排序数组
Posted 一棵灬胡杨树
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了排序数组相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
LeetCode912–排序数组
前言
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-an-array/submissions/
首先,这个题如果使用常用的冒泡排序以及选择排序都会导致时间超时,所以大概可以能用以下几种方法来实现:
一、快速排序–hoare法
hoare法的基本思想是给定一个key值,在第一轮排序中,使得ke y值在曲轴点,使得key的左边都比key值小,右边比key值大。接着在从划分好的两边重复以上步骤。总的来看是一个递归的思想,下面是实现方法:
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
//hoare法
static void Swap(int *a,int *b)
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
static int Paratition(int *nums,int left,int right)
int low = left;
int high = right - 1;
int key = nums[low];
while (low < high)
while(low < high && nums[high] >= key)
high--;
Swap(&nums[low],&nums[high]);
while(low < high && nums[low] < key)
low++;
Swap(&nums[low],&nums[high]);
return low;
static void QuickSort(int *nums,int left,int right)
if (left >= right)
return;
int pos = Paratition(nums,left,right);
QuickSort(nums,left,pos);
QuickSort(nums,pos + 1,right);
int* sortArray(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize)
*returnSize = numsSize;
QuickSort(nums,0,*returnSize);
return nums;
```

这个方法由于多次调用了Swap函数不停的交换值,所以导致程序的效率低下,故为了改进,我们提出挖坑法
二、快速排序–挖坑法
挖坑法的主要思想与hoare法基本相同,只不过在程序用一个临时空间存储key的值,通过高位nums[high]与key值比较,如果nums[high] > key,则将nums[high]赋给nums[low],紧接着换比较方向,最后剩下的位置就是key的所在位置。此程序用了覆盖的思想代替了Swap函数,所以效率也会提高,下面是实现方法:
//挖坑法
static int Partition(int *nums,int left,int right)
int low = left;
int high = right - 1;
int key = nums[low];
while (low < high)
while (low < high && nums[high] > key)
high--;
//将高位置与低位置交换
nums[low] = nums[high];
//下面改变比较方向
while(low < high && nums[low] <= key)
low++;
nums[high] = nums[low];
nums[low] = key;
return low;
static void QuickSort(int *nums,int left,int right)
if (left >= right)
return;
int pos = Partition(nums,left,right);
QuickSort(nums,left,pos);
QuickSort(nums,pos + 1, right);
int* sortArray(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize)
*returnSize = numsSize;
QuickSort(nums,0,*returnSize);
return nums;

三、快速排序–前后指针法
所谓的前后指针法基本思想还是需要找到曲轴点,只不过前后指针摒弃了上面2个通过交换和赋值的思想,通过以快一慢指针来寻找曲轴点。令初始的key值为:nums[left];pos = left; i = pos +1;当i的值小于key值时,pos++,此时要判断pos是否等于i值,如果不等于,则需要将nums[pos],nums[i]交换,如果等于,则不交换。当i达到边界条件时,循环退出,最后将nums[left]和nums[pos]交换,就找到了key的曲轴点,下面是实现方法:
//前后指针
static void Swap(int *a,int *b)
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
static int Paratition(int *nums,int left,int right)
