bingc++(智能指针类型转化c++11)
Posted 月屯
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了bingc++(智能指针类型转化c++11)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录标题
智能指针
原理
使用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <memory>
struct A
int a;
int b;
int c;
;
void TestAutoPtr()
auto_ptr<int> ap1(new int);
*ap1 = 100;
auto_ptr<A> ap2(new A);
ap2->a = 100;
// auto_ptr的实现:将ap2管理的资源转移给ap3管理
// ap2不管理任何资源---内部的指针指向nullptr
auto_ptr<A> ap3(ap2);
auto_ptr<A> ap4;
ap4 = ap3;
ap3->b = 100;
ap3->c = 200;
int* pa = new int;
int* pb(pa);
*pa = 10;
*pb = 20;
delete pa;
c++11解决auto_ptr(unique_ptr)
不允许拷贝和赋值
#include <memory>
int main()
unique_ptr<int> up1(new int(10));
//unique_ptr<int> up2(up1);
unique_ptr<int> up2;
// up2 = up1;
*up1 = 100;
return 0;
shared_ptr
#include <memory>
void TestSharedPtr()
shared_ptr<int> sp1(new int);
*sp1 = 10;
cout << sp1.use_count() << endl;
shared_ptr<int> sp2(sp1);
shared_ptr<int> sp3;
sp3 = sp2;
cout << sp1.use_count() << endl;
cout << sp2.use_count() << endl;
cout << sp3.use_count() << endl;
*sp2 = 100;
*sp3 = 200;
shared_ptr<int> sp4(new int);
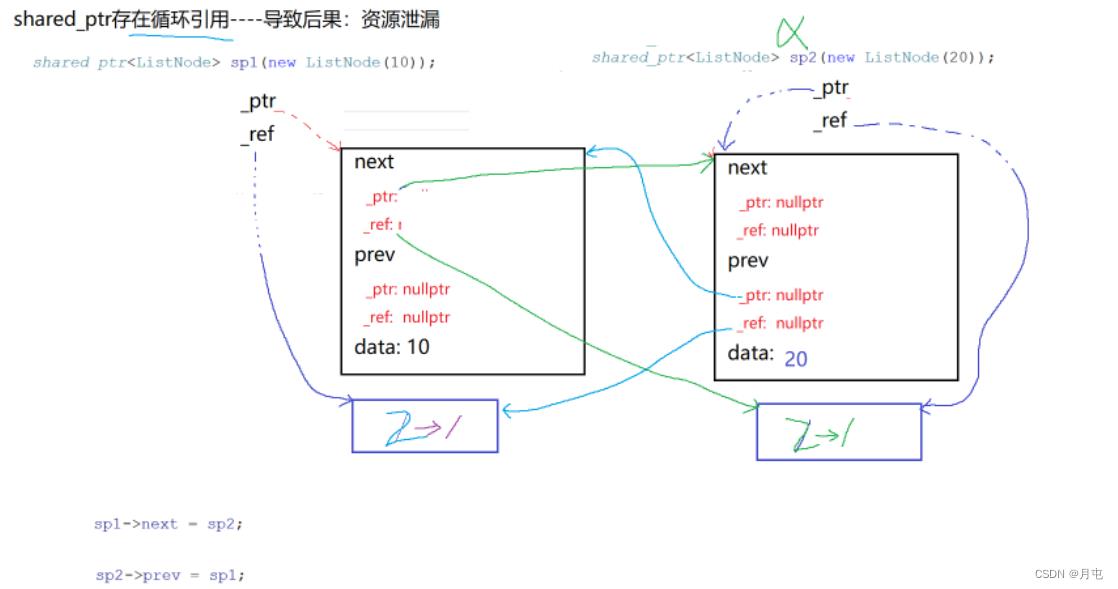
解决循环引用
shared_ptr中存在的循环引用问题解决方式: weak_ptr的唯一作用就是协助shared_ptr解决循环引用为题,即weak_ptr不能独立管理资源的
struct ListNode
weak_ptr<ListNode> prev;
weak_ptr<ListNode> next;
int data;
ListNode(int val = 0)
: data(val)
cout << "create ListNode" << endl;
~ListNode()
cout << "destroy ListNode" << endl;
;
void TeststdSharedPtr()
shared_ptr<ListNode> sp1(new ListNode(10));
shared_ptr<ListNode> sp2(new ListNode(20));
cout << sp1.use_count() << endl;
cout << sp2.use_count() << endl;
sp1->next = sp2;
sp2->prev = sp1;
cout << sp1.use_count() << endl;
cout << sp2.use_count() << endl;
RAII扩展学习
// C++11的库中也有一个lock_guard,下面的LockGuard造轮子其实就是为了学习他的原理
template<class Mutex>
class LockGuard
public:
LockGuard(Mutex& mtx)
:_mutex(mtx)
_mutex.lock();
~LockGuard()
_mutex.unlock();
LockGuard(const LockGuard<Mutex>&) = delete;
private:
// 注意这里必须使用引用,否则锁的就不是一个互斥量对象
Mutex& _mutex;
;
mutex mtx;
static int n = 0;
void Func()
for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i)
LockGuard<mutex> lock(mtx);
++n;
int main()
int begin = clock();
thread t1(Func);
thread t2(Func);
t1.join();
t2.join();
int end = clock();
