Shiro安全框架SpringBoot版
Posted @WAT
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Shiro安全框架SpringBoot版相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
- Shiro安全框架
Shiro安全框架
一、 入门概述
1.1、Shiro是什么
Apache Shiro 是一款功能强大的且易于使用的Java的安全框架。Shiro可以完成:认证、加密、会话管理、与web集集成等。借助SHiro可以帮助我们快速轻松的保护任何应用程序。
shiro官网:Apache Shiro | Simple. Java. Security.
1.2、为什么使用Shiro
与Shiro的特性密不可分:
- 易于使用
- 全面
- 灵活
- 强力支持Web
- 兼容性强
- 社区支持
1.3、Shiro与Spring Security的区别
-
SpringSecurity基于Spring开发,项目若使用Spring 可以与SpringSecurity作权限更加方便,而Shiro需要与Spring进行整合
-
Spring Security功能更加丰富
-
Spring Security社区资源更加丰富
看到这里,是不是有些人就认为Spring Security功能更发面都比Shiro好,为什么不学习SpringSecurity。有一句话:
存在即合理。下面看看Shiro的特点
-
Shiro的配置和使用比较简单,SpringSecurity使用比较复杂
-
Shiro的依赖性低,不需要任何的容器与框架,可以独立运行
-
Shiro不仅仅可以使用在Web端,可以使用在任何的场景。
1.4、基本功能
了解Shiro的功能,我们可以去官网下载一张Shiro的功能结构图来进行补充学习:
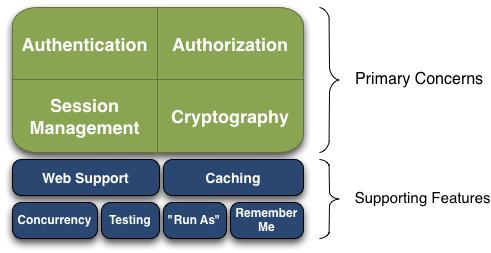
1.4.1、主要功能
- 认证登录(Authentication)
- 授权验证(Authorization)
- 会话管理(Session Management)
- 密码加密(Cryptography)
1.4.2 、次要功能
- Web支持(web support)
- 缓存(caching)
- 多线程并发验证(Concurrency)
- 测试(Testing)
- 另外身份登录(Run as)
- 记住我(Remember me)
1.5、架构原理
从外部来看Shiro,即从应用程序的角度来观察使用Shiro完成工作
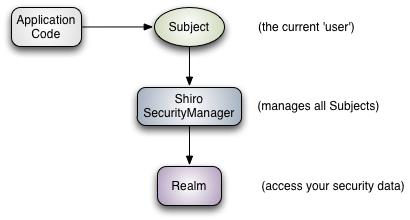
应用程序—>(登录)---->subject(对象)进行身份校验---->安全管理器(SecurityManager)---->Reaim(用户登陆的用户信息)
从内部的架构来看Shiro

二、基本使用
2.1、环境准备
1、Shiro不依赖容器,可以直接利用Maven使用
2、添加依赖
<!-- Shiro依赖 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3、创建Maven工程
结构如下:

2.2、配置ini文件
在创建好的工程的Resources目录下,创建一个shiro.ini文件

[users]
zhangsan=z3
lisi=l4
2.3、登录认证
2.3.1、登录认证概念
(1)身份认证:一般需要提供身份ID等一些表示用户登陆这信息身份的标识,如提供email、用户名\\密码来认证
(2)在Shiro中、用户需要提供principals(身份)和credentials(证明)给shiro。从而应用能验证用户身份。
2.3.2、登录认证的流程
- 收集用户二点身份/凭证,及如用户名/密码
- 调用Subject.login进行登录,如果失败则将得到的相应的AuthenticationException异常,根据异常提示用户登录错误信息,否则登陆成功。
- 创建自定义的Realm类,继承org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticationRealm类,实现doGetAuthenticationInfo()方法
2.3.3、登录认证示例
创建测试类,获取认证对象,进行登录认证,如下:
public class ShiroRun
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args)
// 1、获取Shiro初始化 通过ini文件获取用户信息
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
IniSecurityManagerFactory factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
try
// 通过工厂创建SecurityManager
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 2、获取Subject对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 3、获取外部参数 通过页面获取的用户名和密码 创建token对象
AuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangsan", "z31");
// 4、完成登录
subject.login(token);
System.out.println("登陆成功...");
catch (UnknownAccountException e)
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("用户名不存在...");
catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e)
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("密码错误...");
catch (AuthenticationException e)
System.out.println("登陆失败...");
登陆成功:

密码错误:

账户错误:
2.4、角色、授权
2.4.1、授权
授权:也叫做访问控制,即在应用中控制谁访问哪些资源授权中需要了解的概念:主体(Subject)、资源(Resources)、权限(Permission)、角色(Role)
- **主体:**访问应用的用户,用户经授权才可访问指定资源
- **资源:**在应用中用户可以访问的URL,比如JSP页面,查看/编辑某些权限
- **权限:**表示在应用中用户能不能访问某个资源(有没有权利去访问某一个资源)
Shiro支持粗粒度的授权(用户模块的所有权限的授权)、也支持细粒度的授权(某个模块下的某个功能,比如查询)
2.4.1.1、授权方式
- 编程式授权:通过IF-ELSE授权
if(subject.hasRole("admin"))
// 有admin的权限
else if(subject.hasRole("commons"))
// 普通用户的权限
else
// 没有权限
- 注解式:通过执行的Java方法上加上注解完成,没有泉下今年的将抛出异常
@RequriesRole("admin")
public void queryALL()
// 具体的业务逻辑
- JSP/GSP标签,在JSP/GSP页面通过相应的标签完成
<shiro:hasRole name="admin">
<input type="button" class="queryAll" name="queryAll" value="查询所有"/>
</shiro:hasRole>
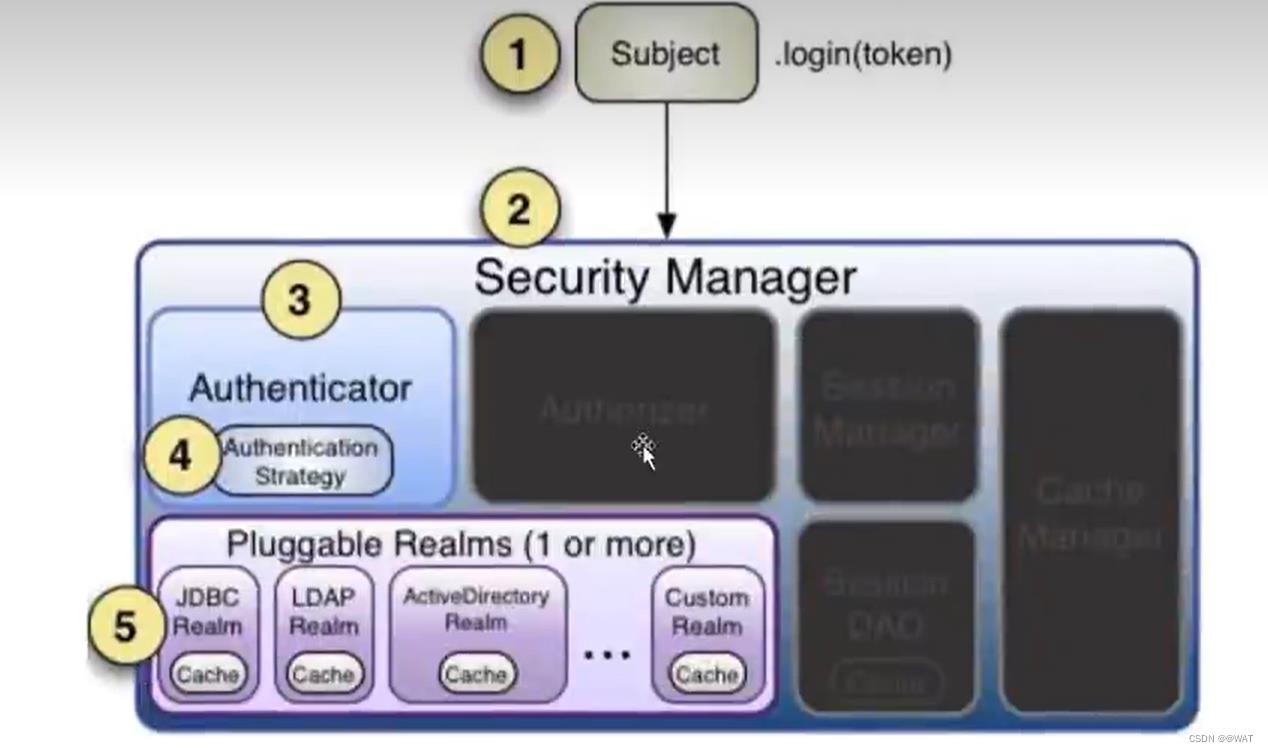
2.4.1.2、授权流程
- 首先调用
Subject.isPermitted*/hasRole*接口,其余委托SecurityManager。而SecurityManager接着会委托给Authorizer。 - Authorizer是真正的授权者,如果调用isPermitted(“user:view”),其首先会通过PermissionResolver把字符串转化成相应的Permission示例。
- 再授权之前,其会调用相应的Realm获取Subject相应的角色/权限用于匹配传入的角色/权限
- Authorizer会判断Realm的角色/权限是否与传过来的匹配,如果有多个Realm,则会委托给ModularRealmAuthorizer进行循环判断,如果匹配如
isPermitted*/hasRole*会返回true,否则返回false表示授权失败。
- Authorizer会判断Realm的角色/权限是否与传过来的匹配,如果有多个Realm,则会委托给ModularRealmAuthorizer进行循环判断,如果匹配如

