stack和queue使用及模拟实现
Posted DR5200
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了stack和queue使用及模拟实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
- 一.stack介绍
- 二.stack使用
- 三.stack模拟实现
- 四.queue介绍
- 五.queue使用
- 六.queue模拟实现
- 七. priority_queue的介绍
- 八.priority_queue的使用
- 九.priority_queue模拟实现
一.stack介绍
template <class T, class Container = deque<T> > class stack;
(1). stack是一种容器适配器,专门用在具有后进先出操作的上下文环境中,其删除只能从容器的一端进行元素的插入与提取操作。
(2). stack是作为容器适配器被实现的,容器适配器即是对特定类封装作为其底层的容器,并提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素,将特定类作为其底层的,元素特定容器的尾部(即栈顶)被压入和弹出。
(3). stack的底层容器可以是任何标准的容器类模板或者一些其他特定的容器类,这些容器类应该支持以下操作:
empty:判空操作
back:获取尾部元素操作
push_back :尾部插入元素操作
pop_back :尾部删除元素操作
(4). 标准容器vector、deque、list均符合这些需求,默认情况下,如果没有为stack指定特定的底层容器,默认情况下使用deque。
二.stack使用
(1). push
(2). pop
(3). top
(4). empty
(5). size
void test_stack()
stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);
while (!st.empty())
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
cout << endl;
cout << st.size() << endl;
三.stack模拟实现
适配器模式(Adapter Pattern)将某个类的接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口表示,主要目的是兼容性,让原本因接口不匹配不能一起工作的两个类可以协同工作。也称包装器(Wrapper),属于结构型模式。适配器模式主要分为三类:类适配器模式、对象适配器模式、接口适配器模式
工作原理
将一个类的接口转换成另一种接口,让原本接口不兼容的类可以兼容。从用户的角度看不到被适配者,是解耦的。用户调用适配器转化出来的目标接口方法,适配器再调用被适配者的相关接口方法,用户收到反馈结果,感觉只是和目标接口交互。
简单来说,适配器模式就像个插头转换器,让不同标准的插头和插座可以一起使用,而插座就是原来的接口,插头是用户期望的接口。或者类比电源适配器,把原来的220V电压转换成5V电压等。
namespace lyp
// 可以使用 deque/list/vector
template<class T, class Container = std::deque<T> >
class stack
public:
// 尾插
void push(const T& x)
return _con.push_back(x);
// 尾删
void pop()
return _con.pop_back();
// 获取栈顶元素
T& top()
return _con.back();
// 获取栈顶元素
const T& top()
return _con.back();
// 判空
bool empty()
return _con.empty();
// 数据个数
size_t size()
return _con.size();
private:
Container _con;
;
四.queue介绍
template <class T, class Container = deque<T> >
class queue;
(1). 队列是一种容器适配器,专门用于在FIFO上下文(先进先出)中操作,其中从容器一端插入元素,另一端提取元素。
(2). 队列作为容器适配器实现,容器适配器即将特定容器类封装作为其底层容器类,queue提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从队尾入队列,从队头出队列。
(3). 底层容器可以是标准容器类模板之一,也可以是其他专门设计的容器类。该底层容器应至少支持以下操作:
empty:检测队列是否为空
size:返回队列中有效元素的个数
front:返回队头元素的引用
back:返回队尾元素的引用
push_back:在队列尾部入队列
pop_front:在队列头部出队列