cout << n << endl;
cout << "cost time:" << end - begin << endl;
return 0;
类型转化
标准C++为了加强类型转换的可视性,引入了四种命名的强制类型转换操作符:static_cast、reinterpret_cast、const_cast、dynamic_cast
static_cast
用于非多态类型的转换(静态转换),编译器隐式执行的任何类型转换都可用static_cast,但它不能用于两个不相关的类型进行转换
int main()
double d = 12.34;
int a = static_cast<int>(d);
cout<<a<<endl;
return0;
reinterpret_cast
操作符通常为操作数的位模式提供较低层次的重新解释,用于将一种类型转换为另一种不同的类型
typedef void (* FUNC)();
int DoSomething (int i)
cout<<"DoSomething" <<endl;
return 0;
void Test ()
//
// reinterpret_cast可以编译器以FUNC的定义方式去看待DoSomething函数
// 所以非常的BUG,下面转换函数指针的代码是不可移植的,所以不建议这样用
// C++不保证所有的函数指针都被一样的使用,所以这样用有时会产生不确定的结果
//
FUNC f = reinterpret_cast< FUNC>(DoSomething );
f();
const_cast
最常用的用途就是删除变量的const属性,方便赋值
void Test ()
const int a = 2;
int* p = const_cast< int*>(&a );
*p = 3;
cout<<a <<endl;
dynamic_cast
dynamic_cast用于将一个父类对象的指针/引用转换为子类对象的指针或引用(动态转换)
向上转型:子类对象指针/引用->父类指针/引用(不需要转换,赋值兼容规则) 向下转型:父类对象指针/引用- >子类指针/引用(用dynamic_cast转型是安全的)
注意: 1. dynamic_cast只能用于含有虚函数的类 2. dynamic_cast会先检查是否能转换成功,能成功则转换,不能则返回0
class A
public :
virtual void f()
;
class B : public A
;
void fun (A* pa)
// dynamic_cast会先检查是否能转换成功,能成功则转换,不能则返回
B* pb1 = static_cast<B*>(pa);
B* pb2 = dynamic_cast<B*>(pa);
cout<<"pb1:" <<pb1<< endl;
cout<<"pb2:" <<pb2<< endl;
int main ()
A a;
B b;
fun(&a);
fun(&b);
return 0;
explicit
explicit关键字阻止经过转换构造函数进行的隐式转换的发生
class A
public :
explicit A (int a)
cout<<"A(int a)" <<endl;
A(const A& a)
cout<<"A(const A& a)" <<endl;
private :
int _a ;
;
int main ()
A a1 (1);
// 隐式转换-> A tmp(1); A a2(tmp);
A a2 = 1;
typeid
int main()
A a(1,2);
//a = 100;
cout << typeid(a).name() << endl;
return 0;
c++11
列表初始化
C++11扩大了用大括号括起的列表(初始化列表)的使用范围,使其可用于所有的内置类型和用户自定
义的类型,使用初始化列表时,可添加等号(=),也可不添加。
内置类型初始化
int main()
// 内置类型变量
int x1 = 10;
int x210;
int x3 = 1+2;
int x4 = 1+2;
int x51+2;
// 数组
int arr1[5] 1,2,3,4,5;
int arr2[]1,2,3,4,5;
// 动态数组,在C++98中不支持
int* arr3 = new int[5]1,2,3,4,5;
// 标准容器
vector<int> v1,2,3,4,5;
map<int, int> m1,1, 2,2,,3,3,4,4;
return 0;
自定义类型初始化
class Point
public:
Point(int x = 0, int y = 0): _x(x), _y(y)
private:
int _x;
int _y;
;
int main()
Pointer p 1, 2 ;
return 0;
多个对象的列表初始化
多个对象想要支持列表初始化,需给该类(模板类)添加一个带有initializer_list类型参数的构造函数即
可。注意:initializer_list是系统自定义的类模板,该类模板中主要有三个方法:begin()、end()迭代器
