Android P 显示流程分析---获取显示屏配置
Posted Give.Me.Five
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android P 显示流程分析---获取显示屏配置相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android P 显示管理上已经分析了,SurfaceFlinger初始化的第一部分,并分析了第一块Display设备的插入检测过程。因为里面有众多类,接口 , 分析起来很乱,下面是我总结了一个UML的类图。
UML类图
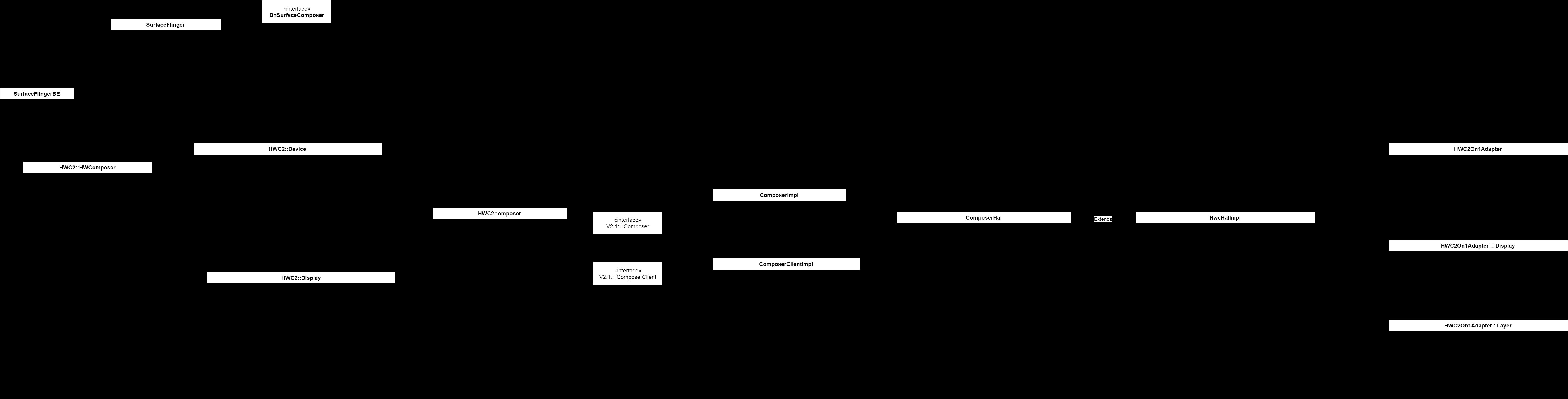
首先SurfaceFlinger里有个mBE,也就是SurfaceFlingerBE的对象,它其它就是用于与HAL层进行通讯的,它里面的有一个mHwc(HWComposer对象),里面的成员变量mDevice与mDisplay, 其对应调用的是V2_1::IComposer, 这个就与HAL里的Composer模块联系起来了,因为Treble框架引入了,同时也为了兼顾调用的效率,Composer模块采用了Passthrough的方式来进行HIDL的调用。因为HAL层里都采用了模块类的编写方法,使得看代码有些头大。IComposer与IComposerClient分别由ComposerImpl与ComposerClientImpl来实现,然后两者都调用到对象进行ComposerHal下一步调用。因为使用了passthrough的方式,之后调用HwcHalImpl调用initWithModule的方式来加载Composer.xxx.so库。在So库中再现模块类+Hook混 合使用,加入了一个mInitDispatch, 通过将函数描述符,查找成具体的调用函数指针,最终都落下HWC2On1Adapter类上,同时其内部类的Device和Display上。
获取显示屏的配置
上篇文章中我们分析到SurfaceFlinger初始化时,调用到了onInitializeDisplays(),我们看到getActiveConfig也是在这里开始的。
void SurfaceFlinger::onInitializeDisplays()
...
const auto& activeConfig = getBE().mHwc->getActiveConfig(HWC_DISPLAY_PRIMARY);
//period是指Display刷新的周期
const nsecs_t period = activeConfig->getVsyncPeriod();
....