(4). 标准容器类deque和list满足了这些要求。默认情况下,如果没有为queue实例化指定容器类,则使用标准容器deque。
五.queue使用
(1). push
(2). pop
(3). front
(4). back
(5). empty
(6). size
void test_queue()
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
while (!q.empty())
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
cout << endl;
cout << q.size() << endl;
六.queue模拟实现
namespace lyp
// 可以使用 deque/list
template<class T, class Container = std::deque<T> >
class queue
public:
// 尾插
void push(const T& x)
_con.push_back(x);
// 头删
void pop()
_con.pop_front();
// 队列的首元素
T& front()
return _con.front();
// 队列的首元素
const T& front()
return _con.front();
// 队列的末尾元素
T& back()
return _con.back();
// 队列的末尾元素
const T& back()
return _con.back();
// 判空
bool empty()
return _con.empty();
// 数据个数
size_t size()
return _con.size();
private:
Container _con;
;
七. priority_queue的介绍
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>,
// 这里的 typename 是为了告诉编译器 Contain::value_type 是一种类型,使其编译能通过
// 当类模板没有实例化的时候,Container不是一个具体的类,编译器无法识别 Contain::value_type 是一种类型
class Compare = less<typename Container::value_type> >
class priority_queue;
(1). 优先队列是一种容器适配器,根据严格的弱排序标准,它的第一个元素总是它所包含的元素中最大的。
(2). 优先队列类似于堆,在堆中可以随时插入元素,并且只能检索最大堆元素(优先队列中位于顶部的元素)。
(3). 优先队列被实现为容器适配器,容器适配器即将特定容器类封装作为其底层容器类,priority_queue 提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的“尾部”弹出,其称为优先队列的顶部。
(4). 底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是其他特定设计的容器类。容器应该可以通过随机访问迭代器访问,并支持以下操作:
empty():检测容器是否为空
size():返回容器中有效元素个数
front():返回容器中第一个元素的引用
push_back():在容器尾部插入元素
pop_back():删除容器尾部元素
(5). 标准容器类vector和deque满足这些需求。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue类实例化指定容器类,则使用vector。
(6). 需要支持随机访问迭代器,以便始终在内部保持堆结构。容器适配器通过在需要时自动调用算法函数make_heap、push_heap和pop_heap来自动完成此操作。
仿函数
仿函数也叫做函数对象,即这个类的对象可以像函数一样使用
template <class T>
struct less : binary_function <T,T,bool>
bool operator() (const T& x, const T& y) const
return x<y;
;
我们定义一个对象,去调用 operator() 函数,会发现使用起来像函数一样
less LessFunc;
LessFunc(1,2); // 相当于 LessFunc.operator()(1,2)
八.priority_queue的使用
优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中元素构造成堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆,所有需要用到堆的位置,都可以考虑使用priority_queue。注意:默认情况下priority_queue是大堆。
priority_queue提供以下接口
(1). push
(2). pop
(3). top
(4). empty
