cpu设计和实现(协处理器cp0)
Posted 嵌入式-老费
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了cpu设计和实现(协处理器cp0)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【 声明:版权所有,欢迎转载,请勿用于商业用途。 联系信箱:feixiaoxing @163.com】
除了通用计算器负责控制和计算之外,cpu如果需要正常有序地运行,还需要一定地协处理器来帮助完成对应地工作。在mips下面,这样地协处理器称之为cp0。协处理器的工作一般包括这几个方面,
1)处理中断和异常;
2)处理mmu和tlb;
3)处理cache;
4)处理其他cpu的相关属性。
之前我们在谈到乘法和除法的时候,涉及到hi和lo这两个寄存器。其实,cp0的处理方法和他们是差不多的。如果是mf读操作,那么这个动作是在exe阶段完成的;如果是写操作,那么这个动作也是在wb阶段完成的。
1、准备cp0_reg.v
`include "defines.v"
module cp0_reg(
input wire clk,
input wire rst,
input wire we_i,
input wire[4:0] waddr_i,
input wire[4:0] raddr_i,
input wire[`RegBus] data_i,
// input wire[31:0] excepttype_i,
input wire[5:0] int_i,
// input wire[`RegBus] current_inst_addr_i,
// input wire is_in_delayslot_i,
output reg[`RegBus] data_o,
output reg[`RegBus] count_o,
output reg[`RegBus] compare_o,
output reg[`RegBus] status_o,
output reg[`RegBus] cause_o,
output reg[`RegBus] epc_o,
output reg[`RegBus] config_o,
output reg[`RegBus] prid_o,
output reg timer_int_o
);
always @ (posedge clk) begin
if(rst == `RstEnable) begin
count_o <= `ZeroWord;
compare_o <= `ZeroWord;
//status寄存器的CU为0001,表示协处理器CP0存在
status_o <= 32'b00010000000000000000000000000000;
cause_o <= `ZeroWord;
epc_o <= `ZeroWord;
//config寄存器的BE为1,表示Big-Endian;MT为00,表示没有MMU
config_o <= 32'b00000000000000001000000000000000;
//制作者是L,对应的是0x48,类型是0x1,基本类型,版本号是1.0
prid_o <= 32'b00000000010011000000000100000010;
timer_int_o <= `InterruptNotAssert;
end else begin
count_o <= count_o + 1 ;
cause_o[15:10] <= int_i;
if(compare_o != `ZeroWord && count_o == compare_o) begin
timer_int_o <= `InterruptAssert;
