Linux字符设备驱动注册流程
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux字符设备驱动注册流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
其中一部分从伯乐在线和网络上摘抄的内容,不用于商业用途。
一、linux系统将设备分为3类:字符设备、块设备、网络设备。
- 字符设备:是指只能一个字节一个字节读写的设备,不能随机读取设备内存中的某一数据,读取数据需要按照先后数据。字符设备是面向流的设备,常见的字符设备有鼠标、键盘、串口、控制台和LED设备等。
- 块设备:是指可以从设备的任意位置读取一定长度数据的设备。块设备包括硬盘、磁盘、U盘和SD卡等。
每一个字符设备或块设备都在/d ev目录下对应一个设备文件。linux用户程序通过设备文件(或称设备节点)来使用驱动程序操作字符设备和块设备。大体框架如下:
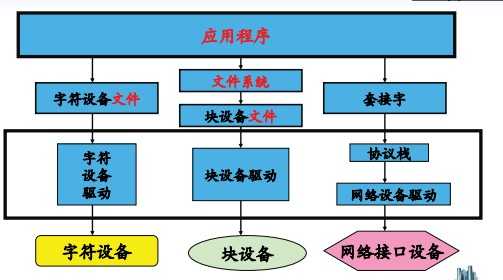
二、字符设备驱动模型
写的已经很详细了。
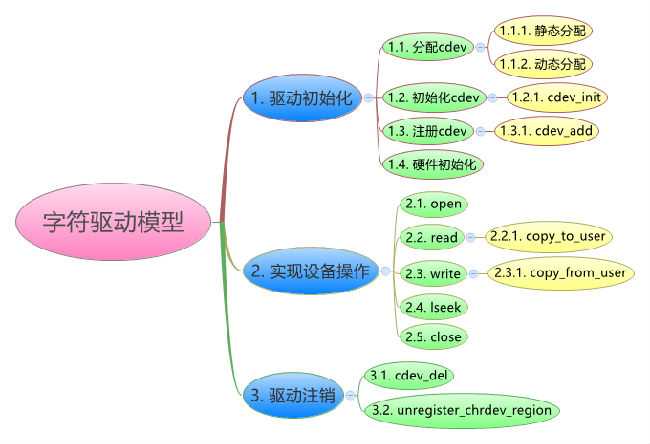
三、自己总结的字符设备驱动流程
1.申请字符类设备号
- 静态申请 :
num_dev = MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor);
ret = register_chrdev_region(num_dev,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM,DEVICE_NAME);
- 动态申请:
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&num_dev,numdev_minor,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM,DEVICE_NAME); numdev_major = MAJOR(num_dev);/*获得主设备号*/
2.注册字符类设备
num_dev = MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor);
1.分配内存空间 kmalloc();
struct reg_dev { char *data; unsigned long size; struct cdev cdev; }; struct reg_dev *my_devices; my_devices = kmalloc(DEVICE_MINOR_NUM * sizeof(struct reg_dev),GFP_KERNEL);
/*cdev字符设备文件结构体 在头文件include/linux/cdev.h */ struct cdev { struct kobject kobj; struct module *owner; const struct file_operations *ops; struct list_head list; dev_t dev; unsigned int count; };
2.字符设备初始化 cdev_init (指明owner 和file_operations 的系统调用接口)
/*数据初始化*/ cdev_init(&dev->cdev,&my_fops); dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE; dev->cdev.ops = &my_fops;
3.字符设备注册
/*注册到系统*/ err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev,devno,1);
3.生成字符类设备节点
1.创建class类文件 class_create
static struct class *myclass; //只用到了2个元素 .owner=THISMODULE .name =DEVICENAME
class结构体变量
– class是设备驱动模型中通用的设备类结构
– 在头文件include/linux/device.h的280行
struct class { const char *name; struct module *owner; struct class_attribute *class_attrs; struct device_attribute *dev_attrs; struct bin_attribute *dev_bin_attrs; struct kobject *dev_kobj; int (*dev_uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env); char *(*devnode)(struct device *dev, mode_t *mode); void (*class_release)(struct class *class); void (*dev_release)(struct device *dev); int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state); int (*resume)(struct device *dev); const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *ns_type; const void *(*namespace)(struct device *dev); const struct dev_pm_ops *pm; struct subsys_private *p; };
myclass = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME);
释放设备class函数class_destroy
参数1:myclass
2.创建设备节点函数 device_create
device_create(myclass,NULL,MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor+i),NULL,DEVICE_NAME"%d",i);
四、编写简单的应用脚本测试驱动程序
