Hibernate Validator 使用详解
Posted 在奋斗的大道
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Hibernate Validator 使用详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
SpringBoot 中使用Hibernate Validator
代码开发过程中,请求参数的有效性校验是一项很繁琐的工作, 如果参数简单,可以直接通过if...else可以搞定,如果参数太多,你如何校验呢? 仍使用if...else就是体力活了, HibernateValidator 是很好的选择。
Hibernate Validator的依赖
SpringBoot 项目,那么spring-boot-starter-web中就已经依赖hibernate-validator
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Spring + Spring MVC + MyBatis 项目,可以直接添加hibernate-validator依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.17.Final</version>
</dependency>
Hibernate Validator 支持注解
温馨提示:Hibernate-Validator 支持的注解数量大于是22个作用,下面我们按照功能划分执行注解类。
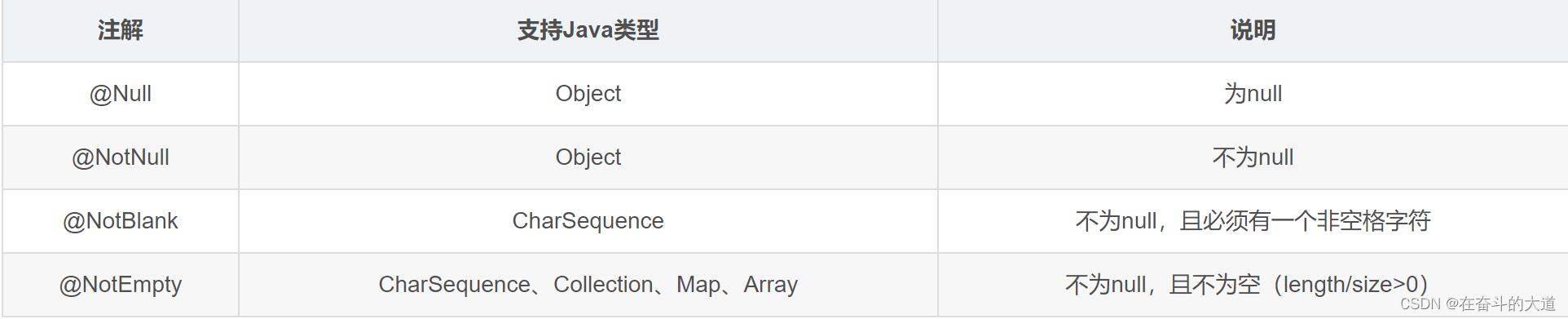
空与非空检查
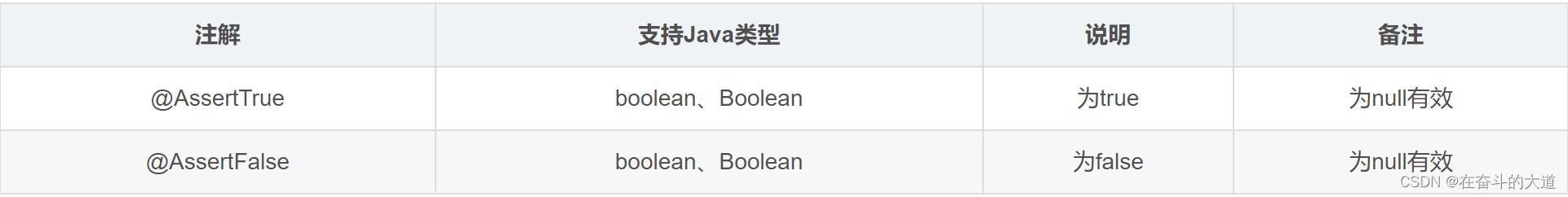
Boolean值检查
日期检查

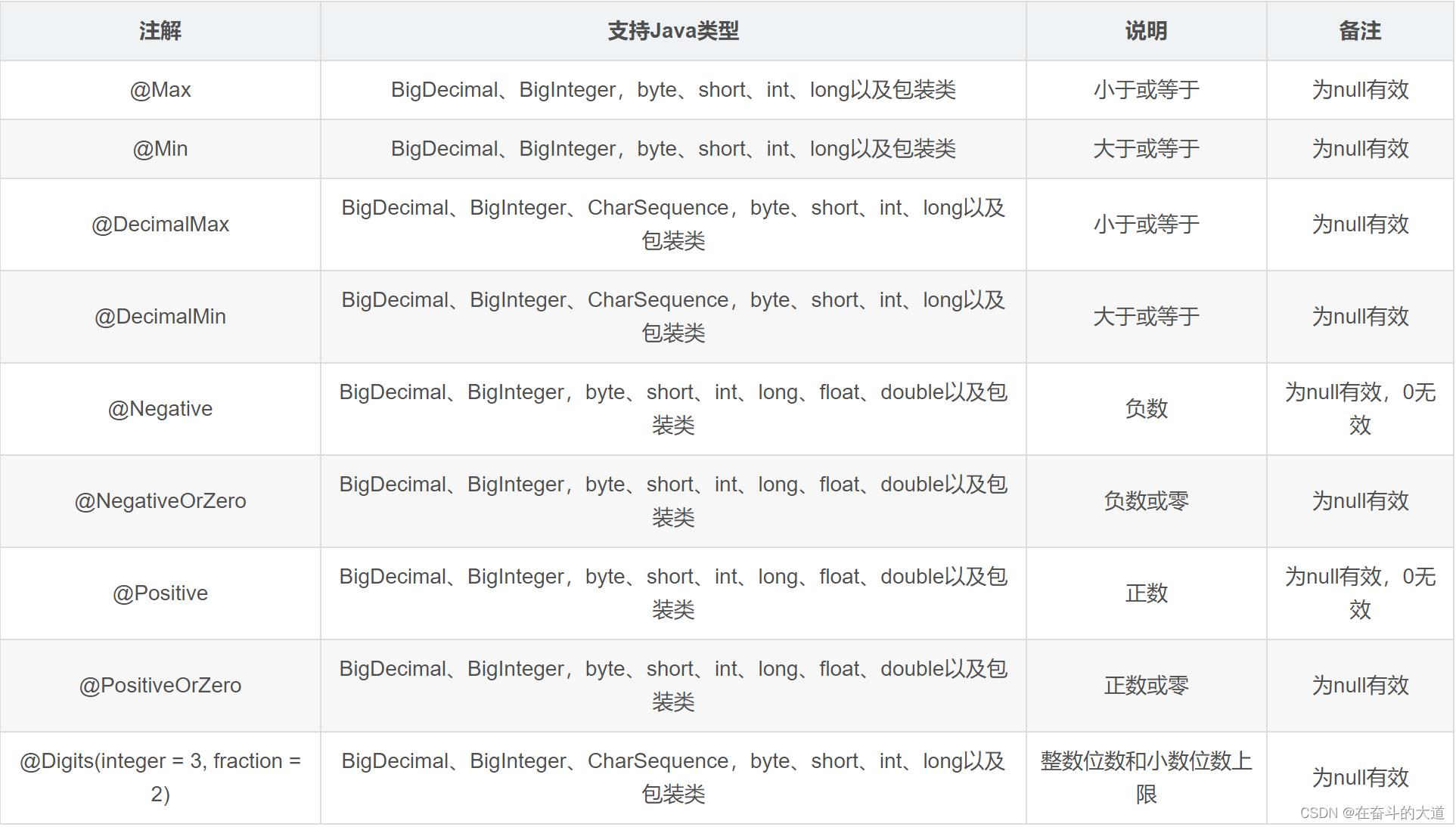
数值检查
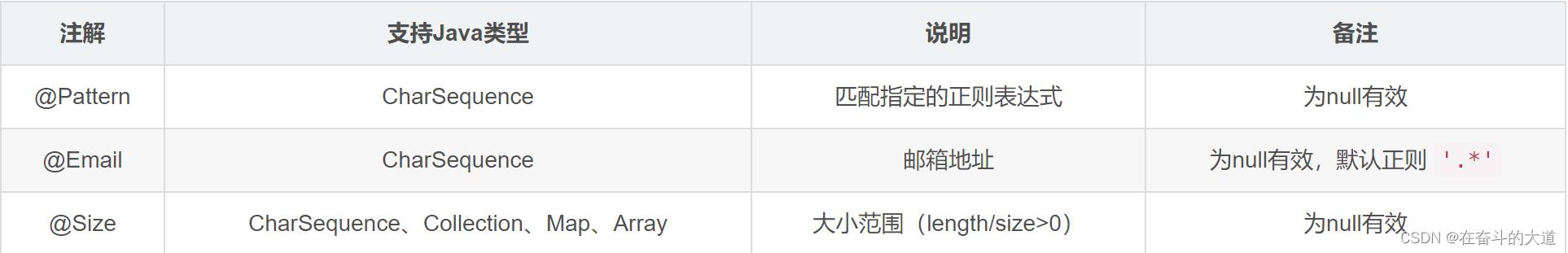
其他
Hibernate-validator扩展约束

Hibernate Validator 校验
简单对象校验
@Data
public class Person
@NotBlank(message = "姓名不能为空")
private String name;
@NotNull(message = "年龄不能为空")
@Range(min = 0, max = 100, message = "年龄必须在min和max之间")
private Integer age;
@NotNull(message = "是否已婚不能为空")
private Boolean isMarried;
@NotEmpty(message = "家庭成员不能为空")
private Collection collection;
@NotEmpty(message = "个人学历不能为空")
private String[] array;
@Email
private String email;
/*
真实场景下面可能还有几十个字段
省略 ... ...