end
if(we_i == `WriteEnable) begin
case (waddr_i)
`CP0_REG_COUNT: begin
count_o <= data_i;
end
`CP0_REG_COMPARE: begin
compare_o <= data_i;
//count_o <= `ZeroWord;
timer_int_o <= `InterruptNotAssert;
end
`CP0_REG_STATUS: begin
status_o <= data_i;
end
`CP0_REG_EPC: begin
epc_o <= data_i;
end
`CP0_REG_CAUSE: begin
//cause寄存器只有IP[1:0]、IV、WP字段是可写的
cause_o[9:8] <= data_i[9:8];
cause_o[23] <= data_i[23];
cause_o[22] <= data_i[22];
end
endcase //case addr_i
end
end //if
end //always
always @ (*) begin
if(rst == `RstEnable) begin
data_o <= `ZeroWord;
end else begin
case (raddr_i)
`CP0_REG_COUNT: begin
data_o <= count_o ;
end
`CP0_REG_COMPARE: begin
data_o <= compare_o ;
end
`CP0_REG_STATUS: begin
data_o <= status_o ;
end
`CP0_REG_CAUSE: begin
data_o <= cause_o ;
end
`CP0_REG_EPC: begin
data_o <= epc_o ;
end
`CP0_REG_PrId: begin
data_o <= prid_o ;
end
`CP0_REG_CONFIG: begin
data_o <= config_o ;
end
default: begin
end
endcase //case addr_i
end //if
end //always
endmodule2、id添加译码
if(inst_i[31:21] == 11'b01000000000 &&
inst_i[10:0] == 11'b00000000000) begin
aluop_o <= `EXE_MFC0_OP;
alusel_o <= `EXE_RES_MOVE;
wd_o <= inst_i[20:16];
wreg_o <= `WriteEnable;
instvalid <= `InstValid;
reg1_read_o <= 1'b0;
reg2_read_o <= 1'b0;
end else if(inst_i[31:21] == 11'b01000000100 &&
inst_i[10:0] == 11'b00000000000) begin
aluop_o <= `EXE_MTC0_OP;
alusel_o <= `EXE_RES_NOP;
wreg_o <= `WriteDisable;
instvalid <= `InstValid;
reg1_read_o <= 1'b1;
reg1_addr_o <= inst_i[20:16];
reg2_read_o <= 1'b0;
end3、ex阶段
1)增加数据读取操作
`EXE_MFC0_OP: begin
cp0_reg_read_addr_o <= inst_i[15:11];
moveres <= cp0_reg_data_i;