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> /*argv[1] is cmd , argv[2] is io_arg*/ int main(int argc , char **argv){ int fd; char *lednode = "/dev/chardevnode0"; /*O_RDWR只读打开,O_NDELAY非阻塞方式*/ if((fd = open(lednode,O_RDWR|O_NDELAY))<0){ printf("APP open %s failed!\\n",lednode); } else{ printf("APP open %s success!\\n",lednode); ioctl(fd,atoi(argv[1]),atoi(argv[2])); printf("APP ioctl %s ,cmd is %s! io_arg is %s!\\n",lednode,argv[1],argv[2]); } close(fd); }
全部代码:
/*包含初始化宏定义的头文件,代码中的module_init和module_exit在此文件中*/ #include <linux/init.h> /*包含初始化加载模块的头文件,代码中的MODULE_LICENSE在此头文件中*/ #include <linux/module.h> /*定义module_param module_param_array的头文件*/ #include <linux/moduleparam.h> /*定义module_param module_param_array中perm的头文件*/ #include <linux/stat.h> /*三个字符设备函数*/ #include <linux/fs.h> /*MKDEV转换设备号数据类型的宏定义*/ #include <linux/kdev_t.h> /*定义字符设备的结构体*/ #include <linux/cdev.h> /*分配内存空间函数头文件*/ #include <linux/slab.h> /*包含函数device_create 结构体class等头文件*/ #include <linux/device.h> /*Linux中申请GPIO的头文件*/ #include <linux/gpio.h> #include <mach/gpio-exynos4.h> #include <plat/gpio-cfg.h> #define DEVICE_NAME "chardevnode" #define DEVICE_MINOR_NUM 2 #define DEV_MAJOR 0 #define DEV_MINOR 0 #define REGDEV_SIZE 3000 #define LED_NUM 2 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); /*声明是开源的,没有内核版本限制*/ MODULE_AUTHOR("iTOPEET_dz"); /*声明作者*/ int numdev_major = DEV_MAJOR; int numdev_minor = DEV_MINOR; /*输入主设备号*/ module_param(numdev_major,int,S_IRUSR); /*输入次设备号*/ module_param(numdev_minor,int,S_IRUSR); static struct class *myclass; static int led_gpios[] = { EXYNOS4_GPL2(0),EXYNOS4_GPK1(1), }; struct reg_dev { char *data; unsigned long size; struct cdev cdev; }; struct reg_dev *my_devices; /************ 驱动 ***************************************************************************/ static int chardevnode_open(struct inode *inodes, struct file *files) { printk(KERN_EMERG "chardevnode_open success! \\n"); return 0; } static int chardevnode_release (struct inode *inodes, struct file *files) { printk(KERN_EMERG "chardevnode_release success! \\n"); return 0; } static long chardevnode_unlocked_ioctl(struct file *files, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) { printk(KERN_EMERG "chardevnode_unlocked_ioctl success! \\n cmd is %d ,arg is %ld\\n",cmd ,arg); gpio_set_value(led_gpios[arg], cmd); return 0; } static ssize_t chardevnode_read(struct file *files, char __user *buf , size_t count, loff_t *f_ops) { return 0; } static ssize_t chardevnode_write(struct file *files, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_ops) { return 0; } static loff_t chardevnode_llseek(struct file *files, loff_t offset, int ence) { return 0; } struct file_operations my_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = chardevnode_open, .release = chardevnode_release, .unlocked_ioctl = chardevnode_unlocked_ioctl, .read = chardevnode_read, .write = chardevnode_write, .llseek = chardevnode_llseek, }; /******************************************************************************************************/ /*设备注册到系统*/ static void reg_init_cdev(struct reg_dev *dev,int index){ int err; int devno = MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor+index); /*数据初始化*/ cdev_init(&dev->cdev,&my_fops); dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE; dev->cdev.ops = &my_fops; /*注册到系统*/ err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev,devno,1); if(err){ printk(KERN_EMERG "cdev_add %d is fail! %d\\n",index,err); } else{ printk(KERN_EMERG "cdev_add %d is success!