*/
测试功能代码:
public class ValidateTest
//初始化一个校验器工厂
private static ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation
.byProvider(HibernateValidator.class)
.configure()
//校验失败是否立即返回: true-遇到一个错误立即返回不在往下校验,false-校验完所有字段才返回
.failFast(false)
.buildValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
/**
* 简单对象校验
*/
@Test
public void testSimple()
Person s=new Person ();
s.setAge(5);
s.setName(" ");
s.setEmail("email");
Set<ConstraintViolation<Person>> result=validator.validate(s);
System.out.println("遍历输出错误信息:");
//getPropertyPath() 获取属性全路径名
//getMessage() 获取校验后的错误提示信息
result.forEach(r-> System.out.println(r.getPropertyPath()+":"+r.getMessage()));
演示结果:
遍历输出错误信息:
email:不是一个合法的电子邮件地址
collection:家庭成员不能为空
array:个人学历不能为空
name:姓名不能为空
isMarried:是否已婚不能为空
嵌套对象校验
在实际代码开发过程中,需要数据校验的对象大多数是嵌套对象。
组织机构实体类嵌套关系:机构->雇员->人
|--Org
|----Employee
|------List<Person>
Org.java
温馨提示:对于嵌套对象校验要注意, 需要在内部引用的对象上用到@Valid注解,否则不会校验被引用对象的内部字段
@Data
public class Org
@NotNull
private Integer id;
@Valid //如果此处不用Valid注解,则不会去校验Employee对象的内部字段
@NotNull(message = "employee不能为空")
private Employee employee;
Employee.java
@Data
public class Employee
@Valid
@NotNull(message = "person不能为空")
/**
* 此处用到容器元素级别的约束: List<@Valid @NotNull Person>
* 会校验容器内部元素是否为null,否则为null时会跳过校验
* NotNull注解的target包含ElementType.TYPE_USE,因此NotNull可以给泛型注解
*/
private List<@Valid @NotNull Person> people;
Person.java
@Data
public class Person
@NotBlank(message = "姓名不能为空")
private String name;
@NotNull(message = "年龄不能为空")
@Range(min = 0, max = 100, message = "年龄必须在min和max之间")
private Integer age;
@NotNull(message = "是否已婚不能为空")
private Boolean isMarried;
@NotNull(message = "是否有小孩不能为空")
private Boolean hasChild;
@NotNull(message = "小孩个数不能为空")
private Integer childCount;
@NotNull(message = "是否单身不能为空")
private Boolean isSingle;
测试功能代码:
@Test
public void test()
Person p=new Person();
p.setAge(30);
p.setName("zhangsan");
//p.setIsMarried(true);
Person p2=new Person();
p2.setAge(30);
//p2.setName("zhangsan2");
p2.setIsMarried(false);
//p2.setHasChild(true);
Org org=new Org();
//org.setId(1);
List<Person> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(p);
list.add(p2);
//增加一个null,测试是否会校验元素为null
list.add(null);
Employee e=new Employee();
e.setPeople(list);
org.setEmployee(e);
Set<ConstraintViolation<Org>> result=validator.validate(org);
System.out.println("遍历输出错误信息:");
result.forEach(r-> System.out.println(r.getPropertyPath()+":"+r.getMessage()));
演示结果:
id:不能为null
Employee.people[0].childCount:小孩个数不能为空
Employee.people[0].isSingle:是否单身不能为空
Employee.people[1].hasChild:是否有小孩不能为空