2.4.2、角色
角色:权限的集合(比如说系统管理员、业务人员、普通用户人员等)
2.4.3、角色授权示例
【角色】
在ini文件里配置用户角色的权限信息:
[users]
zhangsan=z3,admin,commons
lisi=l4,commons
[roles]
admin=user:insert,user:select
commons=user:select
通过以下方式完成用户角色下权限的判断:
if (subject.isPermitted("user:insert"))
System.out.println("用户有插入权限");
else
System.out.println("没有insert权限");
完整示例:
public class ShiroRun
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args)
// 1、获取Shiro初始化 通过ini文件获取用户信息
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
IniSecurityManagerFactory factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
try
// 通过工厂创建SecurityManager
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 2、获取Subject对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 3、获取外部参数 通过页面获取的用户名和密码 创建token对象
AuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lisi", "l4");
// 4、完成登录
subject.login(token);
System.out.println("登陆成功...");
// 5、判断用户角色
if(subject.hasRole("commons"))
System.out.println("拥有commons角色");
else
System.out.println("没有拥有commons角色");
if (subject.isPermitted("user:insert"))
System.out.println("用户有插入权限");
else
System.out.println("没有insert权限");
catch (UnknownAccountException e)
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("用户名不存在...");
catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e)
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("密码错误...");
catch (AuthenticationException e)
System.out.println("登陆失败...");
注意:使用subject.checkPermission(“user:insert”);没有权限则会抛异常
【授权】
首先现在ini文件里为用户添加相应的角色(zhangsan添加admin、commons角色;lisi添加commons角色)
[users]
zhangsan=z3,admin,commons
lisi=l4,commons
使用以下方式判断角色:
if(subject.hasRole("commons"))
System.out.println("拥有commons角色");
else
System.out.println("没有拥有commons角色");
完整示例:
public class ShiroRun
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args)
// 1、获取Shiro初始化 通过ini文件获取用户信息
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
IniSecurityManagerFactory factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
try
// 通过工厂创建SecurityManager
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 2、获取Subject对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 3、获取外部参数 通过页面获取的用户名和密码 创建token对象
AuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangsan", "z3");
// 4、完成登录
subject.login(token);
System.out.println("登陆成功...");
// 5、判断用户角色
if(subject.hasRole("commons"))
System.out.println("拥有commons角色");
else
System.out.println("没有拥有commons角色");
catch (UnknownAccountException e)
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("用户名不存在...");
catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e)
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("密码错误...");
catch (AuthenticationException e)
System.out.println("登陆失败...");
2.5、密码加密
在实际的开发中,一些敏感的信息需要加密,比如说用户的密码,shiro内嵌了很多的加密算法
2.5.1、使用Shiro进行加密
public class ShiroMD5
public static void main(String[] args)
String salt = "salt";
// 1、密码明文
String password = "z3";
// 2、使用MD5加密
Md5Hash MD5 = new Md5Hash(password);
System.out.println("使用MD5加密后的密码:" + MD5.toHex());
// 3、给MD5加盐值 在加密玩的再次拼接一段字符串
Md5Hash MD5_2 = new Md5Hash(password, salt);
System.out.println("使用MD5(带盐值)加密后的密码:" + MD5_2.toHex());
// 3、给MD5加盐值 多次加密
Md5Hash MD5_3 = new Md5Hash(password, salt,3);
System.out.println("使用MD5(带盐值三次加密)加密后的密码:" + MD5_3.toHex());

三、Shiro整合SpringBoot
3.1、整合依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.wei</groupId>
<artifactId>dhcc_ShiroProject</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>dhcc_ShiroSpringBoot</artifactId>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring.shiro.version>1.9.0</spring.shiro.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId>
<version>$spring.shiro.version</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!--页面模板依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--热部署依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MyBatis-plus -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
3.2、yml配置文件
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*Mapper.xml
spring:
datasource