int key = nums[left];
int pos = left;
for (int i = pos + 1;i < right;++i)
if (nums[i] < key)
pos++;
if (pos != i)
Swap(&nums[i],&nums[pos]);
Swap(&nums[left],&nums[pos]);
return pos;
static void QuickSort(int *nums,int left,int right)
if (left >= right)
return;
int pos = Paratition(nums,left,right);
QuickSort(nums,left,pos);
QuickSort(nums,pos + 1,right);
int* sortArray(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize)
*returnSize = numsSize;
QuickSort(nums,0,*returnSize);
return nums;

四、快速排序–前后指针法(改进一)
前后指针法的改进是在当数组的size小于M(M = 5,书上说M的值在25-30)时,可以直接调用插入排序法。故改进的代码如下:
#define M 10
static void Swap(int *a,int *b)
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
static void InsertSort(int *nums,int left,int right)
for (int i = left + 1;i < right;++i)
int j = i;
int tmp = nums[j];
while (j > left && tmp < nums[j - 1])
nums[j] = nums[j - 1];
j--;
nums[j] = tmp;
static int Paratition(int *nums,int left,int right)
int key = nums[left];
int pos = left;
for (int i = pos + 1;i < right;++i)
if (nums[i] < key)
pos++;
if (pos != i)
Swap(&nums[i],&nums[pos]);
Swap(&nums[left],&nums[pos]);
return pos;
static void QuickSort(int *nums,int left,int right)
if (left >= right)
return;
if (right - left <= M)
//直接调用插入比较函数
InsertSort(nums,left,right);
int pos = Paratition(nums,left,right);
QuickSort(nums,left,pos);
QuickSort(nums,pos + 1,right);
int* sortArray(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize)
*returnSize = numsSize;
QuickSort(nums,0,*returnSize);
return nums;

四、快速排序–前后指针法(改进二)
在快速排序算法中,每次划分时用于比较的基准元素的选择对于算法的性能有很大的影响。如果基准元素选择不合适,会导致算法的性能大幅度退化。若能更加合理的选择基准元素,使得每次划分所得的两个字序列中的元素个数尽可能的接近,就可以加快排序速度。但每次元素都是随机的,很难办到。退而求其次,希望至少能够避免最坏情况发生(比如元素逆序排好了)。还有一种改进方法就是在序列中随机选择一个元素作为基准元素,这样最坏情况发生的可能性就很小。但是更为彻底的改进方法就是,去基准对象时采用从序列左端点left,右端点right和中间点mid,mid = (left + right - 1) / 2中取中间值,并且交换到left(也可以交换到right),然后再对整个序列进行划分,代码如下:
#define M 10
static void Swap(int *a,int *b)
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
static int GetMidIndex(int *nums,int left,int right)
int mid = (left + right - 1) / 2;
if (nums[left] < nums[mid] && nums[mid] < nums[right - 1])
return mid;
if (nums[left] > nums[mid] && nums[left] < nums[right - 1])
return left;
if (nums[left] > nums[mid] && nums[mid] < nums[right - 1])
return mid;
return right - 1;
static void InsertSort(int *nums,int left,int right)
for (int i = left + 1;i < right;++i)
int j = i;
int tmp = nums[j];
while (j > left && tmp < nums[j - 1])