Employee.people[0].isMarried:是否已婚不能为空
Employee.people[1].name:姓名不能为空
Employee.people[1].childCount:小孩个数不能为空
Employee.people[2].<list element>:不能为null
Employee.people[0].hasChild:是否有小孩不能为空
Employee.people[1].isSingle:是否单身不能为空
Hibernate Validator 分组校验
功能需求:当People对象为已婚时(isMarried字段为true),需要校验”配偶姓名“、”是否有小孩“等字段不能为空,当People对象为未婚时,需要校验“是否单身”等其他字段不能为空, 这种需求可以通过分组检验来实现,将校验逻辑分为两个组,然后每次调用校验接口时指定分组即可实现不同的校验。 如果不管“是否已婚”都需要校验的字段(如姓名、年龄这些字段等),则可以同时指定两个分组。
静态分组
静态分组主要在类上面是使用@GroupSequence注解指定一个或者多个分组,用于处理不同的校验逻辑。
@GroupSequence( Group.UnMarried.class, Group.Married.class )
public class People
... ...
静态分组不是我们关注的重点,已经知晓它的使用,我们直接跳过当前章节。
动态分组
“未婚”和“已婚”两个分组的动态功能代码如下。
温馨提示:分组标识必须是一个Class,而且没有要求实现特定的接口和实现类,仅仅只是一个标记而已,因此我采用接口实现分组标记。
public interface Group
//已婚情况的分组校验
interface Married
//未婚情况的分组校验
interface UnMarried
校验对象:People.java
@Data
public class People
//不管是否已婚,都需要校验的字段,groups里面指定两个分组
@NotBlank(message = "姓名不能为空",groups = Group.UnMarried.class, Group.Married.class)
private String name;
@NotNull(message = "年龄不能为空",groups = Group.UnMarried.class, Group.Married.class)
@Range(min = 0, max = 100, message = "年龄必须在min和max之间",groups = Group.UnMarried.class, Group.Married.class)
private Integer age;
@NotNull(message = "是否已婚不能为空",groups = Group.UnMarried.class, Group.Married.class)
private Boolean isMarried;
//已婚需要校验的字段
@NotNull(message = "配偶姓名不能为空",groups = Group.Married.class)
private String spouseName;
//已婚需要校验的字段
@NotNull(message = "是否有小孩不能为空",groups = Group.Married.class)
private Boolean hasChild;
//未婚需要校验的字段
@NotNull(message = "是否单身不能为空",groups = Group.UnMarried.class)
private Boolean isSingle;
测试功能代码:通过isMarried的值来动态指定分组校验
@Test
public void testGroup()
People p=new People();
p.setAge(30);
p.setName(" ");
p.setIsMarried(false);
Set<ConstraintViolation<People>> result;
//通过isMarried的值来动态指定分组校验
if(p.getIsMarried())
//如果已婚,则按照已婚的分组字段
result=validator.validate(p, Group.Married.class);
else
//如果未婚,则只校验未婚的分组字段
result=validator.validate(p, Group.UnMarried.class);
System.out.println("遍历输出错误信息:");
result.forEach(r-> System.out.println(r.getPropertyPath()+":"+r.getMessage()));
测试结果,p.setIsMarried(true)
遍历输出错误信息:
name:姓名不能为空
isSingle:是否单身不能为空
测试结果,p.setIsMarried(false)
遍历输出错误信息:
name:姓名不能为空
hasChild:是否有小孩不能为空
spouseName:配偶姓名动态分组优化
针对数据校验,我最初的想法是全部委托给Hibernate-Validator 框架,但在动态分组的校验测试功能代码时,还是添加了额外的业务逻辑判断功能代码:
//通过isMarried的值来动态指定分组校验
if(p.getIsMarried())
//如果已婚,则按照已婚的分组字段
result=validator.validate(p, Group.Married.class);
else
//如果未婚,则只校验未婚的分组字段
result=validator.validate(p, Group.UnMarried.class);
还有没有优化提升的空间呢?