根据上面之前类图说明,我们就跳过中转一层层的调用,直接到HWC2On1Adapter里去看,后面的分析都会直接跳过这些步骤:
Error HWC2On1Adapter::Display::getActiveConfig(hwc2_config_t* outConfig)
auto configId = mActiveConfig->getId();
ALOGV("[%" PRIu64 "] getActiveConfig --> %u", mId, configId);
*outConfig = configId;
void HWC2On1Adapter::Display::initializeActiveConfig()
...
auto activeConfig = mDevice.mHwc1Device->getActiveConfig(
mDevice.mHwc1Device, mHwc1Id);
if (activeConfig >= 0)
for (const auto& config : mConfigs)
if (config->hasHwc1Id(activeConfig))
mActiveConfig = config;
if (config->getColorModeForHwc1Id(activeConfig, &mActiveColorMode) != Error::None)
mActiveColorMode = HAL_COLOR_MODE_NATIVE;
break;
...
相当于调用libhwcomposer里方法里的getActiveConfig。
static int hwc_device_open(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device)
...
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = HWC_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_5;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module);
dev->device.common.close = hwc_device_close;
dev->device.prepare = hwc_prepare;
dev->device.set = hwc_set;
dev->device.eventControl = hwc_eventControl;
dev->device.setPowerMode = hwc_setPowerMode;
dev->device.query = hwc_query;
dev->device.registerProcs = hwc_registerProcs;
dev->device.dump = hwc_dump;
dev->device.getDisplayConfigs = hwc_getDisplayConfigs;
dev->device.getDisplayAttributes = hwc_getDisplayAttributes;
dev->device.getActiveConfig = hwc_getActiveConfig;
dev->device.setActiveConfig = hwc_setActiveConfig;
*device = &dev->device.common;
...
这个是hal层module里加载的,然后调用对应hwc_getActiveConfig的接口了,这里hwcomposer的module里实现的还是使用framebuffer的方式, getActiveConfig主要是获取period(刷新时间),从而设置图层的合成间隔时间。
void SurfaceFlinger::onInitializeDisplays()
...
const auto& activeConfig = getBE().mHwc->getActiveConfig(HWC_DISPLAY_PRIMARY);
const nsecs_t period = activeConfig->getVsyncPeriod();
mAnimFrameTracker.setDisplayRefreshPeriod(period);
setCompositorTimingSnapped(0, period, 0);
void SurfaceFlinger::setCompositorTimingSnapped(nsecs_t vsyncPhase,
nsecs_t vsyncInterval, nsecs_t compositeToPresentLatency)
...
getBE().mCompositorTiming.interval = vsyncInterval;
...
SurfaceFlinger启动的线程
SurfaceFlinger在启动时,新建了几个线程,mEventThread, mSfEventThread ,mEventControlThread
// start the EventThread
mEventThreadSource =
std::make_unique<DispSyncSource>(&mPrimaryDispSync, SurfaceFlinger::vsyncPhaseOffsetNs,
true, "app");
mEventThread = std::make_unique<impl::EventThread>(mEventThreadSource.get(),
[this]() resyncWithRateLimit(); ,
impl::EventThread::InterceptVSyncsCallback(),
"appEventThread");
mSfEventThreadSource =
std::make_unique<DispSyncSource>(&mPrimaryDispSync,
SurfaceFlinger::sfVsyncPhaseOffsetNs, true, "sf");
mSFEventThread =
std::make_unique<impl::EventThread>(mSfEventThreadSource.get(),
[this]() resyncWithRateLimit(); ,
[this](nsecs_t timestamp)
mInterceptor->saveVSyncEvent(timestamp);
,
"sfEventThread");
mEventQueue->semStartPropertySetThread = new StartPropertySetThread(true);EventThread(mSFEventThread.get());
mVsyncModulator.setEventThread(mSFEventThread.get());
...
mEventControlThread = std::make_unique<impl::EventControlThread>(
[this](bool enabled) setVsyncEnabled(HWC_DISPLAY_PRIMARY, enabled); );
...
mStartPropertySetThread = new StartPropertySetThread(true);
同时创建了4个线程, EventThread主要处理plug事件和sync事件, EventControlThread主要是处理开关sync, StartPropertySetThread主要是为了启动BootAnimation开机动画的。
到这里SurfaceFlinger的启动初始化就完成了,下一篇我们来分析界面刷新过程。
以上是关于Android P 显示流程分析---获取显示屏配置的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章