nums[j] = nums[j - 1];
j--;
nums[j] = tmp;
static int Paratition(int *nums,int left,int right)
int mid_index = GetMidIndex(nums,left,right);
if (mid_index != left)
Swap(&nums[mid_index],&nums[left]);
int key = nums[left];
int pos = left;
for (int i = pos + 1;i < right;++i)
if (nums[i] < key)
pos++;
if (pos != i)
Swap(&nums[i],&nums[pos]);
Swap(&nums[left],&nums[pos]);
return pos;
static void QuickSort(int *nums,int left,int right)
if (left >= right)
return;
if (right - left <= M)
//直接调用插入比较函数
InsertSort(nums,left,right);
int pos = Paratition(nums,left,right);
QuickSort(nums,left,pos);
QuickSort(nums,pos + 1,right);
int* sortArray(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize)
*returnSize = numsSize;
QuickSort(nums,0,*returnSize);
return nums;

这里我写的代码按照原理来说没问题,但是不知道为什么性能还下降了,还求大神指出。。。
五、2路归并排序
归并排序(Merge Sort):归并的含义是将两个或者两个以上的有序表组合成一个新的有序表。实现方法与顺序表或者链表合并思路一样,都需要借助一个与原先表一样大的空间实现排序。假设初始序列含有n个纪律,则可以看为n个有序的子序列,每个子序列的长度为1,然后两两归并,得到 n / 2个长度为2或1 的有序子序列;再两两并归,如此重复,直至得到一个长度为n 的有序序列为止。如果所示:

实现代码如下:
//归并排序
static void MergeSort(int *nums,int left,int right,int *tmp)
if (left >= right)
return;
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
MergeSort(nums,left,mid,tmp);//分解左边分支
MergeSort(nums,mid + 1,right,tmp);//分解右边分支
//开始归并
int begin1,end1,begin2,end2;
begin1 = left;end1 = mid;begin2 = mid + 1;end2 = right;
int k = left;
while(begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
if (nums[begin1] < nums[begin2])
tmp[k++] = nums[begin1++];
else
tmp[k++] = nums[begin2++];
//走到这有两种情况,1: bengin1长,2:begin2 长
while(begin1 <= end1)
tmp[k++] = nums[begin1++];
while (begin2 <= end2)
tmp[k++] = nums[begin2++];
//把tmp拷贝到nums中,考虑到有边界值,所以+left
memcpy(nums + left,tmp + left,sizeof(int) * (right - left + 1));
int* sortArray(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize)
int left = 0;
int right = numsSize;
*returnSize = numsSize;
int *tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize);
MergeSort(nums,left,right - 1,tmp);
return nums;
free(tmp);

六、希尔排序
希尔排序的基本思想是:先将整个待排序序列分割为若干个子序列分别进行直接插入排序,待整个序列基本有序时,再对全体序列进行一次直接插入排序,如图所示:
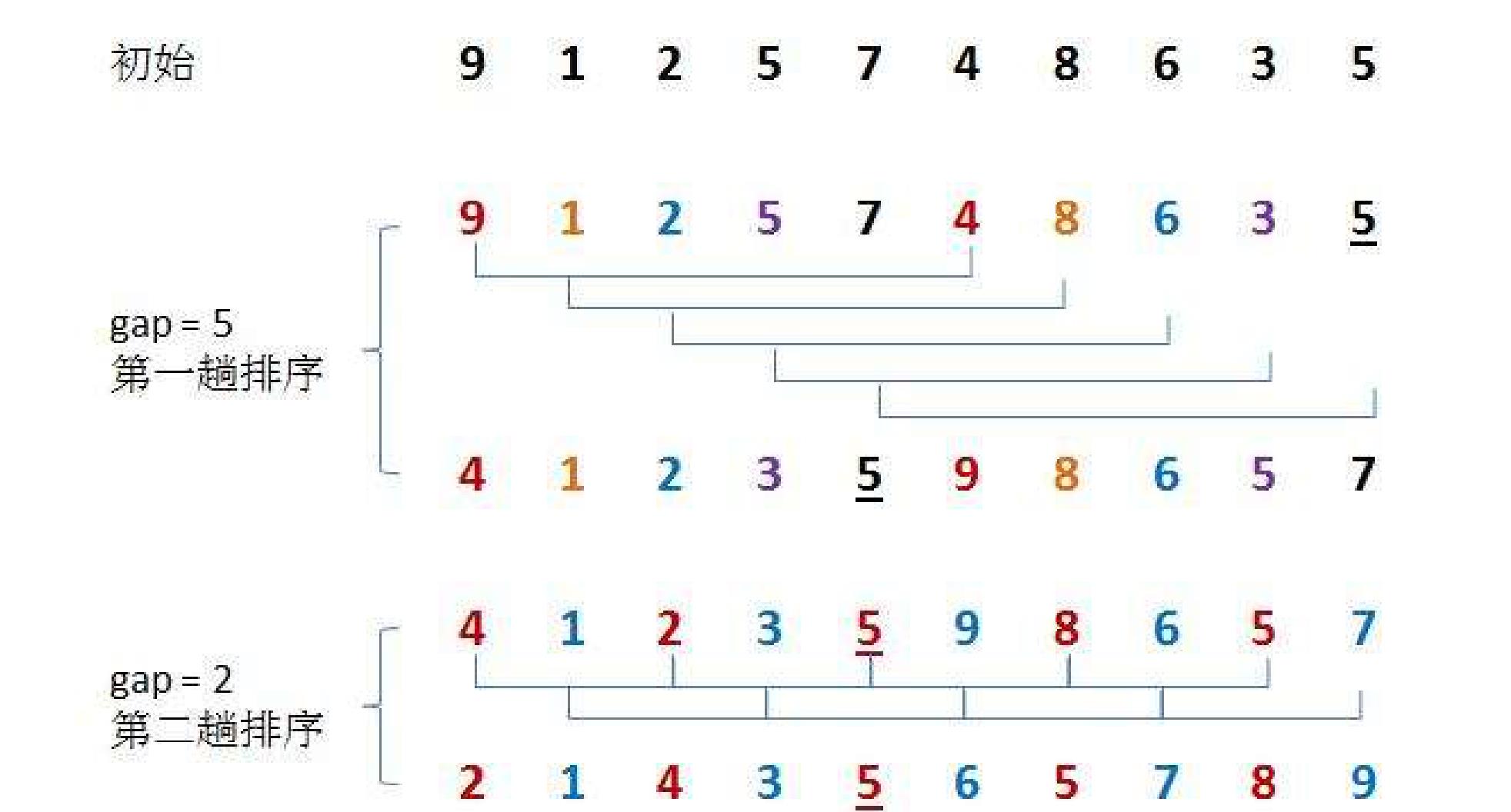
实现代码如下:
//希尔排序
static int* ShellSort(int *nums,int numsSize)
int gap = numsSize;
while (gap > 0)
gap = gap / 2;
for (int i = gap;i < numsSize;++i)
int j = i;
int tmp = nums[i];
while (j >= gap && tmp < nums[j - gap])
nums[j] = nums[j - gap];
j -= gap;
nums[j以上是关于排序数组的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章