\\n",numdev_minor+index); } } static int gpio_init(void) { int ret,i; for(i=0;i<2;i++) { ret = gpio_request(led_gpios[i],"LED"); if (ret) { printk("%s: request GPIO %d for LED failed, ret = %d\\n", DEVICE_NAME,i,ret); return -1; } s3c_gpio_cfgpin(led_gpios[i], S3C_GPIO_OUTPUT); gpio_set_value(led_gpios[i],1); } return 0; } static int scdev_init(void) { int ret = 0,i; dev_t num_dev; printk(KERN_EMERG "numdev_major is %d!\\n",numdev_major); printk(KERN_EMERG "numdev_minor is %d!\\n",numdev_minor); if(numdev_major){ num_dev = MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor); ret = register_chrdev_region(num_dev,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM,DEVICE_NAME); } else{ /*动态注册设备号*/ ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&num_dev,numdev_minor,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM,DEVICE_NAME); /*获得主设备号*/ numdev_major = MAJOR(num_dev); printk(KERN_EMERG "adev_region req %d !\\n",numdev_major); } if(ret<0){ printk(KERN_EMERG "register_chrdev_region req %d is failed!\\n",numdev_major); } myclass = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME); my_devices = kmalloc(DEVICE_MINOR_NUM * sizeof(struct reg_dev),GFP_KERNEL); if(!my_devices){ ret = -ENOMEM; goto fail; } memset(my_devices,0,DEVICE_MINOR_NUM * sizeof(struct reg_dev)); /*设备初始化*/ for(i=0;i<DEVICE_MINOR_NUM;i++){ my_devices[i].data = kmalloc(REGDEV_SIZE,GFP_KERNEL); memset(my_devices[i].data,0,REGDEV_SIZE); /*设备注册到系统*/ reg_init_cdev(&my_devices[i],i); /*创建设备节点*/ device_create(myclass,NULL,MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor+i),NULL,DEVICE_NAME"%d",i); } ret = gpio_init(); //初始化IO printk(KERN_EMERG "scdev_init!\\n"); /*打印信息,KERN_EMERG表示紧急信息*/ return 0; fail: /*注销设备号*/ unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor),DEVICE_MINOR_NUM); printk(KERN_EMERG "kmalloc is fail!\\n"); return ret; } static void scdev_exit(void) { int i; printk(KERN_EMERG "scdev_exit!\\n"); /*除去字符设备*/ for(i=0;i<DEVICE_MINOR_NUM;i++){ cdev_del(&(my_devices[i].cdev)); /*摧毁设备节点函数d*/ device_destroy(myclass,MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor+i)); } /*释放设备class*/ class_destroy(myclass); /*释放内存*/ kfree(my_devices); /*释放GPIO*/ for(i=0;i<LED_NUM;i++){ gpio_free(led_gpios[i]); } unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(numdev_major,numdev_minor),DEVICE_MINOR_NUM); } module_init(scdev_init); /*初始化函数*/ module_exit(scdev_exit); /*卸载函数*/
以上是关于Linux字符设备驱动注册流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章