解决办法:第一步:通过DefaultGroupSequenceProvider接口,可以实现真正的动态分组校验。
定义PeopleGroupSequenceProvider类实现DefaultGroupSequenceProvider接口,覆写getValidationGroups方法,在其中判断Person.isMarried值,来实现动态设置分组,也就是将校验的额外判断逻辑从校验框架外层转移到了校验框架中,外层业务代码只需要调用校验接口即可,而无需关注具体的校验逻辑.
public class PeopleGroupSequenceProvider implements DefaultGroupSequenceProvider<People>
@Override
public List<Class<?>> getValidationGroups(People bean)
List<Class<?>> defaultGroupSequence = new ArrayList<>();
// 这里必须将校验对象的类加进来,否则没有Default分组会抛异常,这个地方还没太弄明白,后面有时间再研究一下
defaultGroupSequence.add(People.class);
if (bean != null)
Boolean isMarried=bean.getIsMarried();
///System.err.println("是否已婚:" + isMarried + ",执行对应校验逻辑");
if(isMarried!=null)
if(isMarried)
System.err.println("是否已婚:" + isMarried + ",groups: "+Group.Married.class);
defaultGroupSequence.add(Group.Married.class);
else
System.err.println("是否已婚:" + isMarried + ",groups: "+Group.UnMarried.class);
defaultGroupSequence.add(Group.UnMarried.class);
else
System.err.println("isMarried is null");
defaultGroupSequence.add(Group.Married.class);
defaultGroupSequence.add(Group.UnMarried.class);
else
System.err.println("bean is null");
return defaultGroupSequence;
第二步:People类使用@GroupSequenceProvider注解指定一个GroupSequenceProvider
@GroupSequenceProvider(PeopleGroupSequenceProvider.class)
public class People
//字段同上
//... ...
测试校验代码:
@Test
public void testGroupSequence()
People p=new People();
p.setAge(30);
p.setName(" ");
System.out.println("----已婚情况:");
p.setIsMarried(true);
Set<ConstraintViolation<People>> result=validator.validate(p);
System.out.println("遍历输出错误信息:");
result.forEach(r-> System.out.println(r.getPropertyPath()+":"+r.getMessage()));
System.out.println("----未婚情况:");
p.setIsMarried(false);
result=validator.validate(p);
System.out.println("遍历输出错误信息:");
result.forEach(r-> System.out.println(r.getPropertyPath()+":"+r.getMessage()));
测试结果:
----已婚情况:
遍历输出错误信息:
name:姓名不能为空
spouseName:配偶姓名不能为空
hasChild:是否有小孩不能为空
----未婚情况:
遍历输出错误信息:
name:姓名不能为空
isSingle:是否单身不能为空
Hibernater-Validator 自定义约束注解
定义自定义约束,有三个步骤
- 创建约束注解
- 实现一个验证器
- 定义默认的错误信息
实战:自定义手机号码校验器
@Documented
@Target(METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE)
@Constraint(validatedBy = MobileValidator.class)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(Mobile.List.class)
public @interface Mobile
/**
* 错误提示信息,可以写死,也可以填写国际化的key
*/
String message() default "手机号码不正确";
Class<?>[] groups() default ;
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default ;
String regexp() default "^1([38][0-9]|4[579]|5[0-3,5-9]|6[6]|7[0135678]|9[89])\\\\d8$";
@Target(METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Documented
@interface List
Mobile[] value();
知识点拓展:自定义约束重点属性讲解
message错误提示信息,可以写死,也可以填写国际化的keygroups分组信息,允许指定此约束所属的验证组(下面会说到分组约束)payload有效负载,可以通过payload来标记一些需要特殊处理的操作
@Repeatable注解和@List定义可以让该注解在同一个位置重复多次,通常是不同的配置(比如不同的分组和消息)
@Constraint(validatedBy = MobileValidator.class)该注解是指明我们的自定义约束的验证器。温馨提示 :自定义验证器必须实现javax.validation.ConstraintValidator接口
public class MobileValidator implements ConstraintValidator<Mobile, String>
/**
* 手机验证规则
*/
private Pattern pattern;
@Override
public void initialize(Mobile mobile)
pattern = Pattern.compile(mobile.regexp());
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context)
if (value == null)
return true;
return pattern.matcher(value).matches();
实战:自定义枚举类校验器
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.AMNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy=EnumValueValidator.class)
public @interface EnumValue
String message() default "EnumValueValidator's value is invalid";
Class<?> groups() default ;
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default ;