以及获取区间中元素个数的方法size()。
#include <initializer_list>
template<class T>
class Vector
public:
// ...
Vector(initializer_list<T> l): _capacity(l.size()), _size(0)
_array = new T[_capacity];
for(auto e : l)
_array[_size++] = e;
Vector<T>& operator=(initializer_list<T> l)
delete[] _array;
size_t i = 0;
for (auto e : l)
_array[i++] = e;
return *this;
// ...
private:
T* _array;
size_t _capacity;
size_t _size;
;
变量类型推导
auto使用的前提是:必须要对auto声明的类型进行初始化,否则编译器无法推导出auto的实际类型。但有时候可能需要根据表达式运行完成之后结果的类型进行推导,因为编译期间,代码不会运行,此时auto也就无能为力。
int main()
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
// 用decltype推演a+b的实际类型,作为定义c的类型
decltype(a+b) c;
cout<<typeid(c).name()<<endl;
return 0;
// 返回值类型追踪
template<class T1, class T2>
auto Add(const T1& left, const T2& right)->decltype(left + right)
return left + right;
int main()
Add(10, 1.2);
return 0;
范围for循环
final与override
智能指针
新增加容器—静态数组array、forward_list以及unordered系列
默认成员函数控制
显式缺省函数
在C++11中,可以在默认函数定义或者声明时加上=default,从而显式的指示编译器生成该函数的默认版本,用=default修饰的函数称为显式缺省函数。
class A
public:
A(int a): _a(a)
// 显式缺省构造函数,由编译器生成
A() = default;
// 在类中声明,在类外定义时让编译器生成默认赋值运算符重载
A& operator=(const A& a);
private:
int _a;
;
A& A::operator=(const A& a) = default;
int main()
A a1(10);
A a2;
a2 = a1;
return 0;
删除默认函数
class A
public:
A(int a): _a(a)
// 禁止编译器生成默认的拷贝构造函数以及赋值运算符重载
A(const A&) = delete;
A& operator(const A&) = delete;
private:
int _a;
;
int main()
A a1(10);
// 编译失败,因为该类没有拷贝构造函数
//A a2(a1);
// 编译失败,因为该类没有赋值运算符重载
A a3(20);
a3 = a2;
return 0;
注意:避免删除函数和explicit一起使
lambda表达式
struct Goods
string _name;
double _price;
;
bool Less(const Goods& left, const Goods& right)
return left._price < right._price;
class Greater
public:
bool operator()(const Goods& left, const Goods& right)
return left._price > right._price;
;
int main()
Goods gds[] = "苹果", 2.1 , "香蕉", 3 , "橙子", 2.2 , "菠萝", 1.5 ;
//sort(gds, gds + sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0]), Less);
//sort(gds, gds + sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0]), Greater());
sort(gds, gds + sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0]), [](const Goods& left, const Goods& right)
return left._price < right._price;
);
[];
以上是关于bingc++(智能指针类型转化c++11)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章