(5). size
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
priority_queue<int> q;
q.push(10);
q.push(15);
q.push(26);
q.push(35);
while (!q.empty())
cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
cout << endl;
cout<<q.size()<<endl;
// 输出结果为 35 26 15 10
// 0
九.priority_queue模拟实现
(1).仿函数
仿函数的实现很简单,在类里重载operator()函数,类的对象调用operator()函数用来对两个元素进行大小比较
template<class T>
struct less
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)const
return x < y;
;
template<class T>
struct greater
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)const
return x > y;
;
(2).push()
因为 priority_queue的默认结构是一个大堆,默认使用vector去适配,因此 priority_queue 的插入就是堆的插入,流程如下图
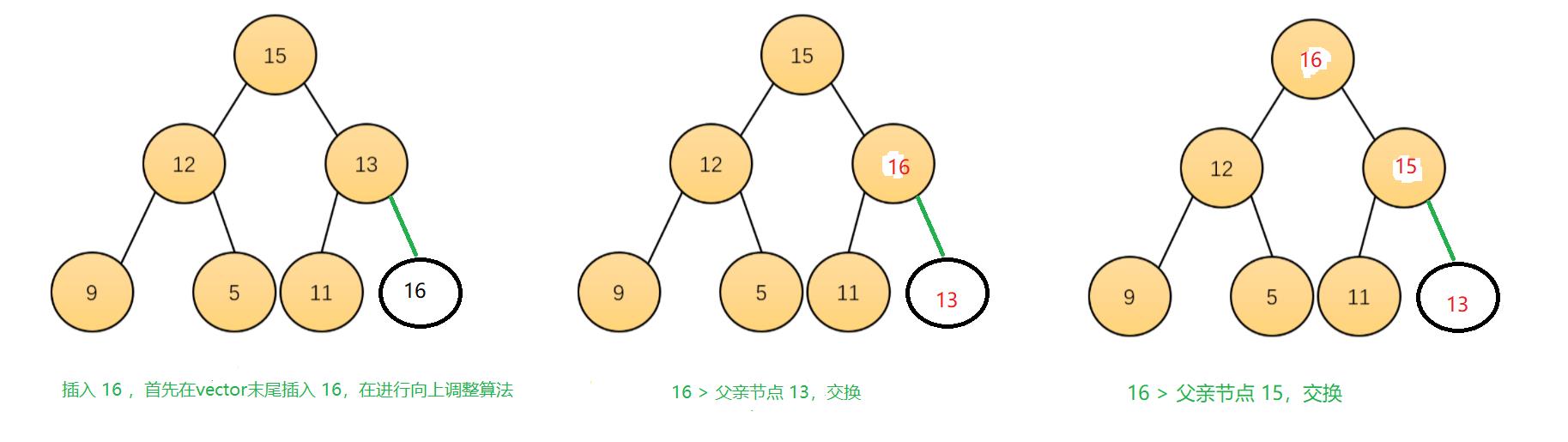
(3).pop()
priority_queue的删除就是堆的删除,过程如下图
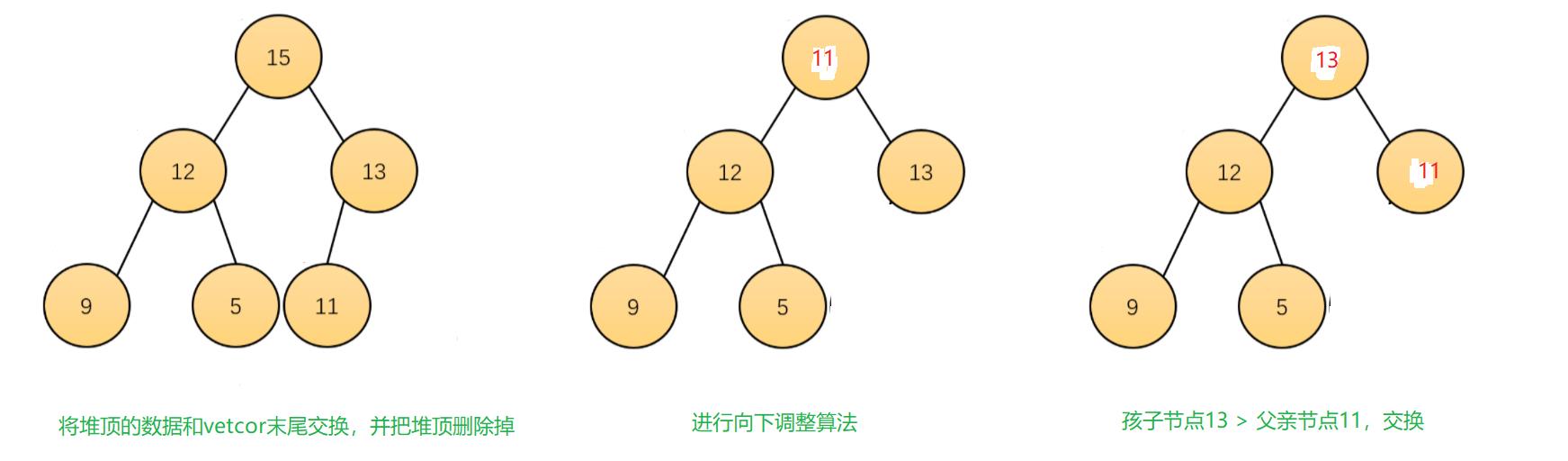
(4). top()
返回vector的首元素即可,默认是堆中最大的元素
(5).empty()
判断vector是否为空即可
(6).size()
返回vector的size即可
(7). 完整模拟实现
namespace lyp
template<class T>
struct less
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)const
return x < y;
;
template<class T>
struct greater
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)const
return x > y;
;
template<class T, class Container = std::vector<T>,class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
public:
void AdjustUp(int child)
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
if (_com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
std::swap(_con[parent],_con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
else
break;
void AdjustDown(int parent,int n)
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
if (child + 1 < n && _com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
child++;
if (_com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
std::swap(_con[parent],_con[child]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
else
break;
void push(const T& x)
_con.push_back(x);
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
void pop()
std::swap(_con[0],_con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0,_con.size());
T& top()
return _con.front();
bool empty()
return _con.empty();
size_t size()
return _con.size();
private:
Container _con;
Compare _com;
;
以上是关于stack和queue使用及模拟实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章