graph slam tutorial : 从推导到应用1(g2o+ceres实现)
Posted chengwei0019
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了graph slam tutorial : 从推导到应用1(g2o+ceres实现)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
例子1:
为了更好的理解这个过程,将用一个很好的例子作说明。如下图所示,假设一个机器人初始起点在0处,然后机器人向前移动,通过编码器测得它向前移动了1m,到达第二个地点。接着,又向后返回,编码器测得它向后移动了0.8米。但是,通过闭环检测,发现它回到了原始起点。可以看出,编码器误差导致计算的位姿和观测到有差异,那机器人这几个状态中的位姿到底是怎么样的才最好的满足这些条件呢?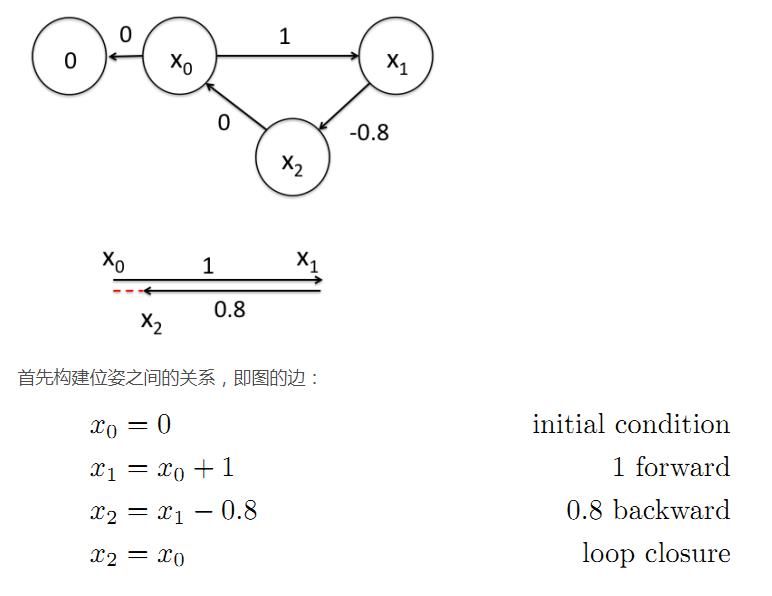
定义顶点和边:
class MyVertex : public g2o::BaseVertex<1, double>
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
virtual void setToOriginImpl()
_estimate = 0.0;
virtual void oplusImpl(const double* update)
_estimate += (*update);
virtual bool read(istream & in) return 0;
virtual bool write(ostream & out) const return 0;
;
class MyEdge : public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<1, double, MyVertex, MyVertex>
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
void computeError()
const MyVertex * v1 = static_cast<const MyVertex*>(_vertices[0]);
const MyVertex * v2 = static_cast<const MyVertex*>(_vertices[1]);
_error(0, 0) = _measurement - (v2->estimate() - v1->estimate());
virtual bool read(istream & in) return 0;
virtual bool write(ostream & out) const return 0;
;主函数:
int main()
// 从x0到x1,编码器测量移动了1m,从x1到x2,编码器测量移动了-0.8,观测发现x2和x0重合。
double edge1 = 1, edge2 = -0.8, edge3 = 0;
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<1, 1>> Block;
// std::unique_ptr<Block::LinearSolverType> linearSolver( new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>());
// std::unique_ptr<Block> solver_ptr ( new Block(std::move(linearSolver)));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
Block::LinearSolverType * linearSolver;
linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>();
Block * solver_ptr = new Block(std::unique_ptr< Block::LinearSolverType>(linearSolver));
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg * solver
= new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(std::unique_ptr < Block>(solver_ptr));
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
MyVertex *v1 = new MyVertex;
v1->setId(0);
v1->setEstimate(0);
v1->setFixed(true);
optimizer.addVertex(v1);
MyVertex *v2 = new MyVertex;
v2->setId(1);
v2->setEstimate(1);
v2->setFixed(false);
optimizer.addVertex(v2);
MyVertex *v3 = new MyVertex;
v3->setId(2);
v3->setEstimate(0);
v3->setFixed(false);
optimizer.addVertex(v3);
MyEdge * e1 = new MyEdge;
MyEdge * e2 = new MyEdge;
MyEdge * e3 = new MyEdge;
e1->setId(1);
e1->setVertex(0, v1);
e1->setVertex(1, v2);
e1->setMeasurement(1);
e1->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity());
e2->setId(2);
e2->setVertex(0, v2);
e2->setVertex(1, v3);
e2->setMeasurement(-0.8);
e2->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity());
e3->setId(3);
e3->setVertex(0, v3);
e3->setVertex(1, v1);
e3->setMeasurement(0);
e3->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity());
optimizer.addEdge(e1);
optimizer.addEdge(e2);
optimizer.addEdge(e3);
cout << "start optimization" << endl;
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
cout << v1->estimate() << ' ' << v2->estimate() << ' ' << v3->estimate() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
运行结果:

ceres实现:
例子2:
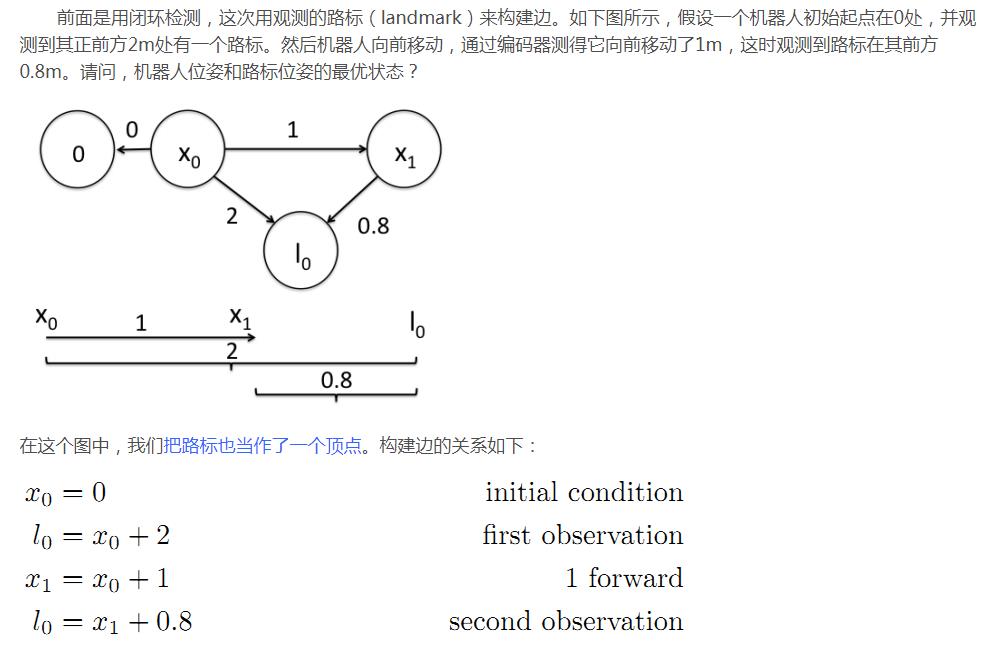
顶点和边的定义一样,主函数如下:
int main()
// 从x0处观测到前方2m存在路标,移动到x1,编码器测量移动了1m,此时观测到路标在其前方0.8m。
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<1, 1>> Block;
// std::unique_ptr<Block::LinearSolverType> linearSolver( new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>());
// std::unique_ptr<Block> solver_ptr ( new Block(std::move(linearSolver)));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
Block::LinearSolverType * linearSolver;
linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>();
Block * solver_ptr = new Block(std::unique_ptr< Block::LinearSolverType>(linearSolver));
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg * solver
= new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(std::unique_ptr < Block>(solver_ptr));
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
MyVertex *v0 = new MyVertex;
v0->setId(0);
v0->setEstimate(0);
v0->setFixed(true);
optimizer.addVertex(v0);
MyVertex *v1 = new MyVertex;
v1->setId(1);
v1->setEstimate(1);
v1->setFixed(false);
optimizer.addVertex(v1);
MyVertex *lank = new MyVertex;
lank->setId(2);
lank->setEstimate(2);
lank->setFixed(false);
optimizer.addVertex(lank);
MyEdge * e1 = new MyEdge;
e1->setId(0);
e1->setVertex(0, v0);
e1->setVertex(1, lank);
e1->setMeasurement(2);
e1->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity());
optimizer.addEdge(e1);
MyEdge * e2 = new MyEdge;
e2->setId(1);
e2->setVertex(0, v1);
e2->setVertex(1, lank);
e2->setMeasurement(0.8);
e2->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity());
optimizer.addEdge(e2);
MyEdge * e3 = new MyEdge;
e3->setId(1);
e3->setVertex(0, v0);
e3->setVertex(1, v1);
e3->setMeasurement(1);
e3->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity() * 10);// 这里的10为传感器权重
optimizer.addEdge(e3);
cout << "start optimization" << endl;
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
cout << v0->estimate() << ' ' << v1->estimate() << ' ' << lank->estimate() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
运行结果:

ceres实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
// 代价函数的计算模型(不是很熟悉这种模型定义)
struct fun0
fun0(double x) :_x(x)
template<typename T>
bool operator()(
const T* const x0,
T* residual)const
residual[0] = T(_x) - x0[0];
return true;
const double _x;
;
struct fun1
fun1(double x) :_x(x)
template<typename T> bool operator()(
const T* const x0,
const T* const x1,
T* residual) const
residual[0] = T(_x) - (x1[0] - x0[0]);
return true;
const double _x;
;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
double x0 = 0.0;
double x1 = 1.0;
double mark = 2;
// 构建最小二乘问题
ceres::Problem problem;
ceres::LossFunction* loss_function = NULL;
//ceres::LossFunction* loss_function = new ceres::CauchyLoss(0.5);// 过滤外点,使用损失函数
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<fun0, 1,1>(new fun0(0)),
NULL,
&x0);
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<fun1, 1, 1, 1>(new fun1(2)),
NULL,
&x0,
&mark);
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<fun1, 1, 1, 1>(new fun1(1)),
NULL,
&x0,
&x1);
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<fun1, 1, 1, 1>(new fun1(0.8)),
NULL,
&x1,
&mark);
// 配置求解器
ceres::Solver::Options options; // 这里有很多配置项可以填
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR; // 增量方程如何求解
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; // 输出到cout
ceres::Solver::Summary summary; // 优化信息
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary); // 开始优化
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << " seconds. " << endl;
// 输出结果
cout << summary.BriefReport() << endl;
cout << "x0: " << x0 << " " << "x1: " << x1 << " " << "mark: " << mark << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;

《end here》
下一篇,写一个基于g2o的完整slam后端
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/heyijia0327/article/details/47686523
https://blog.csdn.net/wphkadn/article/details/90317006
以上是关于graph slam tutorial : 从推导到应用1(g2o+ceres实现)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章