(fd, &key_info, sizeof(struct input_event)); if (key_info.type == EV_KEY) if (key_info.code == KEY_HOME) printf("---<APP>--- KEY_HOME %s\\n", key_info.value ? "down" : "up"); } close(fd); return 0; }
以上是关于Linux学习:输入子系统 input的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章