Class<? extends StringCodeEnum> enumClass();
boolean isRequired() default false;
import javax.annotation.Nonnull;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
import com.zzg.common.base.web.formatter.StringCodeEnum;
public class EnumValueValidator implements ConstraintValidator<EnumValue, Object>
private Class<? extends StringCodeEnum> enumClass = null;
private Boolean isRequired = null;
private static <E extends StringCodeEnum> E off(@Nonnull Class<E> classType, String value)
for(E enumConstant: classType.getEnumConstants())
if(enumConstant.getCode().equalsIgnoreCase(value))
return enumConstant;
return null;
@Override
public void initialize(EnumValue constraintAnnotation)
enumClass = constraintAnnotation.enumClass();
isRequired = constraintAnnotation.is
@Override
publlic boolean isValid(Object o, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext )
if(o == null)
return !isRequired;
try
StringCodeEnum enumObj = off(enumClass, String.valueof(o));
return enumObj == null ? Boolean.FALSE : Boolean.TRUE;
catch(Exception e)
return Boolean.TRUE;
public BaseOrg
******
@ApiModeProperty("企业备案类别")
@NotBlank(message ="企业备案类别不能为空")
@EnumValue(message ="企业备案类别不在取值范围内", enumClass=EQYLBValue, isRequired=true)
private String qylb;
******
SpringBoot 中使用Hibernate Validator
上面介绍了Validator的一些使用,还有注解的介绍,那么在Spring中我们怎么去使用Hibernate Validator做验证呢?或者说再Web项目中怎么使用Hibernate Validator?
spring-boot-starter-web中是添加了hibernate-validator依赖的,说明Spring Boot本身也是使用到了Hibernate Validator验证框架的
配置Validator
@Configuration
public class ValidatorConfig
/**
* 配置验证器
*
* @return validator
*/
@Bean
public Validator validator()
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.byProvider(HibernateValidator.class)
.configure()
// 快速失败模式
.failFast(true)
// .addProperty( "hibernate.validator.fail_fast", "true" )
.buildValidatorFactory();
return validatorFactory.getValidator();
可以通过方法 failFast(true)或 addProperty("hibernate.validator.fail_fast", "true")设置为快速失败模式,快速失败模式在校验过程中,当遇到第一个不满足条件的参数时就立即返回,不再继续后面参数的校验。否则会一次性校验所有参数,并返回所有不符合要求的错误信息。
Controller层 请求参数验证
在Controller参数前加上@Valid或Spring的 @Validated注解,这两种注释都会导致应用标准Bean验证。如果验证不通过会抛出BindException异常,并变成400(BAD_REQUEST)响应;或者可以通过Errors或BindingResult参数在控制器内本地处理验证错误。另外,如果参数前有@RequestBody注解,验证错误会抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException异常。
第一种情况:请求参数被@Valid + @RequestBody 修饰情况
@Api(tags="楼栋信息", value="楼栋信息")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/base/building")
public class BaseBuildingController
@Resource
private IBaseBuildingService baseBuildingService;
/**
* 验证不通过抛出 `MethodArgumentNotValidException`
*/
@ApiOperation(tags="楼栋信息新增", value="楼栋信息新增")
@PostMapping(value="/insert")
public BaseBuildingVO insert(@RequestBody @Validated BaseBuildingDTO dto)
BaseBuildingBO bo = BeanCopierUtil.copy(dto, BaseBuildingBO.class);
String id = baseBuildingService.saveGeneratedId(bo);
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(id))
return BeanCopierUtil.copy(baseBuildingService.selectById(id), BaseBuildingVO.class);
return null;
配置全局异常处理器。
@ControllerAdvice
public Class CommmonGlobalExceptionHandler
public static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CommmonGlobalExceptionHandler.clas);
/**
* hibernate validator 数据绑定验证异常拦截
*
* @param e 绑定验证异常
* @return 错误返回消息
*/
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public R validateErrorHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException e)
ObjectError error = e.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().get(0);
LOG.info("数据验证异常:", error.getDefaultMessage());
return R.fail(error.getDefaultMessage());