if( mem_cp0_reg_we == `WriteEnable &&
mem_cp0_reg_write_addr == inst_i[15:11] ) begin
moveres <= mem_cp0_reg_data;
end else if( wb_cp0_reg_we == `WriteEnable &&
wb_cp0_reg_write_addr == inst_i[15:11] ) begin
moveres <= wb_cp0_reg_data;
end
end 看到这里,大家应该对这个代码不陌生了。之前谈到过,所有的寄存器都是在wb之后,才会真正写到寄存器里面的。但是,mfc0的动作是在exe阶段进行的,那么这个时候势必会出现数据读取错误的情况的。所以,解决这个问题最好的办法就是数据预取。id中寄存器预取、ex阶段hi&lo以及mfc预取、mem阶段llbit预取,本质上都是一回事。
2)增加写操作
always @ (*) begin
if(rst == `RstEnable) begin
cp0_reg_write_addr_o <= 5'b00000;
cp0_reg_we_o <= `WriteDisable;
cp0_reg_data_o <= `ZeroWord;
end else if(aluop_i == `EXE_MTC0_OP) begin
cp0_reg_write_addr_o <= inst_i[15:11];
cp0_reg_we_o <= `WriteEnable;
cp0_reg_data_o <= reg1_i;
end else begin
cp0_reg_write_addr_o <= 5'b00000;
cp0_reg_we_o <= `WriteDisable;
cp0_reg_data_o <= `ZeroWord;
end
end cp0寄存器的写操作是和通用寄存器分开来的。所以这部分代码需要单独用逻辑快来表达。
4、mem阶段
mem阶段对cp0没有什么影响,主要工作就是把之前ex阶段的数据透传下去即可。
cp0_reg_we_o <= cp0_reg_we_i;
cp0_reg_write_addr_o <= cp0_reg_write_addr_i;
cp0_reg_data_o <= cp0_reg_data_i; 5、准备汇编代码测试
.org 0x0
.set noat
.set noreorder
.set nomacro
.global _start
_start:
ori $1,$0,0xf
mtc0 $1,$11,0x0 #写compare寄存器,开始计时
lui $1,0x1000
ori $1,$1,0x401
mtc0 $1,$12,0x0 #将0x401写如status寄存器
mfc0 $2,$12,0x0 #读status寄存器,$2=0x401
_loop:
j _loop
nop
6、将对应的汇编代码翻译成二进制文件
3401000f
40815800
3c011000
34210401
40816000
40026000
08000006
00000000
7、利用iverilog和gtkwave进行波形分析
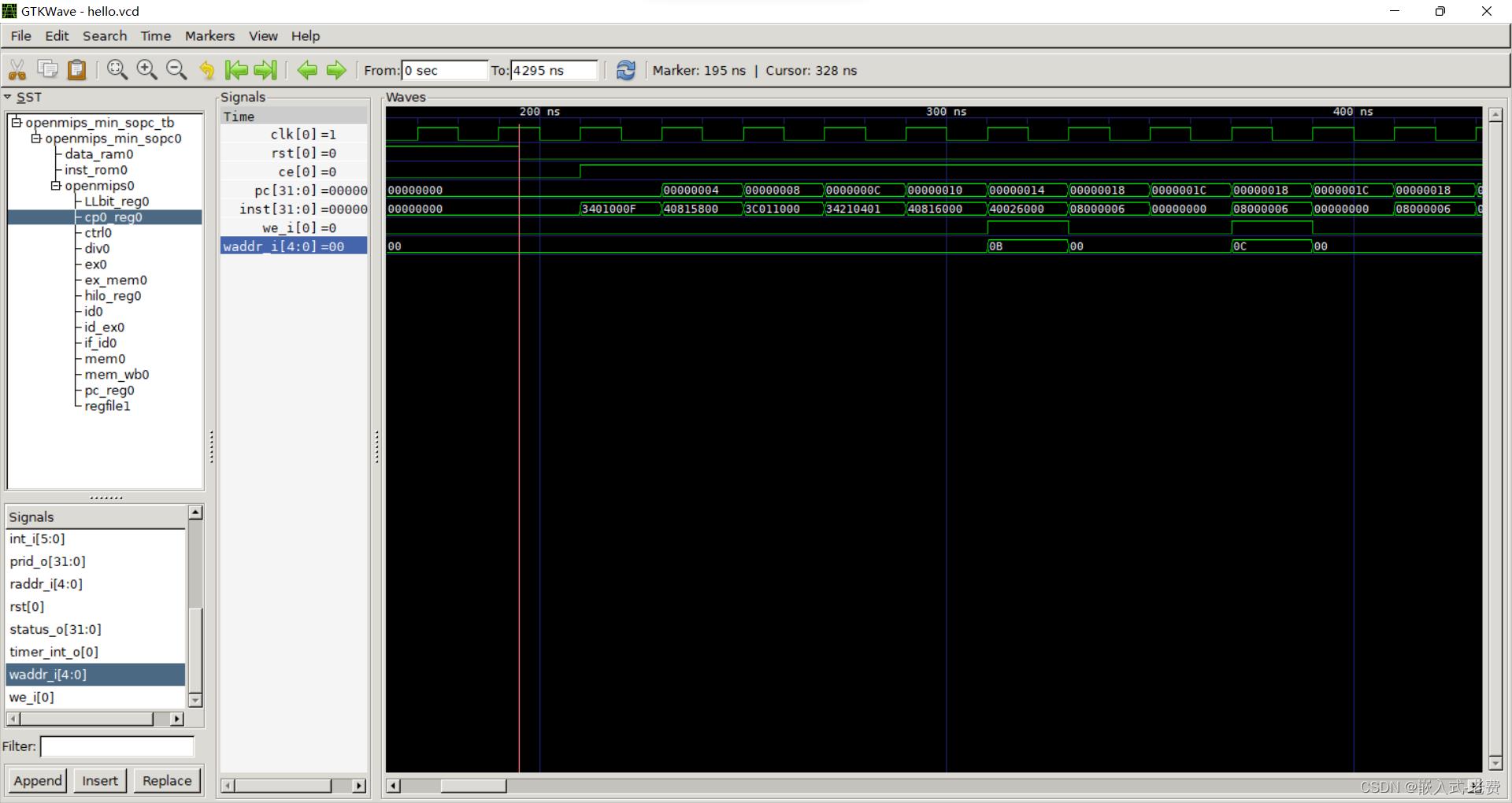
除了通用的pc、inst这些寄存器、wire之外,还可以把cp0_reg0里面的寄存器拉出来看看。重点看看we_i什么时候为高、写入的waddr_i对不对、和之前给出来的汇编代码能不能对的上。最后就是死循环了,因为mips延迟槽的原因,循环肯定是两个pc地址交替进行的。
以上是关于cpu设计和实现(协处理器cp0)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章