第二种情况:请求参数被@Valid + @RequestBody +BindingResult 修饰
@Api(tags="楼栋信息", value="楼栋信息")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/base/building")
public class BaseBuildingController
@Resource
private IBaseBuildingService baseBuildingService;
/**
* 验证不通过抛出 `MethodArgumentNotValidException`
*/
@ApiOperation(tags="楼栋信息新增", value="楼栋信息新增")
@PostMapping(value="/insert")
public BaseBuildingVO insert(@RequestBody @Validated BaseBuildingDTO dto, ,BindingResult result)
// 在控制器内本地处理验证错误
if (result.hasErrors())
result.getAllErrors().forEach(s -> System.out.println(s.getDefaultMessage()));
throw new CommonBaseException(ERespCode.ERROR);
BaseBuildingBO bo = BeanCopierUtil.copy(dto, BaseBuildingBO.class);
String id = baseBuildingService.saveGeneratedId(bo);
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(id))
return BeanCopierUtil.copy(baseBuildingService.selectById(id), BaseBuildingVO.class);
return null;
Hibernate Validator 业务校验工具
在Controller层添加Hibernate-Validator 注解标签基本就能满足日常开发需求,但是还有一种情况下是满足不了的,就是非HTTP接口,在使用Service服务就不能使用这种方式,需要另外的在业务代码中进行校验。这个时候就无法使用BindingResult来直接获取校验结果。怎么办呢?
第一步:添加Hibernate-Validator 业务校验工具类;
public class ValidatorUtil
private static final Validator validatorFast = Validation.byProvider(HibernateValidator.class)
.configure()
.failFast(true)
.buildValidatorFactory()
.getValidator();
private static final Validator validatorAll = Validation.byProvider(HibernateValidator.class)
.configure()
.failFast(false)
.buildValidatorFactory()
.getValidator();
/**
* 快速校验: 校验所有字段,抛出第一个不合法字段的异常信息
*
*/
public static <T> void validateFast(Collection<T> cols, Class<?>... groups)
for(T entity : cols)
validateFast(entity, groups);
/**
* 快速校验: 校验所有字段,抛出第一个不合法字段的异常信息
*
*/
public static <T> void validateFast(T entity, Class<?>... groups>)
Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> validateResult = validatorFast.validate(entity, groups);
if(validateResult.size() > 0)
throw new CommonException("", validateResult.iterator().next().getMessage());
/**
* 快速校验: 校验所有字段,返回第一个不合法字段的异常信息
*
*/
public static <T> ConstraintViolation<T> getValidatorFastResult(T entity, Class<?>... groups)
Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> validateResult = validatorFast.validate(entity, groups);
if(validateResult.size() > 0)
return validateResult.iterator().next();
return null;
/**
* 全部校验: 校验所有字段,抛出所有不合法字段的异常信息
*
*/
public static <T> void validateALL(Collection<T> cols, Class<?>... groups)
for(T entity : cols)
validateAll(entity, groups);
/**
* 全部校验: 校验所有字段,抛出所有不合法字段的异常信息
*
*/
public static <T> void validateAll(T entity, Class<?>... groups)
Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> validateResult = validatorAll .validate(entity, groups);
if(validateResult.size() > 0)
Iterator<ConstraintViolation<T>> iterator = validateResult.iterator();
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(";");
while(iterator.hasNext())
joiner.add(iterator.next().getMessage());
throw new CommonException("", joiner.toString());
/**
* 全部校验: 校验所有字段,返回不合法字段的信息
*
*/
public static <T> Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> getValidatorAllResult(T entity, Class<?>... groups)
return validatorAll.validate(entity, groups);
第二步:在Service中调用Hibernate-Validator 工具类。
private void writerValidatorMessage(BaseHouse house)
Set<ConstraintViolation<BaseHouse>> validateResult = ValidatorUtil.getValidatorAllResult(house);
List<BaseDataDealDetail> errorRecordList= new CopyWriteArrayList<BaseDataDealDetail>();
if(validateResult.size() > 0 )
validateResult.parallelStream().forEach((validateItem ->
// 插入字段错误详情记录信息
))
以上是关于Hibernate Validator 使用详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章